KIN 320 - Post Midterm 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/237
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:46 AM on 12/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
238 Terms
1
New cards
Two adult mice are born from the same litter but one is significantly larger than the other. Why?
the smaller one is not releasing growth hormones
2
New cards
growth results from an interaction of what 4 factors?
1. genes
2. hormones
3. nutrients
4. environment
3
New cards
Say whether each factor is environmental, genetic, or interaction: Language, eye color, weight, skin color, religion, blood type

4
New cards
genes establish the ______,__ environment determines if the potential is _____________
* potential
* obtained
* obtained
5
New cards
What is inherited is ___ everything else is ______
* DNA
* developed
* developed
6
New cards
What is monozygotic? Dizygotic?
Monozygotic - embryo split, identical twins
Dizygotic - two embryos, fraternal twins
Dizygotic - two embryos, fraternal twins
7
New cards
Who has a greater difference in height, mono or dizygotic?
Height difference greater between DZ than MZ
8
New cards
Label
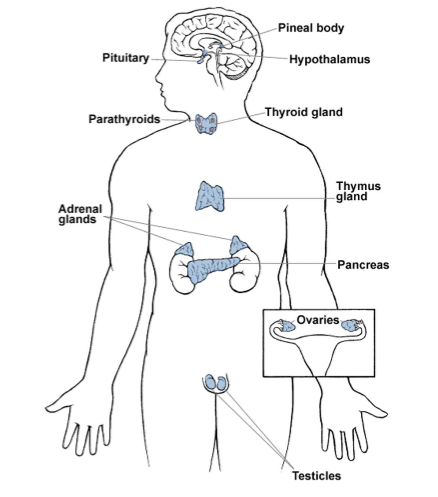
9
New cards
Commander and 2nd in command of endocrine system
* hypothalamus
* pituitary gland
* pituitary gland
10
New cards
What does pituitary release?
* human growth hormones
* trophic hormones that control other glands
* trophic hormones that control other glands
11
New cards
Why was Charles Byrne so tall?
* pituitary tumor
* pituitary tumors associated with acromegly - head, hands, feet begin to grown long after normal growth stops
\
* pituitary tumors associated with acromegly - head, hands, feet begin to grown long after normal growth stops
\
12
New cards
Growth hormones is produced by?
It is secreted in a _______ pattern in response to?
It is secreted in a _______ pattern in response to?
* produced by anterior pituitary
* pulsative pattern
* in response to growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) and somatostatin
* pulsative pattern
* in response to growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) and somatostatin
13
New cards
2 effects of growth hormone
anabolic
* stimulation of bone development
Metabolic
* insulin resistant actions
* stimulation of bone development
Metabolic
* insulin resistant actions
14
New cards
Insulin like growth factor (IGF) function?
* major mediator of growth of skeletal and lean tissue in children
15
New cards
Factors affecting GH and IGF-1
* acute physical activity
* sex hormones during puberty
* nutrition
* genetic
* sex hormones during puberty
* nutrition
* genetic
16
New cards
GH/IGF-I Axis
* anterior pituitary releases GH pulsatile bursts every 2 hours
* GH may stimulate IGF-1 release from the liver
* GH and IGF-1 may both contribute to peripheral tissue growth
* GH may stimulate IGF-1 release from the liver
* GH and IGF-1 may both contribute to peripheral tissue growth
17
New cards
how is GH release stimulated?
by exercise
18
New cards
True or False - repeated bouts of exercise will increase GH concentrations and therefore result in increased final stature
False - repeated bouts do not result in increased finals stature
19
New cards
2 other growth determinants
* insulin
* thyroid hormone
* thyroid hormone
20
New cards
How does insulin effect growth?
