Tumor Immunology
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
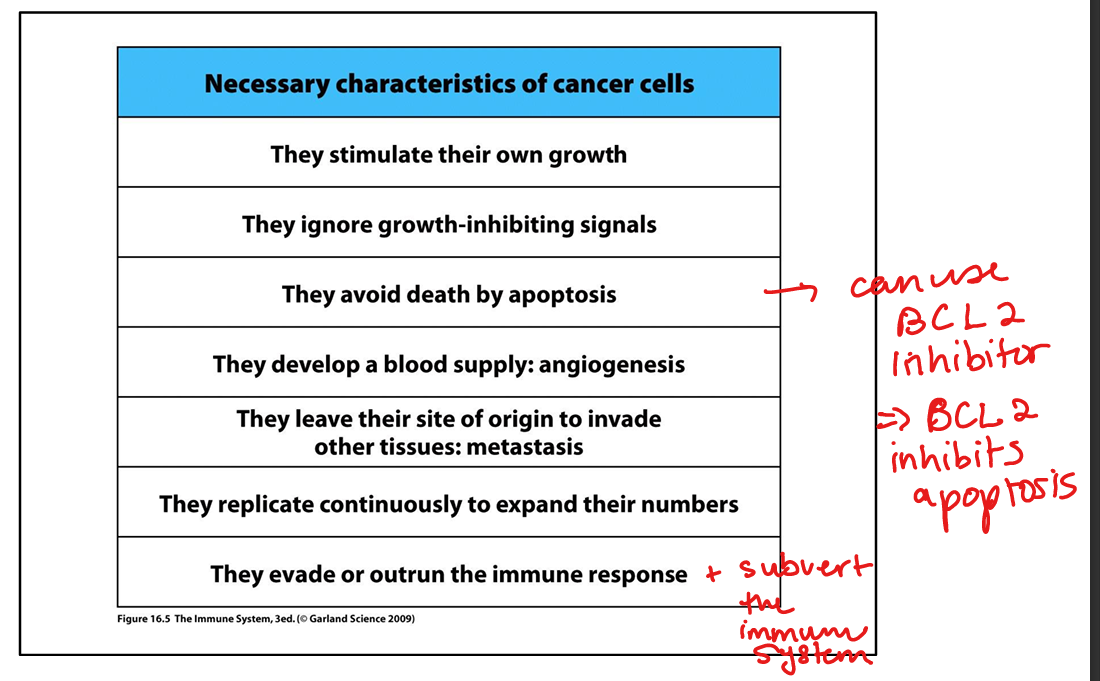
Characteristics of tumor development
Stimulate own growth, ingnore growth inhibiting signals, avoid apoptosis, angiogenesis, metastisis, replicate continuously, evade immune system

Learning Objective: Causes of tumor development
Inherited mutations, spontaneous replication errors, chemical carcinogens, radiation, and dysregulation from oncogenic viruses (HPV, EBV, HBV, HTLV‑1, HHV‑8).


Immune-evasion mechanisms of tumors
Tumors evade immunity by downregulating MHC I(low immunogenicity), losing tumor antigens(antigenic modulation-invisible), inducing T‑cell tolerance, secreting immunosuppressive cytokines (TGF‑β, IL‑10, IDO)=tumor induced immune suppression, recruiting Tregs, expressing inhibitory ligands (PD‑L1), and forming physical barriers.
