AP Psych - Motivation and Emotion
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/50
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
1
New cards
motivation
a need or desire that energizes and directs behavior
2
New cards
instinct
a complex, unlearned behavior that is rigidly patterned throughout a species
3
New cards
instinct theory
__what__?
* biological or genetic programming (motivated by survival)
__why do we do things?__
* evolution, to ensure genetic material is passed on
__aligned perspective:__
* **evolutionary**
* biological or genetic programming (motivated by survival)
__why do we do things?__
* evolution, to ensure genetic material is passed on
__aligned perspective:__
* **evolutionary**
4
New cards
drive-reduction theory
__what__?
* the idea that a physiological need created an aroused tension state (a drive) that motivates an organism to satisfy the need
__why do we do things?__
* to resolve internal tension (biological need, do behavior to reestablish **homeostasis**
__aligned perspective:__
* **biological**
* the idea that a physiological need created an aroused tension state (a drive) that motivates an organism to satisfy the need
__why do we do things?__
* to resolve internal tension (biological need, do behavior to reestablish **homeostasis**
__aligned perspective:__
* **biological**
5
New cards
arousal theory
__what__?
* complete actions to increase/decrease arousal
__why do we do things?__
* to maintain optimal level of arousal
* **Yerkes-Dodson** graph (“**inverted U**”)
__aligned perspective:__
* both **cognitive** and physiological/biological explanations
* *ex. hunger*
* cognitive:
* curiosity (trying new food)
* physiological:
* **glucose, ghrelin/obestatin, lateral hypothalamus/ventromedial hypothalamus**
* complete actions to increase/decrease arousal
__why do we do things?__
* to maintain optimal level of arousal
* **Yerkes-Dodson** graph (“**inverted U**”)
__aligned perspective:__
* both **cognitive** and physiological/biological explanations
* *ex. hunger*
* cognitive:
* curiosity (trying new food)
* physiological:
* **glucose, ghrelin/obestatin, lateral hypothalamus/ventromedial hypothalamus**
6
New cards
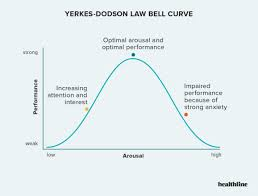
Yerkes-Dodson graph
displays optimal intersection of arousal and performance
7
New cards
homeostasis
a tendency to maintain a balanced or constant internal state
8
New cards
incentive
a positive or negative environmental stimulus that motivates behavior
9
New cards
hierarchy of needs
* Maslow
* proposes that lower-level needs must be met before higher-level needs can be satisfied
* __**P**__eacocks __**S**__eldom __**S**__hare __**E**__ach other’s __**S**__andwiches
* __**P**__hysiological
* __**S**__afety
* __**S**__ocial (belongness and love)
* __**E**__steem
* __**S**__elf-actualization
* proposes that lower-level needs must be met before higher-level needs can be satisfied
* __**P**__eacocks __**S**__eldom __**S**__hare __**E**__ach other’s __**S**__andwiches
* __**P**__hysiological
* __**S**__afety
* __**S**__ocial (belongness and love)
* __**E**__steem
* __**S**__elf-actualization
10
New cards
glucose
* form of sugar that circulates in blood and provides major source of energy for body tissues
* brain monitors blood chemistry, when levels of _____ are low, will trigger hunger
* brain monitors blood chemistry, when levels of _____ are low, will trigger hunger
