Finals Identification Review Cards
1/1286
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Axial Skeleton, Appendicular Skeleton, Joints, Endocrine System, Reproductive System, Urinary System, DIgestive System, Integumentary System, Respiratory System. Cardiovascular (Heart, Circulatory, Blood) System, Histology, Muscles, Tissues: Slides, Models, Dissections)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
1287 Terms
Osteo...
Related to bones
Functions of Skeleton
Support, Protection, Movement, Electrolyte balance, Acid-Base balance, Blood formation
Osteoclast
Bone dissolving cells.
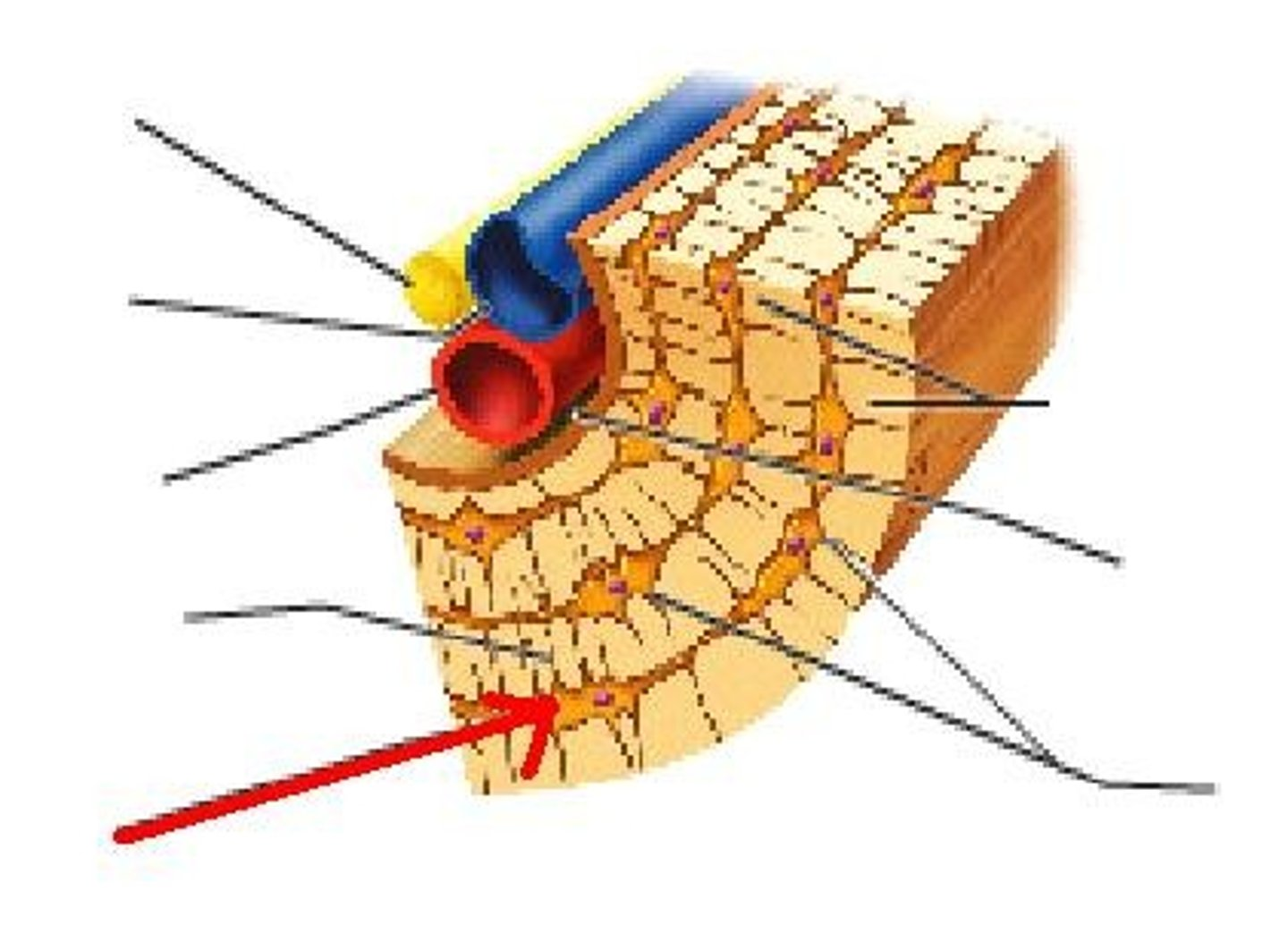
mature Osteoblasts trapped in matrix they deposited. Reside in lacunae.
Osteocytes
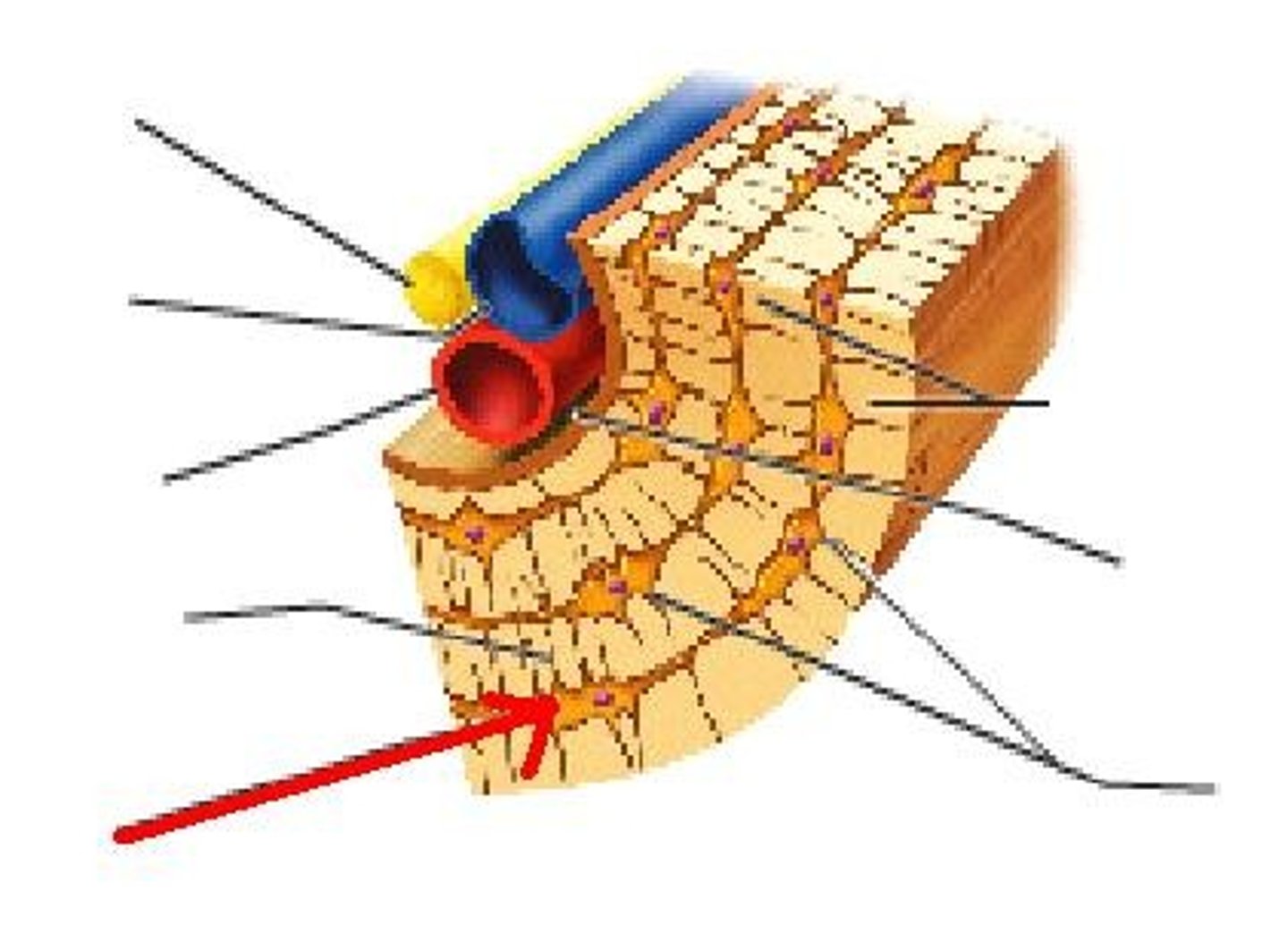
Osteoblast
Bone forming cells..
Structure shown in B
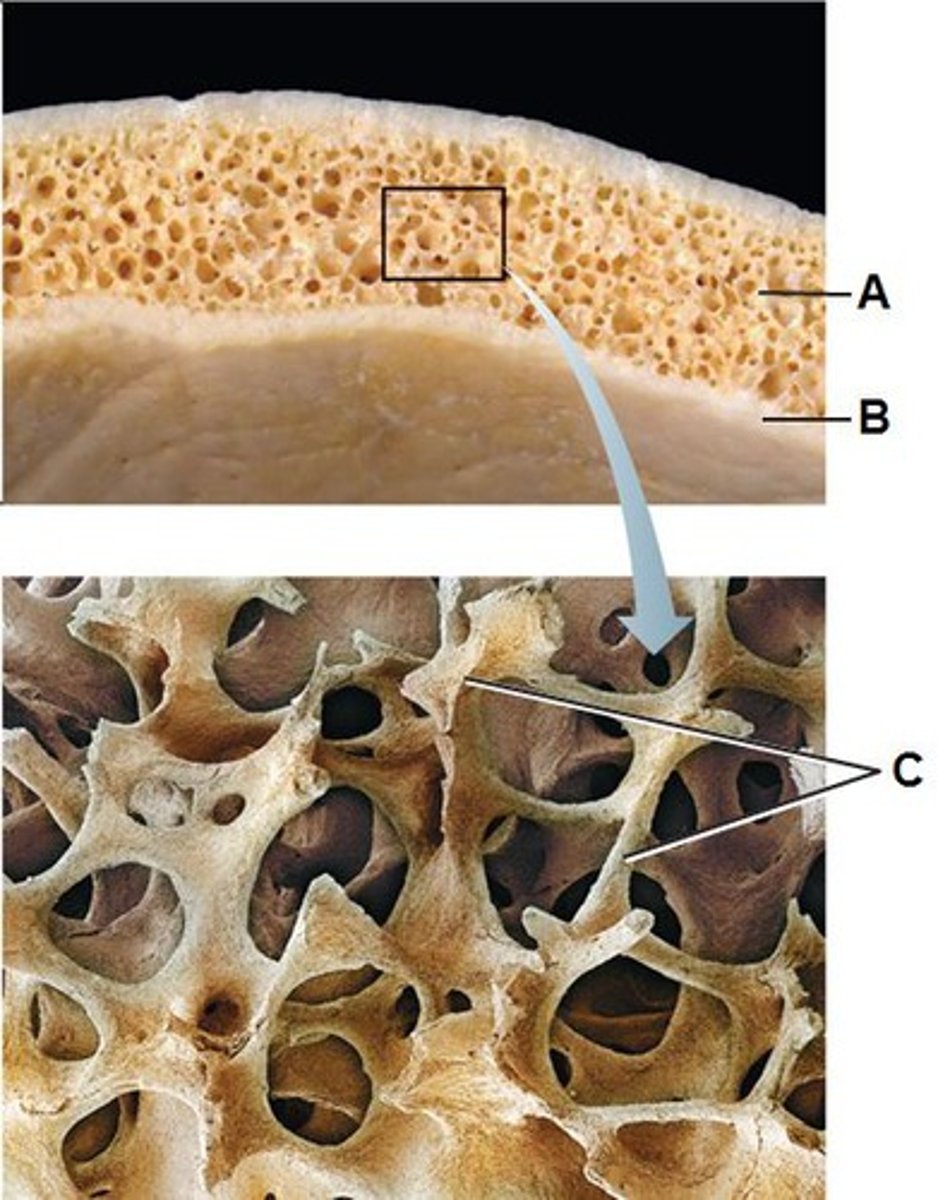
Compact (cortical) bone
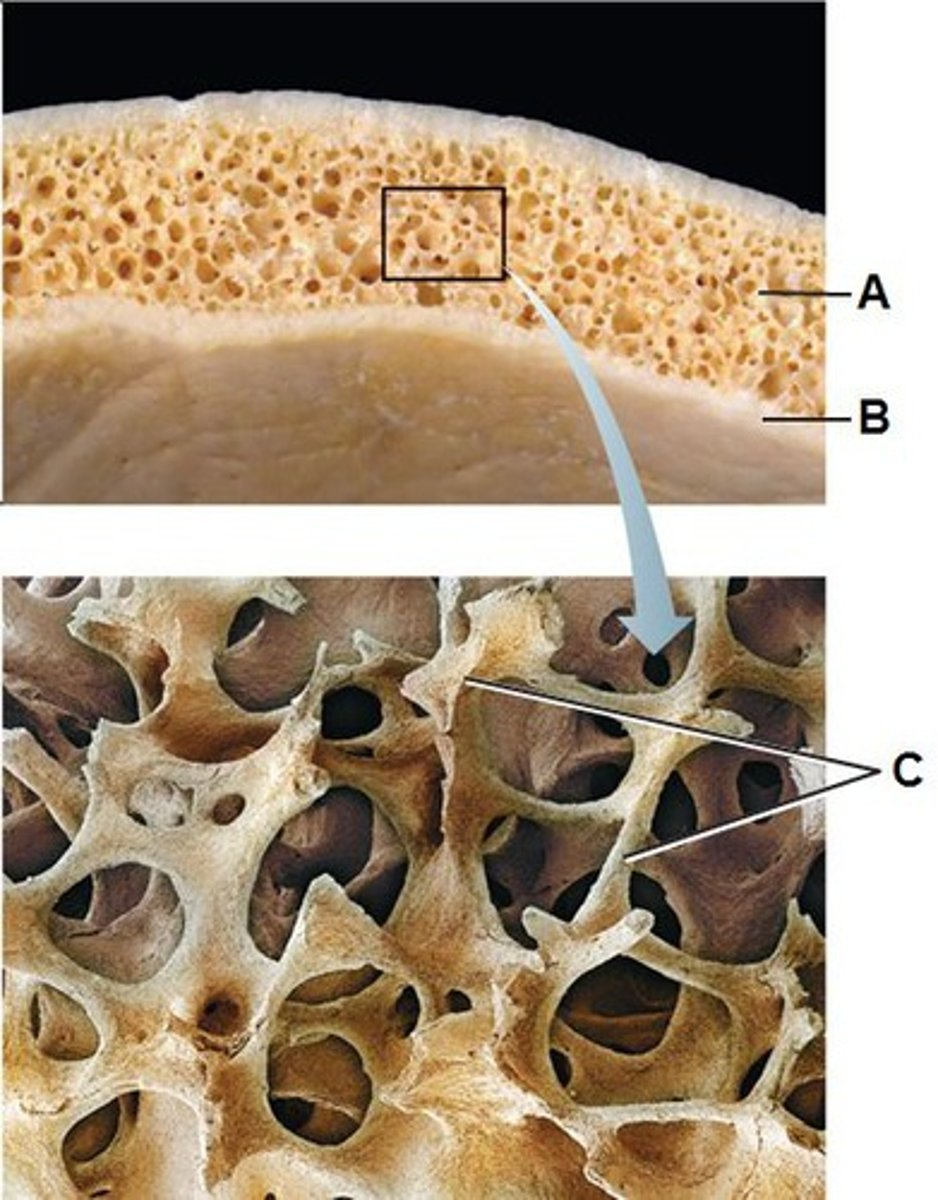
Structure shown in A
Spongy (trabecular) bone
Basic unit of compact bone
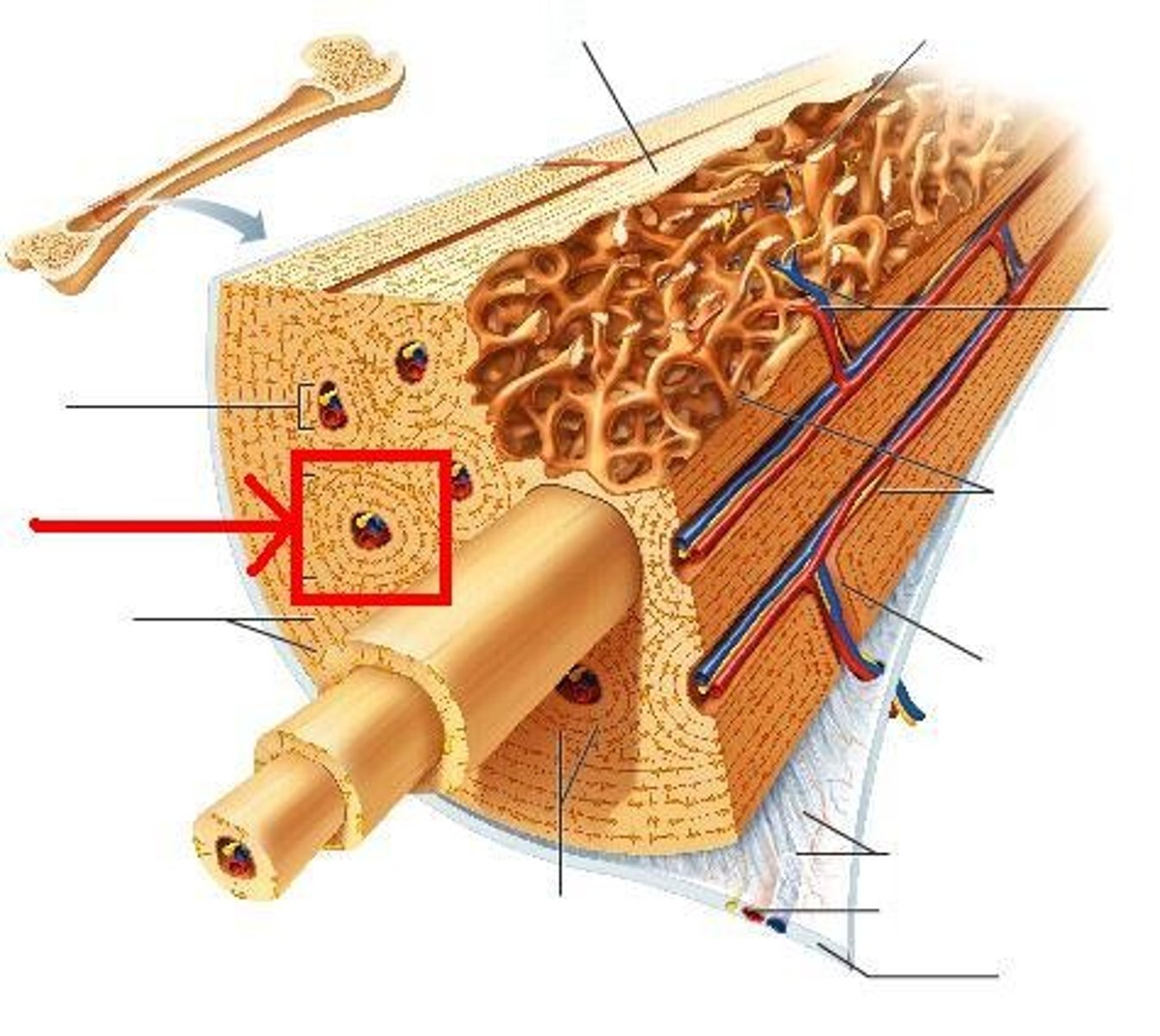
Osteon
