4b: Crude oil
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
1
New cards
what is crude oil
a mixture of different hydrocarbons of similar chain length called fractions
2
New cards
how do the physical properties of hydrocarbons change as the molecule size increases
* boiling point increases
* liquid becomes less volatile, more viscous and darker
* don’t burn as easily
* liquid becomes less volatile, more viscous and darker
* don’t burn as easily
3
New cards
why do the physical properties of hydrocarbons change as the molecule size increases
* increasing attraction between molecules
* more energy needed to break intermolecular forces
* more energy needed to break intermolecular forces
4
New cards
how are the fractions in crude oil separated
by fractional distillation
5
New cards
does the number of carbon atoms in a chain affect properties and boiling points
yes
6
New cards
what is the determining factor for fractional distillation
size and length of each hydrocarbon molecule
7
New cards
what does the size of each hydrocarbon molecule depend on
number of carbon and hydrogen atoms the molecule contains
8
New cards
fractional distillation
* crude oil is heated and vapour is passed into a fractionating column
* the vapour rises up depending on its boiling point
* the vapour rises up depending on its boiling point
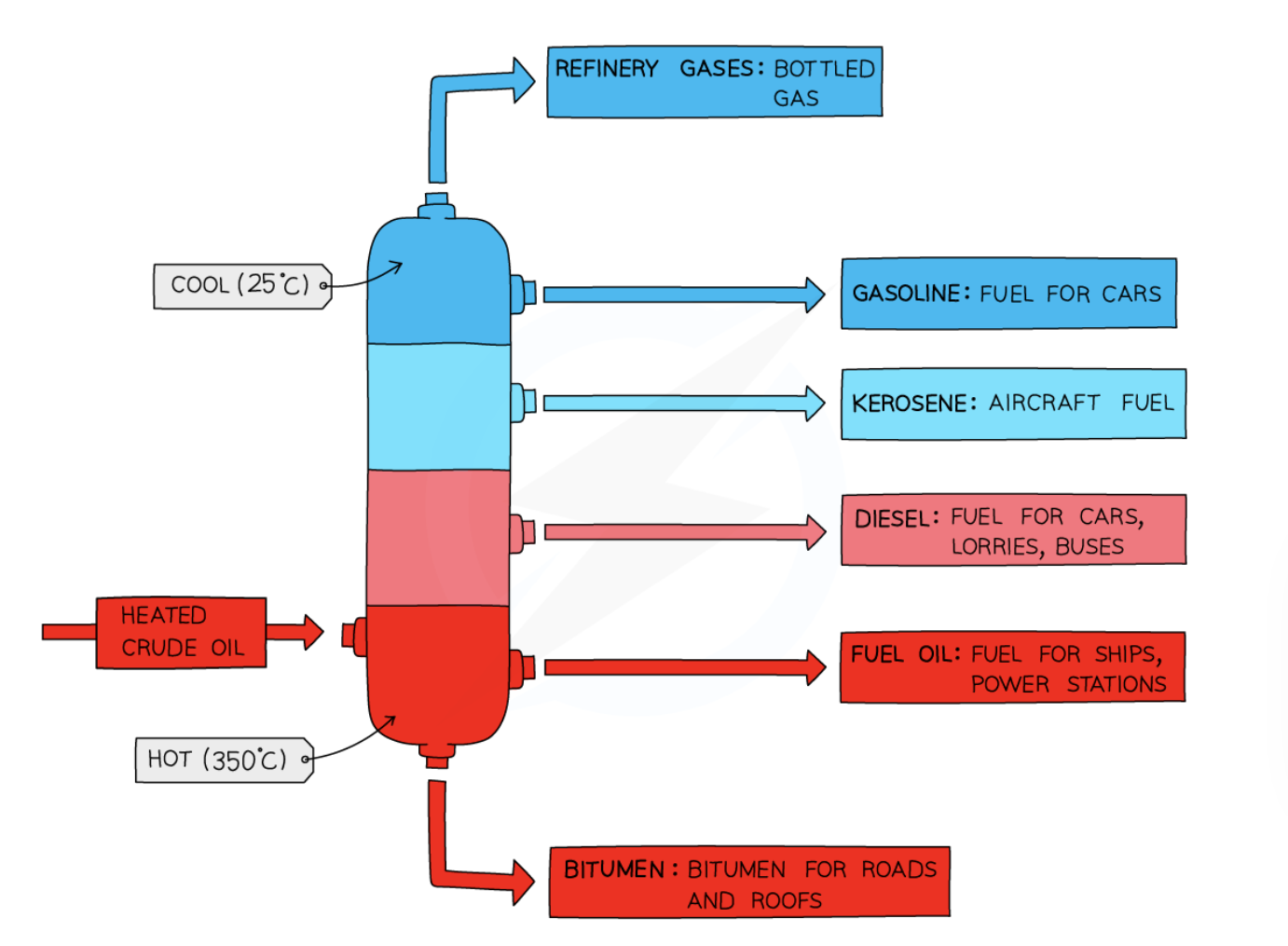
9
New cards
positioning of crude oil in a fractionating column
cool at the top and hot at the bottom
10
New cards
do smaller molecules have lower boiling points or higher
lower
11
New cards
