Economics paper 1
1/100
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
3 main economic groups
Consumers, producers and government
4 factors of production
Land, labour, capital, enterprise
3 key questions for reducing the economic problem
How should goods and services be produced? What should be produced? Who should the goods and services be produced for?
3 types of economies
Market, mixed, controlled
3 sectors
Primary, secondary, tertiary
Benefits of specialisation for producers
Higher output, higher productivity, higher quality, bigger market, economies of scale, saves time and money
Costs of specialisation for producers
Diseconomies of scale, if one part of the process fails the whole production system may stop, may not be able to buy necessary resources or components, movement of workers
Benefits of specialisation for workers
Increased skill (potentially increased wages), increased job satisfaction, increased standards of living
Costs of specialisation for workers
Demotivation, deskilling, unemployment if they are replaced by machines
Benefits of specialisation for regions
Makes best use of its resources, creates nearby jobs for residents, better infrastructure
Costs of specialisation for regions
If demand falls industry may collapse, resources may run out, other region could become better at producing
Benefits of specialisation for countries
Greater efficiency and output, more jobs, international trade with surplus output, improved infrastructure, increased standards of living, government revenue increases
Costs of specialisation for countries
If industry declines unemployment will increase, overspecialisation, over exploitation of resources, negative externalities to the environment
Direction the demand curve slopes
Downward
Movement up the demand curve
Contraction
Movement down the demand curve
Expansion
Causes of shifts in demand
Change in income, marketing, change in taste and fashion, substitutes, complementary goods, expectations of a change in price, population changes, government policies
Impact on demand curve if demand increases
Shifts to the right, price increases, quantity increases
Impact on demand curve if demand decreases
Shifts to the left, price decreases, quantity falls
Formula for PED
Percentage change in quantity/ percentage change in price
PED value= 0
Perfectly inelastic
PED value= Between 0 and -1
Inelastic
PED value= -1
Unitary elastic
PED value= Between -1 and -infinity
Elastic
PED value= Infinity
Perfectly elastic
Perfectly inelastic
No change in quantity as price changes
Inelastic
Change in quantity is less than change in price
Unitary elastic
Change in quantity is equal to change in price
Elastic
Change in quantity is more than change in price
Perfectly elastic
An infinite amount can be demanded at a given price, no change in price
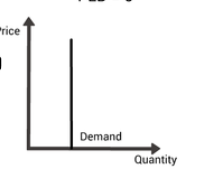
PED- What is it?
Perfectly inelastic
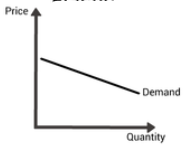
PED- What is it?
Inelastic
PED- What is it?
Unitary elastic
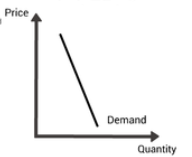
PED- What is it?
Elastic
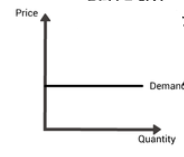
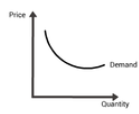
PED- What is it?
Perfectly elastic
Importance of PED for consumers
If a product has inelastic demand they are likely to face price rises and high taxes, allows them to make choices if substitutes available
Importance of PED for producers
Allows producers to maximise total revenue, affects their decision whether to supply the product or not
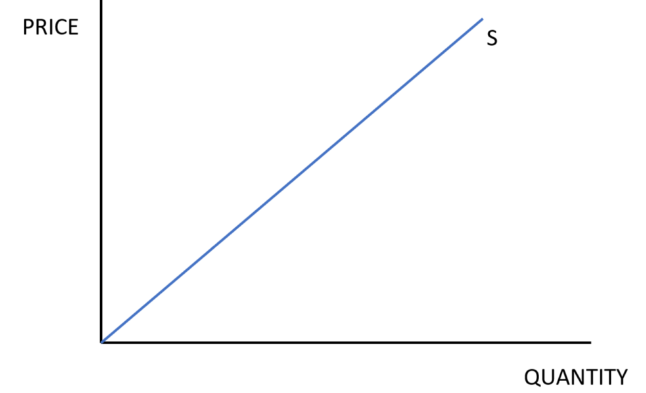
What direction does a supply curve slope
Upwards
Movement up the supply curve
Expansion
Movement down the supply curve
Contraction
Causes of a shift of the supply curve
Costs of production, taxes and subsidies, new technology, climate change, increase in producers/size of firms, government regulation
Impacts on supply curve if supply increases
Shift to the right, prices fall, quantity increases
Impacts on supply curve if supply decreases
Shift to the left, prices rise, quantity decreases
PES value= 0
Perfectly inelastic
PES value= Between 0 and 1
Inelastic
PES value= 1
Unitary elastic
PES value= Between 1 and infinity
Elastic
PES value= infinity
Perfectly elastic
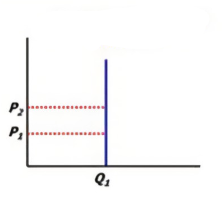
PES- What is it?