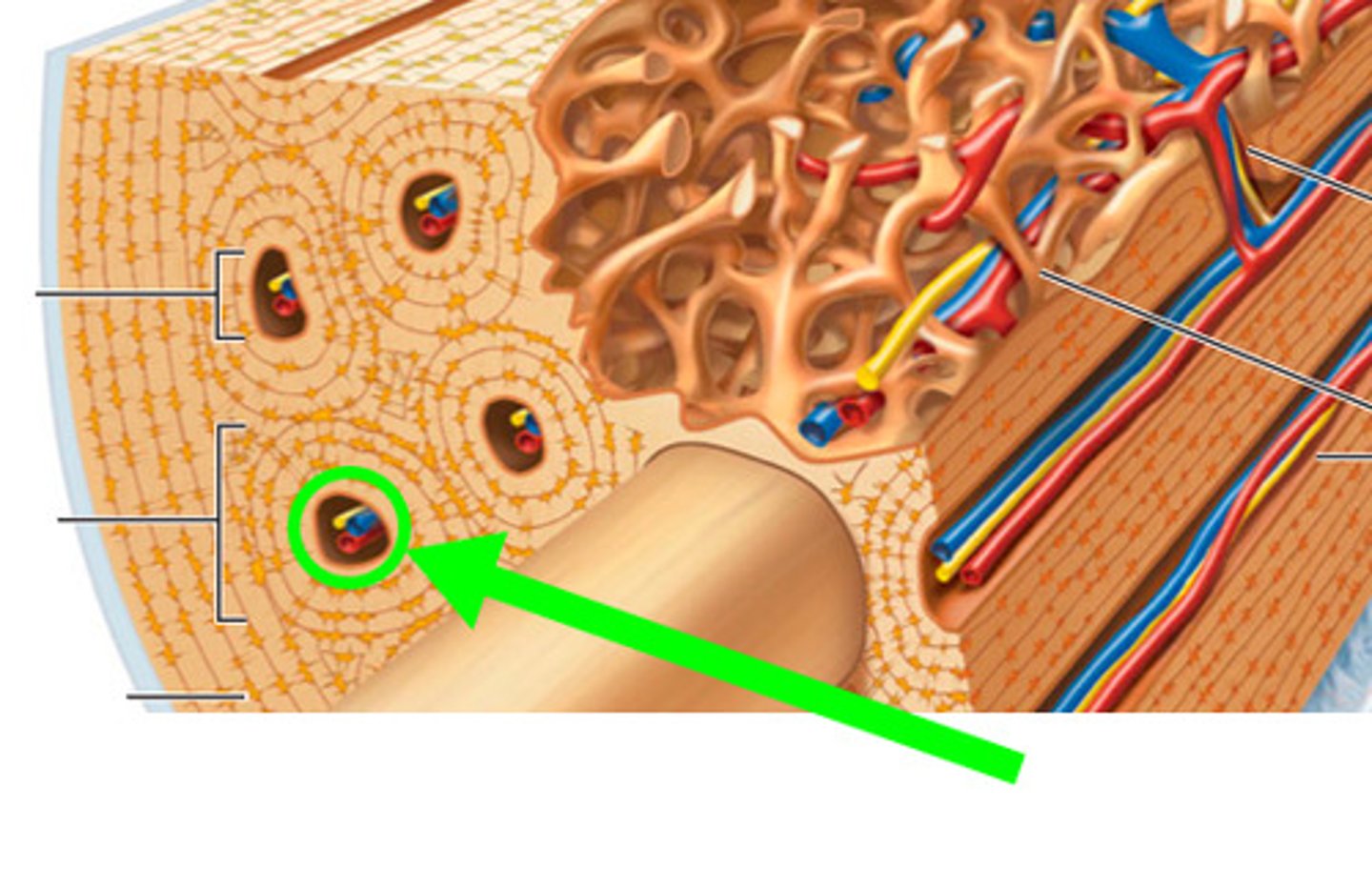
Central (Haversian) Canal
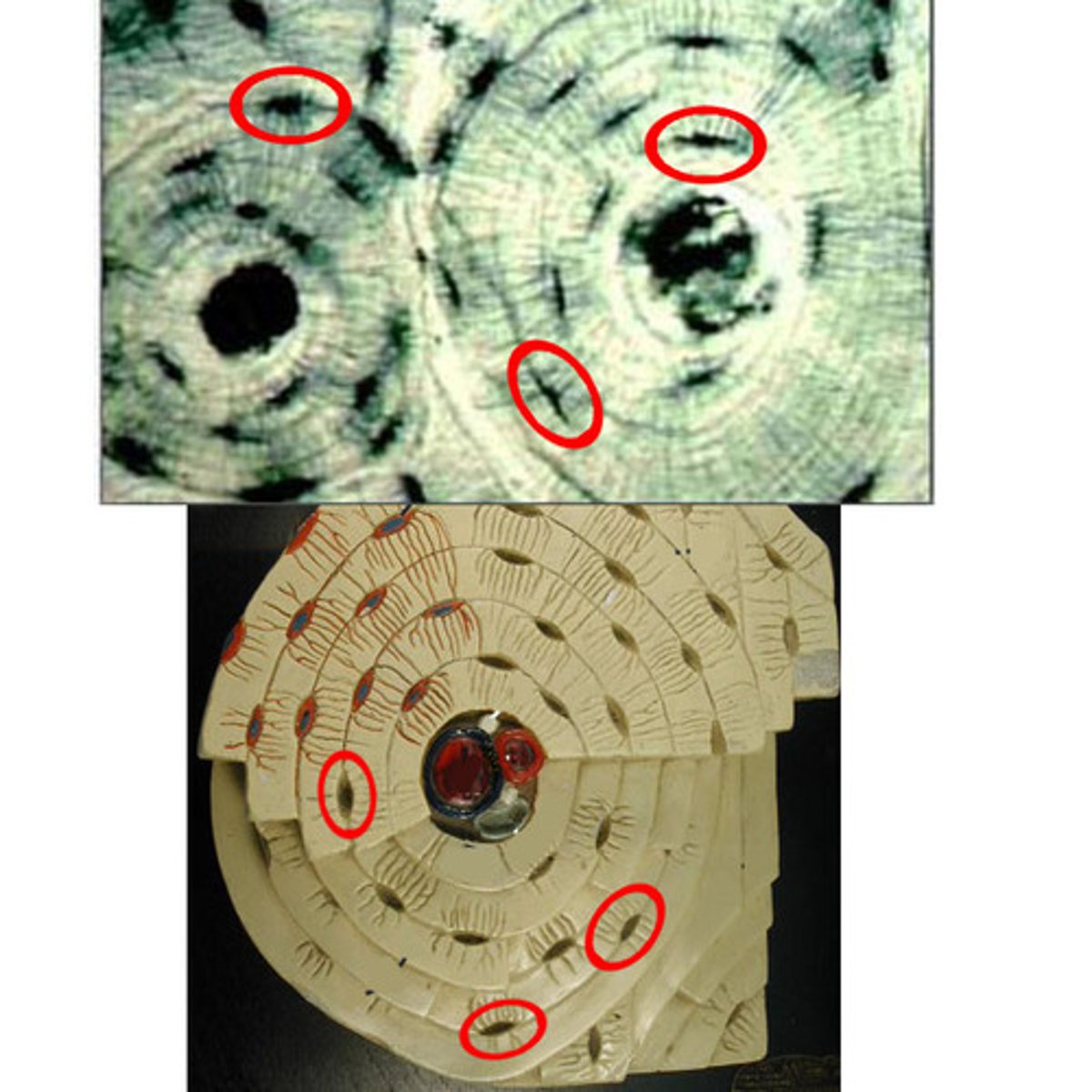
Lacuna
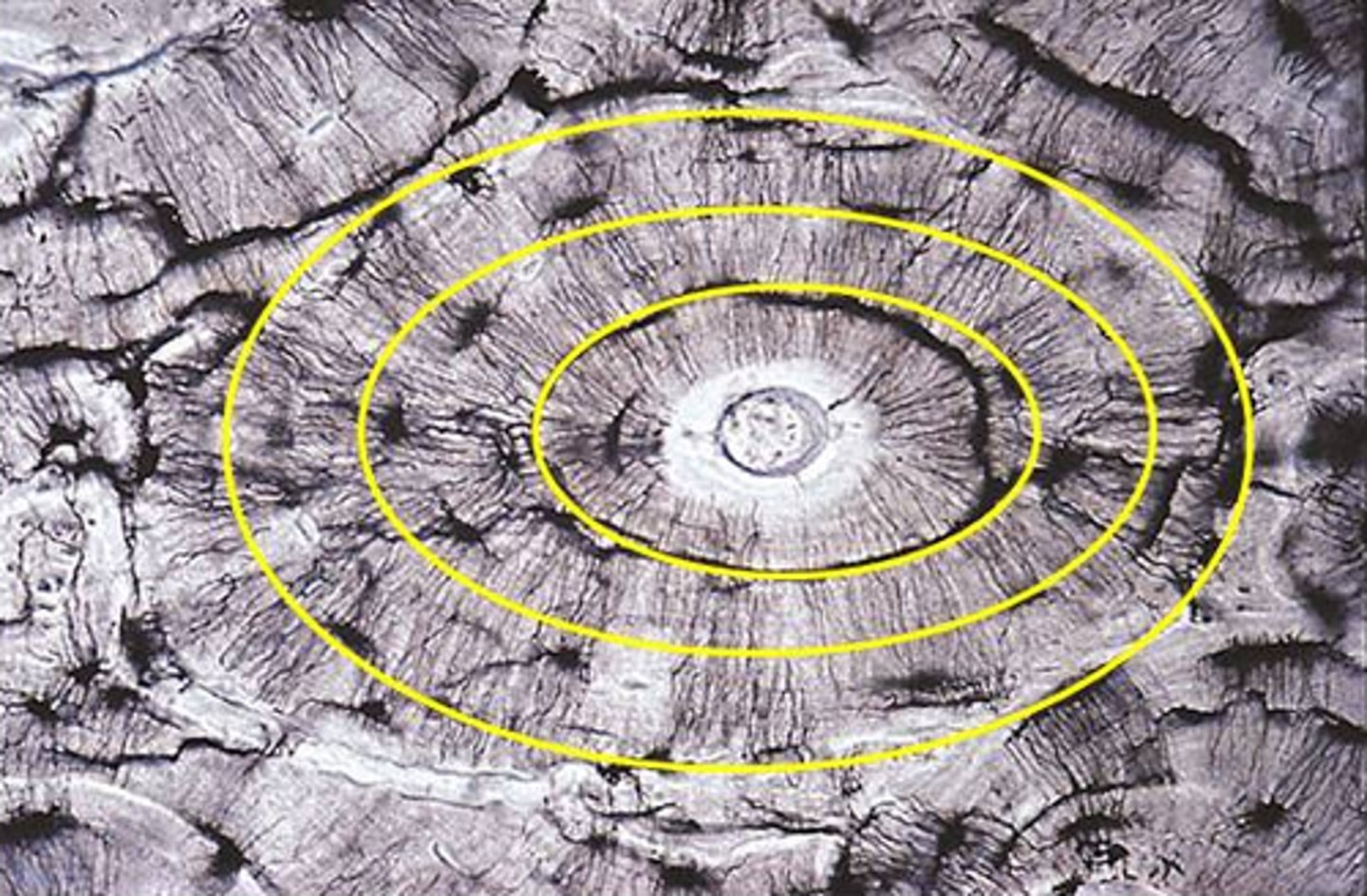
Concentric Lamellae
structure seen in C
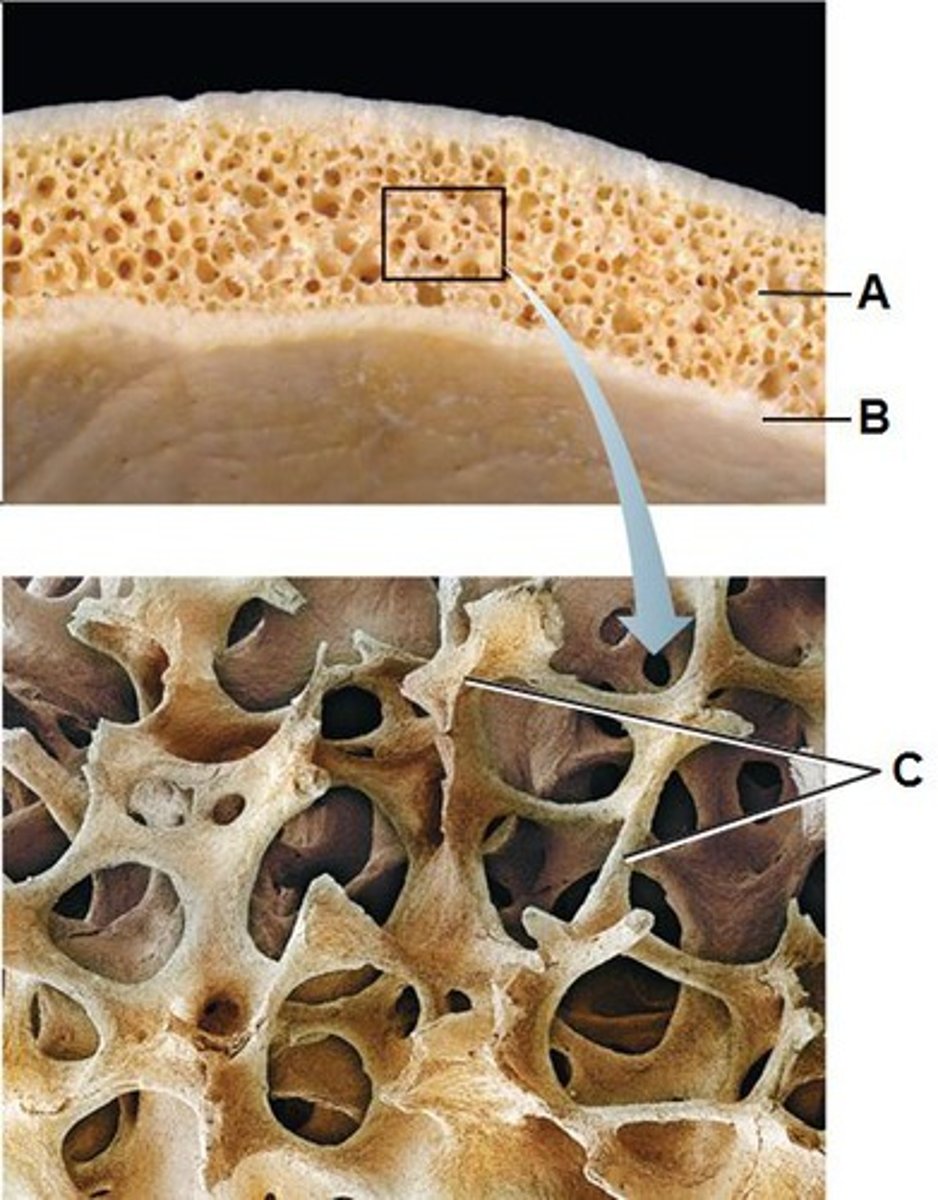
Trabeculae of spongy bone
Flat bones
Cranial bones, scapula, sternum, ribs, and hip bones
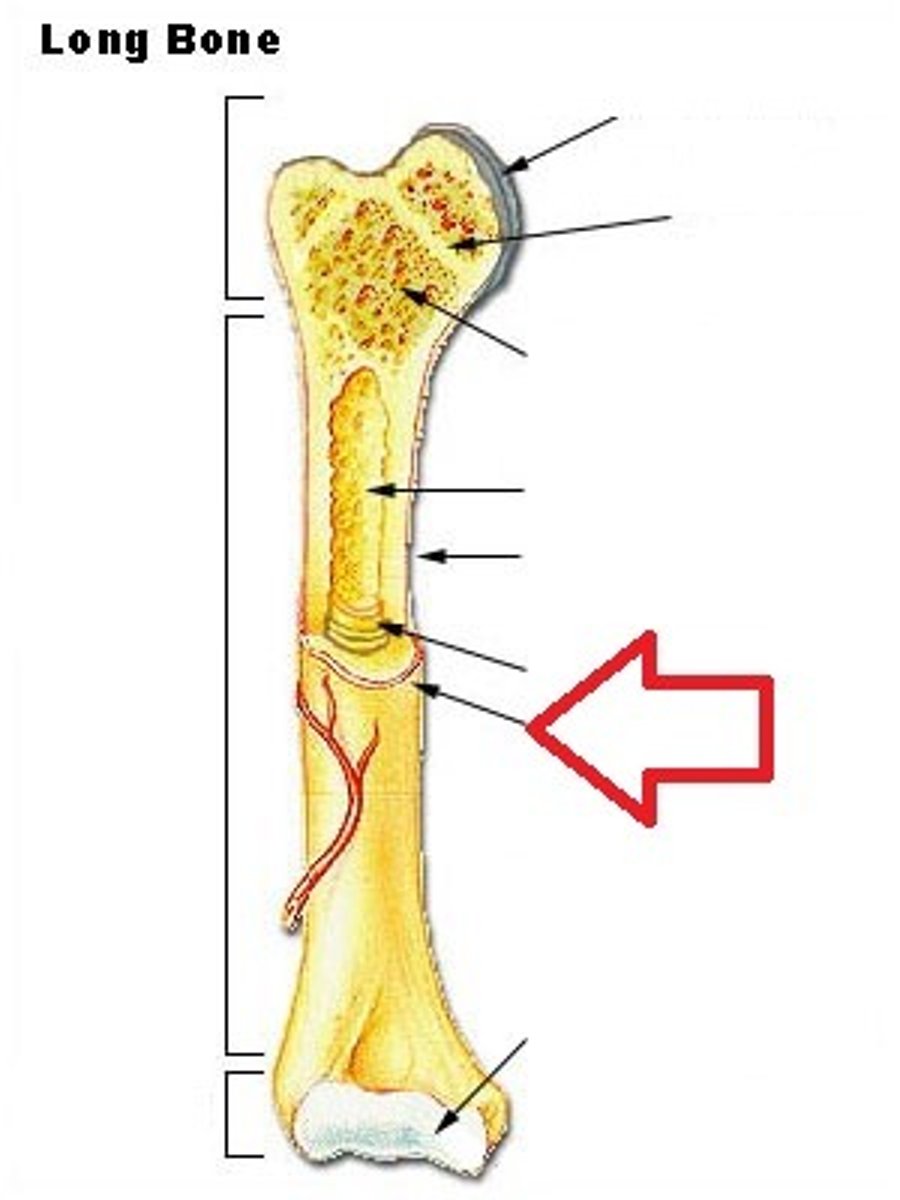
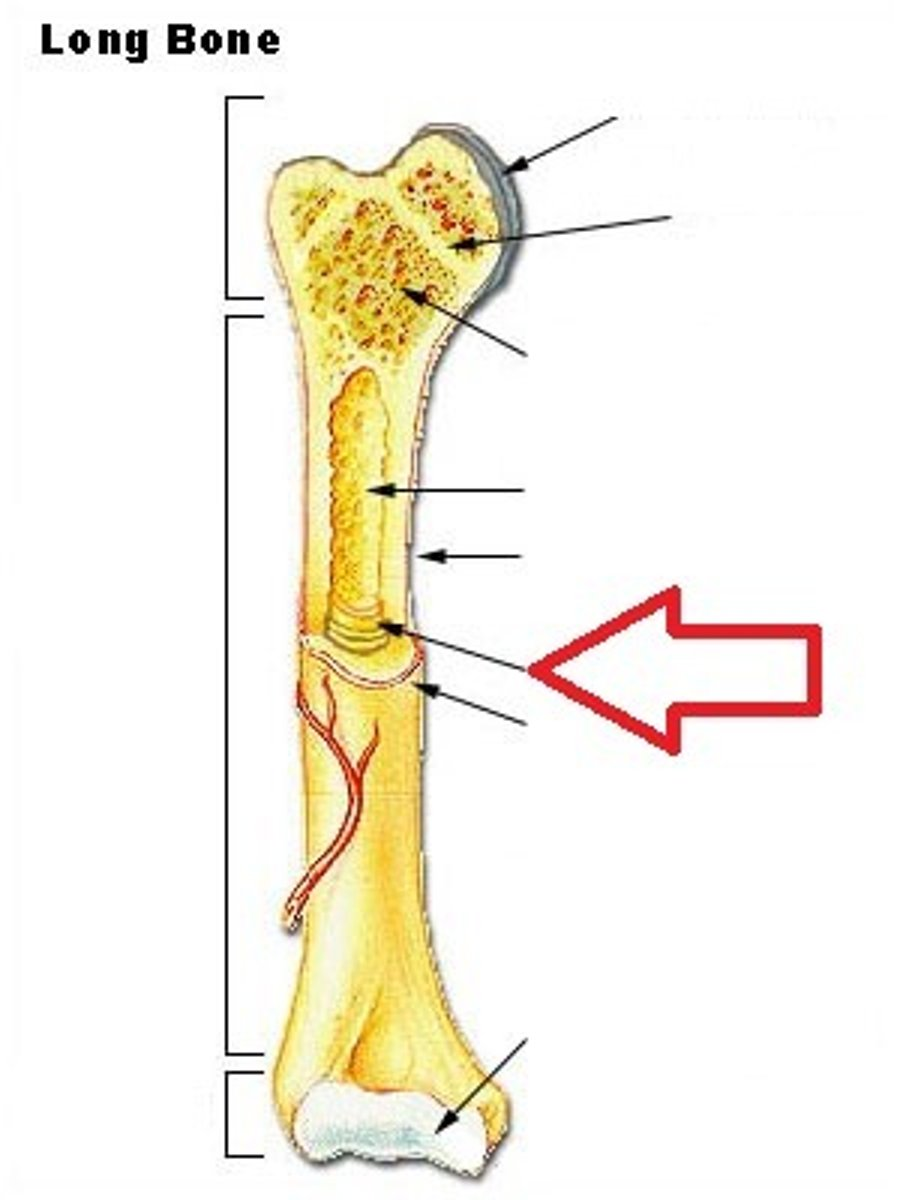
Long bones
Bones of the limbs and hands/feet (NOT wrists and ankles)
Short bones
Carpal and tarsal and patella.