* synergistic effect with growth hormone to increase protein synthesis in the muscle
* IGF -I activity on linear bone growth is facilitated by insulin
* IGF -I activity on linear bone growth is facilitated by insulin
21
New cards
How does thyroid hormone effect growth
* stimulate oxygen uptake and energy expenditure in most tissues
* essential for GH to exert is full affect
* promotes IGF-1
* essential for GH to exert is full affect
* promotes IGF-1
22
New cards
hypothyroidism
* short stature
* lower growth
* delayed bone growth
* cretinism - hypothyroid face - iodine deficiencies during infancy
* lower growth
* delayed bone growth
* cretinism - hypothyroid face - iodine deficiencies during infancy
23
New cards
blood levels of growth hormones during growth
* sharp increase in GH during adolescence
* a consequence of the rise in sex hormones
* a consequence of the rise in sex hormones
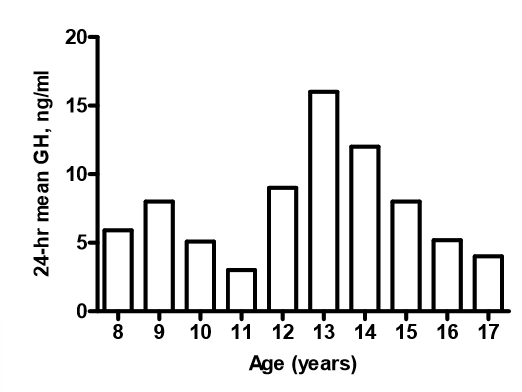
24
New cards
IGF-1 during growth
* sharp increase during adolescence
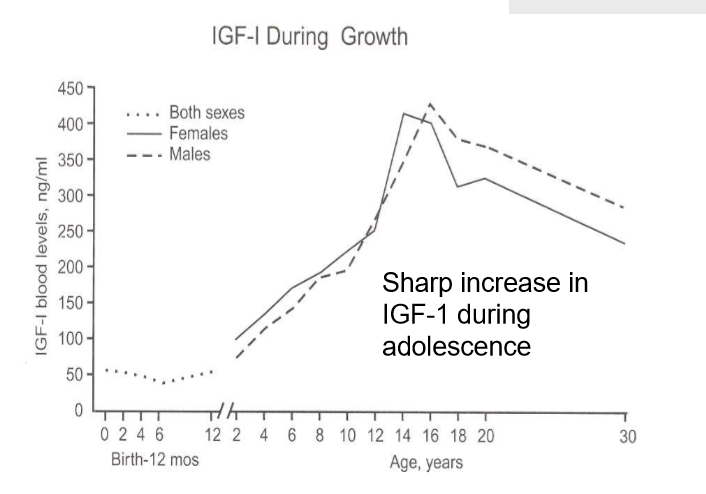
25
New cards
estradiol
* most active of estrogen hormones
* acts to develop sexual function
* stimulated by pulsatile release of FSH follicle stimulating hormones and LH luteinizing hormone
* acts to develop sexual function
* stimulated by pulsatile release of FSH follicle stimulating hormones and LH luteinizing hormone
26
New cards
FSH and LH stimulate the ovary to produce
progesterone
27
New cards
what happens to produce ovarian hormones
pulsative secretion of GnRH into the anterior pituitary leads to release of FSH and LH which produces ovarian hormones
28
New cards
What are the phases of the menstrual cycle. Include and start at menstruation
Follicular phase:
* day 0-14
* day 0-4 menstruation
Luteal phase:
* day 14-28
* day 0-14
* day 0-4 menstruation
Luteal phase:
* day 14-28
29
New cards
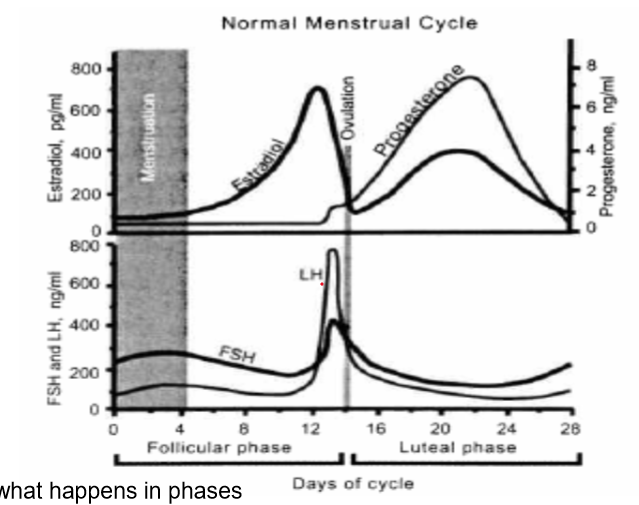
Describe hormone levels in the follicular and luteal phase of the menstrual cycle
Follicular Phase:
* increase in Estradiol, FSH, LH
* FSH and LH peak right before ovulation with LH peaking the highest
Ovulation
Luteal Phase:
* decrease in estradiol, FSH, LH
* increase in progesterone
* if egg is fertilized progesterone will continue to increase
\
* increase in Estradiol, FSH, LH
* FSH and LH peak right before ovulation with LH peaking the highest
Ovulation
Luteal Phase:
