India
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
known to be one of the earliest civilizations–alongsideMesopotamian civilization and Ancient Egypt–which started at around 3300 BCE and
matured from 2600 BCE lasting until 1900 BCE.
ANCIENT INDIA - INDUS VALLEY CIVILIZATION
During the decline of the Indus Valley civilization, people from Asia called Aryans migrated to the Indian subcontinent. This was the period of India’s history called the…
Vedic Age ( 1500 BCE to 500 BCE )
first pan-Indian empire that started around 321 BCE and ended in 185 BCE. As
Alexander the Great’s power waned after seizing control over the areas dominated by the Aryans, Chandra Gupta–the first leader of the empire–strategically took over the area and crowned himself as king.
Mauryan Empire
The decline of the Mauryan empire marked the beginning of the ___ empire
Gupta Empire
was a period in Indian history characterized by a series of 5 dynasties
that governed parts of India from the early 13th to the 16th century
Delhi Sultanate
what was the name of the 5 dynasties during delhi sultanate
Mamluk Dynasty,
Khaljis Dynasty,
Tughlaqs Dynasty,
Sayyids Dynasty,
Lodis Dynasty.
started due to the invasion of Babur in 1526. Babur was a Muslim warrior prince from Central Asia with Mongol roots. During this period Muslim art, culture, and faith spread.
Mughal Empire
the name of the Portuguese explorer, discovery of a sea route which connected Europe and India.
Vasco De Gama’s,
what was the name of the british colonizer ( company) that arrived in india primarily for commerce
British East India Company
the first war of Indian independence was also called the ______ or the _____. This was a period of rebellions against British rule sparked by
Mangal Pandey, a Sepoy in the colonial British army.
Indian Mutiny or the Sepoy Mutiny
was a period in Indian history from 1858 to 1947 wherein India was under the
direct rule of Britain through the proclamation of the Government of India Act of 1858.
The British Raj
was formed on 28th of December 1885 as a national political
organization which aimed at uniting Indians against British colonialism.
attributed to Allan Octavian Hume
Indian National Congres
was created in 1906 that was initially led by Aga Khan and ultimately led by Muhammed Ali Jinnah.
The All Muslim League
legalized and formalized the separation of India and Pakistan.
Indian Independence Act of 1947
who passed the Indian Independence Act of 1947,
British Parliament
separation of India and Pakistan. The _____ laid the outline for this
partition.
The Mountbatten Plan
what triggered the triggered the Indo-Pakistani War of 1947-
1948?
region of Kashmir acceding to India
The India China dispute involves the regions…
Aksai Chin
is controlled by China but is claimed
by India as part of the Ladakh region.
Arunachal Pradesh
is controlled by India but is claimed by China as part of South Tibet.
INDIA AND NEPAL The dispute involves what?
he Kalapani region, specifically the Kali river.
what is the POLITICAL SYSTEM of India?
Democratic Republic with Parliamentary form of government and has a federal structure
India is a Sovereign, Socialist, Secular,
Democratic Republic which follows a
Parliamentary form of government and has a
federal structure with unitary features.
The Parliamentary government of India is similar to the __ model
Westminster model
of the United Kingdom
what is the composition of the Executive Branch
President,
Vice-president,
Prime Minister,
and Council of Ministers
who governs the Union and Attorney General.
what is the composition of the Legislative Branch
bicameral
Rajya Sabha (Council ofStates), which is the upper house,
the Lokh Sabha (House of the People), which is the lower house.
The President can dissolve the Lokh Sabha, upon the advice of the Prime
Minister.
what is the composition of the Judiciary [4]
The Supreme Court,
High Court,
District Courts,
the Subordinate Courts.
POLITICAL STRUCTURE OF THE STATE GOVERNMENT
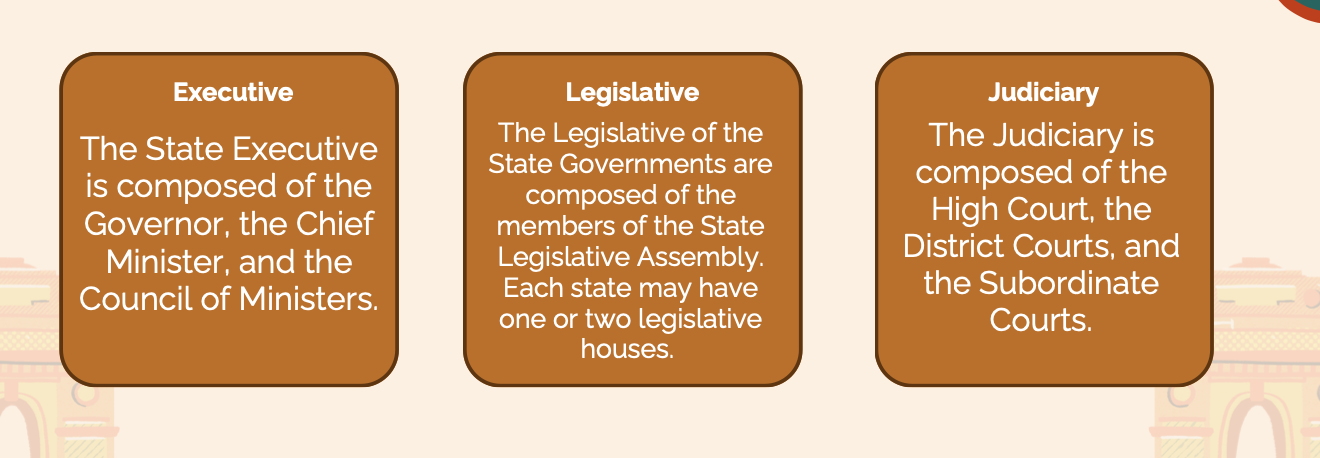
what are the two types of union territories
Union Territories with a government
union territories without a government.
who is the exectuive accountable to
executive is accountable to the Lokh Sabha
India follows what type of electoral system?
First-Past-the-Post electoral
system and Indian citizens vote through the
Electronic Voting Machines. They follow a
“Secret Ballot” system.
India is divided into ___ constituencies wherein each
constituency elects one member of the ____.
India is divided into 543 constituencies wherein each
constituency elects one member of the Parliament.
REMOVAL FROM OFFICE

Is india a multiparty system, or single party?
India is a multiparty system
which has national parties, state parties, and other registered parties.
SOCIAL MOVEMENTS
Quit India Movement
Non-Cooperation Movement
Salt March (1930)
The Farmers' Protest
Indian Against Corruption Movement
what is the caste system?
The caste system is a traditional
social hierarchy which classifies people into groups based on birth
and jobs.
what is indias stance on UKRAINE-RUSSIA
NEUTRAL
India’s stance can be characterized as neutral regarding the Ukraine-Russia conflict. This is due to the strategic autonomy and national interests. However, India supports peace between the two countries but it doesn’t condemn Russia.
what is indias stance on ISRAEL-PALESTINE
2 STATE SOLUTION
India is employing a neutral stance characterized as a balancing act. However, India still supports Palestinian rights
Who is the indian president?
Droupadi Murmu
who is the indian prime minister?
Shri Narendra Modi