Irregular bones
Vertebrae, middle-ear bones
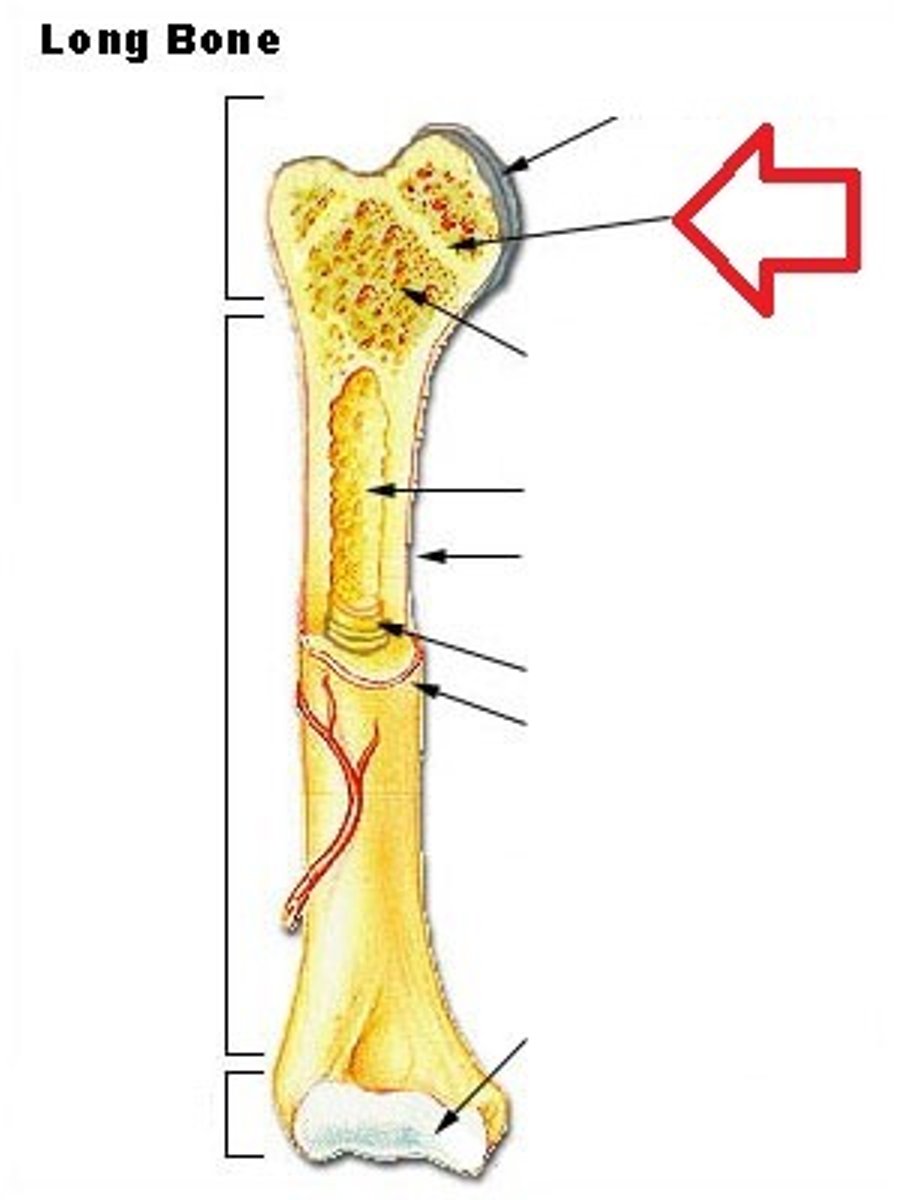
Medullary Cavity
Also known as marrow cavity, contains bone marrow.
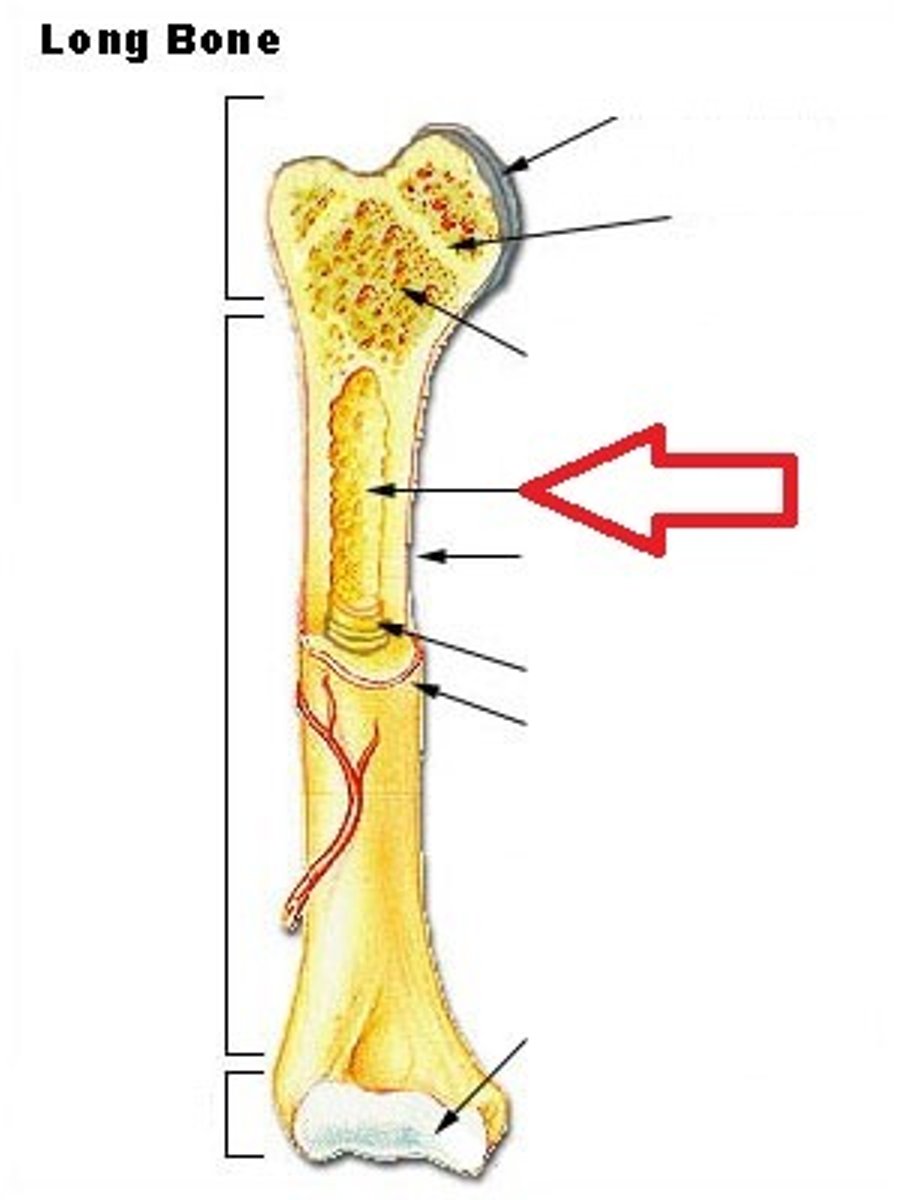
Diaphysis
Shaft of bone. (Leverage)
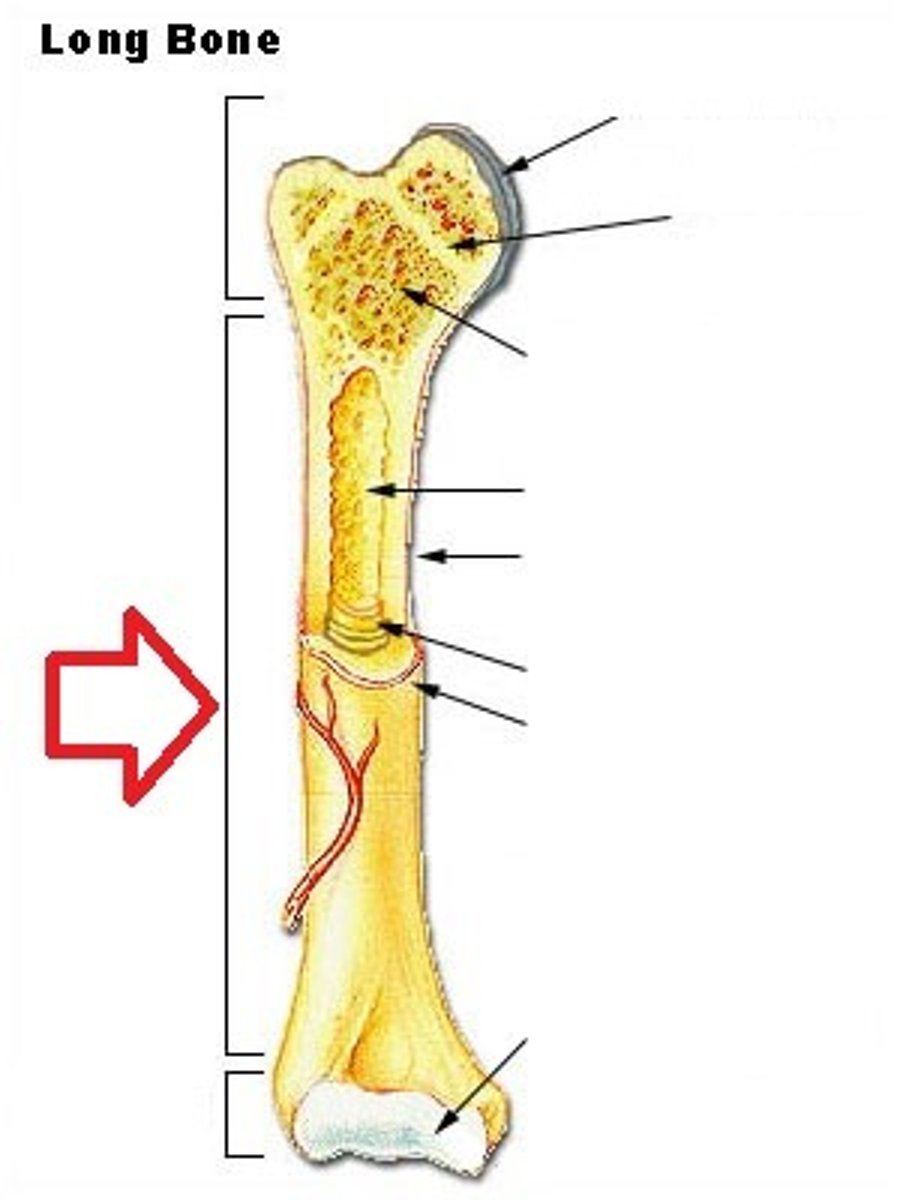
Epiphysis
Enlarged head of bone. (strength joint/provide muscle attachments) Proximal and Distal.
Articular Cartilage
Type of hyaline cartilage found at the articulation (joint) of bones.
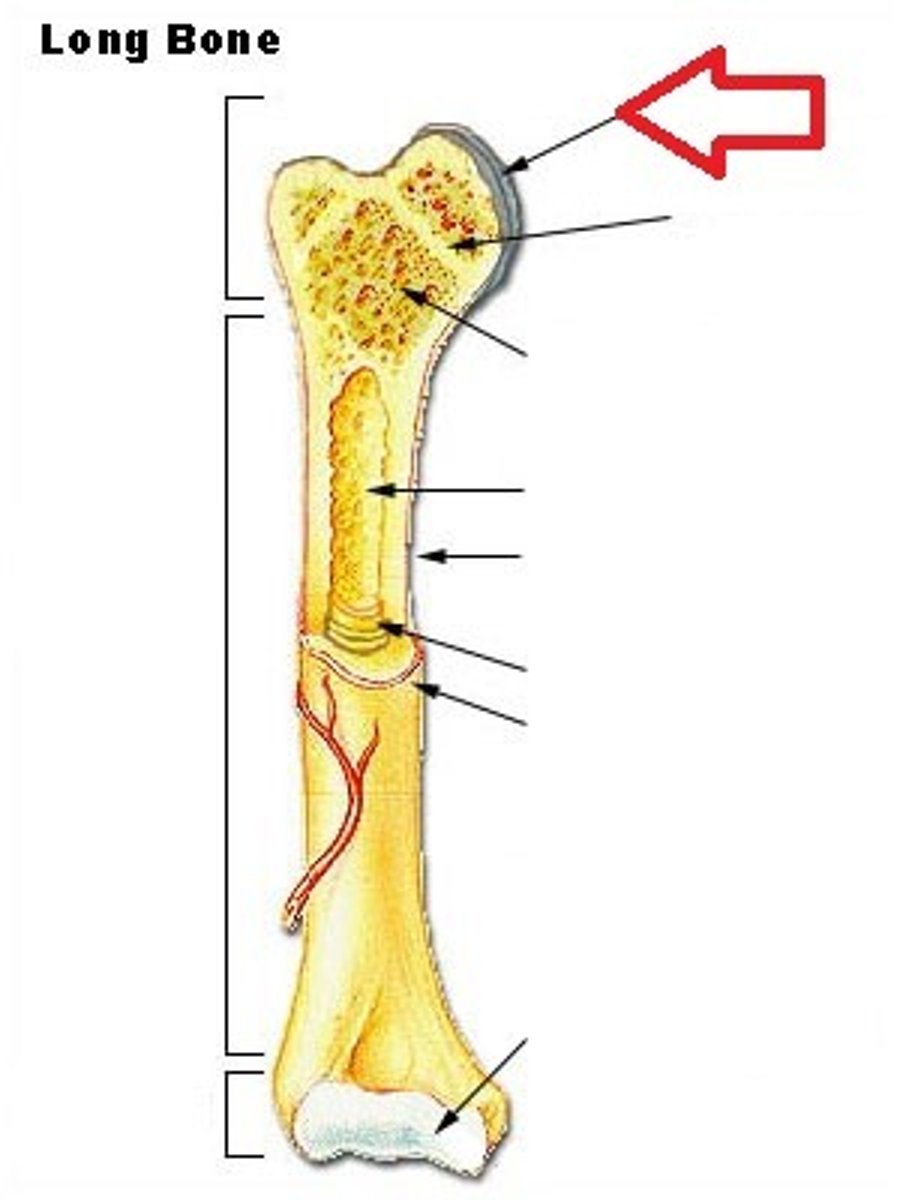
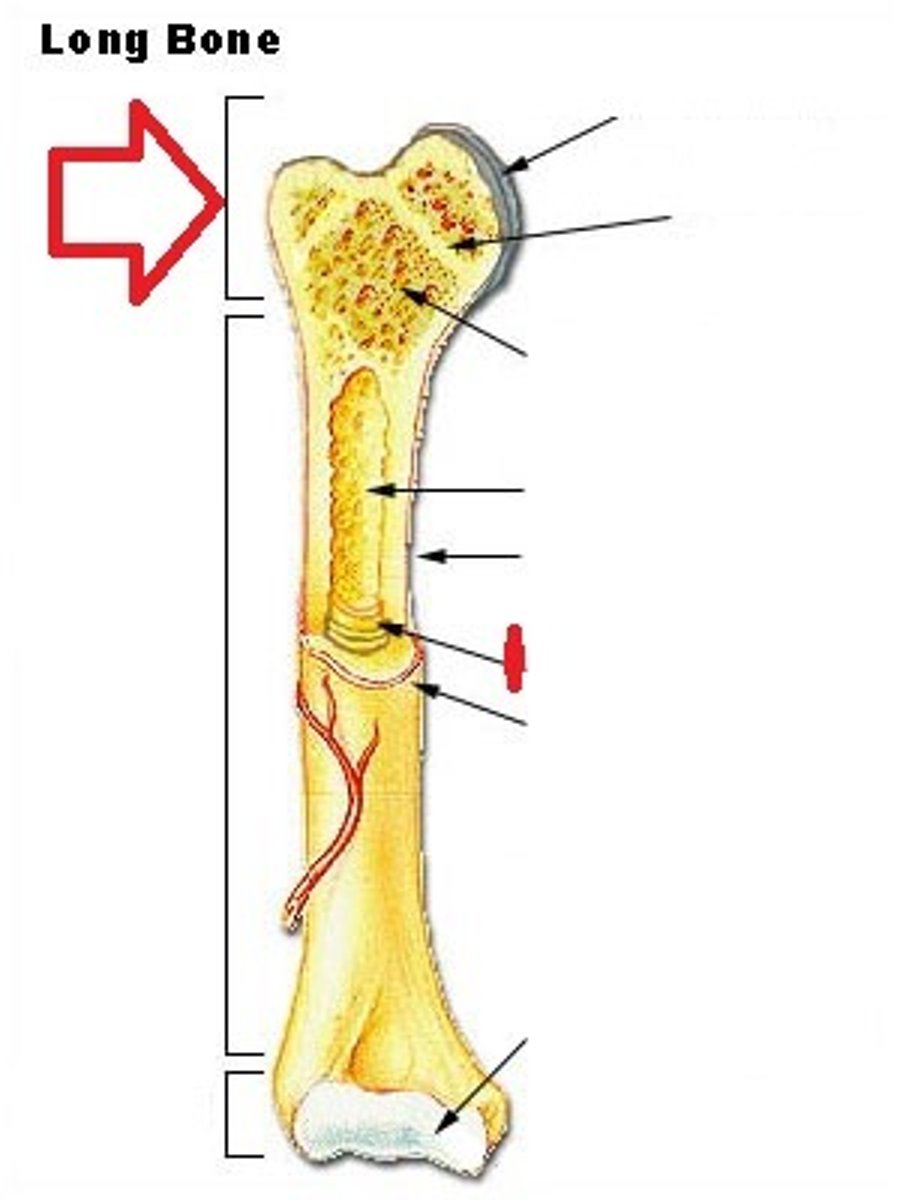
In between Epiphysis and Diaphysis.