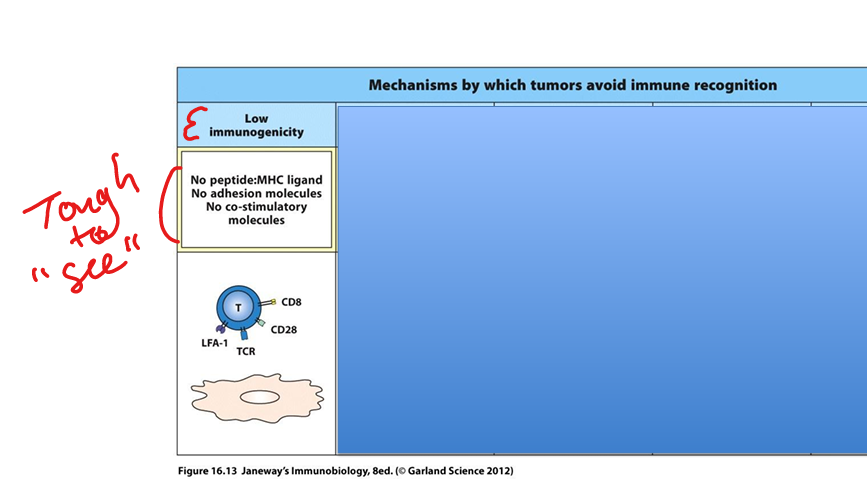
Tumor immune evasion – low immunogenicity
Tumors may lack MHC, co‑stimulatory molecules, or adhesion molecules, preventing effective T‑cell activation.
Tumor immune evasion – antigenic modulation
Antibodies drive internalization/loss of tumor antigens, selecting for antigen‑loss variants.

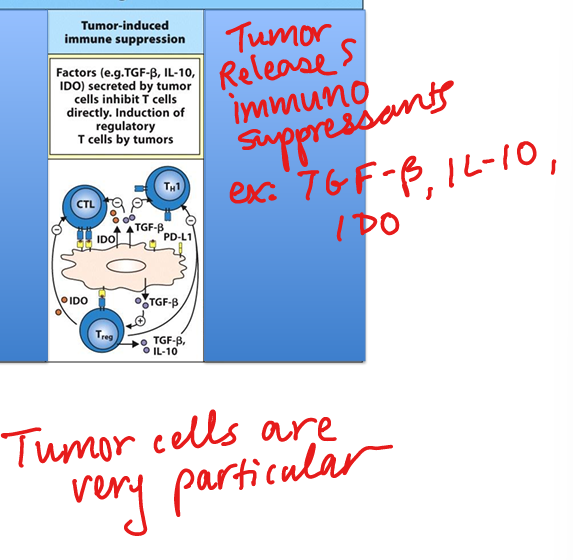
Tumor immune evasion – immunosuppression
Tumors secrete TGF‑β, IL‑10, and IDO and recruit Tregs to inhibit effector T‑cell responses.

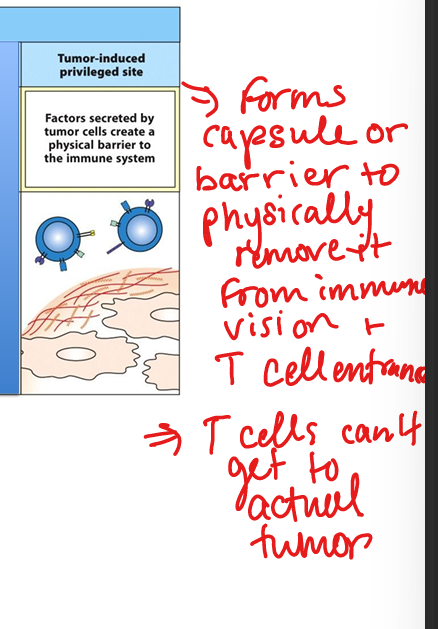
Tumor immune evasion – privileged site formation
Tumors create a physical barrier or immunosuppressive microenvironment that prevents immune cell infiltration.

Role of Tregs in anti‑tumor response
Tregs suppress anti‑tumor immunity by releasing TGF‑β and IL‑10, inhibiting CD4 and CD8 effector T cells and allowing tumor escape.
