Energy Changes in a System
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What is the symbol equation for kinetic energy? Give SI units for all quantities involved.
½mv²
energy (J), mass (kg), velocity (m/s)
What is the word equation for kinetic energy? Give SI units for all quantities involved.
0.5 × mass × (velocity)²
energy (J), mass (kg), velocity (m/s)
What is the symbol equation for elastic potential energy? Give SI units for all quantities involved.
½ke²
energy (J), spring constant (N/m), extension (m)
What is the word equation for elastic potential energy? Give SI units for all quantities involved.
0.5 × spring constant × (extension)²
energy (J), spring constant (N/m), extension (m)
What is the symbol equation for gravity potential energy? Give SI units for all quantities involved.
mgh
energy (J), mass (kg), gravitational field strength (N/kg), height (m)
What is the word equation for gravity potential energy? Give SI units for all quantities involved.
mass × gravitational field strength × height
energy (J), mass (kg), gravitational field strength (N/kg), height (m)
Define the ‘specific heat capacity’ of a substance.
The amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 kilogram of a substance by 1 degree Celsius.
State the units for specific heat capacity.
J/kg°C
What is the definition of ‘power’?
The rate at which energy is transferred.
State two equations for power. Give SI units for all quantities involved.
power = energy transferred / time
power = work done / time
energy (J), work done (J), time (s)
What is the unit of power?
Watts (W)
Two motors lift the same mass through the same height. Motor A does this in half the time of Motor B. Which dissipates the most power?
Motor A.
The energy transferred is the same but the time taken is less (P = E / t).
Describe the energy changes involved when a ball is thrown upwards and then returns to its starting position. Ignore air resistance.
Upwards: KE is converted to GPE
Peak: Maximum GPE, zero KE
Downwards: GPE is converted to KE
KE (Kinetic Energy), GPE (Gravitational Potential Energy)
Describe the energy transfers for a bungee jumper.
When falling, the GPE is converted to KE of jumper
As the cord tightens, KE is converted and stored as Elastic Potential Energy (EPE)
At lowest point, the jumper’s initial GPE equals the EPE stored in the cord
Explain why a bungee jumper slows down once the cord begins to stretch.
Kinetic energy decreases since it is converted to elastic potential energy.
Since KE is proportional to (velocity)², as KE decreases, so does velocity.
Give examples of chemical energy stores.
Food, Fuel (eg. wood, coal, petrol), Batteries
State all the different stores of energy.
kinetic, gravitational potential, elastic potential, chemical, thermal (internal), magnetic, electrostatic, nuclear
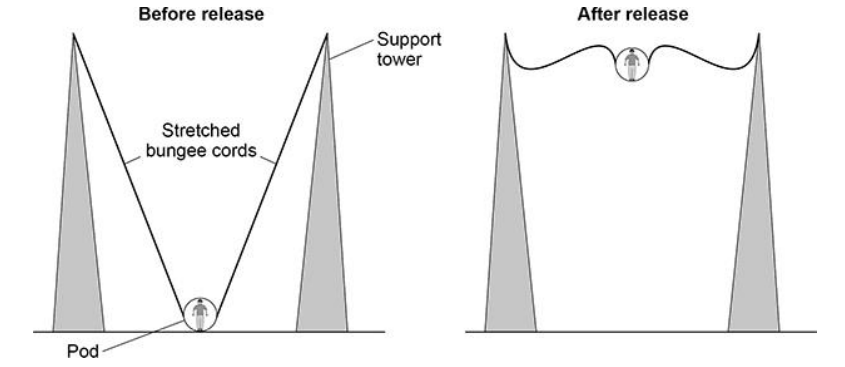
In a ride at a theme park, a person is strapped into a pod that is attached to two stretched bungee cords. The bungee cords behave like springs.
The figure below shows a person using the ride.
Which energy store increases as the bungee cords are stretched?
Elastic potential energy
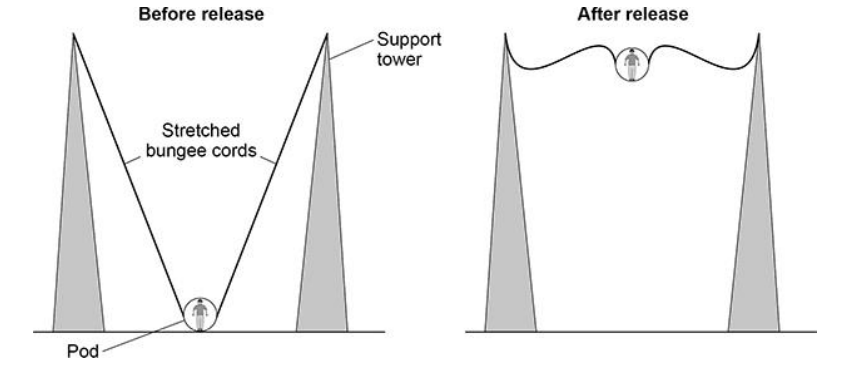
In a ride at a theme park, a person is strapped into a pod that is attached to two stretched bungee cords. The bungee cords behave like springs.