do larger molecules have lower boiling points or higher
higher
12
New cards
what are the different heights that the different fractions condense at dependent on
their boiling points
13
New cards
order of main fractions from coolest to hottest
* refinery gas
* gasoline
* kerosene
* diesel oil
* fuel oil
* bitumen
* gasoline
* kerosene
* diesel oil
* fuel oil
* bitumen
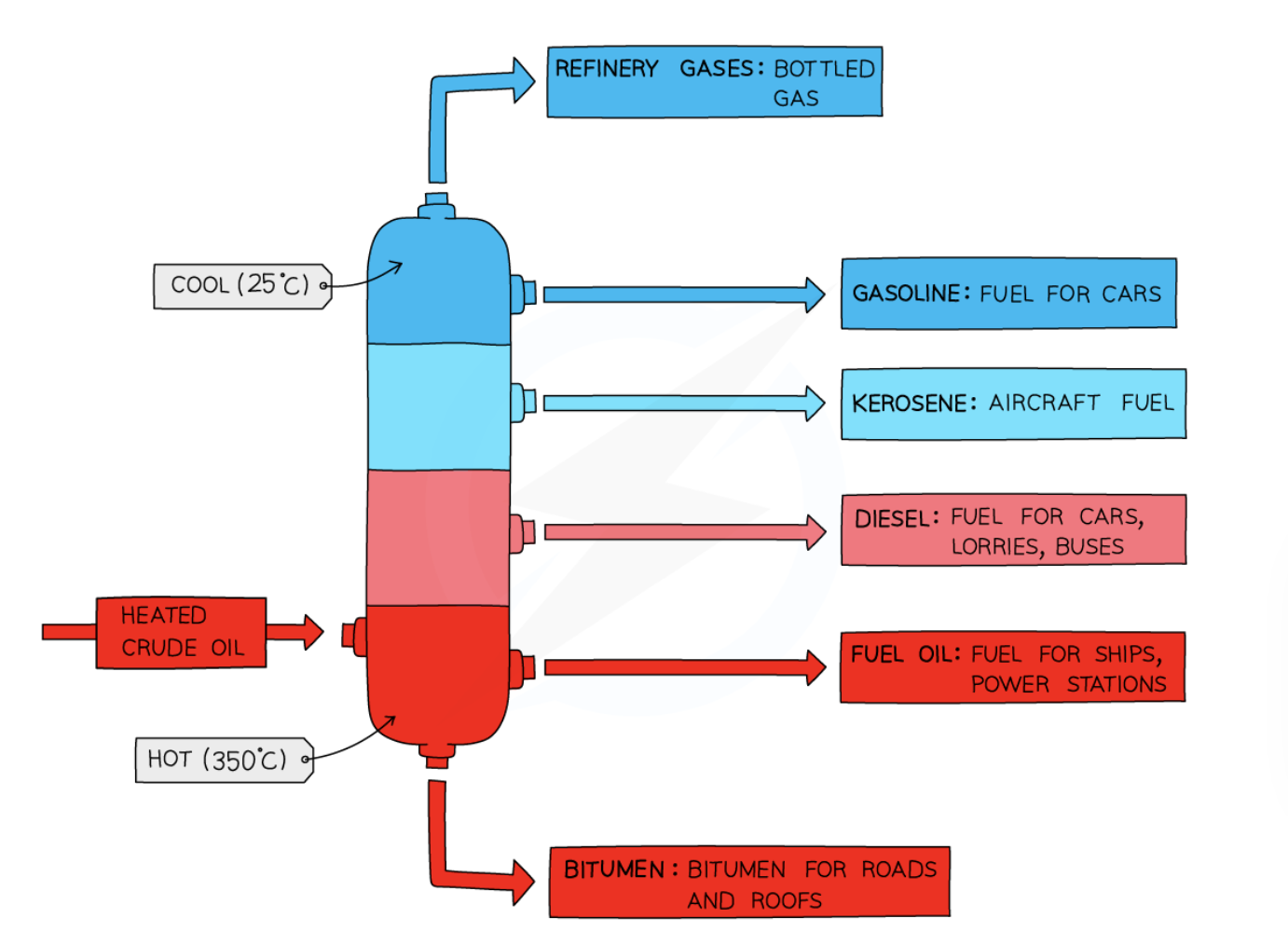
14
New cards
what is refinery gas
a mixture of methane, ethane, propane, butane
15
New cards
uses of refinery gas
used for LPG for domestic heating and cooking
16
New cards
uses of gasoline
fuel in cars
17
New cards
uses of kerosene
fuel for jet aircrafts, domestic heating oil and paraffin
18
New cards
uses of diesel
fuel for buses, lorries, cars, railway engines and conversion into petrol for cracking
19
New cards
uses of fuel oil
fuel for ships and industrial heating
20
New cards
uses of bitumen
melted and mixed with small pieces of rock to make the top surface of roads
21
New cards
what is a fuel
a substance which when burnt releases heat energy
22
New cards
fossil fuels
* coal
* oil
* natural gas
* oil shales
* tar sands
* oil
* natural gas
* oil shales
* tar sands
23
New cards
how are non-renewable fossil fuels obtained
from fractional distillation in crude oil
24
New cards
combustion - products
* carbon dioxide
* carbon monoxide
* oxides of nitrogen
* oxides of sulfur
* unburned hydrocarbons
* carbon particulates
* carbon monoxide
* oxides of nitrogen
* oxides of sulfur
* unburned hydrocarbons
* carbon particulates
25
New cards
complete combustion in hydrocarbon compounds
