2-Cutaneous fungal infections
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What are the 2 growth forms of fungi?
1) Moulds (hyphae)
2) Yeasts
Do fungi reproduce sexually or asexually?
Both
What are the lifestyles of fungi?
- Saphrophytes
- Symbionts
- Pathogens
What is a saphrophyte?
Decomposes decaying organic matter
Which types of fungi infect superficially?
- Dermatophytes
- Malassezia
- Candida
Which types of fungi infect systemically?
- Candida
- Aspergillus
What are dermatophytes?
Group of moulds that cause disease in skin, hair and nail
What does geophilic mean?
Soil is the source
What does zoophilic mean?
Animals are the source
What does anthropophilic mean?
Humans are the source
What is tines pedis?
Athlete's foot
What is tinea unguium?
Fungal nail disease
What is tinea cruris?
Jock itch - fungal disease of the groin
What is tinea corporis?
Ringworm
What is tinea capitis?
Scalp ringworm
What are the presentations of tinea pedis?
- Itching, flaking, fissuring of skin
- Plantar foot dry and scaly
- Can infect toe nails
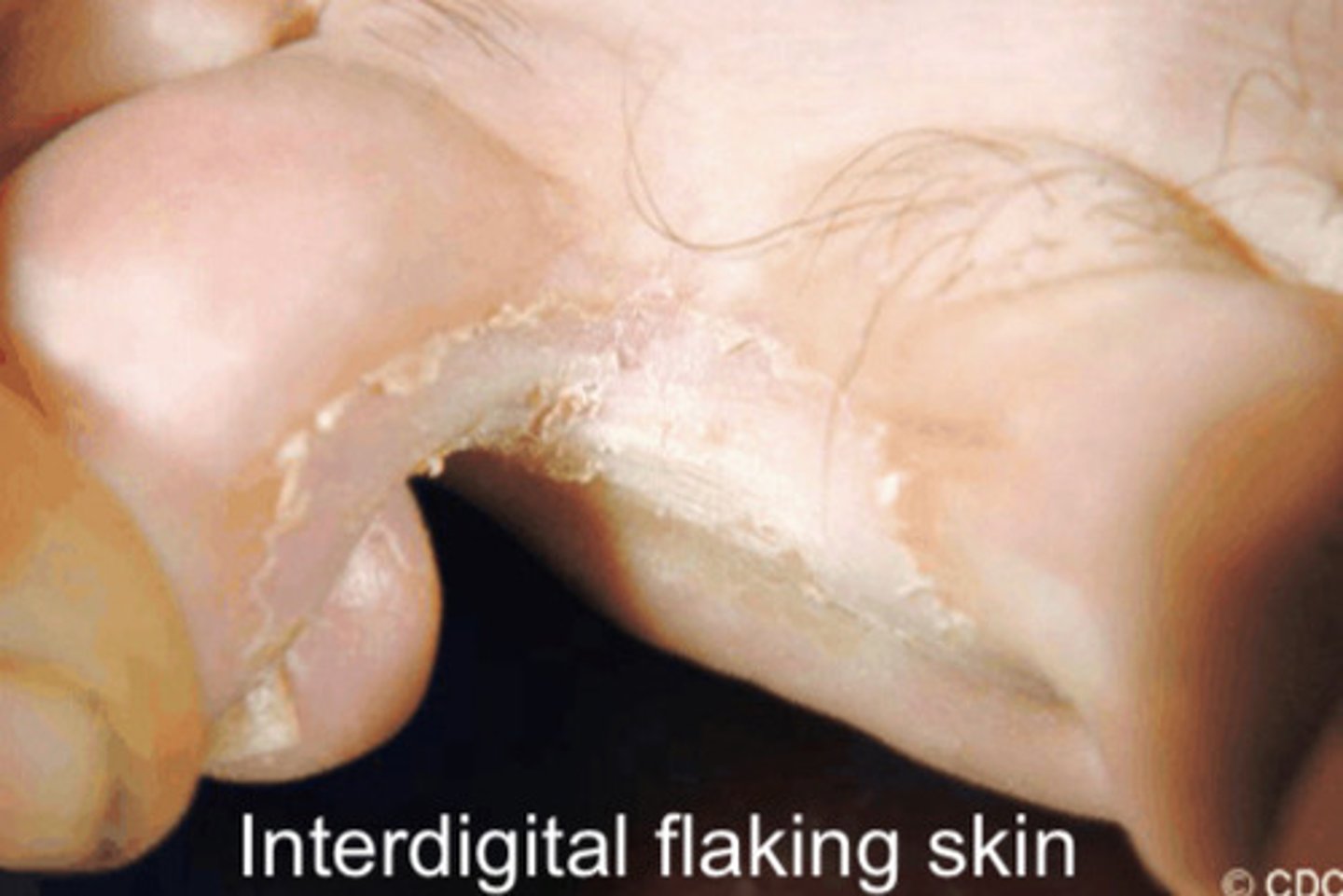
What is the typical cause of tinea pedis?