The figure below shows a person using the ride.
When the pod is released, the pod accelerates upwards.
Before the pod is released the extension of each of the two bungee cords is 8.0 m.
The spring constant of each bungee cord is 735 N/m. The mass of the pod is 240 kg.
gravitational field strength = 9.8 N/kg
Calculate the maximum height reached by the pod. Use the Physics Equations Sheet.
20 m
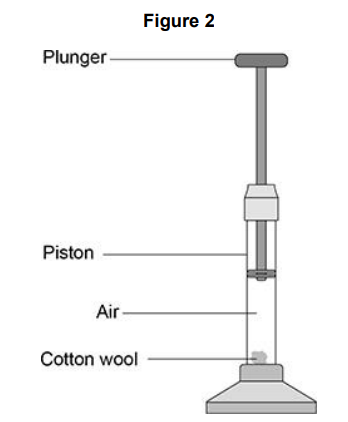
A fire piston is a special type of syringe that can be used to start fires.
Figure 2 shows a fire piston.
The plunger is pushed quickly downwards and compresses the air. When the air is compressed quickly, the temperature of the air increases.
How does an increase in temperature affect the air particles inside the piston?
The mean kinetic energy of the particles increases.
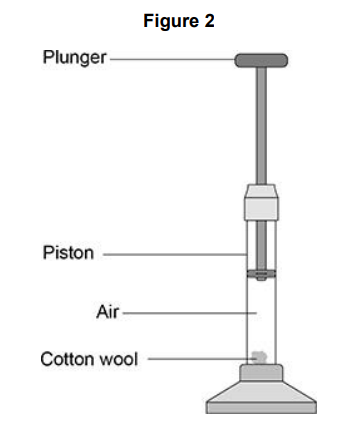
A fire piston is a special type of syringe that can be used to start fires.
Figure 2 shows a fire piston.
The plunger is pushed quickly downwards and compresses the air. When the air is compressed quickly, the temperature of the air increases.
When the air is hot enough, a small piece of cotton wool in the piston catches fire.
The energy transferred to the air in the piston is 0.0130 J.
The mass of air in the piston is 2.60 × 10-8 kg.
specific heat capacity of air = 1.01 kJ/kg °C
Calculate the temperature change of the air. Use the Physics Equations Sheet.
495 °C
A remote village in the UK uses a hydroelectric generator to provide electricity.
In one day, 2 500 000 kg of water passes through the hydroelectric generator.
The change in gravitational potential energy of the water is 367.5 MJ.
gravitational field strength = 9.8 N/kg
Calculate the mean change in vertical height of the water as it moves through the hydroelectric generator. Use the Physics Equations Sheet.
15 m
A remote village in the UK uses a hydroelectric generator to provide electricity.
The generator transfers 3.0 kW of electrical power.
Calculate the time taken for the generator to transfer 2.16 × 107 J of energy.
Use the Physics Equations Sheet. Give your answer in standard form
7.2 × 103 s
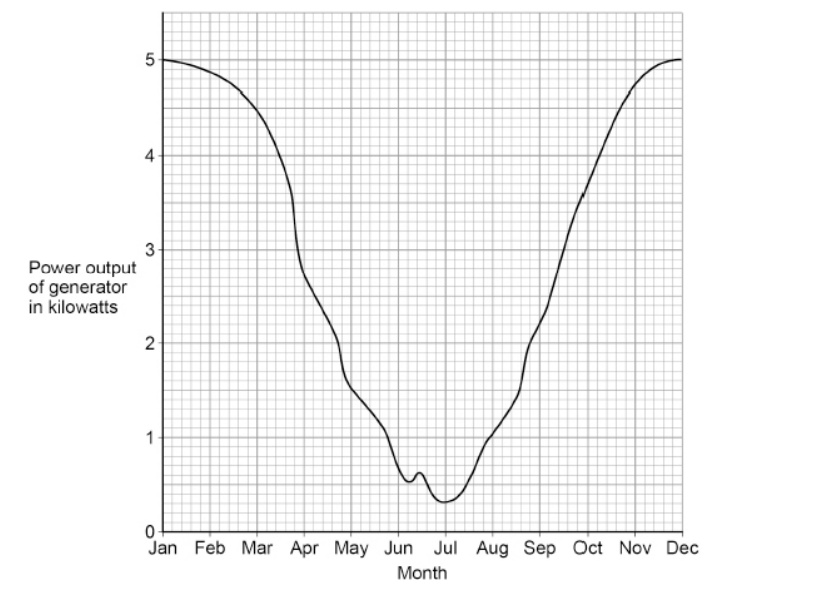
A remote village in the UK uses a hydroelectric generator to provide electricity.
