PD E3: peripheral vascular
1/84
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
what are the 2 most important types of arterial diseases?
microvascular (atherosclerosis) and microvascular (DM)
what are the 2 most important types of venous diseases?
venous stasis and thrombotic disorders
when would you assess the peripheral vasculature?
pain
changes in skin temp or color
edema
ulceration
suspect stroke/PE
cardiac/DM pts
what are risk factors for peripheral vascular dz?
≤ 50 w/ DM + one other atherosclerosis risk factor (smoking, dyslipidemia, HTN)
50-69 and hx of smoking or DM
≥70
leg sx w/ exertion → ischemic rest pain or intermittent claudication/PAD
abnormal LE pulse
atherosclerotic dz of coronary, carotid, or renal arteries
where should BP be measured?
BOTH arms
what should you do if hand perfusion is in question?
allen’s test
what might white discoloration of UE suggest?
raynauds
what might red discoloration of UE suggest?
cellulitis
what might red streaking of UE suggest?
lymphangitis
what might blue discoloration of UE suggest?
cyanosis
How do you rate pulse amplitude?
0 → absent, unable to palpate
1+ → diminished, weaker than expected
2+ → normal, brisk, expected
3+ → bounding
what conditions might small/weak pulses be seen in?
aortic stenosis
hypovolemia
dilated CMP
what conditions might large/bounding pulses be seen in?
aortic regurgitation
hyperthyroidism
fever
anemia
what conditions might bisferiens pulse be seen in?
aortic regurgitation
HOCM
what is normal pulse pressure?
30-40 mmHg
what is pulses alternans?
beat to beat variation but regular rhythm
ex: LHF, ventricular decompensation
what is pulses bigeminus?
irregular rhythm w/ alternating strong and weak beats; often caused by premature ventricular contraction
ex: HCM
what is the main difference between pulses alternans and pulses bigeminus?
alternans → regular rhythm
bigeminus → irregular rhythm
what is a paradoxical pulse?
>10 mm dec in SBP during inspiration
ex: pericardial tamponade, constrictive pericarditis, obstructive airway dz
pulse wave contours
too lazy to type lol
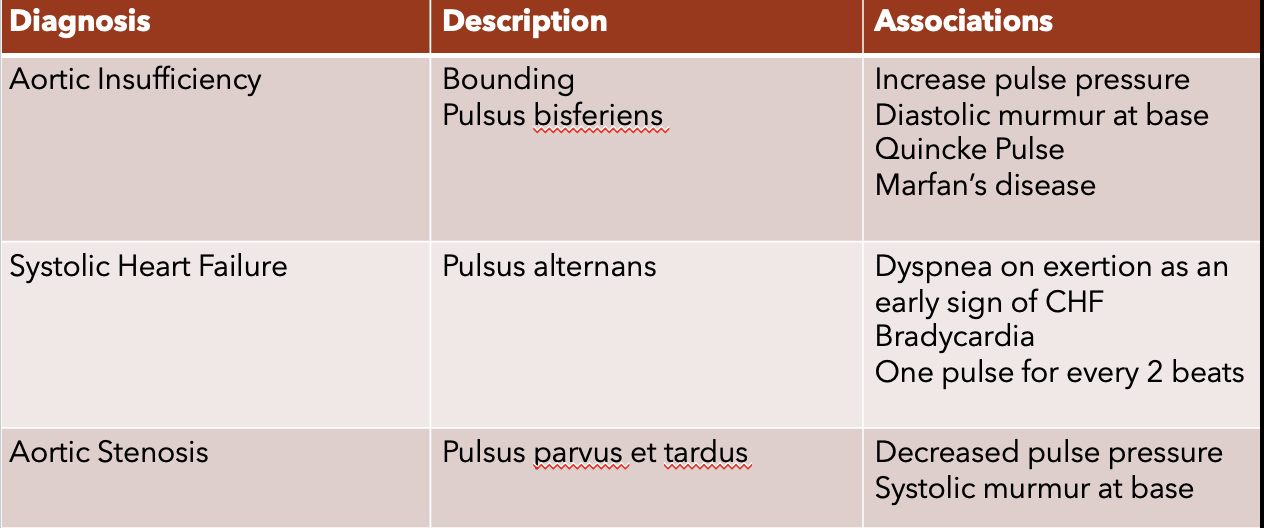
what is the Allen test?
tests patency of ulnar artery prior to puncturing the radial artery
pt clench fist for 30 s
compress both radial and ulnar arteries
pt open fist
release one artery
watch for filling of hand to assess potency of ulnar artery
if patent → palm flushes in 3-5s
eval patency to prevent ischemia to hand
where are the epitrochlear nodes?
