The Foundations of Western Civilization (Chapters 1-7)
1/117
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
What Mesopotamian inventions most influenced later mathematical and astronomical developments?
Algebra, astronomical charts, and the place-value notation system
Why did the art of rhetoric enter into decline under the rule of Augustus?
Rhetorical skills no longer played a crucial role in politics, since the emperor's supremacy ruled out political debate in the public sphere.
Why did Romanization have less effect in the eastern provinces than in the western provinces?
Hellenistic–Near Eastern culture had long been firmly entrenched, thus making it difficult for Romanization to have much sway.
What advantage did serving in the army confer on noncitizens from the provinces?
It granted them the opportunity to learn Latin, live by Roman customs, and receive Roman citizenship upon discharge.
According to Jewish apocalypticism, the world was ruled by
evil powers that would one day be crushed by the Messiah, God's chosen agent, after which the righteous would be rewarded and the evil punished.
Why did the poet Ovid (43 B.C.E.–17 C.E.) fall out of favor with Augustus in 8 B.C.E.?
He became entangled in a scandal involving Augustus's granddaughter.
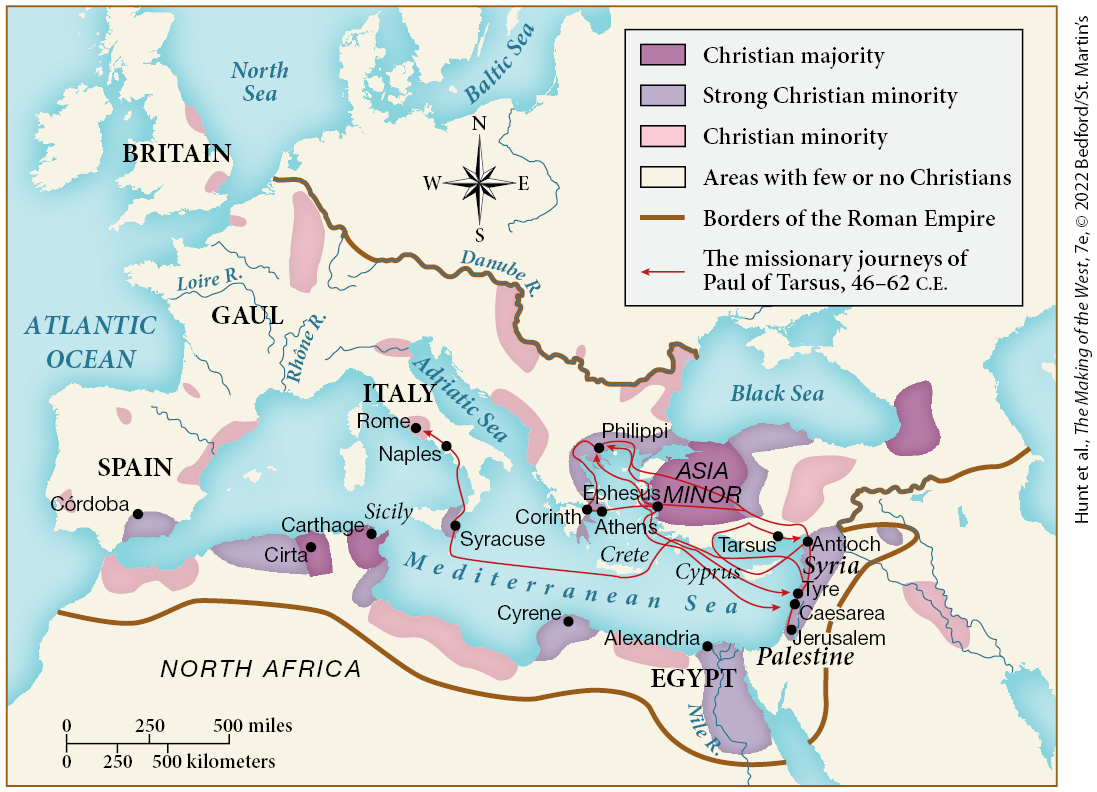
In which of the following regions or cities would Christians have most likely faced intolerance or persecution in the late third century C.E.?
Gaul
What public function did gladiatorial combats provide in the Roman Empire?
They provided communication between ruler and ruled, as ordinary citizens staged protests at events at which the emperor was present.
To resolve disputes over doctrine and practice in the latter first and second centuries, the early Christians
established the office of bishop, which carried decisive authority.
Which landmark poem by Virgil told the story of one of Rome's founders and expressed praise for Roman civilization while also indirectly alluding to problems in it?
The Aeneid
What was one of the ways that Augustus fulfilled his role as Rome's patron?
He created the first public fire department in Western history.
Why did Roman education in the Augustan period remain limited?
There were no free public schools, so the poor received no formal education.
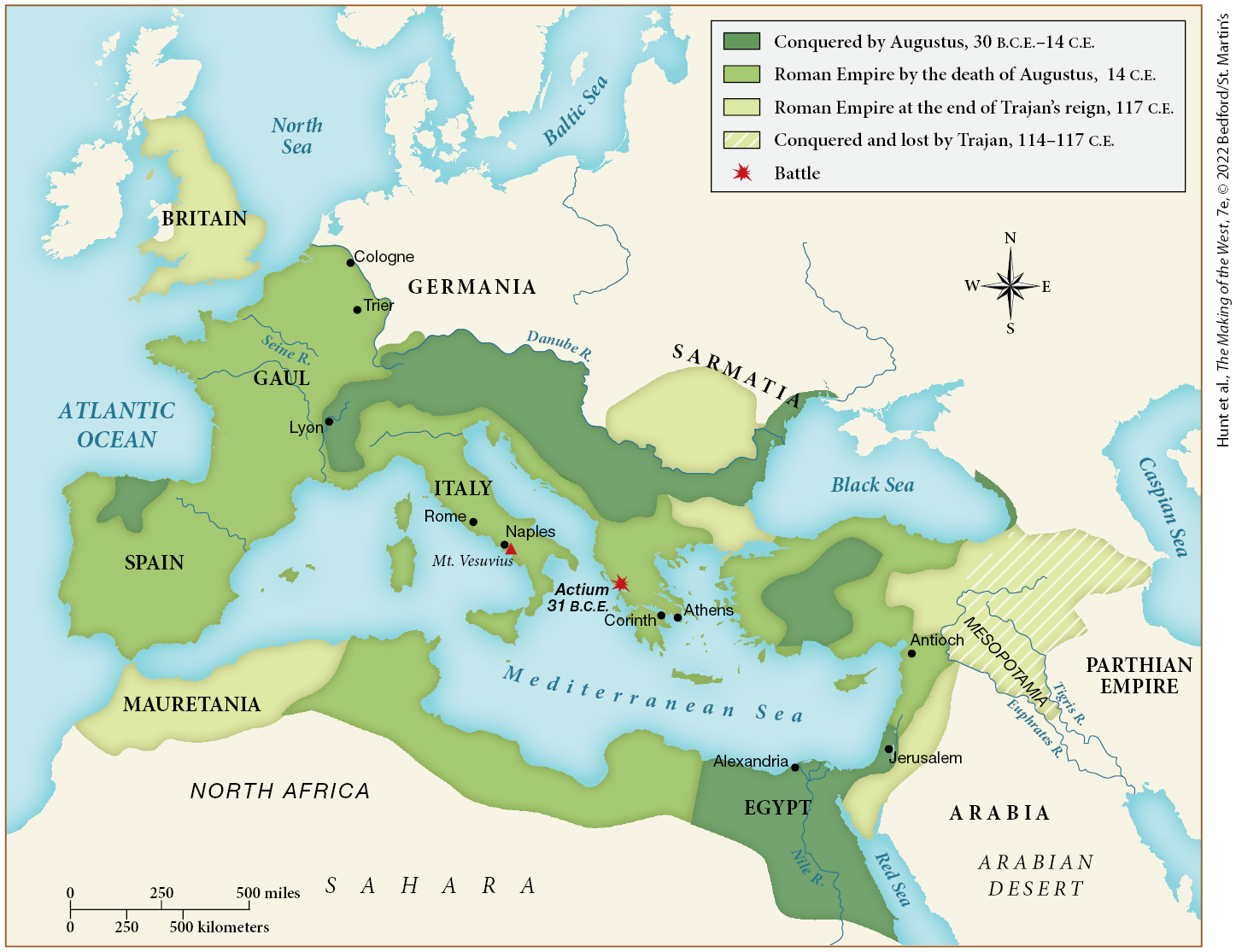
Which of the following regions was conquered by Augustus by 30 C.E.?