The figure below shows how the power output of the generator varied during one year.
A solar power system is installed in the remote village in addition to the hydroelectric generator.
Explain why this improves the reliability of the electricity supply to the village.
Use information from the figure above.
In the summer the power output from the hydroelectric generator would be lower but the solar power output would be greater, so there is less variation in total power output which improves the reliability of the electricity supply.
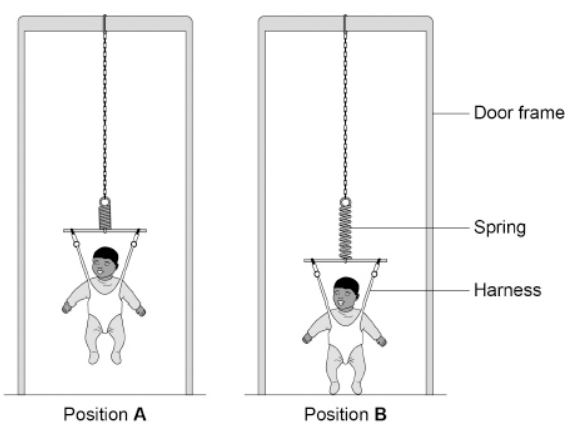
A baby bouncer is a harness attached to a spring that hangs from a door frame.
The figure above shows a baby in a baby bouncer in two positions.
The baby bouncer should not be used with babies that have a mass greater than 12 kg.
Suggest one reason why.
The spring may become permanently extended so the baby’s feet are always on the floor.
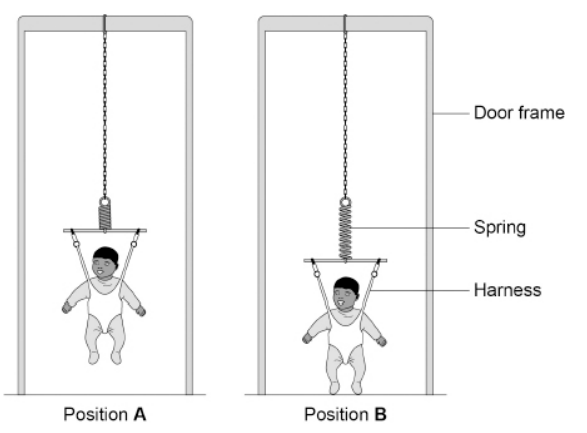
A baby bouncer is a harness attached to a spring that hangs from a door frame.
The figure above shows a baby in a baby bouncer in two positions.
In positions A and B the baby is stationary.
Describe the energy transfers as the baby moves from position A to position B.
In position A the baby has gravitational potential energy, as the baby moves down this gravitational potential energy is transferred to kinetic energy and then elastic potential energy of the spring. In position B all the energy is elastic potential energy.
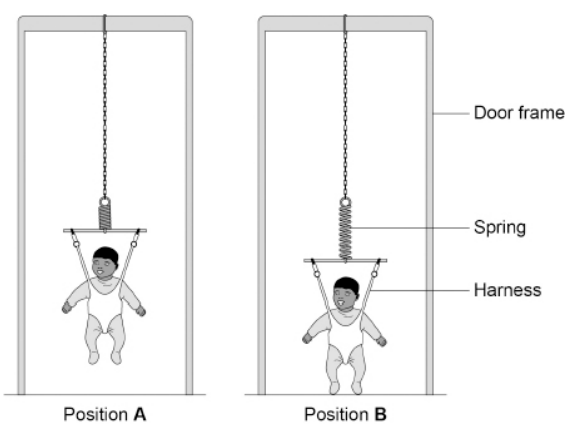
A baby bouncer is a harness attached to a spring that hangs from a door frame.
The figure above shows a baby in a baby bouncer in two positions.
In one position the extension of the spring is 8.0 cm.
The elastic potential energy stored by the spring is 4.0 J.
Calculate the spring constant of the spring. Use the Physics Equations Sheet.
1250 N/m
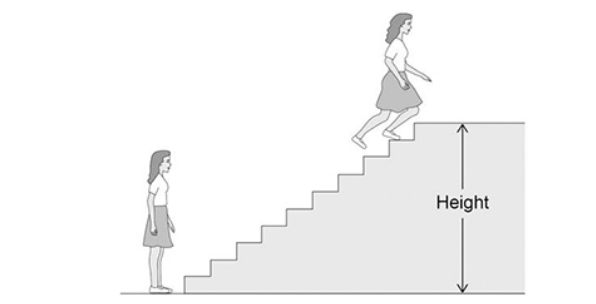
The figure below shows a girl doing an experiment to determine her power output by running to the top of some stairs.