Perfectly inelastic
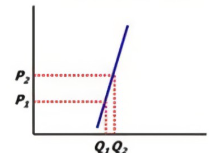
PES- What is it?
Inelastic
PES- What is it?
Unitary elastic
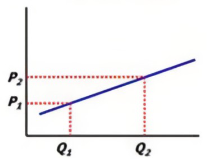
PES- What is it?
Elastic
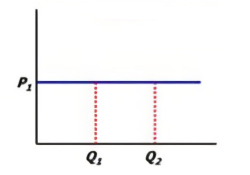
PES- What is it?
Perfectly elastic
Importance of PES for consumers
If the product has inelastic supply they are likely to face high prices to obtain more, may not be able to get more of a product with very inelastic supply, if a product has elastic supply it is easy to purchase more
Importance of PES for producers
Firms would prefer elastic supply so it is easier to response to prices, elastic supply enables a firm to be more flexible, very inelastic supply means price will depend entirely on demand
3 functions of price
Signalling, transmission of preferences, rationing
Effects on equilibrium price and quantity if demand increases
Price increases, quantity increases
Effects on equilibrium price and quantity if demand decreases
Price decreases, quantity decreases
Effects on equilibrium price and quantity if supply increases
Price decreases, quantity increases
Effects on equilibrium price and quantity if supply decreases
Price increases, quantity decreases
2 types of competition
Price and non-price
3 reasons why producers compete
To: enter a new market, survive in a market, make a profit.
Benefits of competition for producers
Increased efficiency: costs cut, innovating, improving productivity
Costs of competition for producers
Lose consumers, replace workers with technology
Benefits of competition for consumers
Cheaper prices, improved quality of goods/services, innovation, increased consumer sovereignty
Costs of competition for consumers
Innovations may be harmful, quality may fall, marketing may be dishonest
Monopoly- control of prices
Able to set prices
Oligopoly- control of prices
Can influence price but is restrained by the reaction of rivals
Competitive- control of prices
Price is set by market forces
Monopoly- level of price and output
Higher price, lower quantity
Oligopoly- level of price and output
Dependent on how strong competitors are
Competitive- level of price and output
Lower price, greater quantity
Monopoly- efficiency
Not seen as efficient but can be if they gain large economies of scale
Oligopoly- efficiency
Not seen as economically efficient
Competitive- efficiency
Efficient
Advantages of an increase in production
Increase in employment, rise in standard of living, increase in profits, gain larger economies of scale, gain greater market share, economic growth
Disadvantages of an increase in production
Workers replaced by machines, diseconomies of scale, other firms lose market share, environmental problems
Impacts of higher productivity
Lower average costs, increased economies of scale, increased profits, increased output, increased exports
Costs of productivity
Unemployment, fall in GDP
Formula for total cost
Total fixed cost + total variable cost
Formula for average cost
Total cost/quantity
Formula for total revenue
Price x quantity
Formula for average revenue
Total revenue/total quantity
Formula for profit
Total revenue- total cost
9 internal economies of scale
Division of labour, financial, increased dimensions, managerial, marketing, bulk buying, risk-bearing, research and development, technical
4 external economies of scale
Concentration of firms, education and training facilities, location, transport
Reasons for lack of labour mobility
Lack of skills, geographical immobility, personal factors, information failure
Factors affecting demand for labour
Demand for products, wage rates, real wages, productivity of labour, profits of firms, state of the economy
Factors affecting supply of labour
Wage rate, other monetary payments, non-monetary payments, education and training, barriers to entry, size of working population
Role of central banks
Issue bank notes, control monetary policy, manages foreign reserves, bank for the commercial banks, bank for the government
Role of commercial banks
Accept deposits, make payments for customers, make payments by accepting cheques, issue loans, provide foreign currencies, offer safe deposit boxes
Role of investment banks
Help firms: in mergers and takeovers, underwriting share issues, with international trade.
Role of building societies
Provide a limited range of services (mainly savings and mortgages), limited as to how much money can be borrowed from the money market
Importance of credit provision for consumers
Can buy now and pay later
Importance of credit provision for producers
Can borrow money to expand
Importance of credit provision for government
Can run a budget deficit or spend before taxes are collected
Importance of liquidity provision for consumers
Can borrow to pay later
Importance of liquidity provision for producers
Banks will provide overdraft facilities so firms can continue trading while waiting for payments
Importance of risk management for consumers
Allows savers to spread their risk by putting their money into a range of companies
Importance of risk management for producers
Reduces risk of not receiving payment on time