Biol 208: Lecture 28 - Nutrient cycling
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What is the RED FIELD RATIO?
106C: 15N: 1P
Describes the elemental composition of our plants biomass (an approx. from phytoplankton)
Energy flow (Carbon flow) always carries nutrient atoms with it; when nutrients are in short supply, biomass creation is limited
With flow through food webs Carbon is RESPIRED and N+P are RECYCLED
Define nutrient pool + nutrient flux
Pool = amount of a particular nutrient stored in a portion or compartment of the ecosystem
Flux = Movement of nutrients between pools of an ecosystem
Phosphorus cycle:
Where is it most + less LIMITING
Where is the LARGEST POOL?
Most limiting = AQUATIC
Least = Terrestrial
Largest pool = Marine sediment + rock
Phosphorus is less likely limiting in terrestrial ecosystems
What are 2 EXCEPTIONS
Very old soil eg. Tropical rain forest
Break down very slowly eg. Canadian shield
Phosphorus cycle
What is P a key component in?
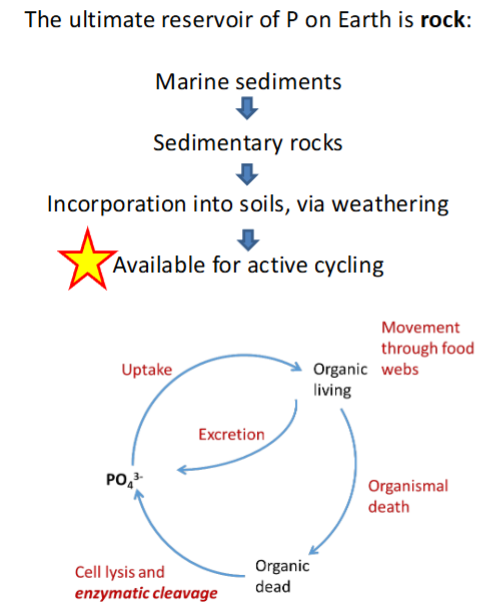
What is the Ultimate reservoir of P on earth
What is the active form
What are 2 sources to make the active form of P available?
Ultimate reservoir = ROCK
E (ATP), DNA/RNA + Phospholipids
Active = PO4-
2 sources:
Marine sediment → sedimentary rock → incorp into soils via weathering = Available for active cycling
Cell lysis + enzymatic cleavage of Organic dead matter → inorganic phosphate
Nitrogen Cycle
what is N a key component in?
Where is it limiting?
What is the Ultimate reservoir of N on earth
How is Biologically available N made?
Component in: Proteins, nucleic acid, chlorophyll _ hemoglobin
Limiting PRIMARY PRODUCTION in MARINE + TERRESTRIAL ecosystems
Ultimate reservoir = ATMOSPHERE (N2 gas)
NITROGEN FIXATION
What are the 3 methods of Nitrogen fixation?
Bacteria/ specialized organisms
Lightning
Industrial production of FERTILIZER (primary avenue)
ENERGETICALLY COSTLY
What are the three forms of Nitrogen that can be used?
NH4+ = Ammonium
NO2- = Nitrite
NO3- = Nitrate
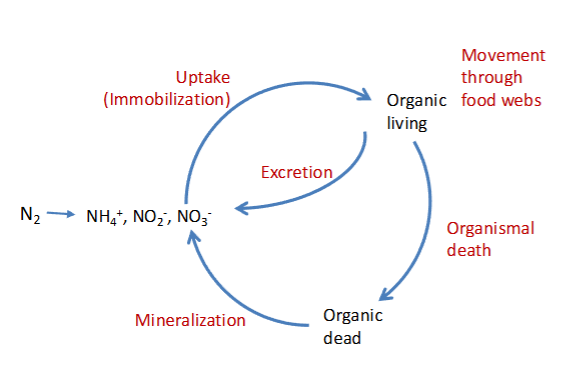
Define:
Ammonification
Nitrification
Denitrification
And how they all relate to each other
Ammonification = Release of N as Ammonium (NH4+) by all organisms (urine + feces) or decomposition
Nitrification = conversion of NH4+ into Nitrite (NO2-) — then quickly → Nitrate (NO3-)
Change in OXIDATION STATE = releases E which allows nitrifying bacteria to create organic matter from CO2
Denitrification = Conversion of NO3- → N2 (dinitrogen gas)
change in REDOX state allows bacteria to use this conversion instead of O2 to break down organic matter
primary process in which N is LOST from ecosystem
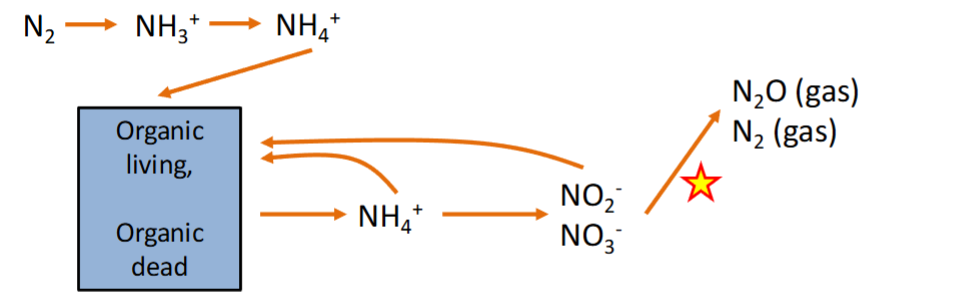
How are Nitrogen transformations intricately linked to the carbon cycle?