Egypt
One stabilizing factor in the reigns of the Golden Age emperors was that the first four emperors
had no surviving sons and were therefore able to use adoption to find the best possible successor.
Claudius (r. 41–54 C.E.) set a crucial precedent when he
bribed the praetorian guard to back him as the new emperor.
Which Roman emperor was assassinated by the praetorian guard in 41 C.E. after a short but brutal reign marked by decadence and corruption?
Caligula
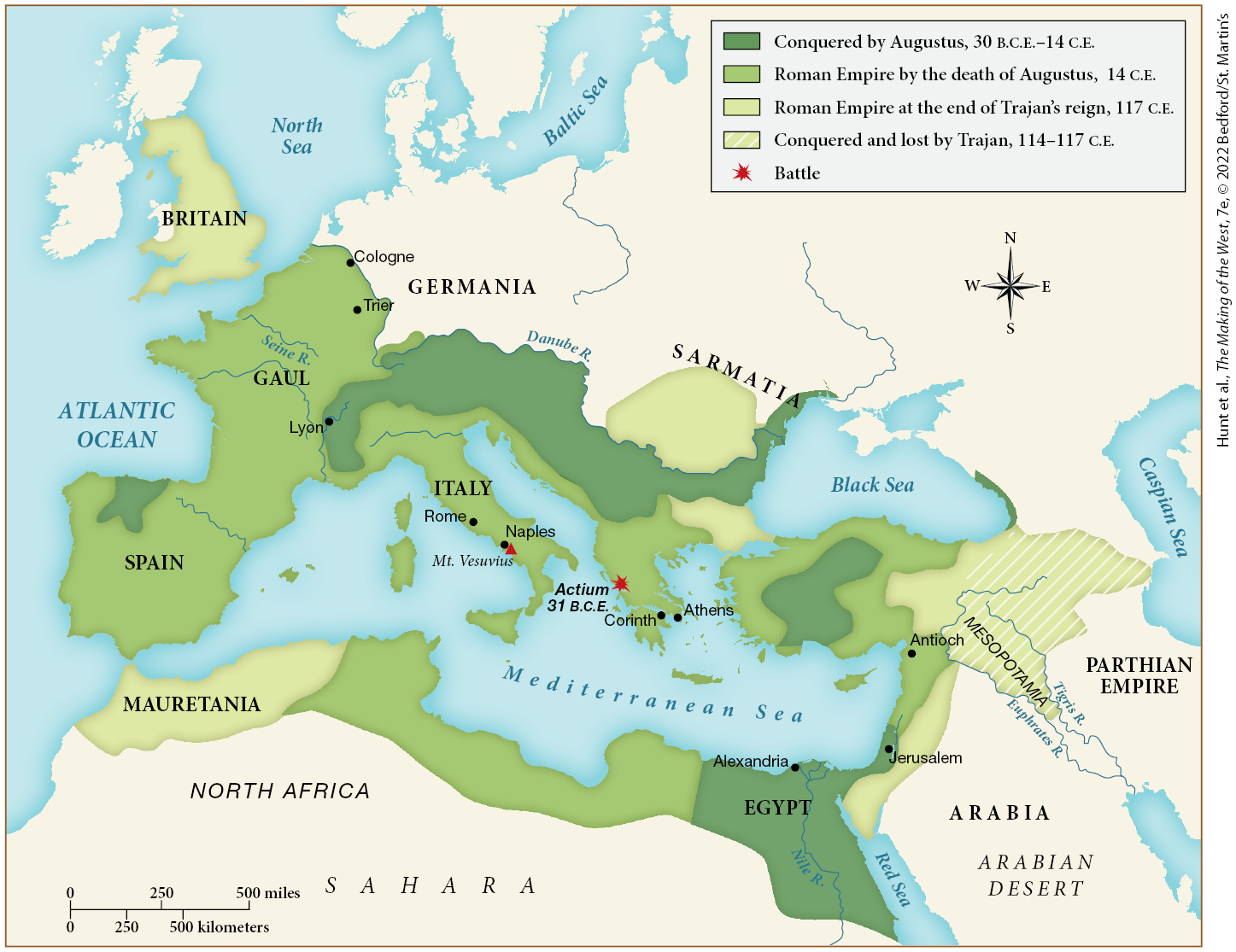
Which of the following statements is supported by this map?
By the time of Augustus’s death, the Roman Empire had expanded significantly.
Whom did the emperor Nero publicly blame for the fire that burned much of Rome in 64 C.E.?
Christians
During the civil wars of the third century C.E., qualifications for becoming emperor had been reduced to
commanding a frontier army and paying off the troops.