3 cm above medial epicondyle; bt biceps and triceps muscle
where is it common to find lymph nodes in children and adolescents?
around neck and bony prominences
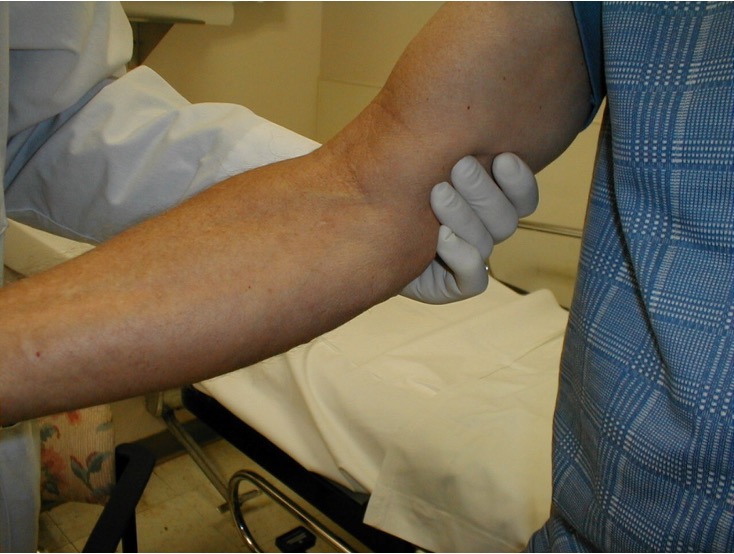
what suggests chronic arterial insufficiency?
pallor of foot when raised to 60 degrees for 1 min
pain when walking; usually assoc w/ intermittent claudication
pale or dusky red color (rubor)
cool temp
no edema
thin/shiny skin
loss of hair
painful ulcerations (trauma)
dry gangrene
dec pulses
what are the 6 P’s of circulation of arterial insufficiency?
pain
pallor
paresthesia
paralysis
pulselessness
poikilothermia
what is buerger’s test?
used to test for arterial deficiency of LE
pt lie flat
raise both legs to 45 degrees and hold them up 1 min
pt sit up and hang legs off bed
observe legs and feet
toes remain pink → negative for PAD
toes pass through pink to red range color due to reactive hyperemia from post hypoxic vasodilation (sunset foot) → positive for PAD
what is ankle-brachial pressure index (ABPI)?
non invasive quick method of evaluating for suspected arterial insufficiency
use handheld doppler and sphygmomanometer
measure brachial SBP
measure ankle SBP at most distal pulse (DP/PT, then average)
ratio of 2 BPs is the ABPI → ankle BP / brachial BP
what are the ranges of ABPI?
normal: 1-1.4
mild PAD: 0.8-1.0
moderate PAD: 0.5-0.8
severe PAD: ≤ 0.5
What will the ABPI appear in a pt w/ calcified arteries?
falsely elevated
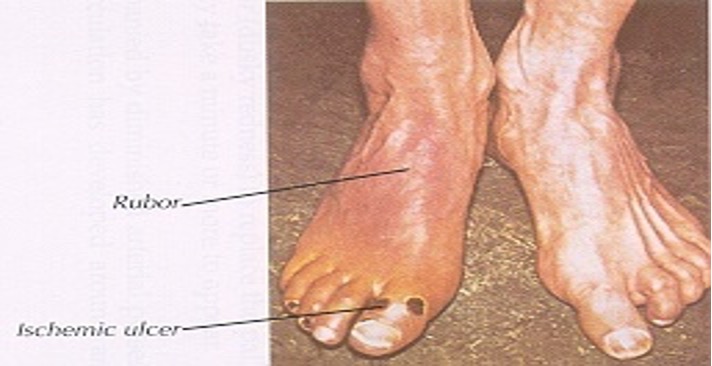
what suggests chronic venous insufficiency?