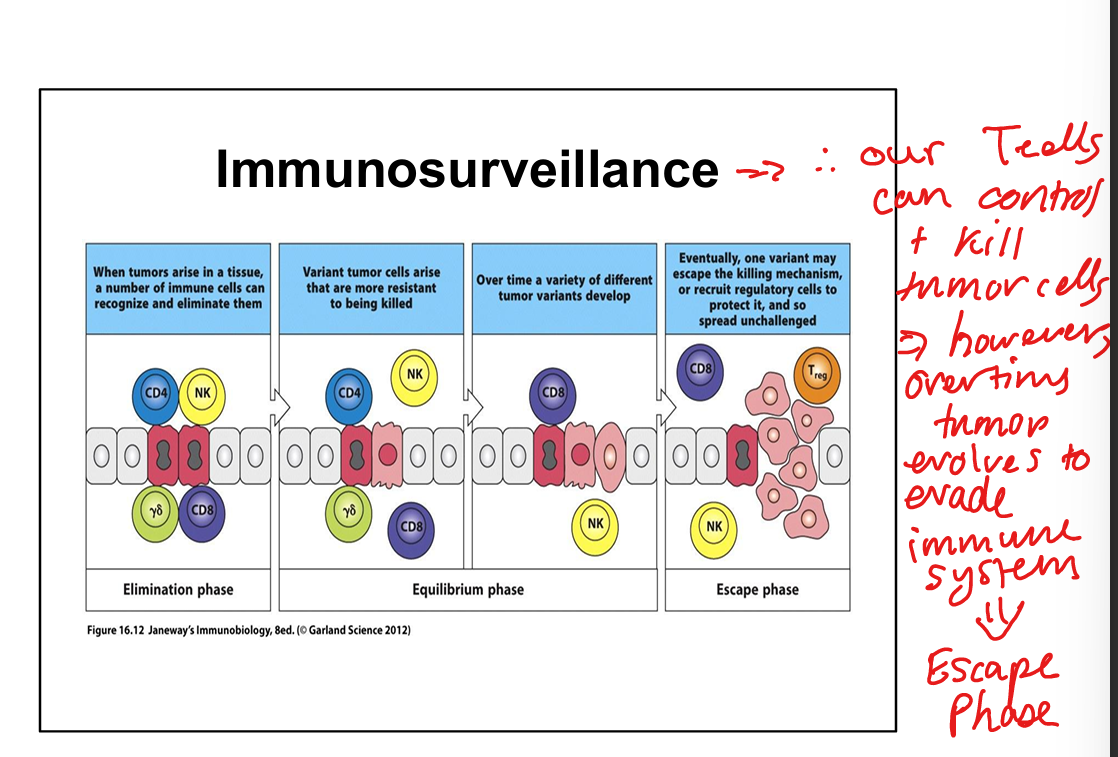
Learning Objective: Immunosurveillance concept
The immune system (NK cells, CD8 T cells, γδ T cells) eliminates early tumor cells, but tumor variants may enter equilibrium and eventually escape immune control.

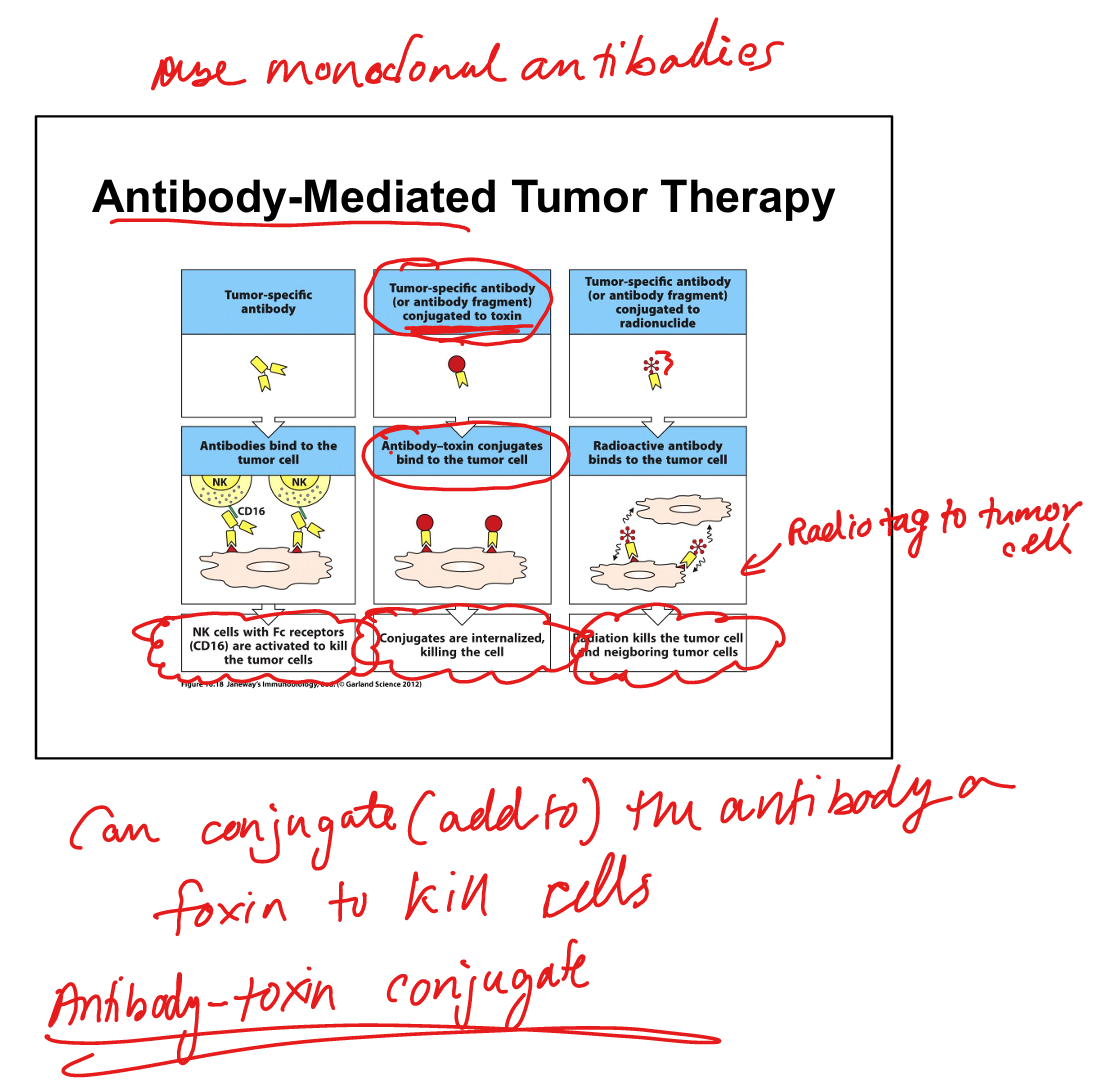