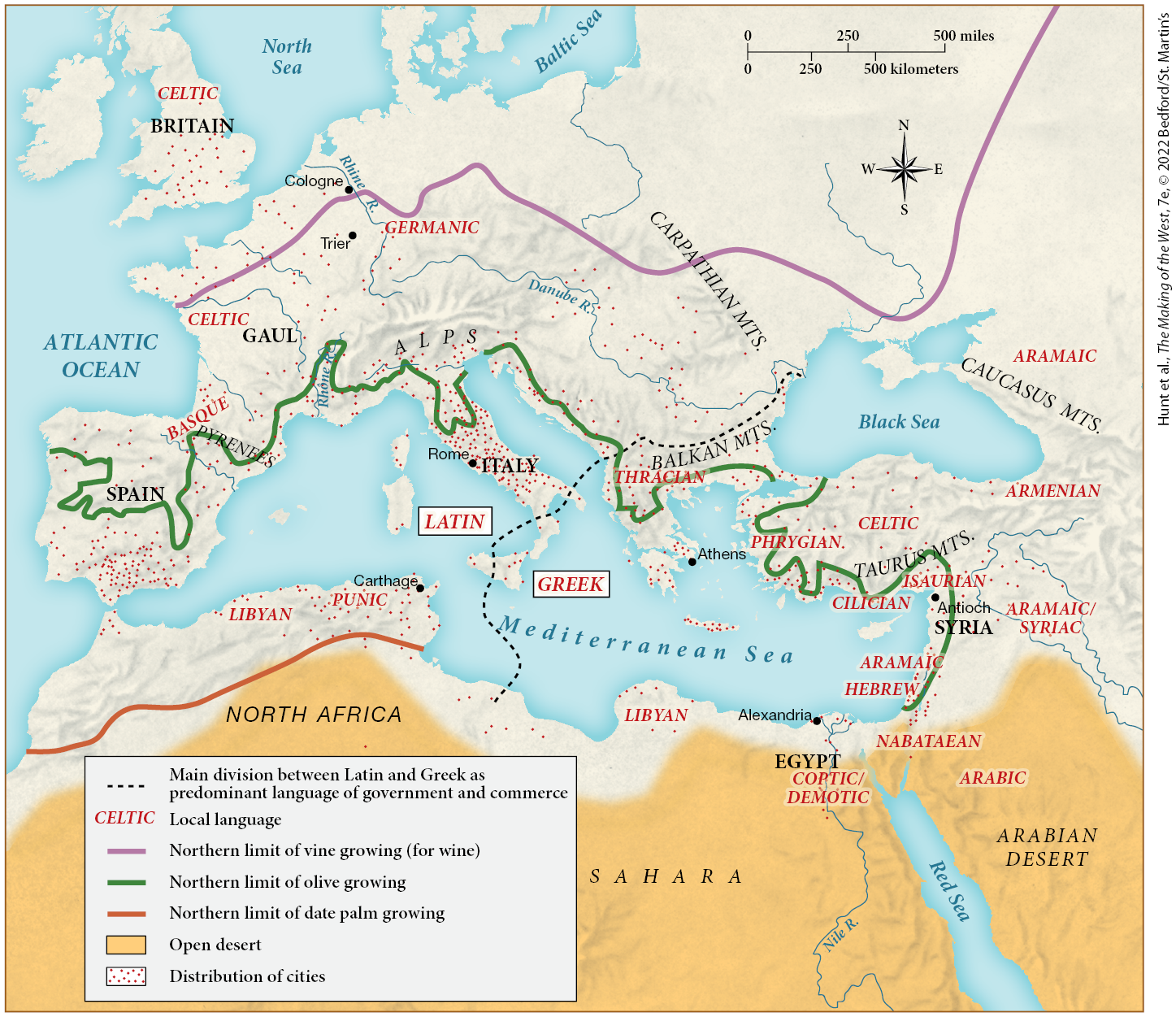
A farmer in Italy would be most likely to grow which of the following?
Olives
How did the construction of the Colosseum demonstrate the Flavian dynasty's commitment to the well-being of the people?
It was deliberately built on the former site of Nero's extravagant private fishpond.
Why did Romanization have less effect in the eastern provinces than in the western provinces?
Hellenistic–Near Eastern culture had long been firmly entrenched, thus making it difficult for Romanization to have much sway.
What generally determined whom wealthier Romans would marry?
Their marriages were arranged by their families.
How did Octavian win the Roman people's support against Antony?
Octavian turned many Romans against Antony by playing on their fear of foreigners and asserting that Antony intended to make Cleopatra their ruler.
Although the Romans wanted to eradicate Christianity, they stopped short of
making it illegal.
Which early Christian facilitated the spread of Christianity by opening the new religion to non-Jews and by not requiring male converts to undergo circumcision?
Paul of Tarsus
How did the praetorian guard, a creation of Augustus, come to exert a critical role in imperial politics?
It played a role in selecting the emperor after the death of the current one.
How did the status of wealthy Roman women differ from that of most Greek women in the Classical Age?
Roman women had a slightly higher status, since they not only managed their households but also were able to play an indirect but important role in politics.
What enraged the Roman consul Sulla just before his campaign against King Mithridates VI in Asia Minor?
His archrival Marius arranged a plebiscite that transferred the command of the campaign to himself.
Why did Rome's most prominent men seek the post of pontifex maximus (“greatest bridge-builder”)?
It bestowed increased political power, since the officeholder was the head of state religion.
What was the main tactic used by the plebeians to force the patricians to make political and economic concessions?
They pressured the patricians by periodically refusing to perform military service.
Concerns about national security and a desire for wealth led the Romans to
undertake expansionist campaigns against their neighbors.
Which statement most accurately describes the complex Roman legal system during the republic?
It evolved in response to protracted conflicts over power.
The tale of the rape of Lucretia reflects which of the following?
The belief that this outrage led the morally virtuous Romans to overthrow the monarchy and establish a republican government
The chastity of the Vestal Virgins was meant to
symbolize the security and stability of the Roman family and by extension the Roman republic itself.