* decrease in estradiol, FSH, LH
* increase in progesterone
* if egg is fertilized progesterone will continue to increase
\
30
New cards
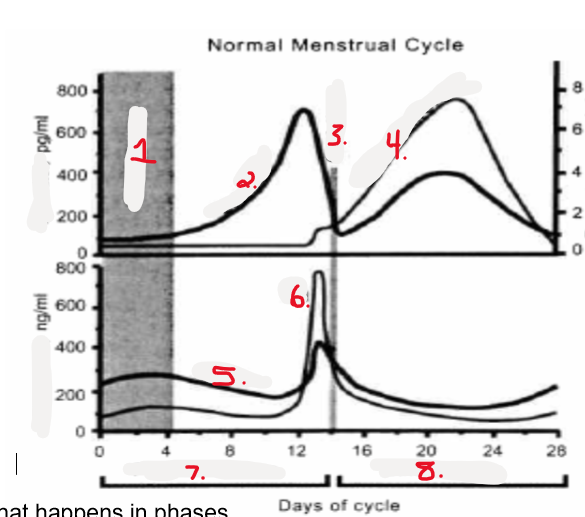
Label
1. menstruation
2. estradiol
3. ovulation
4. progesterone
5. FSH
6. LH
7. follicular phase
8. luteal phase
\
31
New cards
What is the sex hormone in males. Where does it act? what does it release?
* gonadotropic releasing hormone GnRH
* acts on anterior pituitary to release FSH and LH
* LH acts on Leydig cells → testosterone
* FSH stimulates the Sertoli cells → sperm
* acts on anterior pituitary to release FSH and LH
* LH acts on Leydig cells → testosterone
* FSH stimulates the Sertoli cells → sperm
32
New cards
leptin is an appetite ______
suppressant
33
New cards
serum leptin levels is related _______ to body fat
exponentially,
* increased fat= increased leptin, your body makes more to try and suppress
* leptin is produces in adipocytes of subcutaneous fat tissue
* increased fat= increased leptin, your body makes more to try and suppress
* leptin is produces in adipocytes of subcutaneous fat tissue
34
New cards
absence of leptin prevents _______
sex maturation
* so increasing leptin is going to increase maturity
* so increasing leptin is going to increase maturity
35
New cards
Leptins relationship with nutrition status and reproduction
Critical Body Fat hypothesis:
* Frish and Revelle (1970) suggested that a body mass of 48 kg and fat of 22% was needed to trigger a change in metabolic rate that leads to menarche
* Frish and Revelle (1970) suggested that a body mass of 48 kg and fat of 22% was needed to trigger a change in metabolic rate that leads to menarche
36
New cards
agree with critical body fat hypothesis?
may agree with frisch and revelles argument but menarche still initiated below Frisch and Revelle critical values
37
New cards
Stages of amenorrhea
* primary: delayed, absence by 16 yrs
* secondary: absence of 3+ consecutive cycles, most common
* oligomenorrhea: periods longer than 35 days
* luteal deficiency: length of menstruation is normal but progesterone levels low (fertility issues)
* secondary: absence of 3+ consecutive cycles, most common
* oligomenorrhea: periods longer than 35 days
* luteal deficiency: length of menstruation is normal but progesterone levels low (fertility issues)
38
New cards
What sports is ammenorhea higher? lower?