Metaphysis
Periosteum
Sheath of outer fibrous collagen and inner osteogenic layer of bone forming cells.
Sharpey's fibers
Anchors the periosteum to the bone matrix.
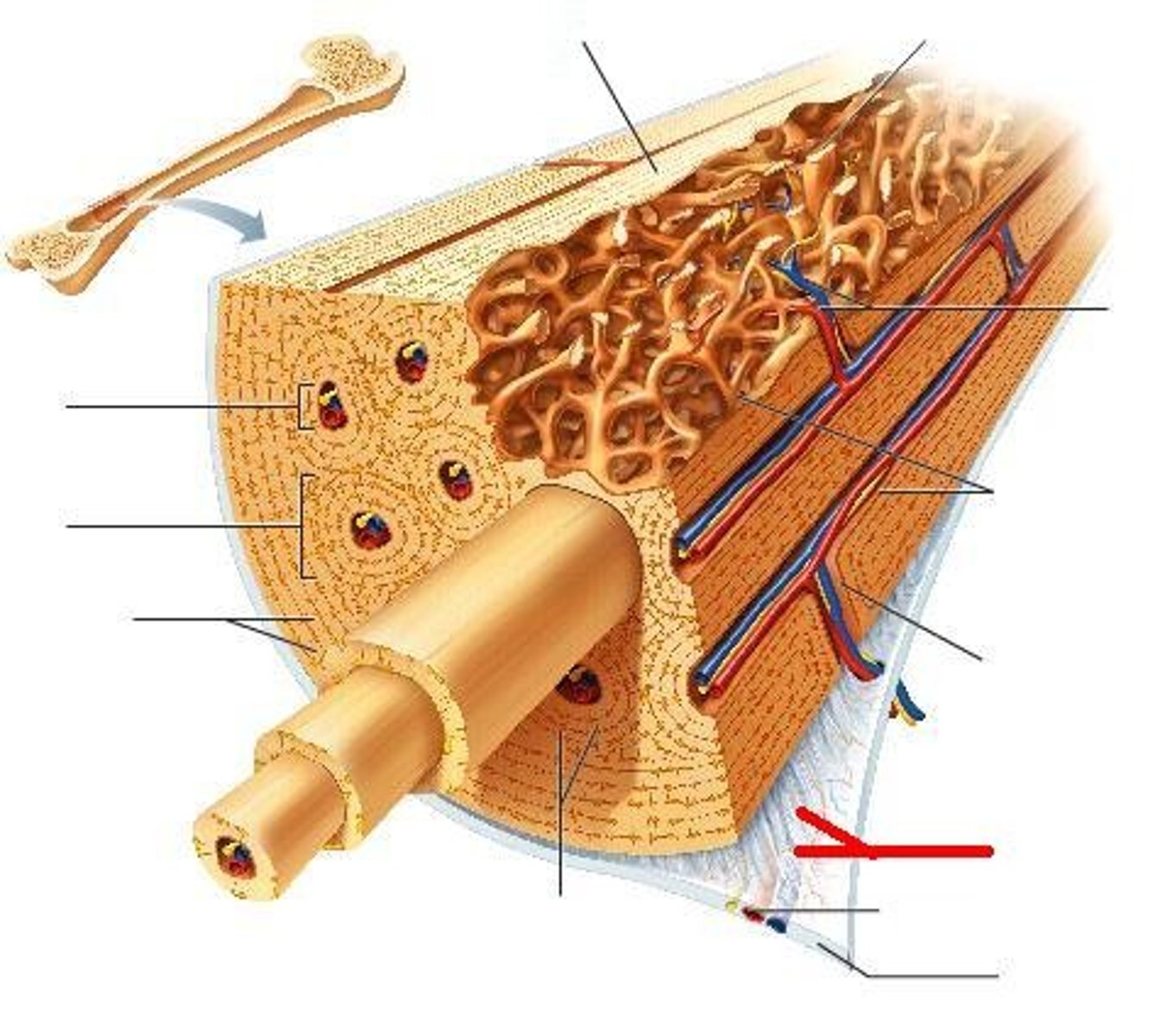
Thin layer of reticular CT lining internal marrow cavity. Also covers honeycomb surfaces of spongy bones and has many osteoclasts.
Endosteum
Epiphyseal plate
Hyaline cartilage separating the marrow spaces in children. Where the bones grow in length. Is just an /epiphyseal line/ in adults.
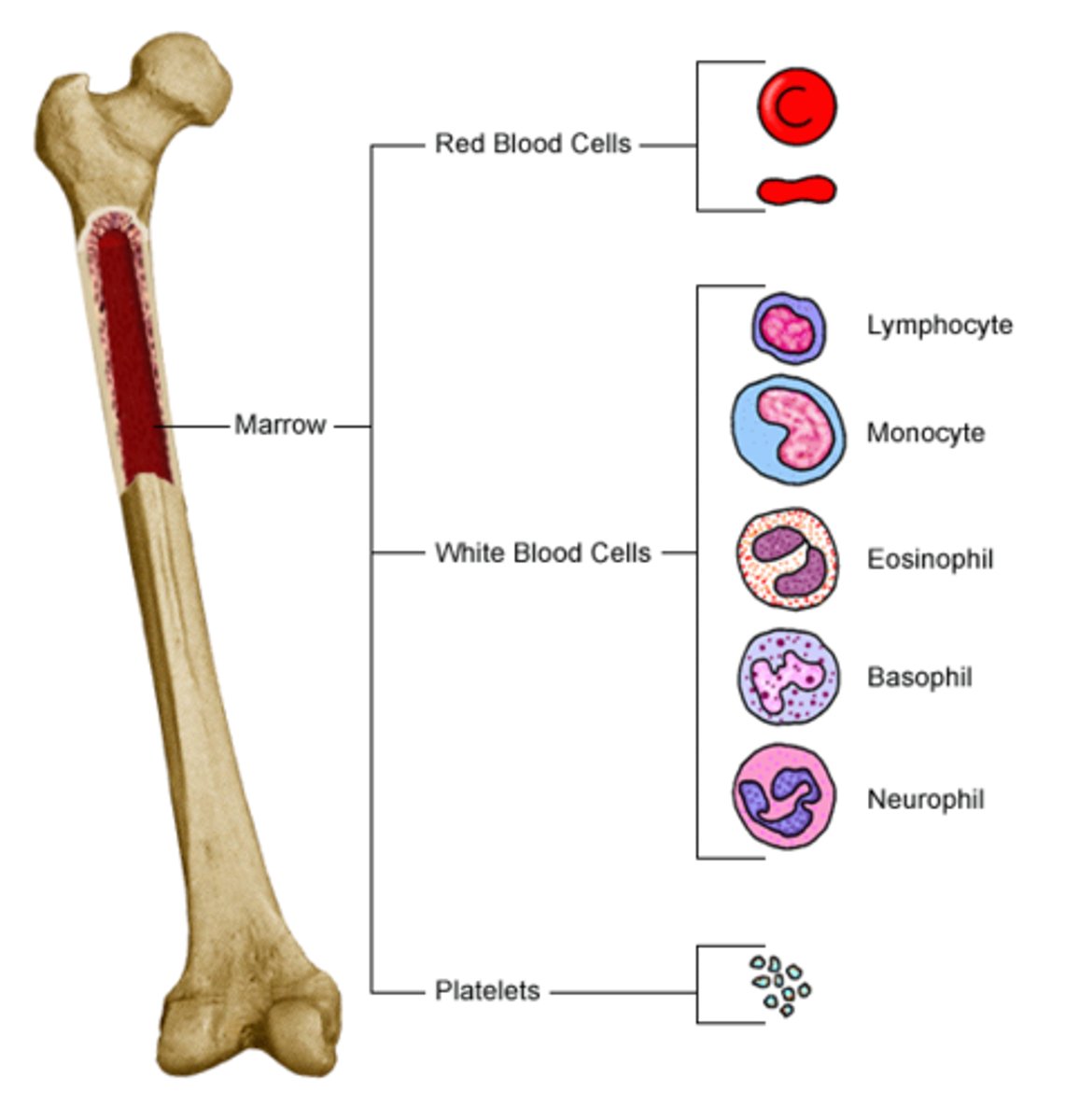
Bone Marrow
soft tissue that occupies marrow cavity of long bones, spaces amid trabeculae of spongy bone, and larger central canals.
Red Bone Marrow
Produces blood cells.
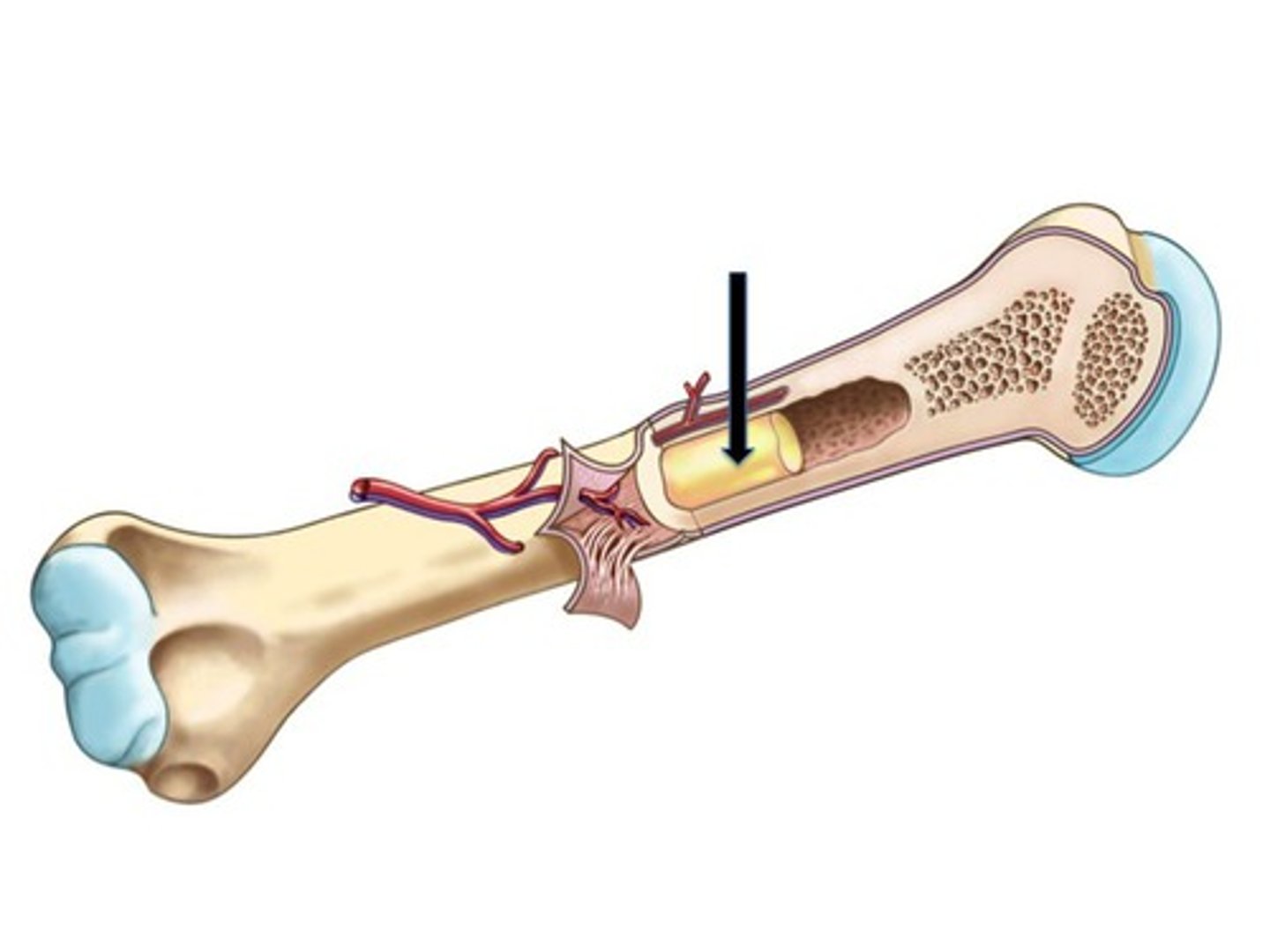
Yellow Bone Marrow
Red marrow of bones in limbs turns into this in adults.