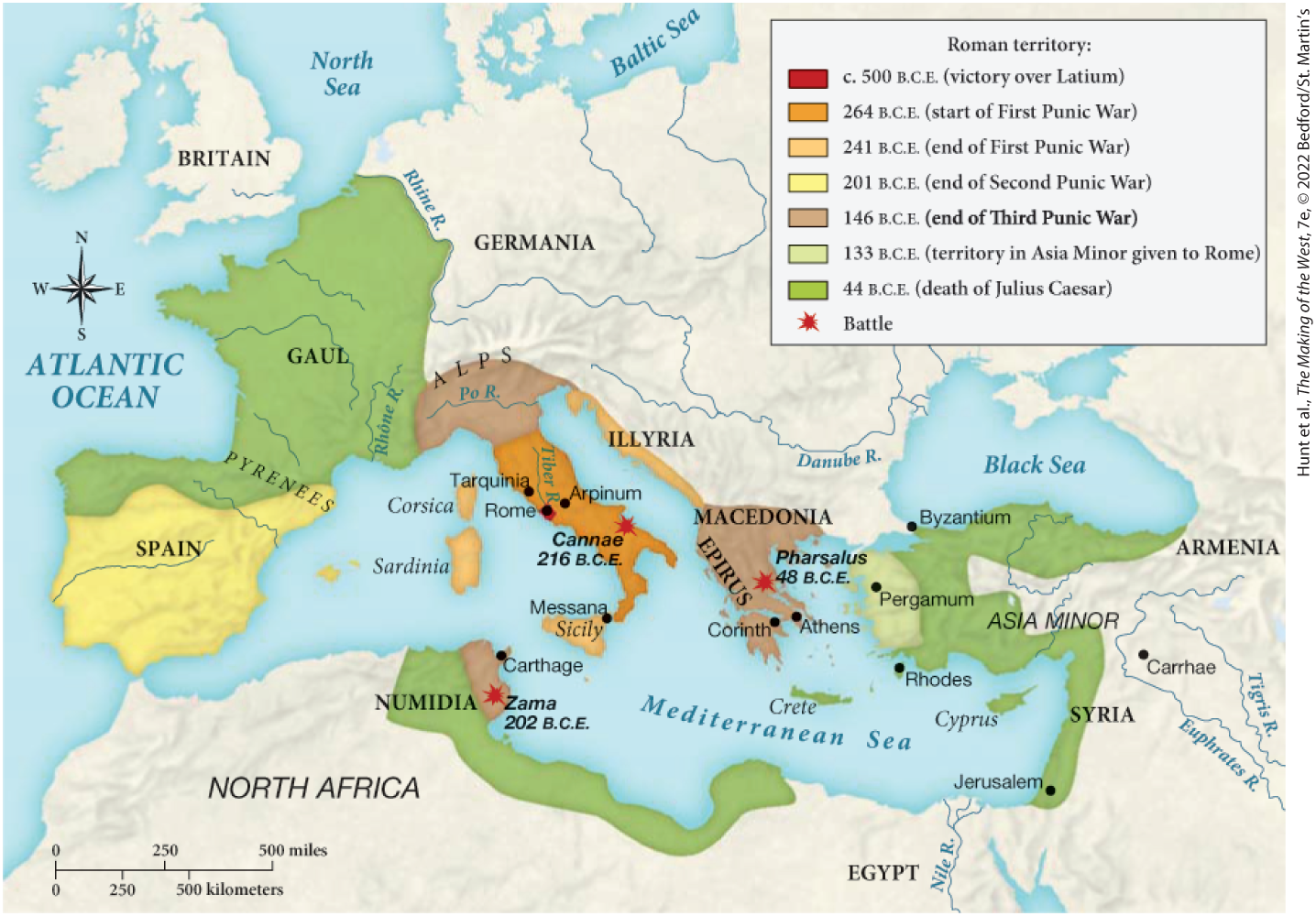
Which of the following territories only came under Roman control between 133 B.C.E. and the death of Julius Caesar?
Gaul
In mid-second century B.C.E., Cato wrote The Origins, which was
the first history of Rome written in Latin.
What triggered the First Punic War between Rome and Carthage?
A dispute over Sicily, where Rome wished to prevent Carthaginian troops from being too close to Roman territory
How did the office of tribune differ from most other political offices?
It was established to serve and protect the plebeian order, not all of society.
The Roman concept of authority was based on the belief that
society had to be hierarchical to be just.
Why was Rome's geography perfect for territorial expansion?
Rome possessed a river, fertile farmland, and a port on the Mediterranean.
Which of the following traits were highly esteemed in the early Roman republic (509–287 B.C.E.)?
Fidelity and perseverance
What was the most important of the Roman assemblies, in which plebeians outnumbered patricians?
The Tribal Assembly
How did the Roman elites who profited from Rome's expansion undermine traditional Roman values?
By using governmental posts in the provinces to extort fortunes from the local inhabitants
How did Gaius Marius's military conquests and election as consul represent a turning point in the Roman republic?
He came from the equites class and not the patrician class, and his armies were more loyal to him than to the republic.
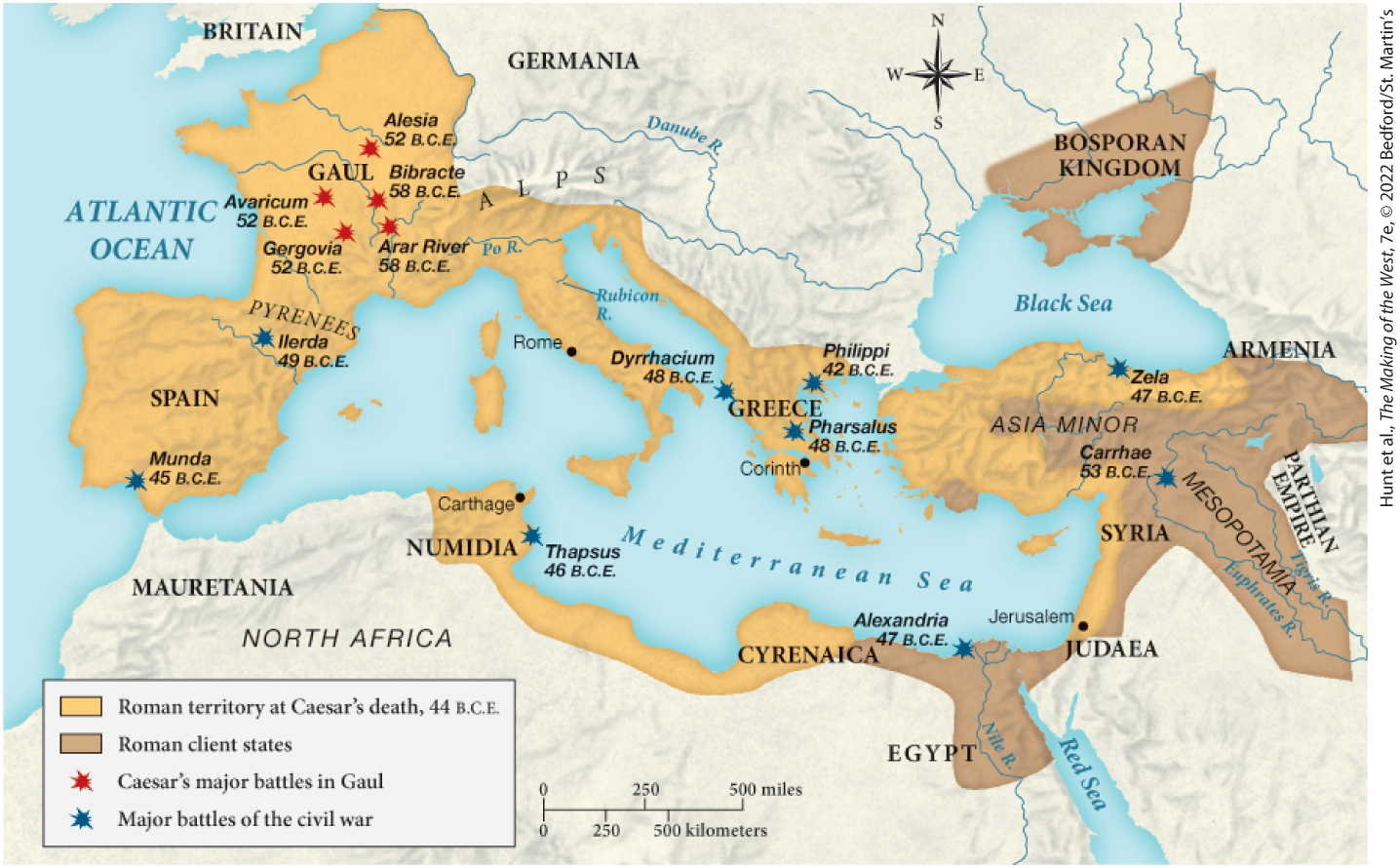
Which of the following was a Roman client state by 44 B.C.E.?