brownish pigment
pitting edema
skin thickening
malleolar ulcers
normal pulses
no pain
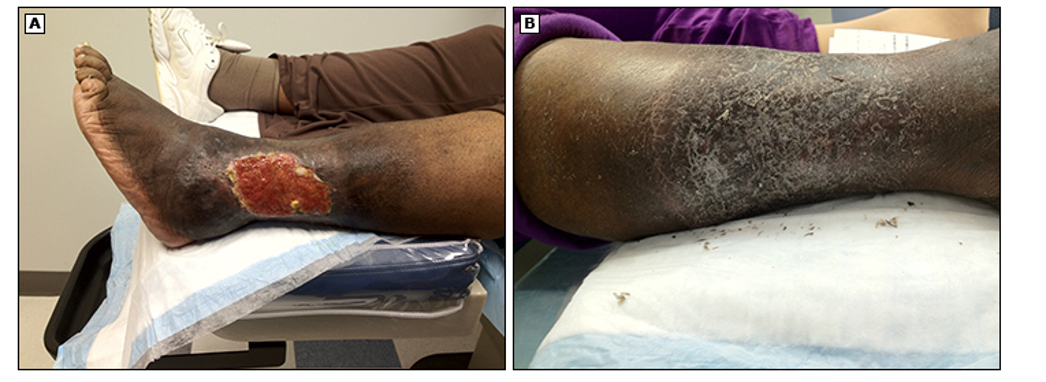
what is BBEDDS?
used for evaluating ulcers
Basics site, size, shape
Base
Edge
Depth
Discharge
Surroundings
what do rolled edges suggest?
BCC
what do everted edges suggest?
SCC
what do flat, sloping edges suggest?
venous
what do punched out edges w/o pain suggest?
neuropathic
what do punched out edges w/ pain suggest?
arterial
what do undermined edges suggest?
pressure sores
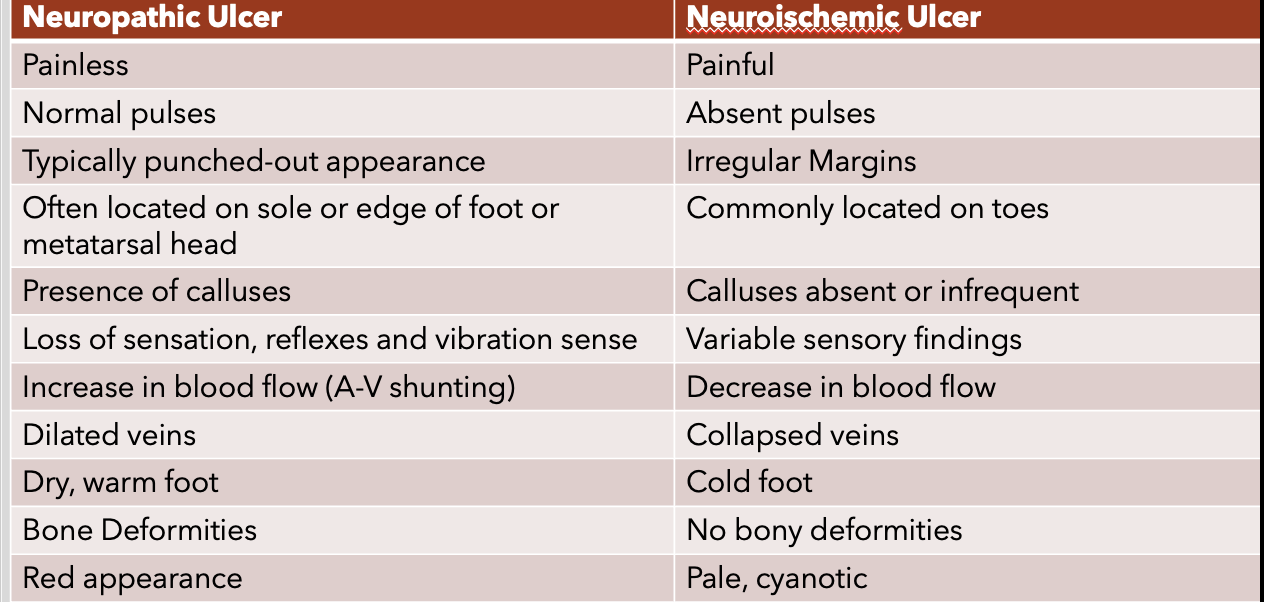
neuropathic vs neuroischemic ulcers
still too lazy to type srry
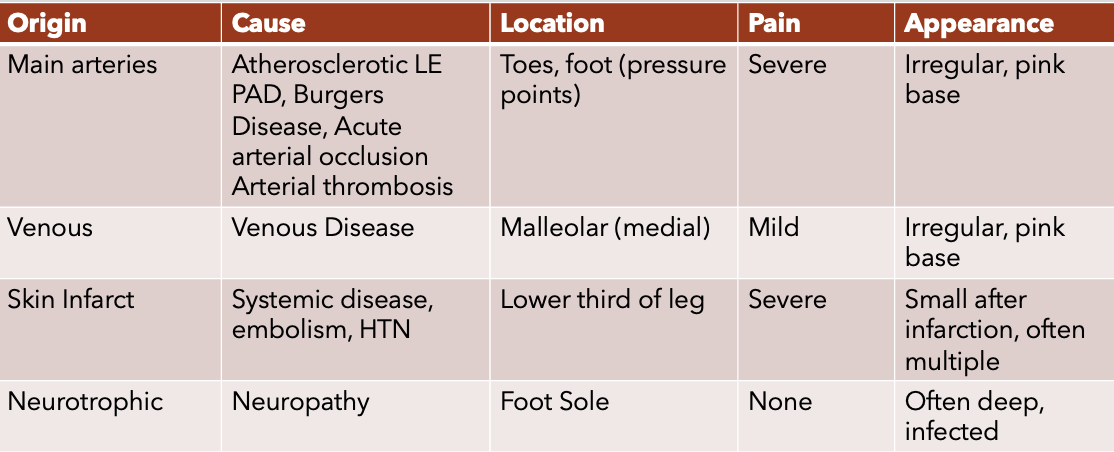
DDX of foot/leg ulcers
he just said to remember the charts in class but still don’t feel like typing
what are varicosities?
dilated, tortuous, thin walled superficial veins