* higher in endurance sports - intensity training correlated with frequency
* lower in swimming - no correlation with intensity
* lower in swimming - no correlation with intensity
39
New cards
two theories of causal mechanisms of Amenorrhea
* exercise stress model
* energy availability model
* energy availability model
40
New cards
Exercise stress model
Exercise stress increases stress hormones (cortisol) which provide negative feedback to hypothalamus which decreases sex hormones (LH, FSH, estrogen)
41
New cards
energy availability model
* increased training + increased caloric demand = nutritional inadequacy and negative caloric balance
* shuts of GnRH pulse generator
* decreases LH, FSH, Estrogren,
* shuts of GnRH pulse generator
* decreases LH, FSH, Estrogren,
42
New cards
A study on the mechanism of Amenorrhea found that Luteal hormone pulsativity is disturbed by _____ rather than _____
* energy unavailability
* exercise
* exercise
43
New cards
physical activity
* any bodily movement produced by skeletal muscles and results in energy expenditure
* has a mechanical ROM, physiological and behavioural (motivation) components
* has a mechanical ROM, physiological and behavioural (motivation) components
44
New cards
exercise
* physical activity that is planned, structured, repetitive, and results in improvement or maintenance of one or more facets of physical fitness
45
New cards
physical fitness
* a set of attributes (cardio-respiratory endurance, power, etc.) that people have or achieve that relate to their ability to perform PA
46
New cards
physical activity characterized in dimensions and contexts. Describe dimensions
* energy expenditure
* FITT formula (frequency, intensity, time, type)
* FITT formula (frequency, intensity, time, type)
47
New cards
physical activity characterized in dimensions and contexts. Describe contexts
**contexts (PA)**
* **leisure-time**
* **occupational**
* **leisure-time**
* **occupational**
48
New cards
energy expenditure
**energy expenditure**
* **TEE = REE + DEE + EEE + adaptive EE**
* **total energy expenditure**
* **Resting energy expenditure (basal)**
* **diet-induced energy expenditure - thermogenesis (digestive process)**
* **exercise induced energy expenditure**
* **TEE = REE + DEE + EEE + adaptive EE**
* **total energy expenditure**
* **Resting energy expenditure (basal)**
* **diet-induced energy expenditure - thermogenesis (digestive process)**
* **exercise induced energy expenditure**
49
New cards
resting energy expenditure
* measured in the morning in a rested and fasted state
* supine position
* room temp (23-25F)
* 20-30 min
* supine position
* room temp (23-25F)
* 20-30 min
50
New cards
exercise-induced energy expenditure
* expended during PA
* most varied
* range from 0 in sedentary to 10-20x REE during intense exercise
* most varied
* range from 0 in sedentary to 10-20x REE during intense exercise
51
New cards
diet-induced energy expenditure
* increase from REE observed 3-4hrs after a meal
* EE for digestion and absorption
* EE for digestion and absorption
52
New cards
metabolic equivalent (MET)
* ratio of exercise to resting energy expenditure
* EEE / REE
* most commonly used
* based on adult values
* EEE per unit body mass during activities is higher in children than adults
* resting metabolic rate of children per unit body mass or surface area is higher in children
* EEE / REE
* most commonly used
* based on adult values
* EEE per unit body mass during activities is higher in children than adults
* resting metabolic rate of children per unit body mass or surface area is higher in children
53
New cards
subjective instruments
* recall questionnaire
* recall interview
* proxy-report
* activity diary
* observation
* recall interview
* proxy-report
* activity diary
* observation
54
New cards
self-report
* self-assessed recall
* proxy reports
* diaries, interviews
* questionnaires
* most widely used
* ease and low cost
* interviewer administered questionnaires have high reliability and validity than self-administered
* however higher cost in terms of observation time
* diaries tend to result in large degree of behaviour change
* proxy reports
* diaries, interviews
* questionnaires
* most widely used
* ease and low cost
* interviewer administered questionnaires have high reliability and validity than self-administered
* however higher cost in terms of observation time
* diaries tend to result in large degree of behaviour change
55
New cards
self-report (concerns)
* not directly assessing PA
* reliance on cognitive ability to recall specific events (memory)
* bias
* grading
* reliance on cognitive ability to recall specific events (memory)
* bias
* grading
56
New cards
observation
* long standing method - video and computer technology allowed complex observational codes
* reliable and observers easily trained
* labor intensive, time, consuming and costly
* mostly done in structured situations (activity classes, sports, etc.)