Mesopotamia
What factor enabled Julius Caesar to triumph in the civil war that lasted from 49 to 45 B.C.E.?
He wielded immense popular support, and his army remained loyal even in the most difficult of times.
What did Roman citizens believe they would receive in return for their honor of the gods?
Divine support
What historical evidence suggests that the average Athenian workingman had a very poor standard of living?
They ate only two meals a day and little or no meat.
In the ideal society described by Plato in The Republic, women
can serve as guardians or rulers because they have the same virtues and abilities as men.
In his study of ethics, Aristotle argued that
an ethical system must help people achieve self-control and overcome the passions.
A number of Hellenistic women wrote epigrams, which were
short poems originally engraved on tombstones to commemorate the dead.
Until the conquests of Philip II and Alexander, the Greeks regarded the Macedonians as
uncivilized barbarians.
Why did Hellenistic science rarely produce practical results?
Leading scientists were more interested in theoretical discoveries, and the technology needed to produce practical applications did not yet exist.
In the ideal society described by Plato in The Republic, women
can serve as guardians or rulers because they have the same virtues and abilities as men.
What political view did Plato and Aristotle share?
Athenian democracy was a bad form of government because it did not restrict decision making to the most educated and moderate citizens.
What did the successor kings rely on in order to maintain their kingdoms?
The administrative services of local urban elites, who were rewarded for their loyalty
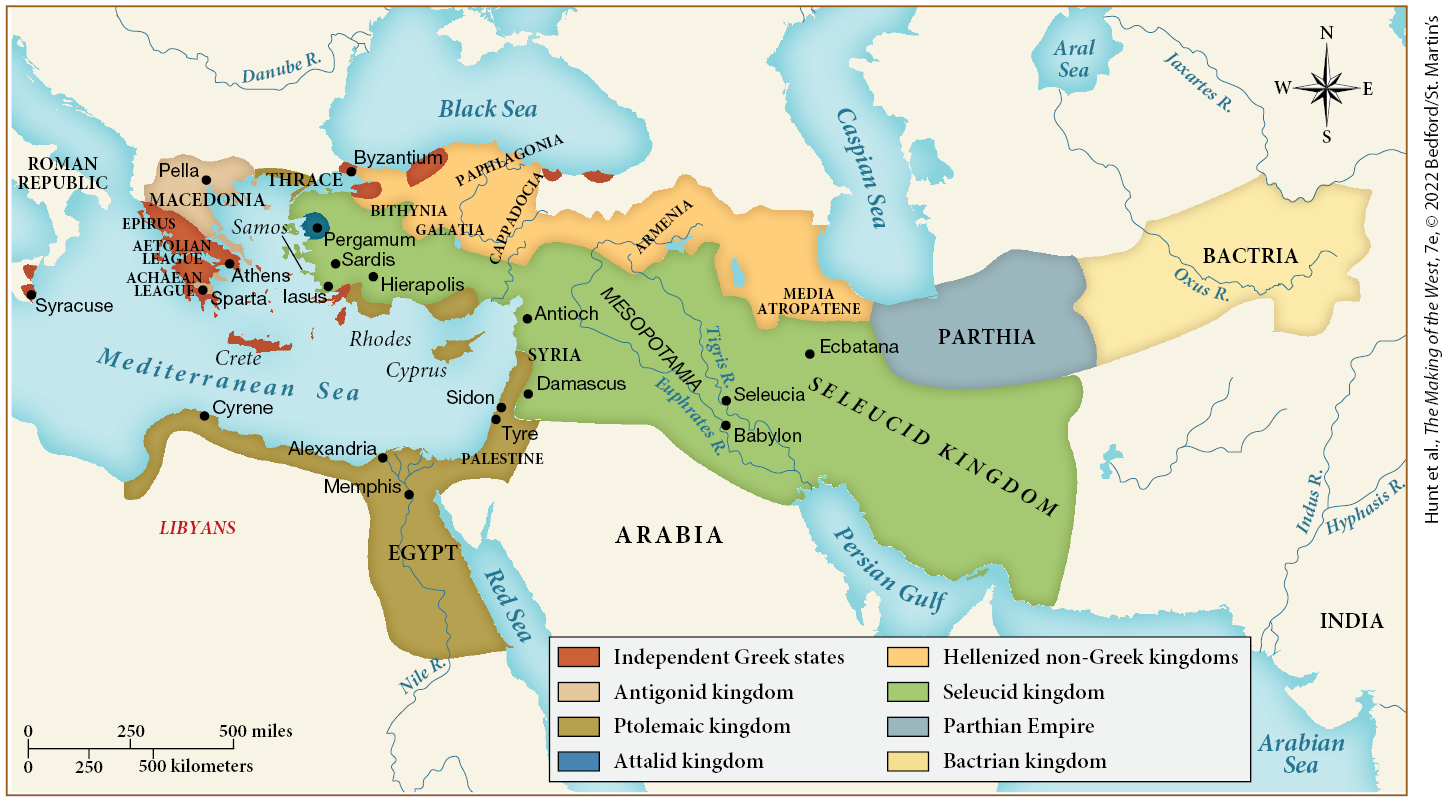
Which of the following kingdoms or empires likely posed the greatest threat of potential invasion and conquering to the Ptolemaic kingdom?
The Seleucid kingdom
Although Aristarchus had proposed a heliocentric model of the solar system as early as the third century B.C.E., later astronomers rejected his model because
he had based his calculations on a circular orbit of the sun rather than an elliptical one.