Sesamoid
Any bone that is embedded in a muscle or tendon.
Hydroxyapatite
Mineral that makes up 2/3 of compact bone.
Canaliculi
Very small canals that connect the lacunae to the Haversian canals.
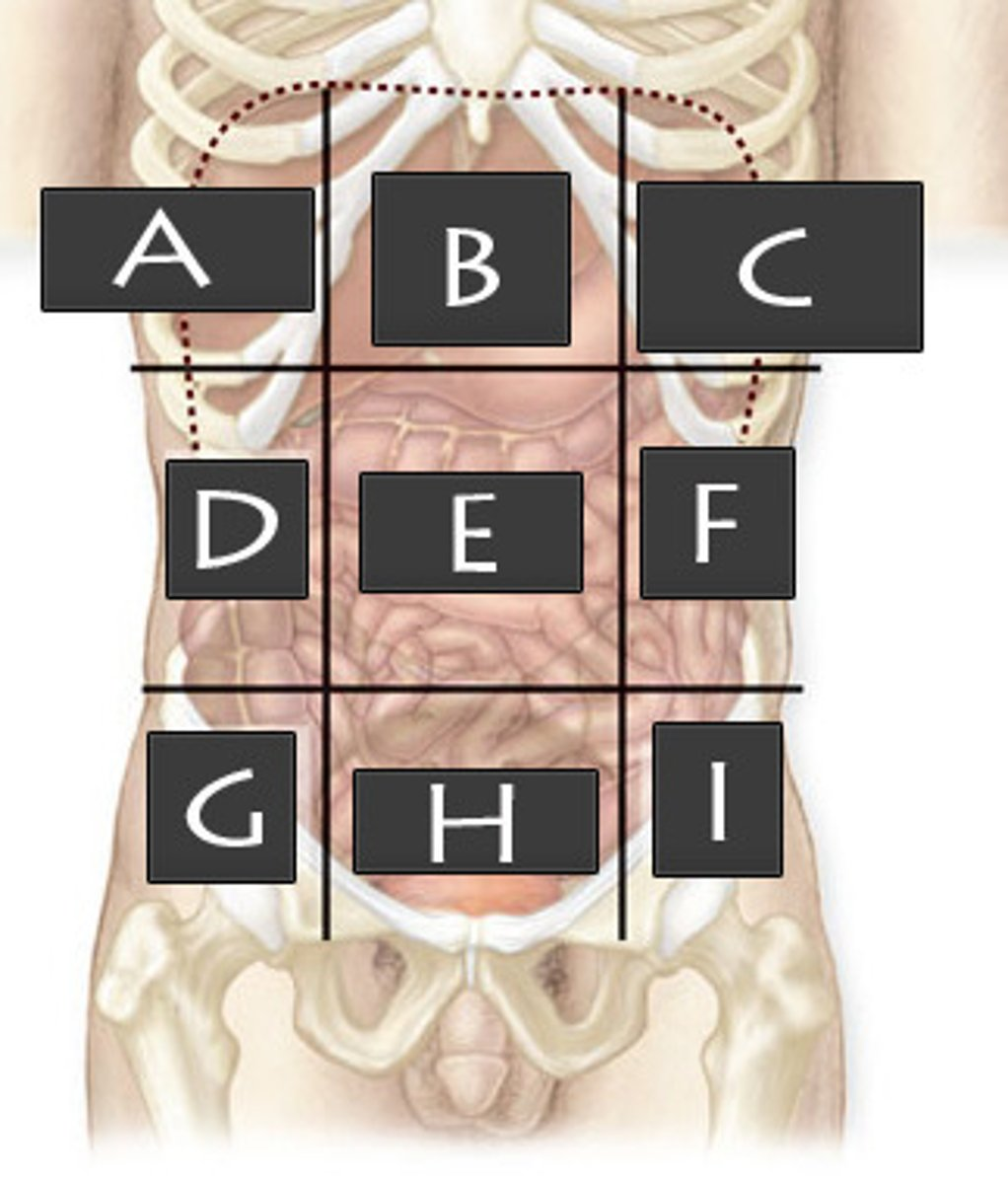
What abdominopelvic region is A?
Right Hypochondriac Region
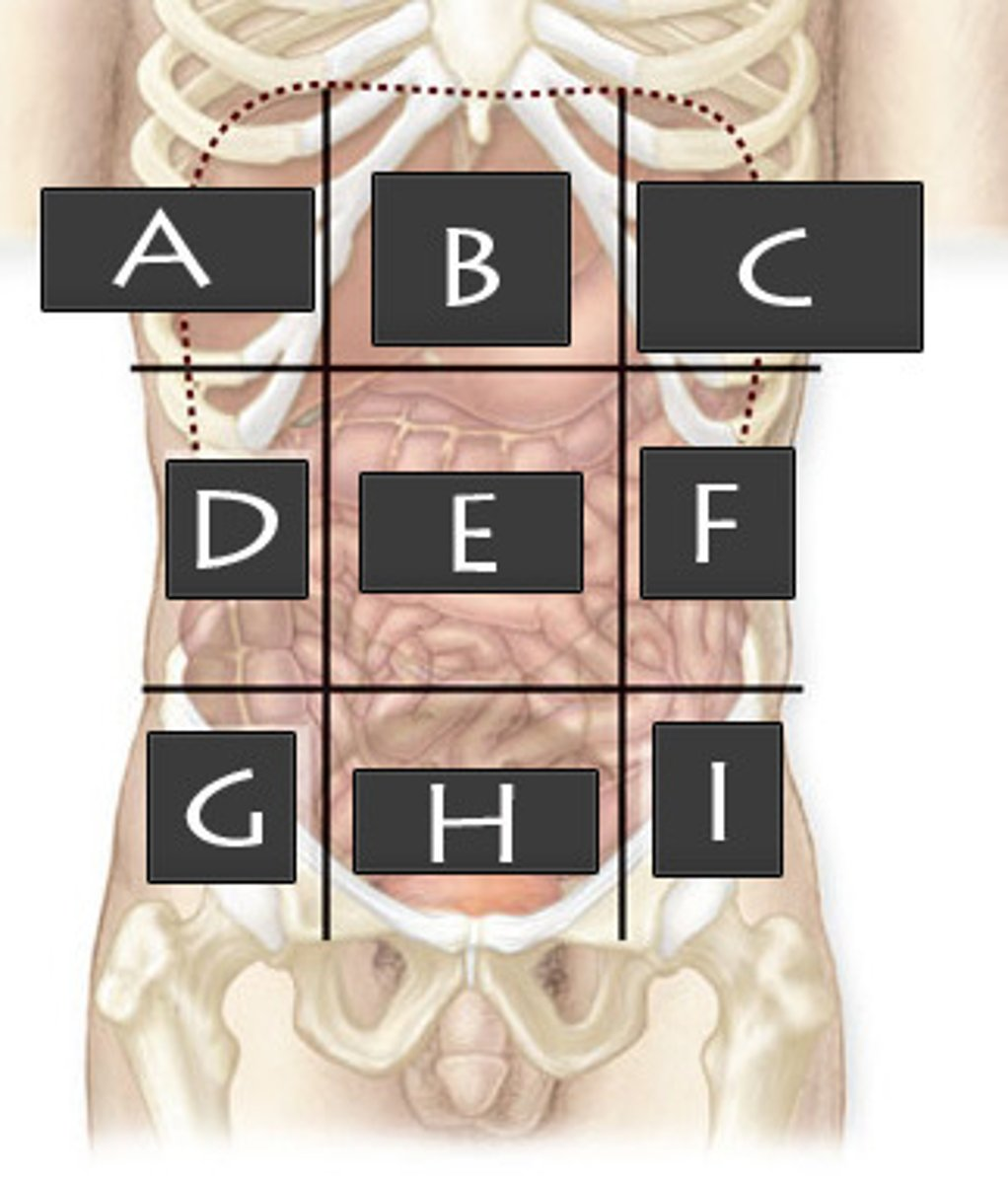
What abdominopelvic region is B?
Epigastric Region
What abdominopelvic region is C?
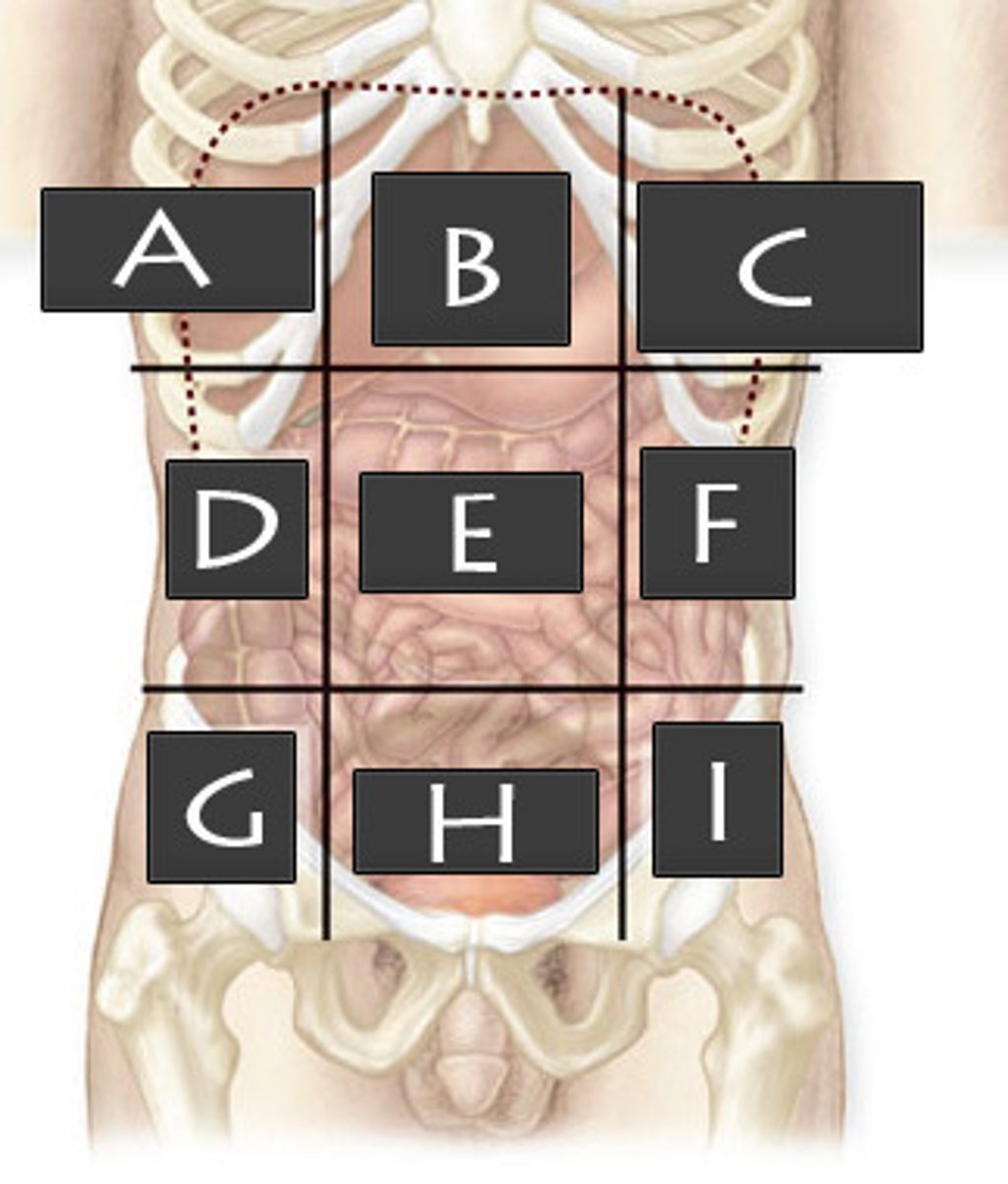
Left Hypochondriac Region
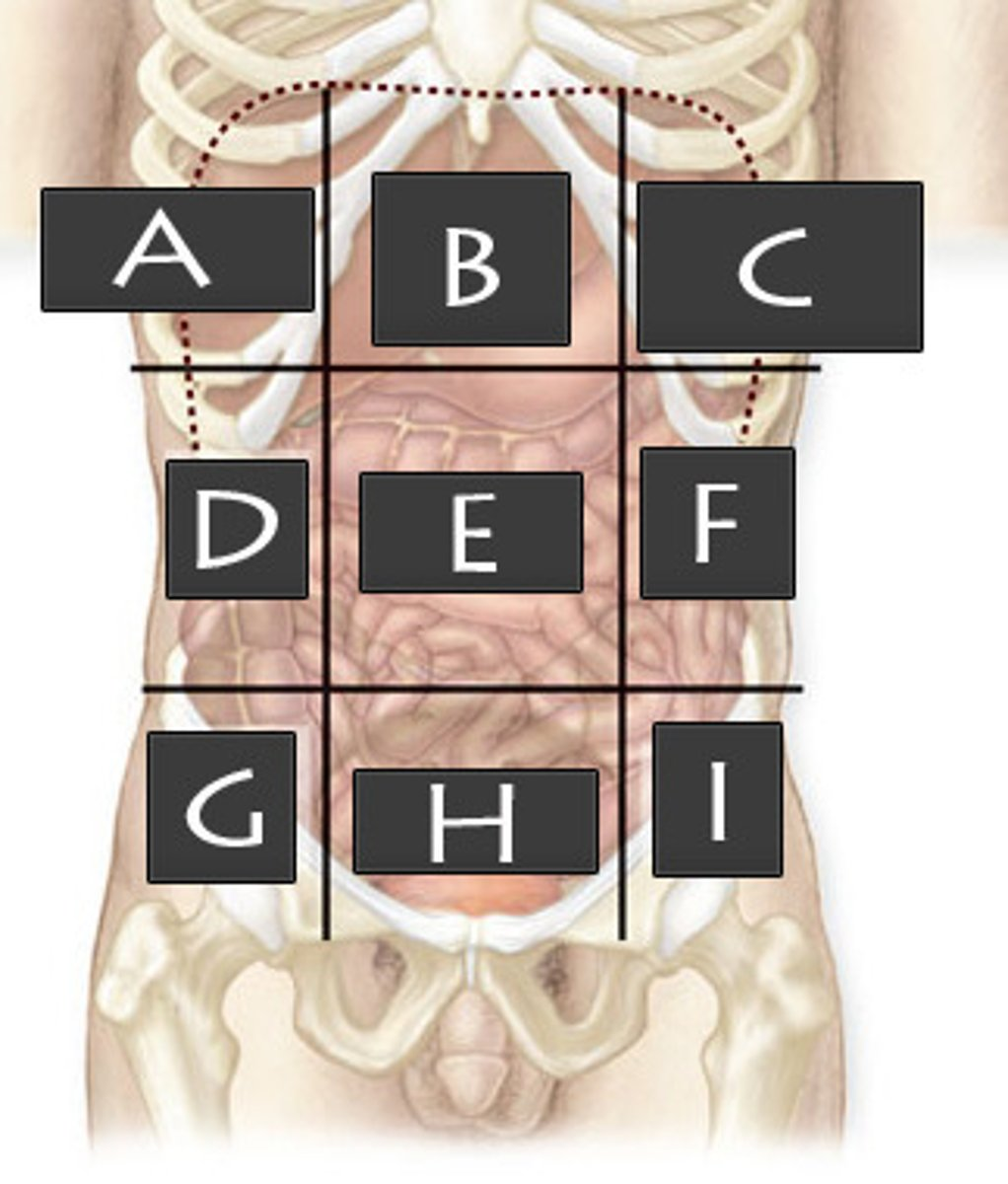
What abdominopelvic region is D?