* reliable and observers easily trained
* labor intensive, time, consuming and costly
* mostly done in structured situations (activity classes, sports, etc.)
57
New cards
objective instruments
* pedometers
* electronic motion sensors
* accelerometers (most common)
* heart rate monitoring
* indirect calorimetry (VO2 max, metabolic carts)
* doubly labelled water (gold standard)
* electronic motion sensors
* accelerometers (most common)
* heart rate monitoring
* indirect calorimetry (VO2 max, metabolic carts)
* doubly labelled water (gold standard)
58
New cards
heart rate monitors
* most popular method for estimating EE over long periods
* assumes two regressions lines for determining EE
* at rest - relatively linear
* during exercise
* commonly used in children (good adherence, minimal restrictions)
* other factors influence HR
* assumes two regressions lines for determining EE
* at rest - relatively linear
* during exercise
* commonly used in children (good adherence, minimal restrictions)
* other factors influence HR
59
New cards
pedometers
* objectively documents mechanical aspect of activity
* counts and registers the number of movements (when attached at waist measures strides)
* not sensitive to intensity only number (can't distinguish between walk and run)
* counts and registers the number of movements (when attached at waist measures strides)
* not sensitive to intensity only number (can't distinguish between walk and run)
60
New cards
accelerometers
* electronic motion detectors
* measure frequency and intensity in vertical plane
* uniaxial
* triaxial (more recent)
* GPS functions (some newer models)
* custom software is used to reduce the raw data into minutes of moderate to vigorous PA per day using intensity cut points and Epochs
* measure frequency and intensity in vertical plane
* uniaxial
* triaxial (more recent)
* GPS functions (some newer models)
* custom software is used to reduce the raw data into minutes of moderate to vigorous PA per day using intensity cut points and Epochs
61
New cards
epoch
* user defined interval of time
* counts every second how many steps you take
* average the steps over that specific amount of time
* want this to be very small with children
* counts every second how many steps you take
* average the steps over that specific amount of time
* want this to be very small with children
62
New cards
cut points
* different types depending on intensity
* data will be analyzed differently
* differs in the activities that are used to create a range of counts/min for different analysis
* data will be analyzed differently
* differs in the activities that are used to create a range of counts/min for different analysis
63
New cards
accelerometers (concerns)
* adherence (7 days during waking hours ideally)
* practicality (can't get wet, not worn during aggressive contact sports)
* application for different context
* cost ($200 US per device)
* cut point consistency (how accurate it is)
* concerns about whether it assess FITT (epochs in children)
* practicality (can't get wet, not worn during aggressive contact sports)
* application for different context
* cost ($200 US per device)
* cut point consistency (how accurate it is)
* concerns about whether it assess FITT (epochs in children)
64
New cards
physiological analyzes
* typically used to assess EE
* assumes 1L O2 consumption = 5kcal
* metabolic cart
* canopy method
* respiration chamber
* doubly labeled water
* assumes 1L O2 consumption = 5kcal
* metabolic cart
* canopy method
* respiration chamber
* doubly labeled water
65
New cards
metabolic cart
* most commonly used is computerized metabolic cart
* minute ventilation
* individual must remain close to metbolic cart
* minute ventilation
* individual must remain close to metbolic cart
66
New cards
portable device
* allow direct measure of VO2 while individual is freely moving
* still limited use in children
* still limited use in children
67
New cards
validity in children
* more diverse range of activities than adults (less structure, more spontaneous)
* less memorable activities (children have poor recall)
* cognitive abilities
* short duration activities
* less memorable activities (children have poor recall)
* cognitive abilities
* short duration activities
68
New cards
patterns of PA participation. 3-10yrs. Intensity? Older children? organization?