11
New cards
basal metabolic rate
body’s resting rate of energy expenditure
12
New cards
hypothalamic role in hunger
* __**l**__**ateral hypothalamus** - “__**l**__ets eat”
* produces hunger-triggering hormone ***orexin***
* **ventromedial hypothalamus** - “stop”
* the hypothalamus also monitors levels of other appetite hormones
* ***ghrelin*** - hunger arousing
* ***obestatin -*** hunger suppressant
* produces hunger-triggering hormone ***orexin***
* **ventromedial hypothalamus** - “stop”
* the hypothalamus also monitors levels of other appetite hormones
* ***ghrelin*** - hunger arousing
* ***obestatin -*** hunger suppressant
13
New cards
insulin
helps **glucose** enter muscle, fat, and liver cells
14
New cards
PYY
hunger suppressant secreted by digestive tract
15
New cards
ADH
* helps blood vessels constrict
* helps kidneys contral amount of water and salt in the body
* helps kidneys contral amount of water and salt in the body
16
New cards
pituitary gland
* controls growth and development, most other endocrine glands
* partially controlled by **hypothalamus**
* together, detect and adapt to hormone levels
* partially controlled by **hypothalamus**
* together, detect and adapt to hormone levels
17
New cards
angiotensin
regulates blood pressure by constricting blood vessels, triggering water and salt intake
18
New cards
sexual response cycle
* **Masters** and **Johnson**
* four stages of sexual responding
* excitement, plateau, orgasm, resolution
* four stages of sexual responding
* excitement, plateau, orgasm, resolution
19
New cards
refractory period
* in sexual motivation, resting period after orgasm in which one cannot achieve another
20
New cards
sexual disorder
problem that consistently impairs sexual arousal or functioning
21
New cards
estrogens
* sex hormones (contribute to sexual characteristics)
* ex. estradiol
* ex. estradiol
22
New cards
testosterone
* sex hormone (contribute to sexual characteristics)
23
New cards
flow
completely involved, focused state of consciousness resulting from optimal engagement of one’s skills
24
New cards
industrial-organizational psychology
application of psychological concepts and methods to optimizing human behavior in workplace
25
New cards
personnel psychology
* subfield of **industrial-organizational psychology**
* focuses on employee recruitment, placement, training
* focuses on employee recruitment, placement, training
26
New cards
organizational psychology
* subfield of **industrial-organizational psychology**
* examines organizational influences on worker satisfaction and productivity
* examines organizational influences on worker satisfaction and productivity
27
New cards
structured interviews
interview process that asks the same job-relevant questions of all applicants, each of whom is rated on established scales
28
New cards
achievement motivation
desire for significant accomplishment
29
New cards
task leadership
goal-oriented leadership that sets standards, organizes work, and focuses attention on goals
30
New cards
social leadership
group-orientated leadership that builds teamwork, mediates conflict, and offers support
31
New cards
theory X
authoritarian management method that focuses on supervision and strict monitoring of employees
32
New cards
theory Y
* management method
* assumes employees are internally motivated and work best w/o direct reward