commonly in legs, but also abdominal wall, anus, vulva, esophagus
What are primary varicose veins associated with?
superficial venous insufficiency
what are secondary varicose veins associated with?
deep venous insufficiency
Primary varicose veins
congenital abnormality
age related
occupation
pregnancy
secondary varicose veins
anything that raises intra-abdominal pressure or raises pressure in deep venous system
trauma
thrombosis
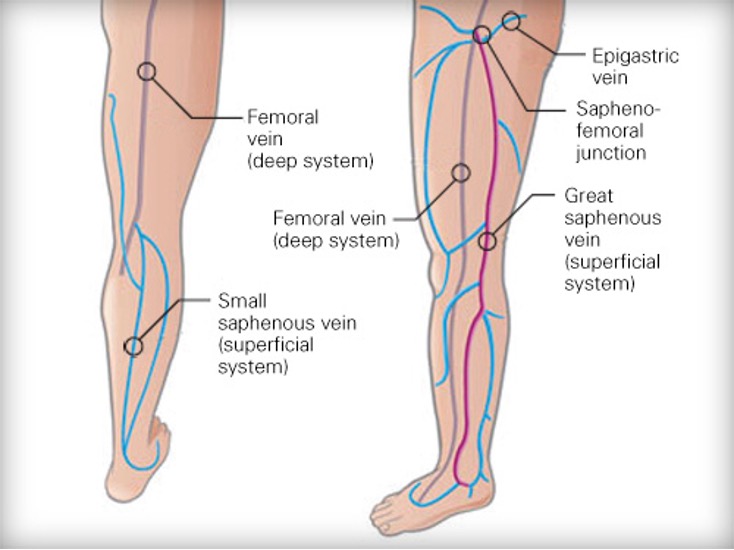
where are you inspecting on the medial side of lower extremities?
along the distribution of the long saphenous vein
where are you inspecting below the knee, posterior and lateral aspects of the legs?
along the distribution of the short saphenous vein
How do you map varicosities?
place fingers on superior aspect
sharply compress vein beneath
feel for pressure wave
what is the trendelenburg test?