* 3-10 years PA is often spontaneous and non-organized and is of intermittent bouts
* high intensity bouts did not last more than 3 seconds and 95% of lasted less than 15 seconds
* PA patterns of older children and adolescents tend to be more organized and of a more regular, prolonged nature
* in adolescence most PA occurs after school
* high intensity bouts did not last more than 3 seconds and 95% of lasted less than 15 seconds
* PA patterns of older children and adolescents tend to be more organized and of a more regular, prolonged nature
* in adolescence most PA occurs after school
69
New cards
Does level of PA or EE or both decline with age?
both
70
New cards
females (young girls)
What sex does PA decline start earlier and more rapidly?
71
New cards
True or False: PA tracks well
false (does not)
72
New cards
Does it appear as if participation in PA is differeing between low and high risk males or females
No it does not appear
73
New cards
When PA is organized by age category, who has increased PA, males or females? When organized by maturity or years from peak height velocity?
Age category
* males increased PA
* females decreased PA
Years from PHV
* no difference between the sexes in PA levels
* males increased PA
* females decreased PA
Years from PHV
* no difference between the sexes in PA levels
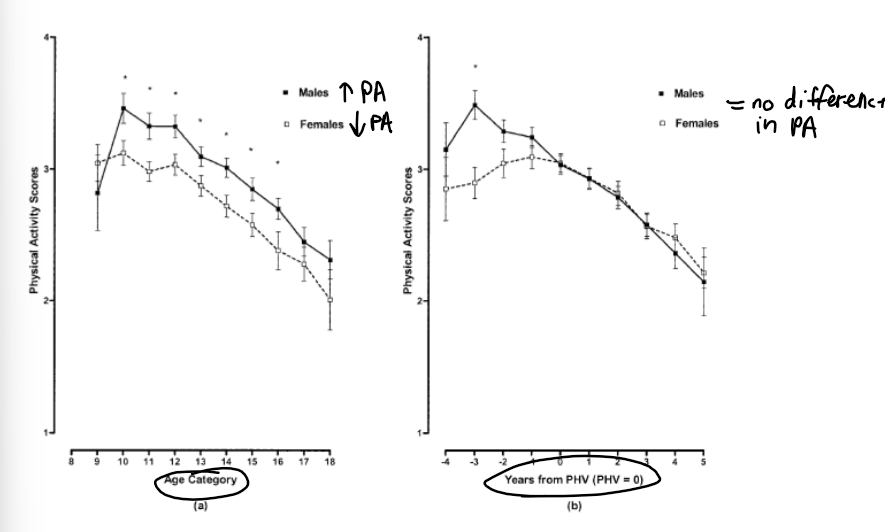
74
New cards
T/F there was an engagement difference in PA when organized by chronological versus biological age
true
75
New cards
Does PA affect stature?
NO
* PA not associated with attained height
* PA has no negative effects on stature
* PA not associated with attained height
* PA has no negative effects on stature
76
New cards
Studies done to prove PA has no effect on stature
* short gymnasts also had short parents
* studies suggested PA increased height, but maturation level was not considered. Maturation is a confounding factor for PA
* studies suggested PA increased height, but maturation level was not considered. Maturation is a confounding factor for PA
77
New cards
Does PA affect physique?