Right Lumber Region
What abdominiopelvic region is E?
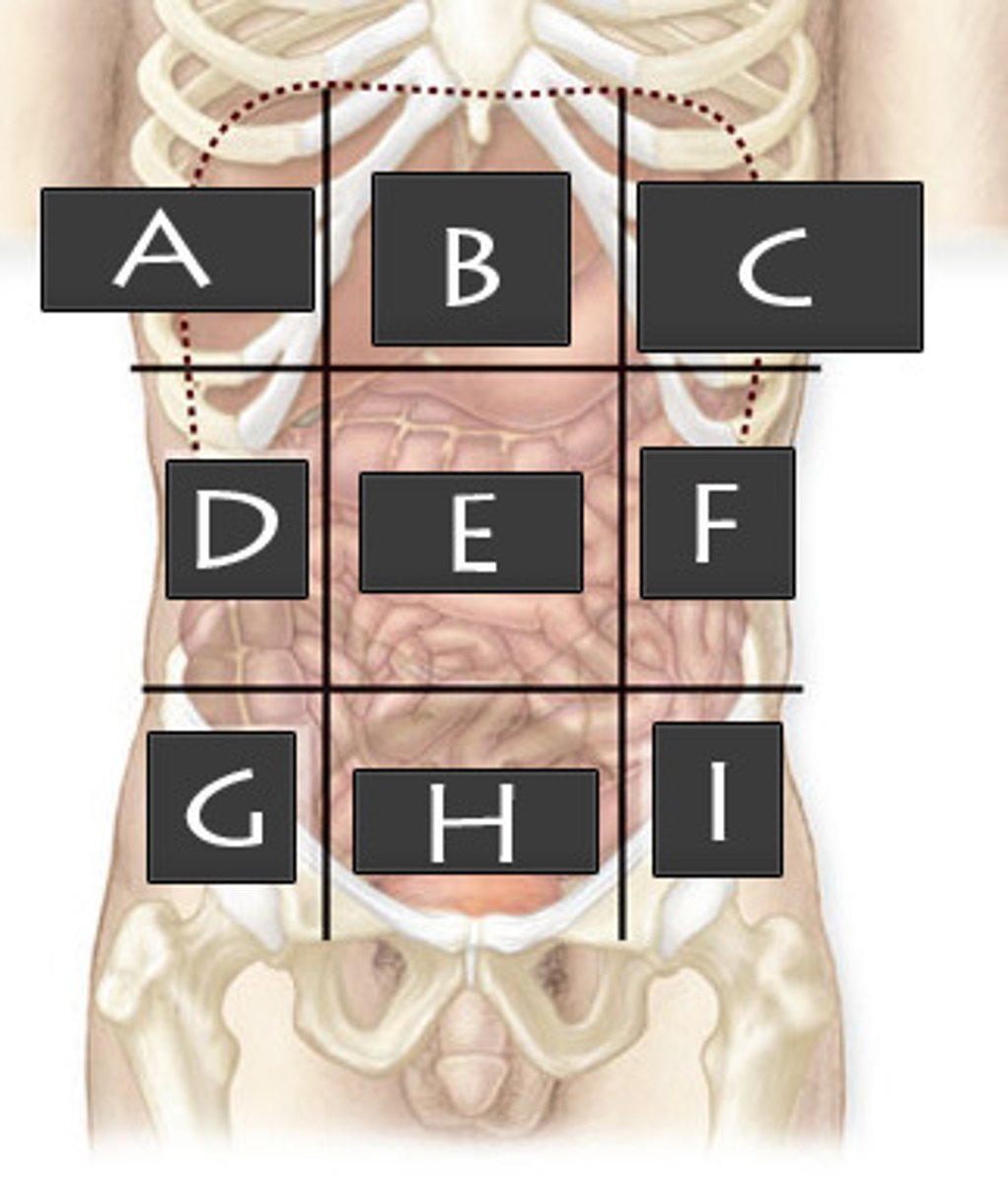
Umbilical Region
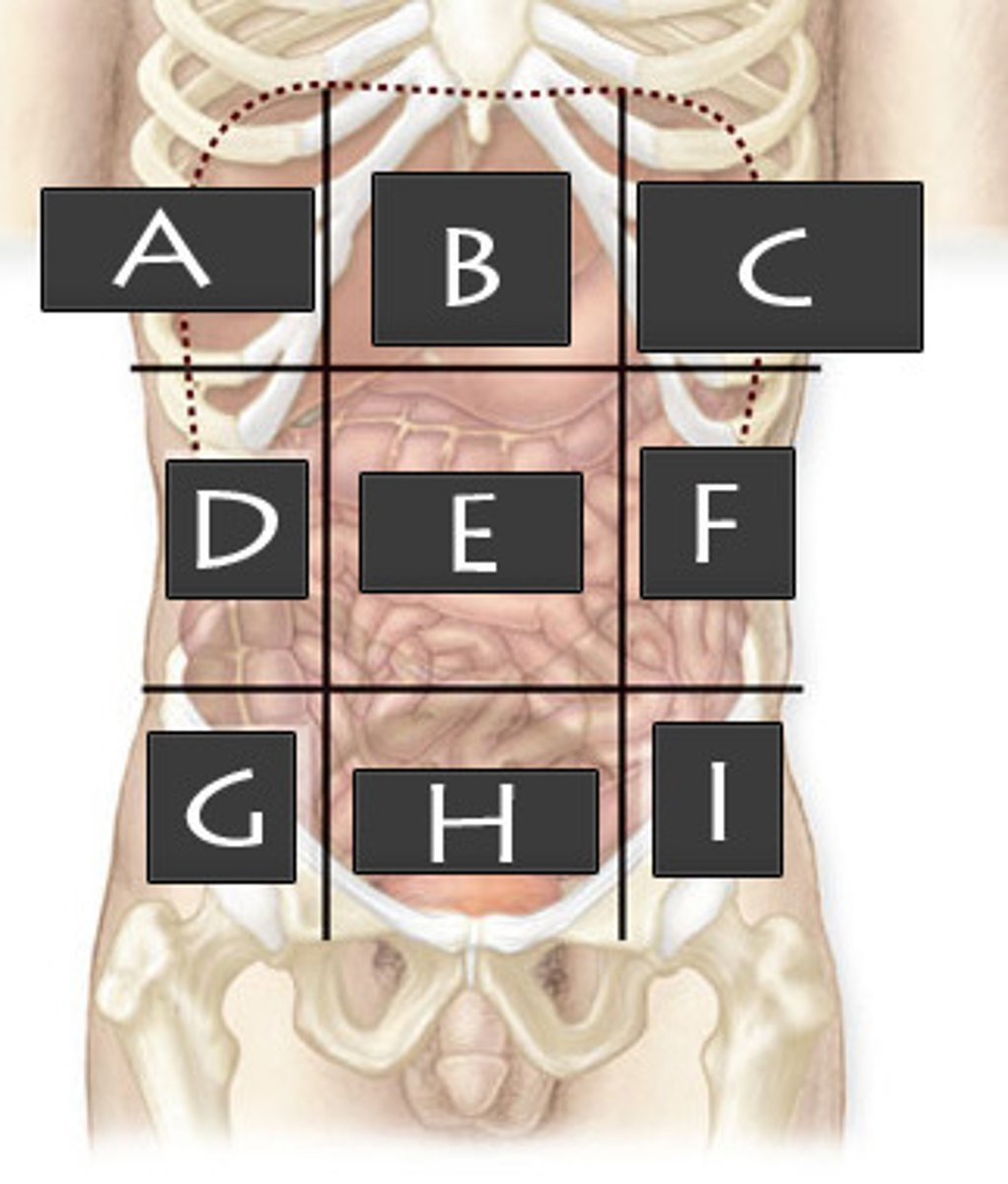
What abdominopelvic region is F?
Left Lumbar Region
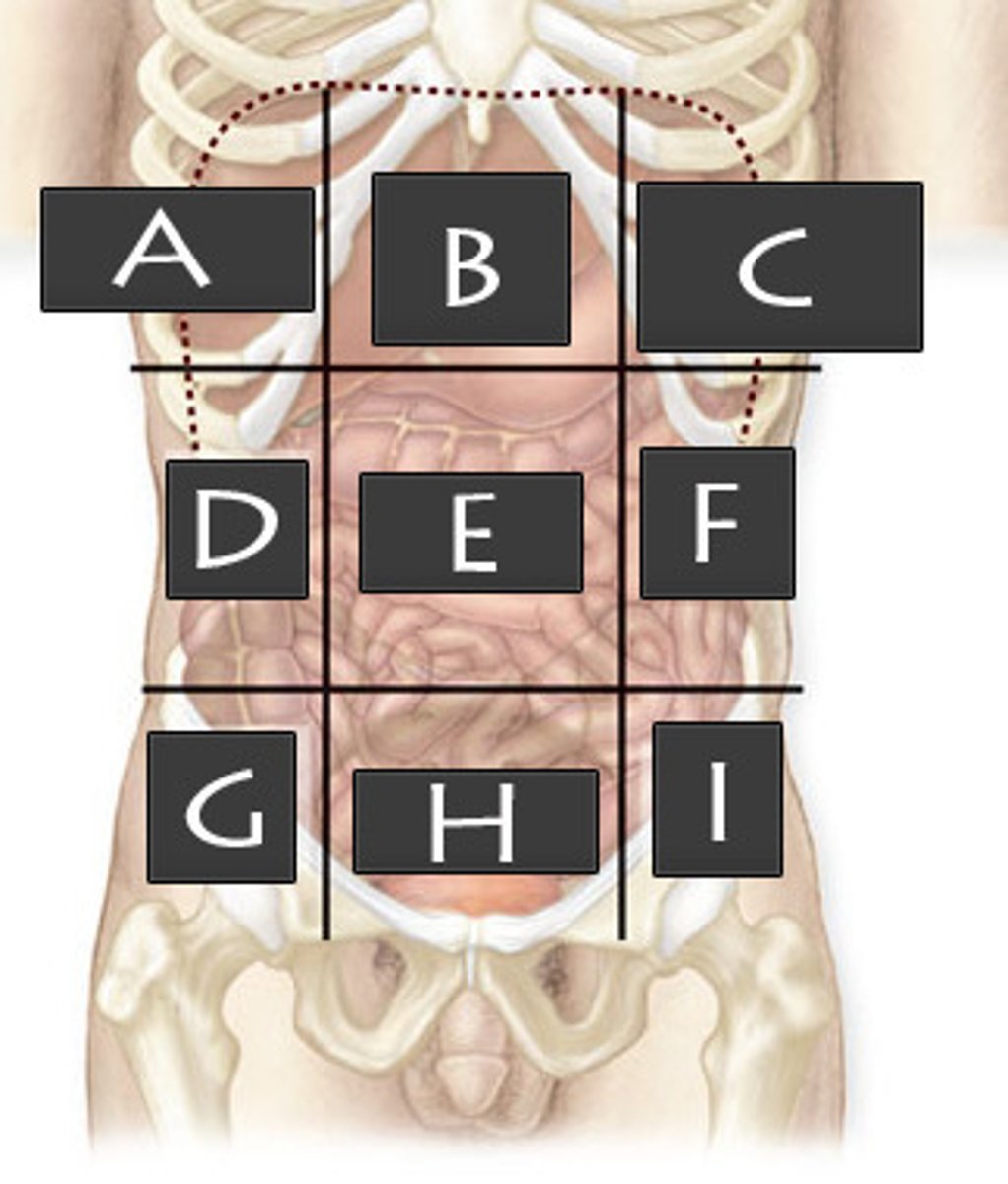
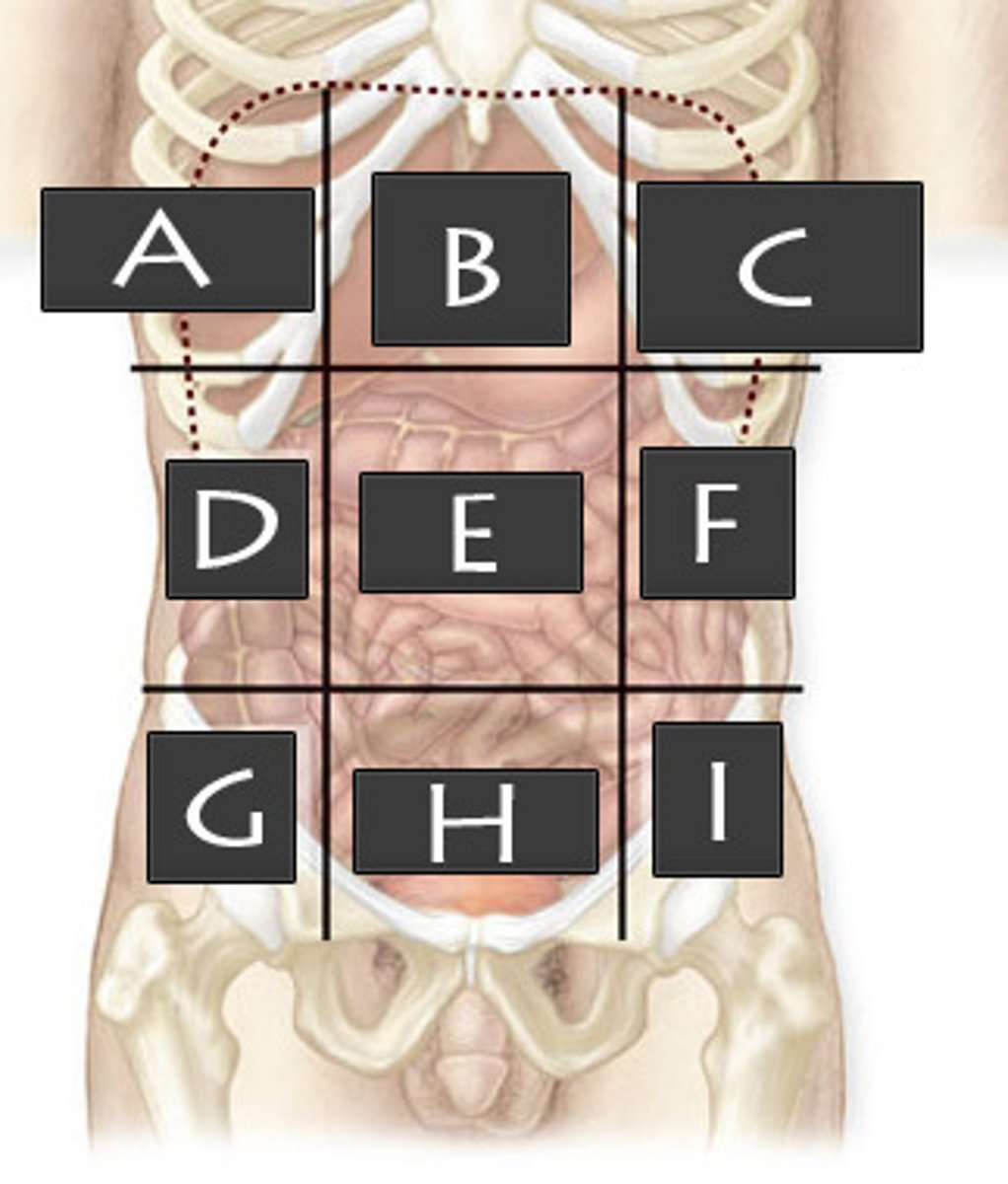
What abdominopelvic region is G?