respiration of organic matter:
When O2 = not available Nitrate (NO3- → N2) replaces O2 as the energy yielding reaction in respiration (CH2O → CO2)
Organic matter Generation:
Reduced (low O2) forms of N give off E when they gain O2 (NH4+ → NO3-). This E release allows CO2 to be fixed as CH2) = Equivalent of photosynthesis
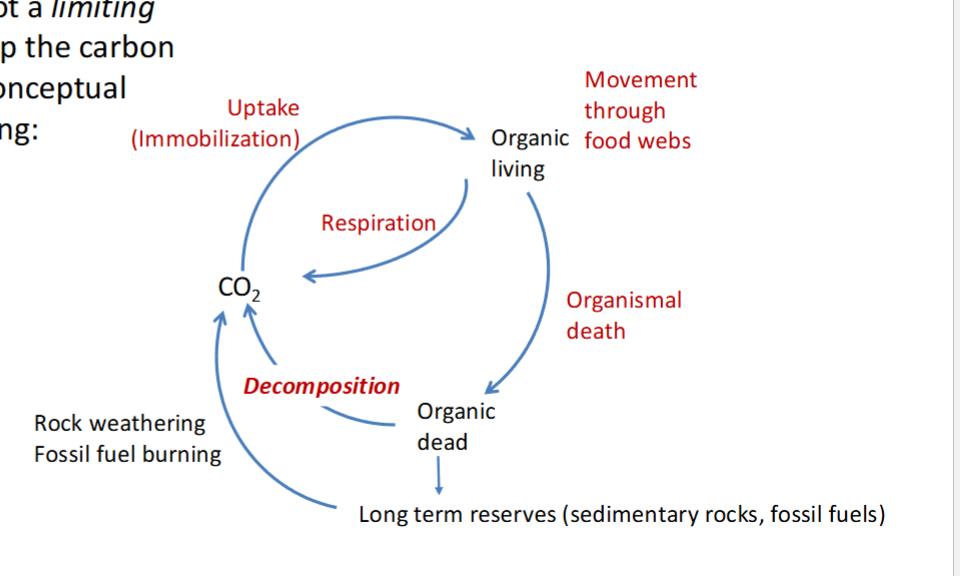
Carbon Cycle
Critical role of Carbon?
Process of removal + return
Long term pools
Is carbon limiting?
critical role = global climate (CO2 + CH4)
Remove = Photosynthesis coupled with uptake of essential nutrients
Return = Respiration coupled with recycling of nutrients PO3- + NH4+
Major pools = Ocean Soil + Sedimentary rocks + fossil fuel
Define decomposition
role?
What controls the rate?
The process by which organic matter is broken down by microbes to nutrients (PO3- and NH4+) + released for uptake by primary producers + release CO2
Rate of nutrient regen by decomp controls the availability of these nutrients which ties the production of organic matter
Controll:
Moisture = Increases Decomp with increase moisture
Temp = increase
Matter composition = Increases with high N (nutrient) content
Soil comp = increases with increased nutrients
What is AET?
Actual Evapotranspiration
measure of the total amount of water that evaporates and transpires from a landscape
Increases with increasing temp + precipitation (combined metric)