Which of the following statements best describes the condition of the poorer local populations in Hellenistic kingdoms?
As many as 80 percent of adults still worked in subsistence agriculture.
Why did the Athenians ally with the Spartans in the battle of Mantinea (362 B.C.E.)?
They feared the growing might of Thebes.
What basic tenet did Plato hold fast to throughout his long career?
Moral values are universal and absolute, not relative.
Why did Hellenistic science rarely produce practical results?
Leading scientists were more interested in theoretical discoveries, and the technology needed to produce practical applications did not yet exist.
Why was Socrates put on trial by his fellow citizens in 399 B.C.E.?
Socrates' accusers charged him with impiety, arguing that his philosophy denied the existence of the gods and lured the youth away from Athenian moral traditions.
Hellenistic sculpture differed from sculpture of the classical era in that it was more likely to
depict suffering and emotional individuals.
Socrates was the first philosopher in ancient Greece to
make ethics and morality the main focus of his teachings.
Why have historians described the democracy created in mid-fifth-century Athens under Pericles as “radical”?
All citizens, regardless of wealth, enjoyed equal protection under the law because the court system was removed from elite control.
Why were the Greeks able to defeat the Persian fleet in the battle of Salamis in 480 B.C.E.?
The Greeks forced the Persians to fight in a narrow strait between the island of Salamis and the coast, where their sturdier ships rammed the flimsier Persian ships.
What was one of Pericles' most important democratic innovations?
Providing a modest salary to any officeholder selected by lottery, thus enabling even poor men to serve as public officials
Aristophanes, an Athenian playwright whose comedies made harsh references to prominent leaders,
won a lawsuit filed against him by a major Athenian political figure who disliked the way he was portrayed in one of Aristophanes' comedies.
In his History of the Peloponnesian War, the Greek historian Thucydides broke with tradition by
describing the moral failures and miscalculations of the Greeks.
According to Thucydides, what reason did Pericles offer for rejecting Sparta's ultimatum?
Pericles argued that giving in to Sparta's demand would be a sign of weakness and would only encourage Sparta to take further advantage of Athens.
What did initiates into Greek mystery cults generally hope to obtain?
Secret knowledge and divine protection
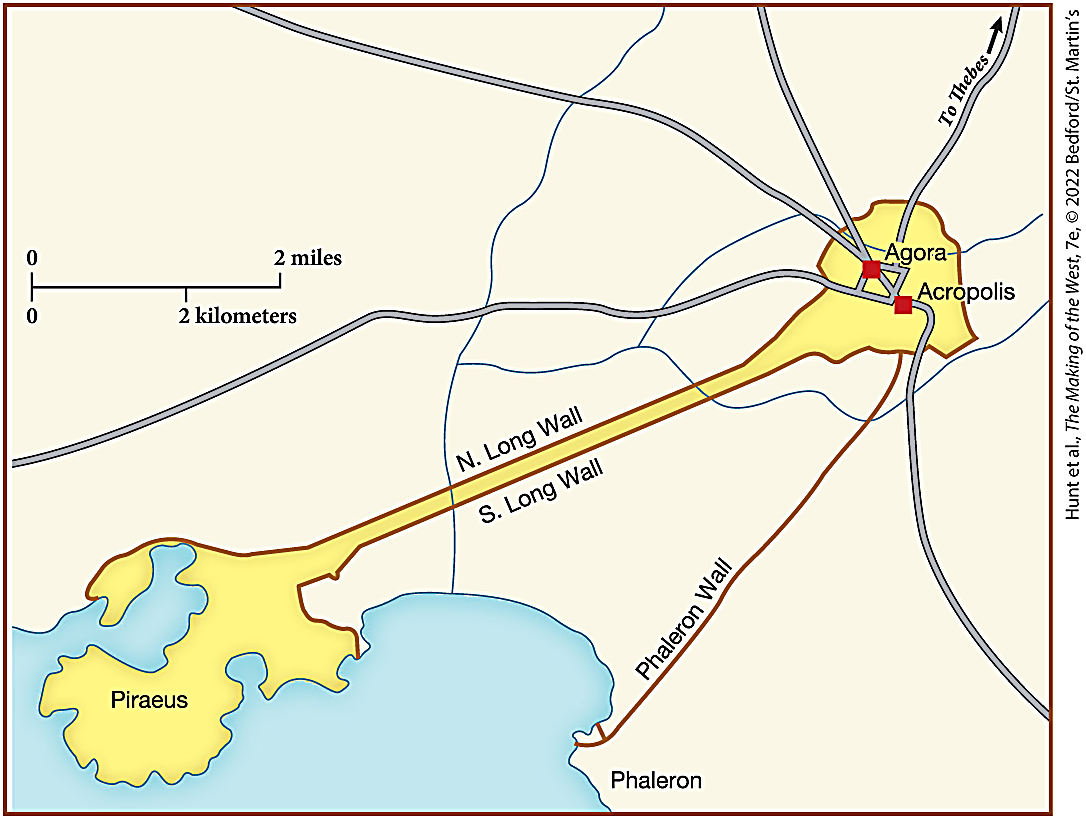
In this portrayal of Athens, the long walls significantly provided
protection for the route between the urban center and the port.
How did the fifth-century Sophist Protagoras offend many Athenians?
He insisted that absolute truth did not exist because every issue had two irreconcilable sides.
What was Pericles' strategy for defeating the superior Spartan army?
To avoid land battles whenever possible while attacking Sparta and its allies by sea
How did Golden Age comedies differ from tragedies?
Comedies were openly critical of contemporary people and policies.
Golden Age sculptors shattered traditions from the Archaic Age not only by creating realistic and perfectly formed bodies, but also by
depicting their subjects in a state of movement.