* occurs in the presence of excess oxygen
* a hydrocarbon burns in air to form carbon dioxide and water
* it also releases heat
* a hydrocarbon burns in air to form carbon dioxide and water
* it also releases heat
26
New cards
incomplete combustion in hydrocarbon compounds
* occurs in presence of insufficient oxygen
* it releases soot, carbon monoxide and water
* it releases soot, carbon monoxide and water
27
New cards
carbon monoxide
toxic and odourless gas causing death
28
New cards
what are the dangers of carbon monoxide
it reduces the ability of the blood to carry oxygen around the body by binding to haemoglobin
29
New cards
how is carbon dioxide harmful for the environment
it’s a greenhouse gas which traps heat radiated from the earth’s surface
30
New cards
what is formed when nitrogen and oxygen react in the high pressure and temperature conditions of internal combustion engines and blast furnaces
NO and NO2
31
New cards
32
New cards
acid rain
formed when water and oxygen in the atmosphere react with sulfur dioxide to product sulfuric acid, or various nitrogen oxides to give nitric acid
33
New cards
how do fossil fuels contribute to acid rain
* they contain a small amount of sulfur which is burned with the fuel and forms sulfur dioxide
* this reacts in the atmosphere with oxygen and water and becomes sulfuric acid
* nitrogen dioxide from car engine reacts with rain water to form nitrous and nitric acids
* this reacts in the atmosphere with oxygen and water and becomes sulfuric acid
* nitrogen dioxide from car engine reacts with rain water to form nitrous and nitric acids