Sports medicine Skeletal System
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Osteo
bone
Prefix
R with a circle around it
right
L with a circle around it
Left
How many bones are in an adult
206
How many bones are in an infant and what happens as they grow
270-300 and they fuse together
Smallest bone
stapes(part of your ear)
Largest bone
femur
Bone
living tissue that makes up the skeleton
Cartilage
main type of connective tissue
Various types and purposes
Where are some places you can find cartilage
joints
Bones
Spine
Lungs
Ears
Nose
Ligaments
tough, elastic connective tissue that surrounds a joint to give support and limit the joint movement
Bone to bone
What are the 2 main parts of a bone
organic and inorganic
Organic
Living cells; make bone resilient
Inorganic
minerals and salts (calcium/Phosphate)
Makes bone solid
What does Wolff’s law state
Bones are constantly changing based on the forces applied to them
What are the functions of the skeletal system
provide support for the body
Protects vital organs
Assists with movement
Production of blood cells
Storage area for minerals
What type of skeleton do humans have
endoskeleton
What are the 2 groups of bones
Axial and appendicular
Axial bones
bones around axis of body
Appendicular bones
extremities
how many vertebrae does the human body have
33
Artho
Joint
B with a circle around it
bilateral
What are the classifications of bones
long
Short
Irregular
Flat
Sesamoid
Long bones
hard/dense
Provide strength, structure, and mobility
Has a shaft and 2 ends
(Can be found in extremeties)
Name some long bones
clavicle
Humerus
Radius
Ulna
Metacarpus
Phalanges
Femur
Tibia
Fibula
Metatarsus
Short bones
short and irregular shaped
Found in wrist and ankle
Provides stability and movement
Examples of short bones
carpals and tarsals
What is each individual bone in the phalanges called
phalanx
Sesamoid bones
Imbedded in tendons
Reinforces and decreases stress on tendons
How many carpals are there
16 total
Examples of Sesamoid bones
patella
Irregular bones
complex shapes
For protection
What are some examples of irregular bones
vertebrae
Zygomatic
Maxilla
Mandible
Flat bones
Thin and flat
Protection or muscle attachment
Makes red blood cells
Examples of flat bones
hip
Rib
Scapula
Sternum
Parietal
Frontal
Epiphysis
Ends
2 total
Epiphyseal plate
Growth plate
(Grows in lengths)
Metaphysis
growth center
Where epiphyseal plate is
Diaphysis
shaft
Somewhat pliable
Marrow cavity
blood cell production
blood vessels
blood supply
Fracture
complete or partial break in the continuity of the bone
Fx
fracture
What are some differences bone growth and formation
Age difference
Sex difference
Racial difference
Age difference
birth to death
Greenstick vs brittle bones disease
Sex difference
bone density M=50% higher peak density
Women have a greater pelvic width
Racial difference
bone density
Rate of density of decline
describe bone growth
bones growth in length at growth plate
Bones grow in width by generation of new cells from marrow cavity
What are some factors that effect bone growth
genetics
Mechanical
metabolic
endocrine
Mechanical
Activity of muscle on bone
Metabolic
dietary
Vitamins and minerals
Endocrine
hormone secretion
Who made wolffs law
Julius Wolff 1892
Rickets
softening and wreaking of bones in children
Caused by extreme vitamin D deficiency or no time outside
Treatment is increase in eating calcium and or vitamin D
Could need brace or surgery
Osteoporosis
body loses to much bone or makes to little
Bone becomes weak
Treatment is medications healthy diet and weight bearing exercise
Crepitus
A grading sound/sensation caused by friction between bone and cartilage or fractured part of bone
Dx
diagnosis
What are the 3 types of joints
fibrous
Cartilaginous
Synovial
Fibrous joint
bones are attached by fibrous tissue
No movement
Also called synarthrotic
Examples of fibrous joint
skull sutures
Cartilaginous joints
Bones connected by cartilage tissue
Little to no movement
Also called amphiarthrotic
Examples of cartilaginous Joints
vertebrae
Synovial joints
freely to move
Also called Diarthrotic
What is an examples of synovial
hip
Shoulder
Knee
What’s inside a synovial joint
Surrounded by an articular capsule filled with synovial fluid
Articular cartilage covers the articular surface of bones
2 or more bones
What are some synovial joint types
ball and socket
Hinge
Saddle
Pivot
Gliding
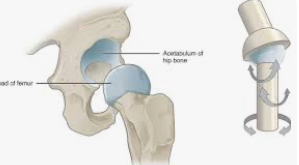
Ball and socket joints
movement in all 3 planes
Hip and shoulder
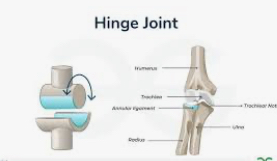
Hinge joints
ROM is flexion/extension
Elbow and knee
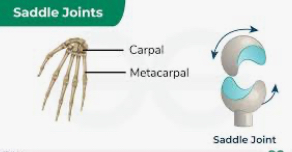
Saddle
movement in all planes
Thumb
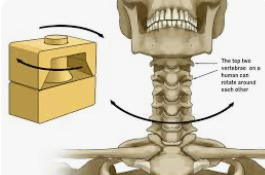
Pivot
ROM is rotation
Skull/neck and radius/ulna
Gliding
ROM is gliding
Intercarpal joints of wrist/AC unit
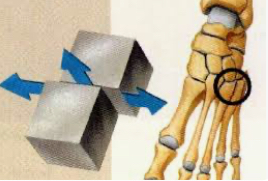
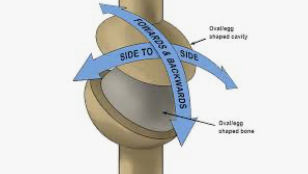
Candyloid/Ellipsoidal
Oval surface of one bone fits in another
Radiocarpal
Effusion
excessive swelling inside a joint
UE
Upper extremeties
Arthritis
group of disease involving inflammation of the joints
2 main types- osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis
Type of autoimmune disease
Osteoarthrits
chronic disease(aging) break down of cartilage/bone overtime.Has pain/stifness
Found in hips and knees
Rheumatoid Arthritis
chronic inflammatory disease of connective tissue/joints
3x more common in females
Starts in ages 35-45
Painful deformity and immobility
Found in fingers,wrist, feet, and ankles