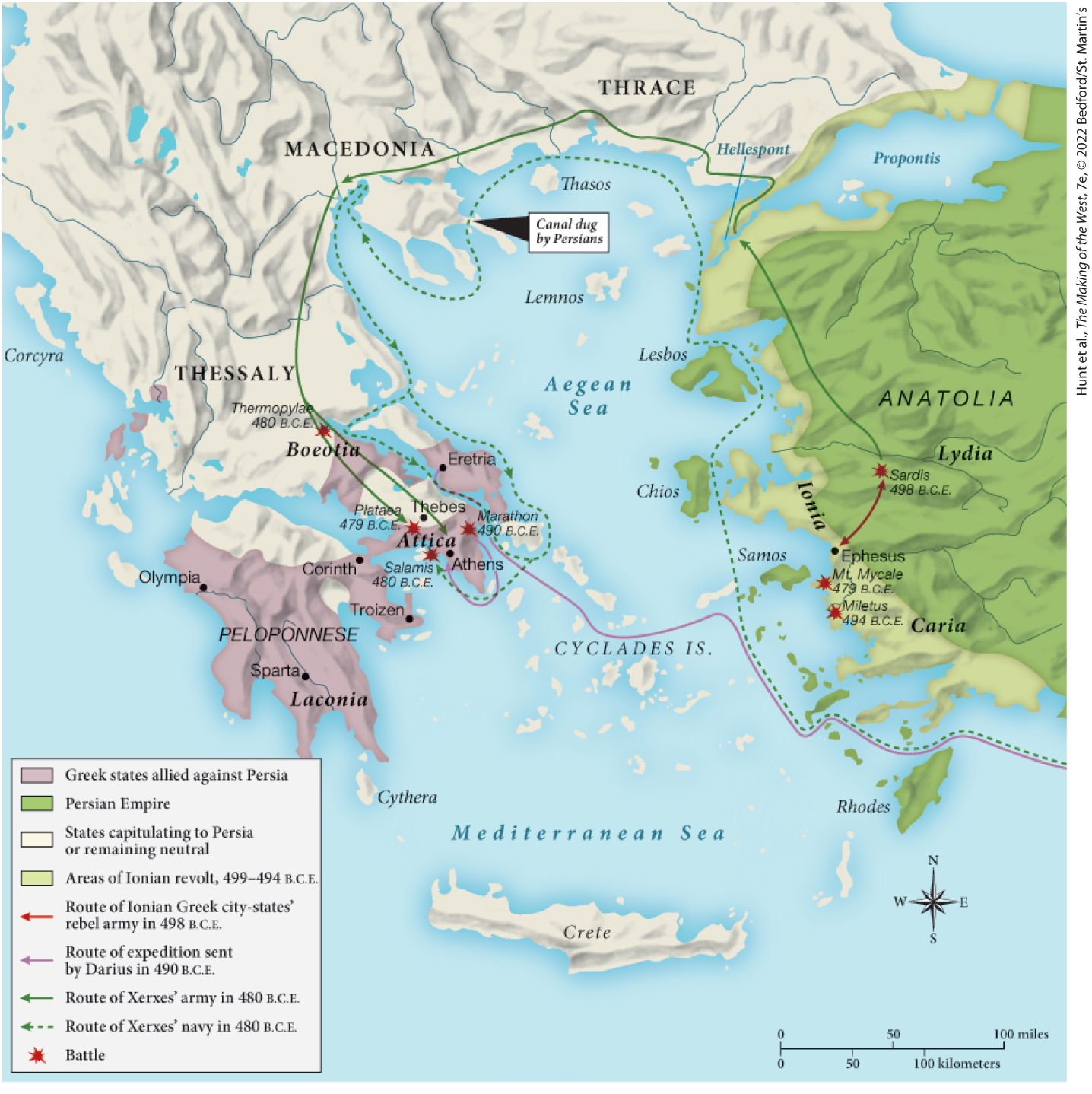
Which of the following was allied against Persia during the Persian Wars?
Laconia
Macedonia, Thebes, and the Persian Empire were all allied with
Sparta.
What does “the Socratic method” refer to?
A manner of teaching that features relentless questioning
Which of the following was one of the educational traditions of Golden Age Athens?
A mentor–protégé relationship whereby a male adolescent would learn from an older man by accompanying him in the course of his public functions, athletic exercises, and social interactions
Aspasia of Miletus exhibited so much knowledge and brilliance that which high-ranking Athenian politician wished to marry her?
Pericles
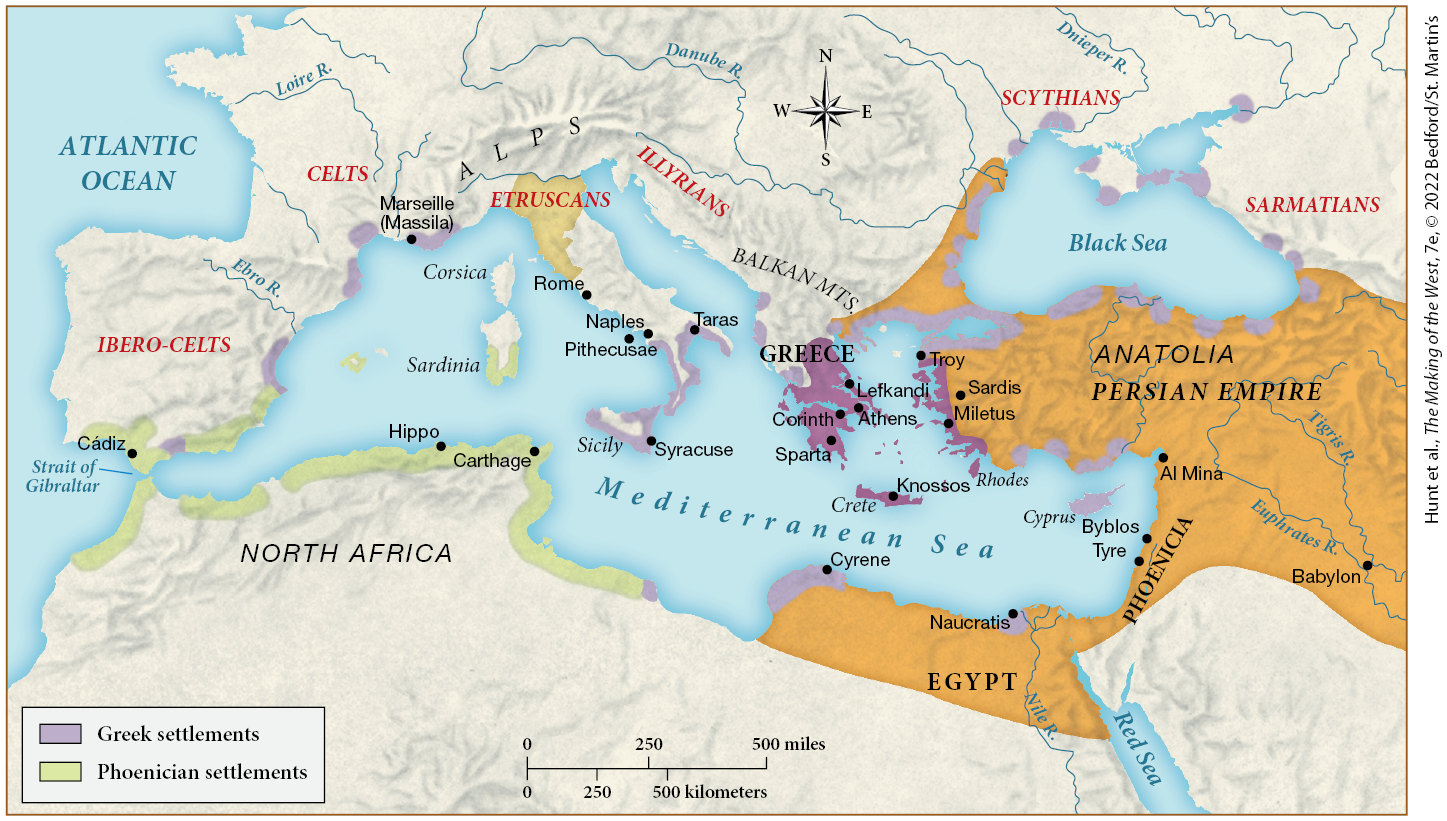
By 500 B.C.E., most of the Phoenician settlements were located
in North Africa.