* assumes employees are internally motivated and work best w/o direct reward
33
New cards
emotion
response involving physiological arousal, expressive behaviors, and conscious experience
34
New cards
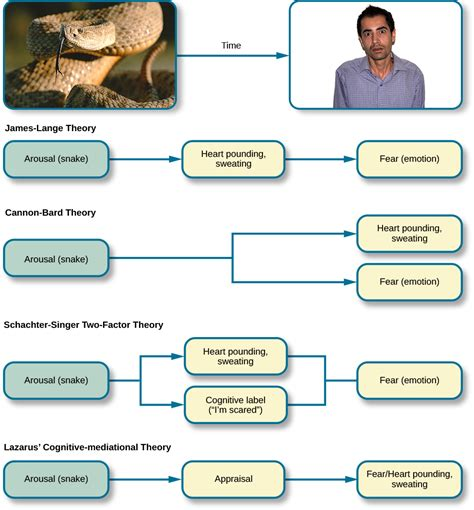
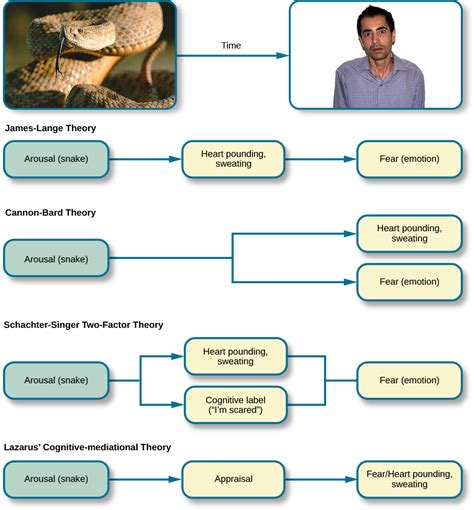
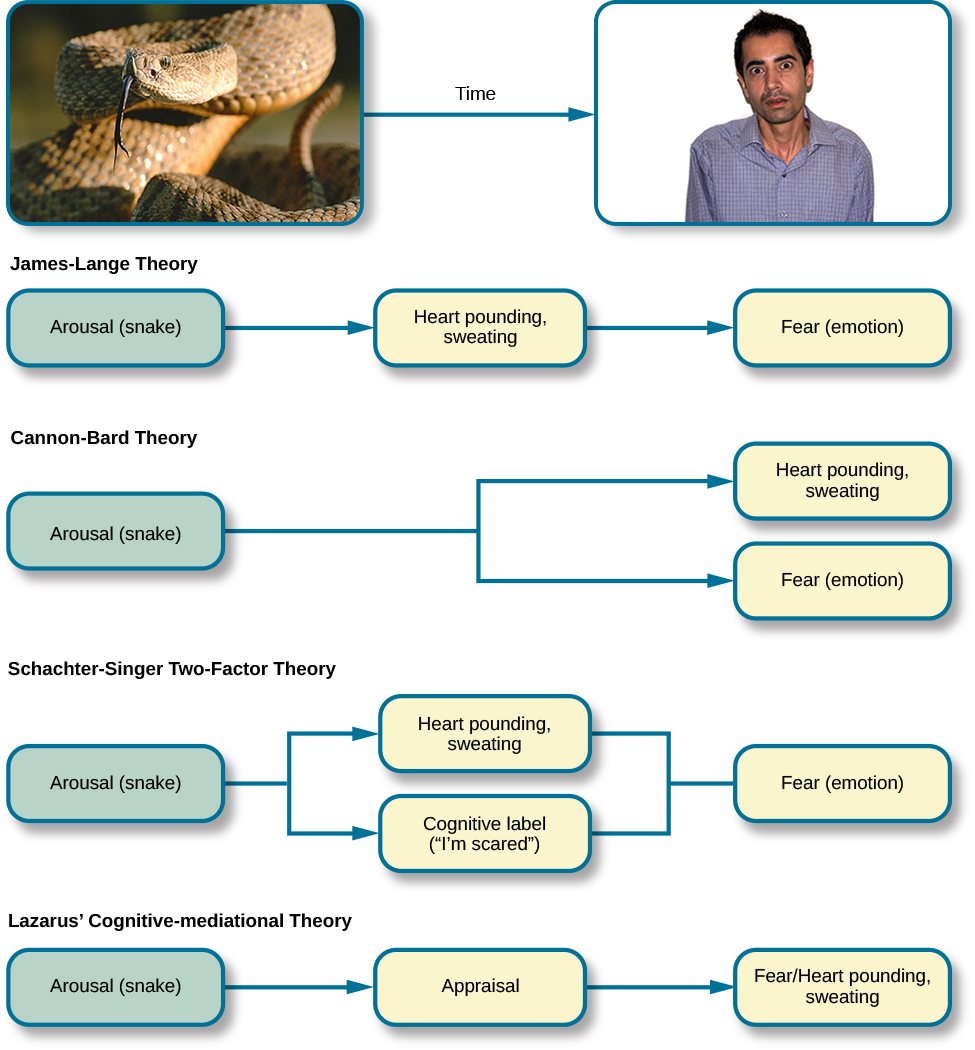
James-Lange Theory
stimulus → physiological response → emotion
*ex. snake → pounding heart → fear*
*ex. snake → pounding heart → fear*
35
New cards
Cannon-Bard Theory
stimulus → simultaneous physiological response + emotion
*ex*. *snake* → *pounding heart* *+ fear*
*ex*. *snake* → *pounding heart* *+ fear*
36
New cards
Schachter-Singer/two-factor theory
stimulus → physiological response + cognitive label → emotion
*ex*. *snake → pounding heart + “I’m afraid” → fear*
*ex*. *snake → pounding heart + “I’m afraid” → fear*
37
New cards
Lazarus Theory
cognitive appraisal → physiological response + emotion
*ex. unknown noise → “oh, it’s just the wind” OR unknown noise → “oh, it’s a bear” → pounding heart + fear*
*ex. unknown noise → “oh, it’s just the wind” OR unknown noise → “oh, it’s a bear” → pounding heart + fear*
38
New cards
Zajonc-Ledoux Theory
some emotions, especially those necessary for immediate survival go straight to **amygdala** w/o conscious appraisal, while others are processed in a cortex before going to amygdala
*ex. snake → amygdala OR friend → cortex → amygdala*
*ex. snake → amygdala OR friend → cortex → amygdala*
39
New cards
spillover theory
the transference of an emotional state into another area of life
40
New cards
polygraph
machine that measures several physiological responses accompanying emotion (like perspiration, heart rate)
41
New cards
catharsis
emotional release
42
New cards
feel-good, do-good phenomenon
people’s tendency to be helpful when in a good mood
43
New cards
subjective well-being
self-perceived happiness or satisfaction with life
44
New cards
adaptation-level phenomenon
our tendency to judge stimuli relative to our previous experiences
45
New cards
relative deprivation
perception that one is worse off relative to others
46
New cards
Abraham Maslow
* Humanistic psychologist
* **Self-actualization**
* **Hierarchy of needs**
* **Self-actualization**
* **Hierarchy of needs**
47
New cards
Ancel Keys
* American physiologist
* studied influence of diet on health
* studied influence of diet on health
48
New cards
A. L. Washburn and Walter Cannon
swallowed balloon, determined impacts of stomach contractions on hunger
49
New cards
Paul Ekman
* American psychologist
* studies interaction btwn emotions and facial expressions
* studies interaction btwn emotions and facial expressions
50
New cards
Carrol Izard
* American psychologist
* **discrete emotion theory** - claim that there is small number of base emotions
* **facial feedback hypothesis -** facial expression directly affects emotional experience
* **discrete emotion theory** - claim that there is small number of base emotions
* **facial feedback hypothesis -** facial expression directly affects emotional experience
51
New cards
William Masters and Virginia Johnson
* American gynecologist/sexologist
* pioneered research about human sexual response and the diagnosis and treatment of sexual dysfunctions
* pioneered research about human sexual response and the diagnosis and treatment of sexual dysfunctions