Antibody mediated tumor therapy 3 types:
Tumor specific antibody, tumor specific antibody conjugated to a toxin, or tumor specific antibody conjugated to radionucleotide

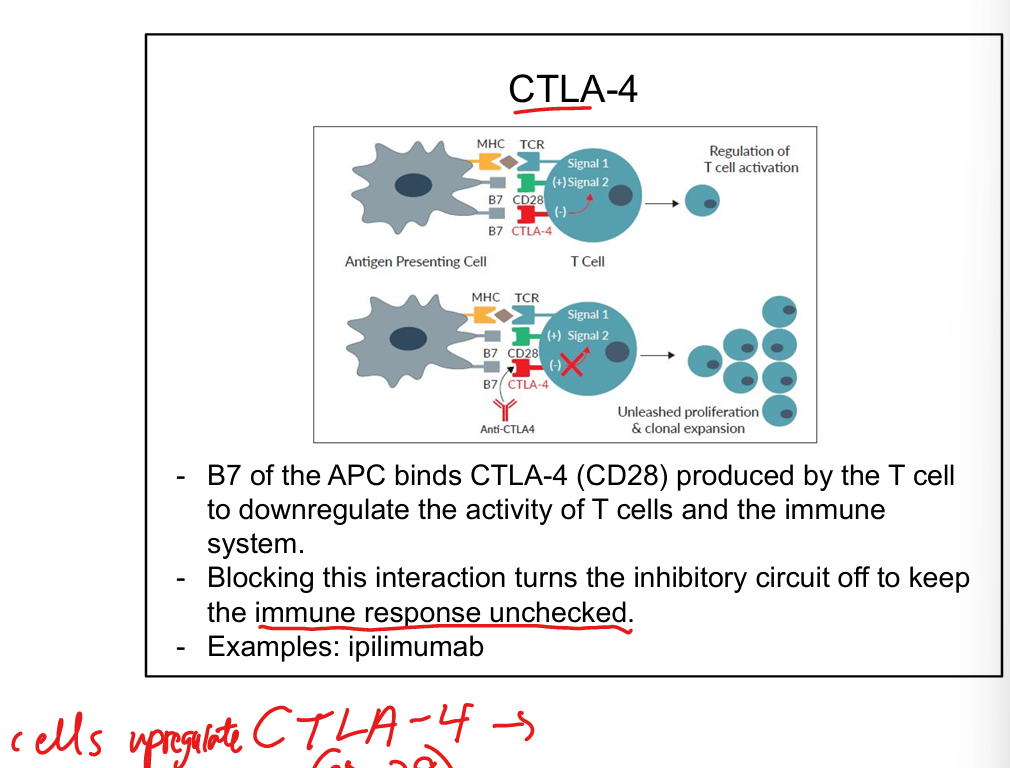
MOA of CTLA-4(competes with CD28) inhibitor drugs
APC binds CTLA-4(CD28) which are produced by