How did Greek settlement in the eastern Mediterranean abroad influence the development of Greek culture during the Archaic Age (c. 750–500 B.C.E.)?
It paved the way for the Greeks to imitate Near Eastern and Egyptian statuary.
Women in Greek city-states could also be citizens, an honor that
did not, however, grant them political rights, such as the right to vote or otherwise participate in political life.
Which new regional power had emerged in Mesopotamia by 900 B.C.E.?
The Neo-Assyrian Empire
How did the Greeks significantly improve the quality of their farm implements and weaponry following their Dark Age?
They learned the skill of iron metallurgy from their eastern trading partners and went on to mine their own iron ore deposits.
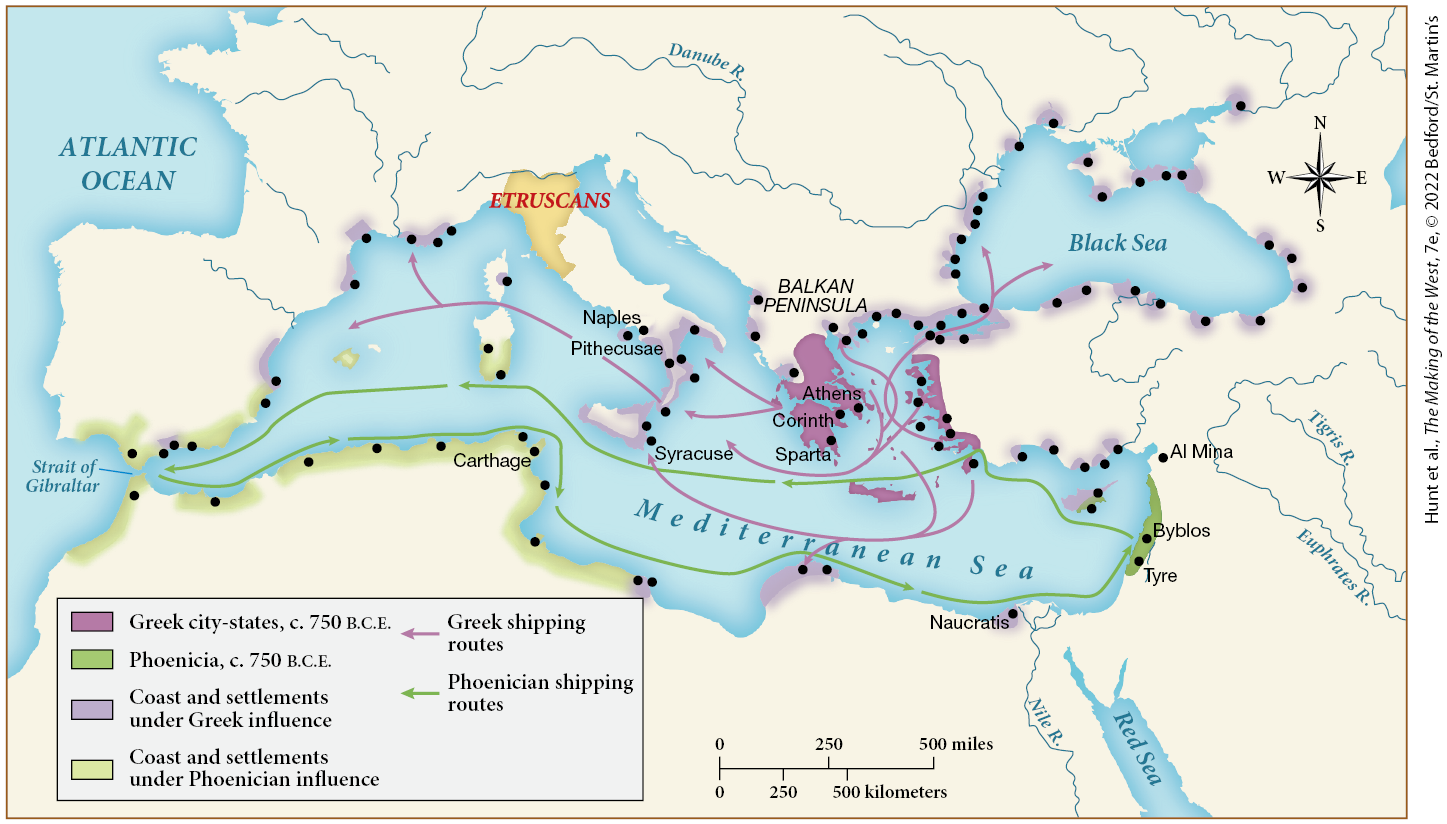
Based on this map, who did Greek city-states tend to trade with from 750 to 500 B.C.E.?
Other Greek city-states and settlements under Greek influence
The concept of miasma—the ritual contamination suffered by the members of a group who failed to punish a criminal in their midst—reflected which of the following?
A sense of communal responsibility for upholding divine law
Who was the lyric poet who wrote about intense emotions, especially love?
Sappho
Which of the following best describes ancient Greece's natural resources?
Greece had a mountainous, rocky terrain that was suitable for the cultivation of olives, grapes, and barley but little else.
Why was the notion of citizenship such a radical innovation in ancient Greece?
The ancient world was otherwise characterized by monarchies and legal inequality.
When the Greeks began writing again about 800 B.C.E., they adopted and adapted an alphabet they received from the
Phoenicians.
The term Diaspora describes the experience of those Jews who
lived outside the Jewish homeland but still followed Jewish law.
What did the Greeks establish as they began to recover from two centuries of economic devastation and population decimation?
A new form of political and social organization known as the polis, or independent city-state
As a result of Solon's reforms, council members who prepared the agenda for the assembly were chosen by
lottery.
What is recounted in Homer's epic poem The Iliad?
The events of the Trojan War
Which strategy did early Persian rulers adopt to rule over their newly conquered peoples?
They allowed local people to keep their own beliefs and customs.
Most early Paleolithic societies were characterized by a form of organization in which
all men and women had a roughly equal say in making important decisions.