Inventory Control
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Inventory control
Why ? Because inventory is money, and its needs to be well utilised
What ? Have the optimum level to minimise the cost of overstocking or stocking out
How ? Understanding better demand and costs
High inventory means …
High cost of carrying inventory - obsolescence, insurance, ect
Low inventory means…
Potential shortage and increasing ordering costs
Why inventory control ?
Inventory is money
Reduces inefficiencies, such as purchasing and sales managers spending more time in following up on orders
inventory is harder to control when:
Demand is unpredictable
Customer demand must be met quickly
Follows made to stock process
Purpose of Inventory
To maintain independence of operations
Each workstation can work at its most efficient schedule, and not depend on incoming material
To meet variation in demand
To allow flexibility in production scheduling
If setup cost is high, it is economical to produce a large number of units
To provide safeguard in variation against supplier's delivery schedule
Supplier cannot produce, or cannot deliver according to required production schedule
To take advantage of economic purchase order size
Dependency
Independent demand (ex: IKEA produces mugs and curtains. Demand for the two are independent)
Dependent demand (ex: IKEA produces frames and slats for beds, demand for both are dependent)
Cost of inventory
Ordering cots
Holding cots
Shortage costs
Holding costs
storage facilites
Breakage obsolescence
Depreciation
Opportunity cost of capital
Ordering costs
Cost of purchasing each order:
Clerical, managerial
calculating order counting quantities
Counting items
Shortage costs
Lost customers
Lost profits
Penalty for late delivery
Penalty for non delivery

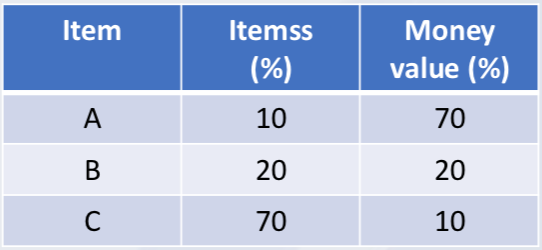
ABC valuation
A ltems:
High usage rate or high cost.
Tight control
B Items:
Less essential
Lower money value
C Items:
Least impact on sales
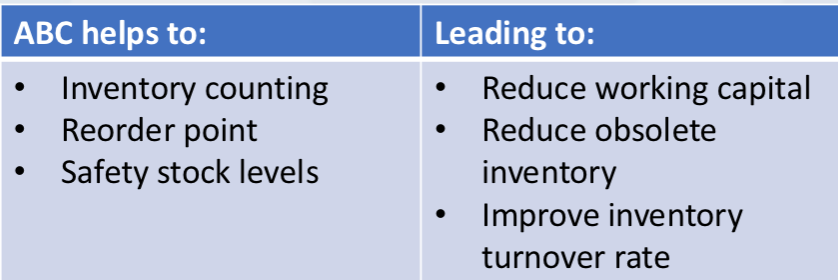
ABC helps to….leading to….
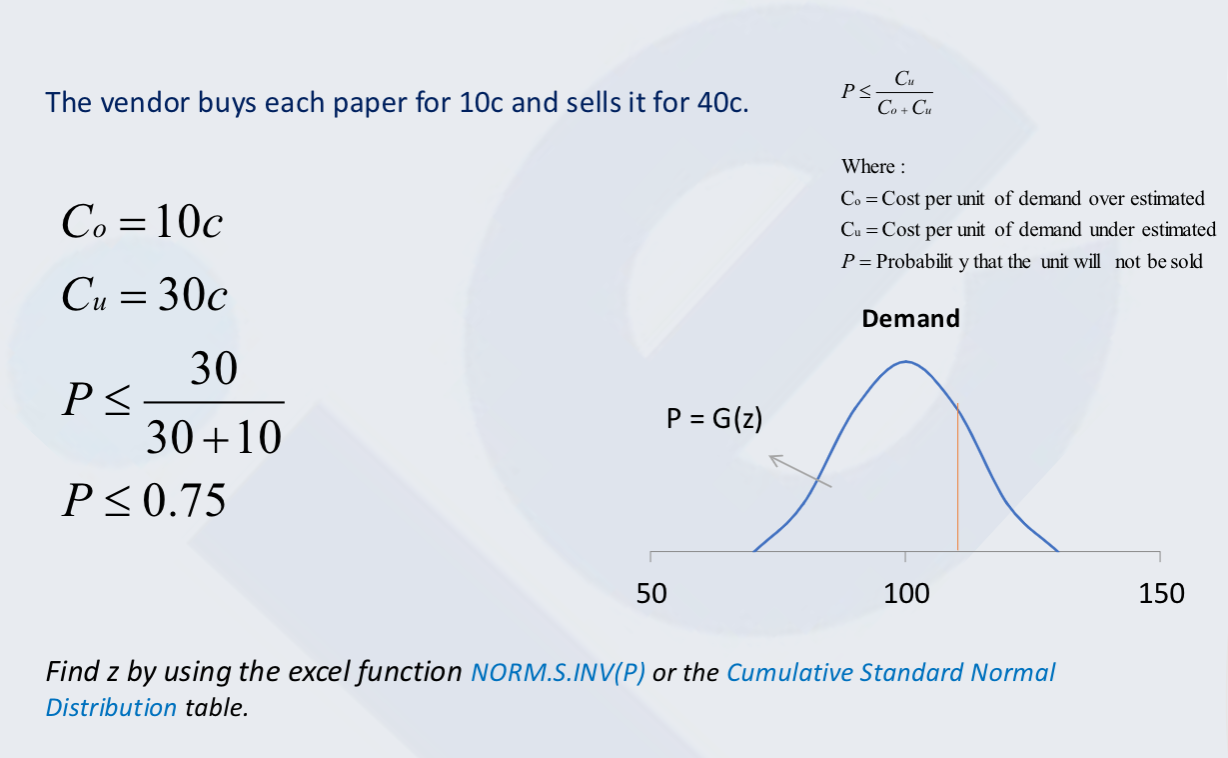
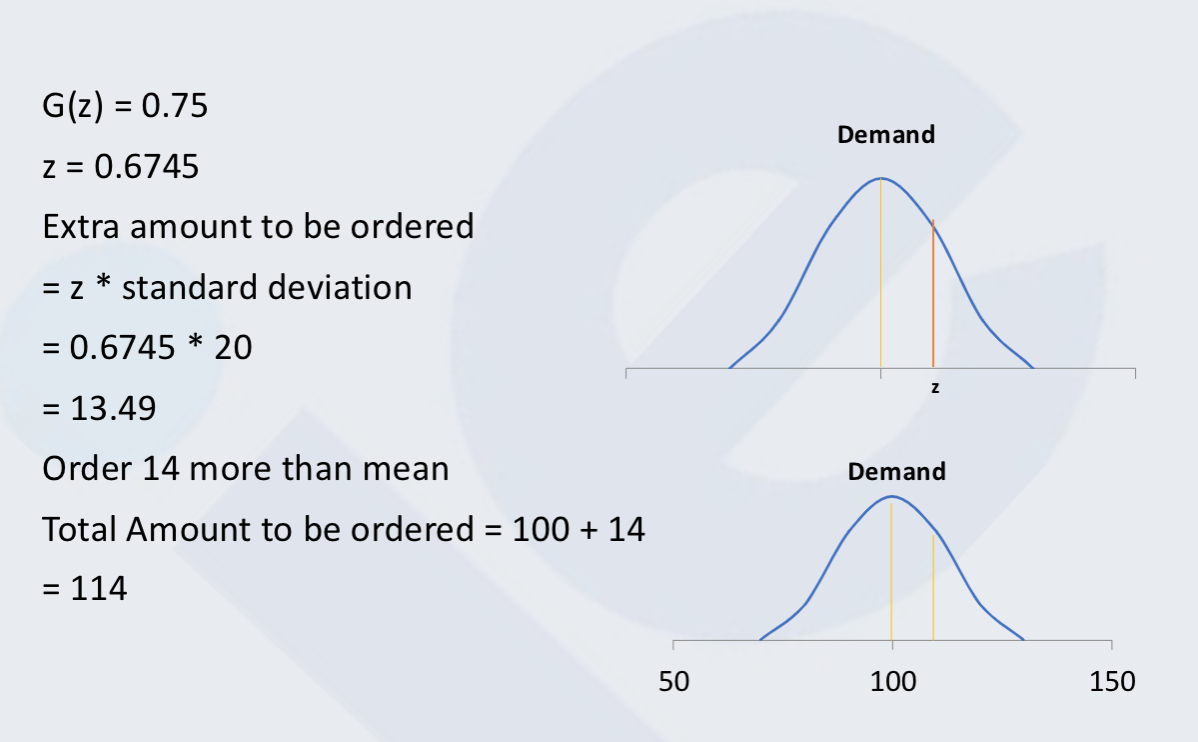
Single Period Inventory Model
One time purchase (ex: Christmas trees, newspapers, airline seat reservation)
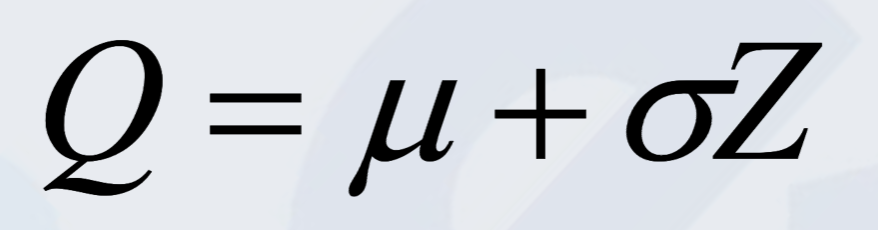
Where
Q is Quantity to be Ordered
μ is Average Demand
σ is Standard Deviation
Z is probability of running out of the item
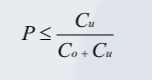
Where :
Co = Cost per unit of demand over estimated
Cu = Cost per unit of demand under estimated
P = Probability that the unit will not be sold