T cell; this down regulates the activity of T cells and decreases immune response. Inhibiting CTLA-4(CD28) keeps the immune response on.

PD-1: PDL-1 mechanism
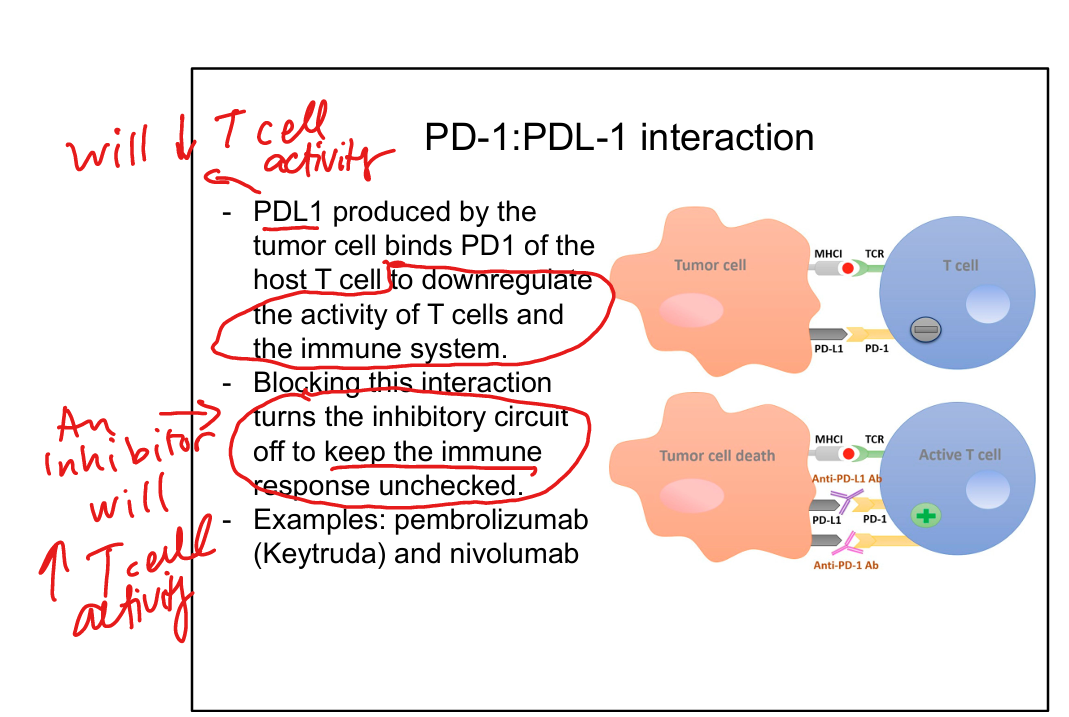
Keeps immune system unchecked and ramped up (taking the brakes off T cells so they can kill cancer)