The mass of the girl was 60.0 kg.
The height of the stairs was 175 cm.
The girl ran to the top of the stairs in 1.40 s.
gravitational field strength = 9.8 N/kg
Calculate the power output of the girl. Use the Physics Equations Sheet.
735 W
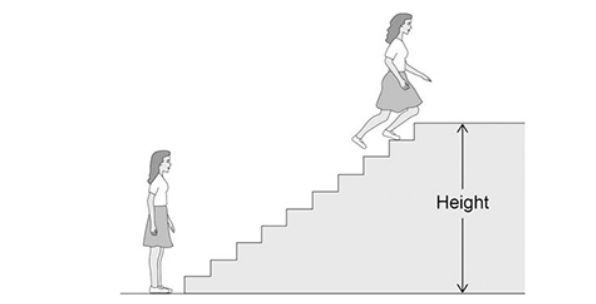
The figure below shows a girl doing an experiment to determine her power output by running to the top of some stairs.
The total power output of the girl was greater than the power output she calculated.
Suggest two reasons why.
The girl increases her kinetic energy as well as increasing her gravitational potential energy.
Some energy is transferred as thermal energy to the surroundings
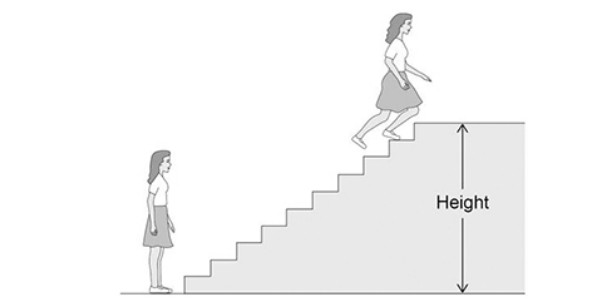
The figure below shows a girl doing an experiment to determine her power output by running to the top of some stairs.
The mass of the girl was 60.0 kg.
The height of the stairs was 175 cm.
The girl ran to the top of the stairs in 1.40 s.
A boy took more than 1.40 s to run up the same stairs.
The power output of the boy was the same as the power output of the girl.
What conclusion can be made about the boy's mass?
The boy’s mass was greater than the girl’s mass
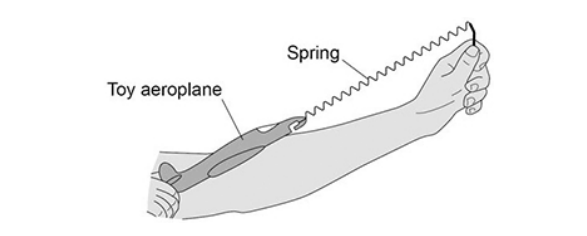
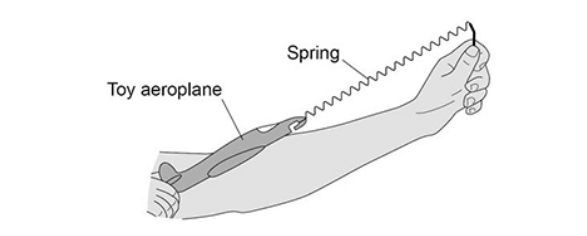
The figure below shows a student launching a toy aeroplane.
To launch the aeroplane, the student pulls on it to stretch the spring and then releases it.
Just before the toy aeroplane is released, the spring has an extension of 0.12 m.
mass of aeroplane = 0.020 kg
spring constant of the spring = 50 N/m
Calculate the maximum speed of the toy aeroplane just after it is launched.
Use the Physics Equations Sheet. Give the unit.
6 m/s
The figure below shows a student launching a toy aeroplane.
To launch the aeroplane, the student pulls on it to stretch the spring and then releases it.
Complete the sentence.
As the aeroplane moves upwards through the air there is a decrease in the ____________________
energy of the aeroplane.
kinetic
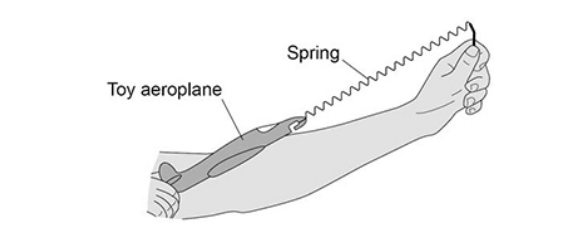
The figure below shows a student launching a toy aeroplane.
To launch the aeroplane, the student pulls on it to stretch the spring and then releases it.
Give one factor which would increase the distance the toy aeroplane travels horizontally before hitting the ground.
Increasing the extension of the spring