* distribution of somatotypes does not appear to be different between active and inactive
* PA individuals have greater MESO, sport specific somatotypes
* PA individuals have greater MESO, sport specific somatotypes
78
New cards
PA effects on body weight
* weight differences minimal between active and inactive
* more differences in the composition of weight (bone mass, fat free, lean)
* more differences in the composition of weight (bone mass, fat free, lean)
79
New cards
training regularly may have the ______ impacts on body composition
largest
80
New cards
PA effects on bone
increased PA = increased bone mineral content and bone geometry
81
New cards
PA and fat free mass
* increased Lean tissue mass: PA beneficial to LTM and muscle mass during adolescence and adulthood
* increased hypertrophy: may be task dependent (weight train yes, endurance inconclusive)
* Fiber type: no evidence to suggest fiber type can change with PA, only fiber size
* increased hypertrophy: may be task dependent (weight train yes, endurance inconclusive)
* Fiber type: no evidence to suggest fiber type can change with PA, only fiber size
82
New cards
PA and fat mass
* reduce fat mass developed (minimal differences subcutaneous at extremities, greatest difference at trunk)
* reduce FM gained during adolescence, especially females
* reduce FM gained during adolescence, especially females
83
New cards
PA effects on skeletal maturity
does not influence skeletal maturity
84
New cards
PA and somatic maturity (measured by age of peak height velocity)
PA does not influence age of PHV,
may influence PA involvement
may influence PA involvement
85
New cards
PA and sexual maturity
* ? inconclusive
* some evidence that age of menarche differs between PA groupings, may be confound by other factors
* no evidence to suggest tanner stages differs between PA groups in males
* some evidence that age of menarche differs between PA groupings, may be confound by other factors
* no evidence to suggest tanner stages differs between PA groups in males
86
New cards
In general, does regular PA effect stature
no
87
New cards
In general, does regular PA effect somatotypes
yes
88
New cards
In general, does regular PA effect body weight (body composition)
no to body weight, but yest to body composition
89
New cards
In general, does regular PA effect bone tissue
yes
90
New cards
In general, does regular PA effect skeletal muscle
yes
91
New cards
In general, does regular PA effect adipose tissue
yes (mostly in females)
92
New cards
In general, does regular PA effect sexual maturity
?
93
New cards
ectoderm
* outer layer
* outermost tissue (skin)
* brain and nervous systems
* outermost tissue (skin)
* brain and nervous systems
94
New cards
mesoderm
* middle layer
* skeleton and bone marrow
* muscle, hear and blood
* skeleton and bone marrow
* muscle, hear and blood
95
New cards
endodern
* inner layer
* linings of internal organs
\
* linings of internal organs
\
96
New cards
Fetal circulation has 3 shunts
1. foramen ovale (connects 2 atria allowing bypass of right ventricle and lungs)
2. ductus arteriosus (connects arteries between lungs and aorta, bypasses lungs)
3. ductus venosus (bypasses liver)
\
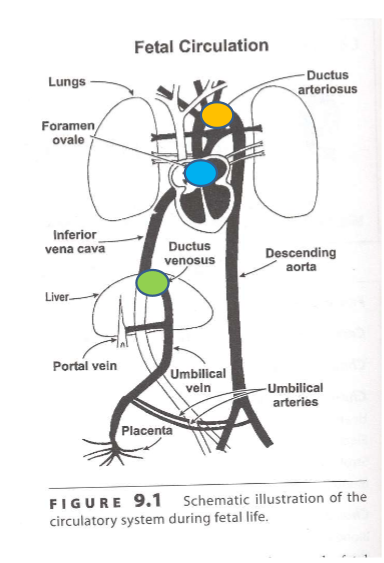
97
New cards
What happens to the shunts
at birth, rapid closing of the shunts to establish post-natal circulation
98
New cards
main reason why shunts close
pressure (taking first breath and blood flows creating pressure)
99
New cards
what would happen if the foramen ovale or the ductus arteriosus did not close?
blood pools in atria
100
New cards
what would happen if the ductus venosus did not close
blood would not go to liver