evaluate for valvular competency
elevate one leg 90 degrees, occlude w/ manual pressure the great saphenous vein and ask pt to stand
keep one vein occluded and watch for filling distally
>35 s indicates incompetent valves
what is the cough test?
pt standing
place fingers over SFJ
ask pt to cough
if thrill felt → incompetence
what is the tap test?
pt standing
place one hand over SFJ, other on varicosities
tap SFJ
if thrill felt → back flow bt SFJ and varicosities → incompetence
what is the perthes test?
ask pt to stand
tourniquets around mid thigh
if veins empty → deep system fine
if veins swell and become painful → deep vessel occlusion
what is the gold standard for evaluating varicosities/incompetency of SFJ/SPJ?
doppler test
what is the doppler test?
find SFJ
place doppler
squeeze either the thigh or calf
1 whoosh as blood goes up → good!
2nd whoosh → BAD
SFJ incompetent
the quicker the 2nd whoosh → the more incompetent the valve
repeat for SPJ in popliteal fossa
How do you find the sapheno-femoral junction (SFJ)?
ask pt to lie down
find femoral pulse (midway bt ASIS and pubic tubercle)
2cm medial and 2 cm inferior to femoral pulse
palpate for sapheno varix- localized dissension of long saphenous vein in groin
How do you evaluate for temperature of extremities?
with the dorsum of your hand;
lift and place don’t rub → “professionalism 0”
what are possible reasons you may not be able to feel a pulse during a physical exam?
occlusion → atherosclerosis, DM
stenosis
congenital anomaly
edema
Where should you check for pitting edema?
dorsum of each foot
behind medial malleolus
over the shins
How do you grade the depth of pitting edema?
1+ → 2 mm
2+ → 4 mm
3+ → 6 mm
4+ → 8 mm
what would cause bilateral symmetrical pitting edema?
CHF
what would cause unilateral soft pitting edema?
DVT
what would cause firm pitting edema w/ hyperpigmentation and thickening of the skin?
chronic venous stasis
what would cause hard, non-pitting edema?
pretibial myxedema
what would cause unilateral, soft to firm tender edema w/ red warm skin?
cellulitis
how does lymphedema appear in early stages?
soft
how does lymphedema appear in later stages?
indurated, hard non pitting edema w/ peu-de-orange skin (dimples like oranges)
what is Homan’s sign?
checks for DVT
calf pain elicited upon active passive dorsiflexion of foot
low sensitivity (rely on physical exam, labs, and diagnostic studies instead)
what should you get when you suspect a DVT?
doppler and u/s
what blood tests would you order for suspected anemia?
CBC w/ ferritin
what blood tests would you order for suspected renal failure or DM?
UA and BMP
what blood tests would you order for suspected atherosclerosis?
fasting lipid panel
what blood tests would you order for suspected CHF?
BNP
What does a murmur-like sound of vascular rather than cardiac origin (bruit) indicate?
partial arterial occlusion
What do you auscultate the carotid arteries with?
bell
How to auscultate the carotids?
one at a time w/ the bell of stethoscope
upright and supine position
listen to at least 3 locations → base of neck, carotid bifurcation, angle of jaw
listen over subclavian artery to determine if transmitted or originates in carotid
ask pt to hold breath while listening for bruits
normal: pulse heard W/O sounds during systole
what does a carotid bruit suggest?
carotid artery stenosis
what does a transmitted murmur heard in the carotids suggest?
aortic stenosis; subclavian artery stenosis
what is a venous hum?
continuous thrill and murmur at root of neck in sitting position that disappears in supine position and w/ compression
*benign and common in children
what does a hyperkinetic carotid pulse suggest?
increased LV SV
what does a hypokinetic carotid pulse suggest?
decreased LV SV
what might a bisferiens carotid pulse suggest?
aortic stenosis + aortic insufficiency
aortic insufficiency alone
HOCM
what might a parvus et tardus carotid pulse suggest?
(slow rising, low amplitude)
severe valvular aortic stenosis
where is the contour of the pulse best palpated and defined?
central sites → carotid, brachial, and femoral arteries
Double pulses include…
pulsus biferiens, bifid pulse, pulsus alternans
What is a double pulse of aortic insufficiency?
pulsus biferiens
what kind of pulses would you expect in pericardial tamponade, constrictive pericarditis, and obstructive airway dz?
paradoxical pulses