Chapter 3: Forces and Pressure
0.0(0)Studied by 5 people
Card Sorting
1/24
Last updated 12:35 PM on 9/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
1
New cards
Graph
________ b- ________ shows what happens when the load is removed.
2
New cards
Graph a
is an extension-load graph for a spring
3
New cards
Graph b
graph shows what happens when the load is removed
4
New cards
Define Moment.
It is the turning effect of a force.

5
New cards
Give equation for moments.
Moments= Force x Perpendicular Distance
6
New cards
What is the principle of moments (equilibrium)?
It states that the sum of the clockwise moments about any point is equal to the sum of the anticlockwise moments about that same point.
7
New cards
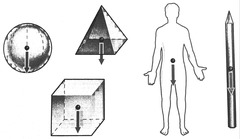
What is centre of mass (gravity)?
It is the effect of gravitational forces act on an object as a single resultant force (the object's weight).
8
New cards
Define stable equilibrium.
It is when the centre of mass rests over a large base (making tripping difficult).
9
New cards
Define unstable equilibrium.
It is when the centre of mass rests over a very small base (making tipping easy).
10
New cards
Define neutral equilibrium.
It is when the centre of mass rests over a round base, allowing movement when force is applied (allowing rolling).
11
New cards
What are the conditions of equilibrium.
1) the sum of the forces in one direction must equal the sum of the forces int he opposite direction.
2) the principle of moments must apply.
2) the principle of moments must apply.
12
New cards
Define pressure.
It is the concentration of a force.
13
New cards
What is the SI unit of pressure?
Pascal (Pa)
14
New cards
State equation for pressure.
Force / Area
15
New cards
State equations for pressure in liquids.
P = density (ρ) x gravity (g) x depth in liquid (h)
16
New cards
Properties of pressure in liquids
1) pressure acts in all directions
2) pressure increases with depth
3) pressure depends on the density of the fluid
4) pressure does NOT depend on the shape of the container/vessel
2) pressure increases with depth
3) pressure depends on the density of the fluid
4) pressure does NOT depend on the shape of the container/vessel
17
New cards
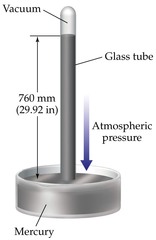
What is the use of barometer?
It is the instrument used to measure atmospheric pressure typically with Mercury (Hg).
18
New cards
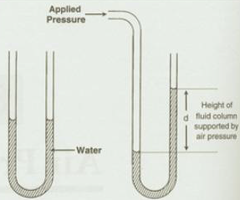
What is the use of manometer?
It is instrument used to measure pressure differences compared to atmospheric pressure.
19
New cards
What is Hooke's Law?
It states that the extension of a spring is proportional to the load applied to it, provided the limit of proportionality is not exceeded.
20
New cards
What is limit of proportionality?
It is the full extension of an elastic object until further force extends more than the spring constant
21
New cards
State equation for hooke's law.
F = k * x
22
New cards
Define boyle's law.
It is for a fixed mass of gas at constant temperature, the pressure is inversely proportional to the volume.
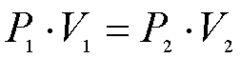
23
New cards
State equation for boyle's law.
P1 x V1 = P2 x V2
24
New cards
Why is the pressure of the gas inversely proportional to volume in boyle's law?
As volume decreases, the gas volume comes close together. As a result they get a chance a to collide more frequently with the walls of container thereby exerting a greater pressure force per unit area, hence pressure increases.
25
New cards
Where is hydraulic system used?
Common use in pedal brakes of car.