Trichophyton interdigitale
What is onychomycosis?
Dermatophyte infection of the nails
What are the 3 starting presentations of onychomycosis?
- Distal-lateral subungual onychomycosis
- Superficial onychomycosis
- Proximal onychomycosis
What does onychomycosis lead to if left untreated?
Total nail dystrophy
What are the presentations of tinea cruris (jock itch)?
- More prevalent in men
- Itching, scaling, erythematous plaques
What are the causes of tinea cruris?
- T. Rubrum
- T. Indotineae
What is the complication with T. Indotineae?
Resistant to antifungal terbinafine
What are the presentations of tinea capitis?
- More prevalent in pre-pubescent children
- Slight inflammation, scaly patches with alopecia
What is kerion celsi?
An infection of the hair follicles of the scalp derived from zoophilic dermatophytes like tinea capitis, resulting in boggy inflamed lesions
What are the presentations of tinea corporis?
- Circular, single or multiple erythematous
- Extend from scalp or groin
For mild dermatophyte infections, what is the treatment?
Topical antifungal therapy with:
- Terbinafine
- Clotrimazole
- Miconazole
For severe dermatophyte infections, what is the treatment?
Systemic oral antifungal therapy with:
- Terbinafine
- Griseofulvin
- Itraconazole
What must you always treat tinea capitis with?
Systemic oral antifungal
What is Malassezia?
- organisms
- Commonly found on skin and ear
What causes malassezia?
- Pityriasis versicolor
What are the presentations of pityriasis versicolor?
- Prevalent between puberty and middle age
- Hyper or hypopigmented lesions
- Seen in upper trunk
What is the treatment of pityriasis versicolor?
Topical antifungals:
- Clotrimazole
Systemic oral antifungals:
- Fluconazole
- Itraconazole
Where does candida colonise?
Mucosal surfaces and GI tract in healthy individuals
What are fungal cells stained with?
Calcofluor
What is acute pseudomembranous oral candidiasis?
- Prevalent in younger patients or due to steroid inhalers for asthma
- Low CD4 count
- Yellow mottling of the oropharynx
What is chronic atrophic candidiasis?
- Denature stomatitis
- Prevalent in older patients
What is candida vulvovaginitis?
- Prevalent in women of child-bearing years
- Itching, burning sensation, discharge
What is the treatment for superficial candidiasis?
- Usually -azoles: oral fluconazole
- Topical clotrimazole pessaries
When mustn't oral -azoles be used to treat superficial candidiasis?
For pregnant women - use topical -azoles
What are the presentations of candida oesophagitis?
- Prevalent ion patients with HIV
- Pain/difficulty swallowing
What are the treatments of systemic candidosis?
- Azoles e.g fluconazole (oral)
- Echinocandins e.g anidulafungin (IV)
- Liposomal amphotericin B (IV)
What sort of fungi is Aspergillus?
Mould
What organ does Aspergillus target?
Lungs
What is the allergic reaction to Aspergillus?
Bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
What is the chronic infection to Aspergillus?
Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis (CPA)
What Aspergillus infects the immunocompromised?
Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis
What are Aspergillomas?
- Present in patients with previous TB infection, forming a ball of fungus
- Usually are slow-growing but can break up causing fatalities
What are the presentation of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis?
- Wheezing
- Dyspnoea
- Bronchiectasis
- Raised IgE
What is the treatment for CPA and invasive aspergillosis?
- Itraconazole
- Variconazole
- Amphotercin B