Right Iliac Region
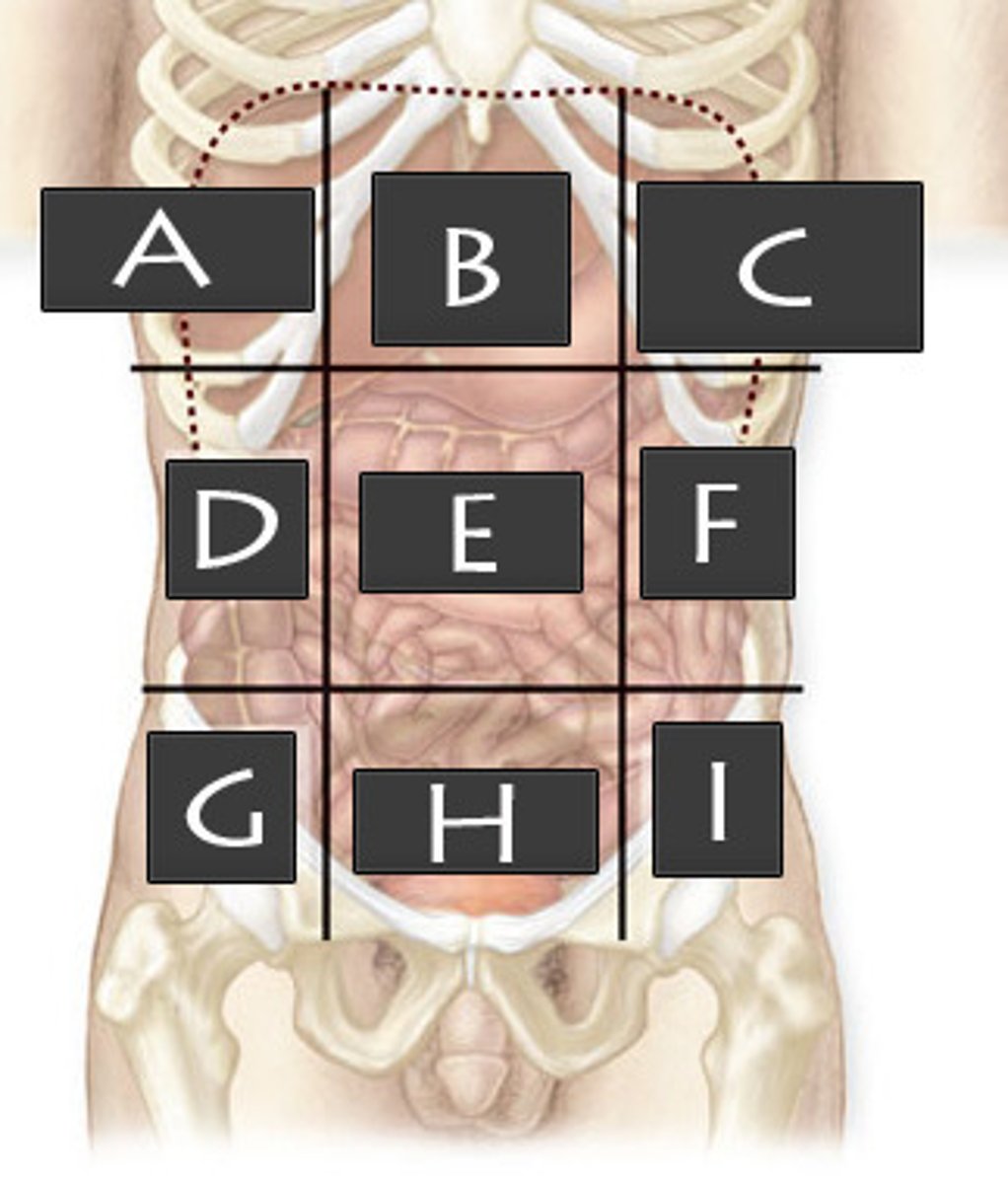
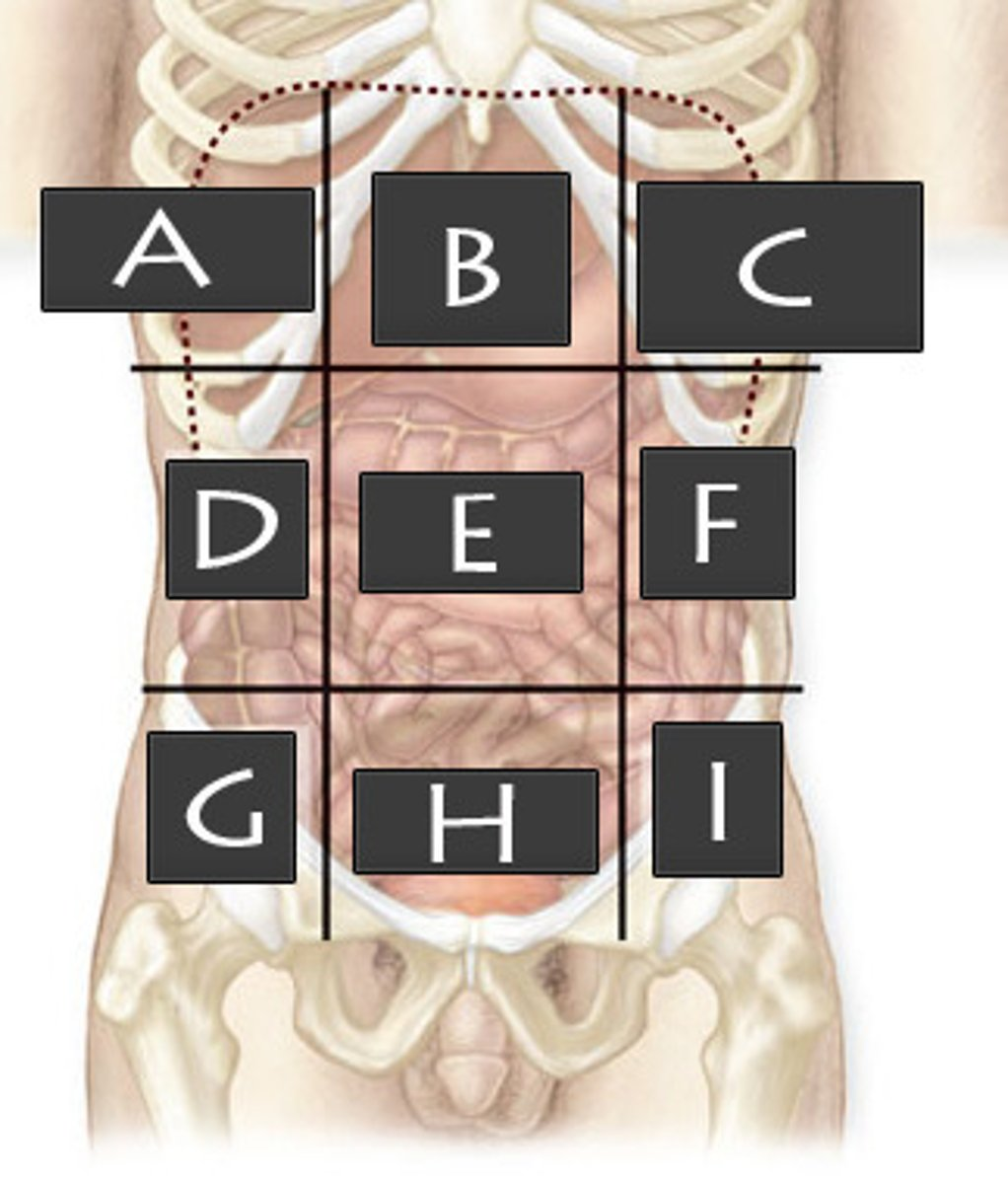
What abdominopelvic region is H?
Hypogastric Region
What abdominopelvic region is I?
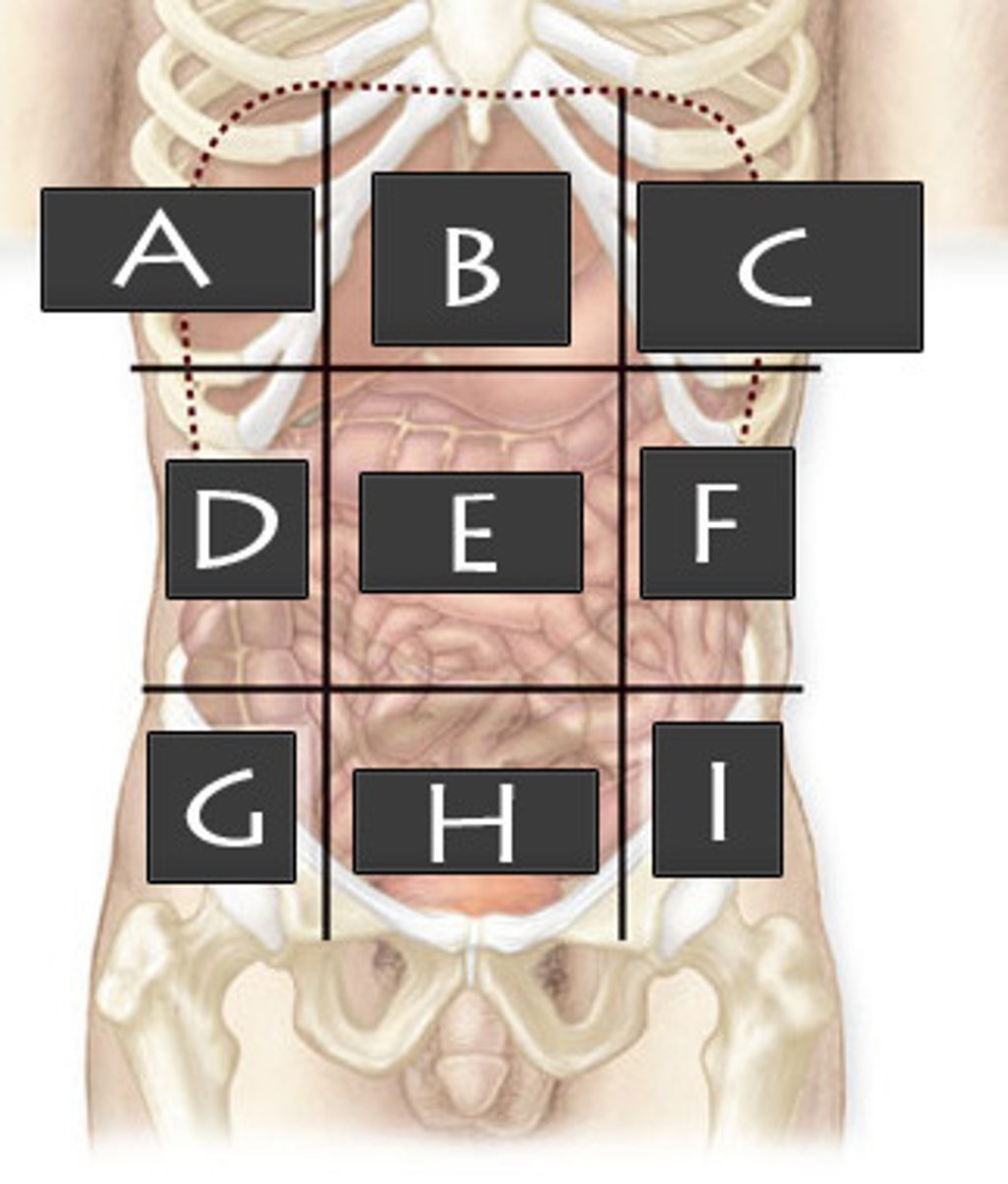
Left Iliac Region
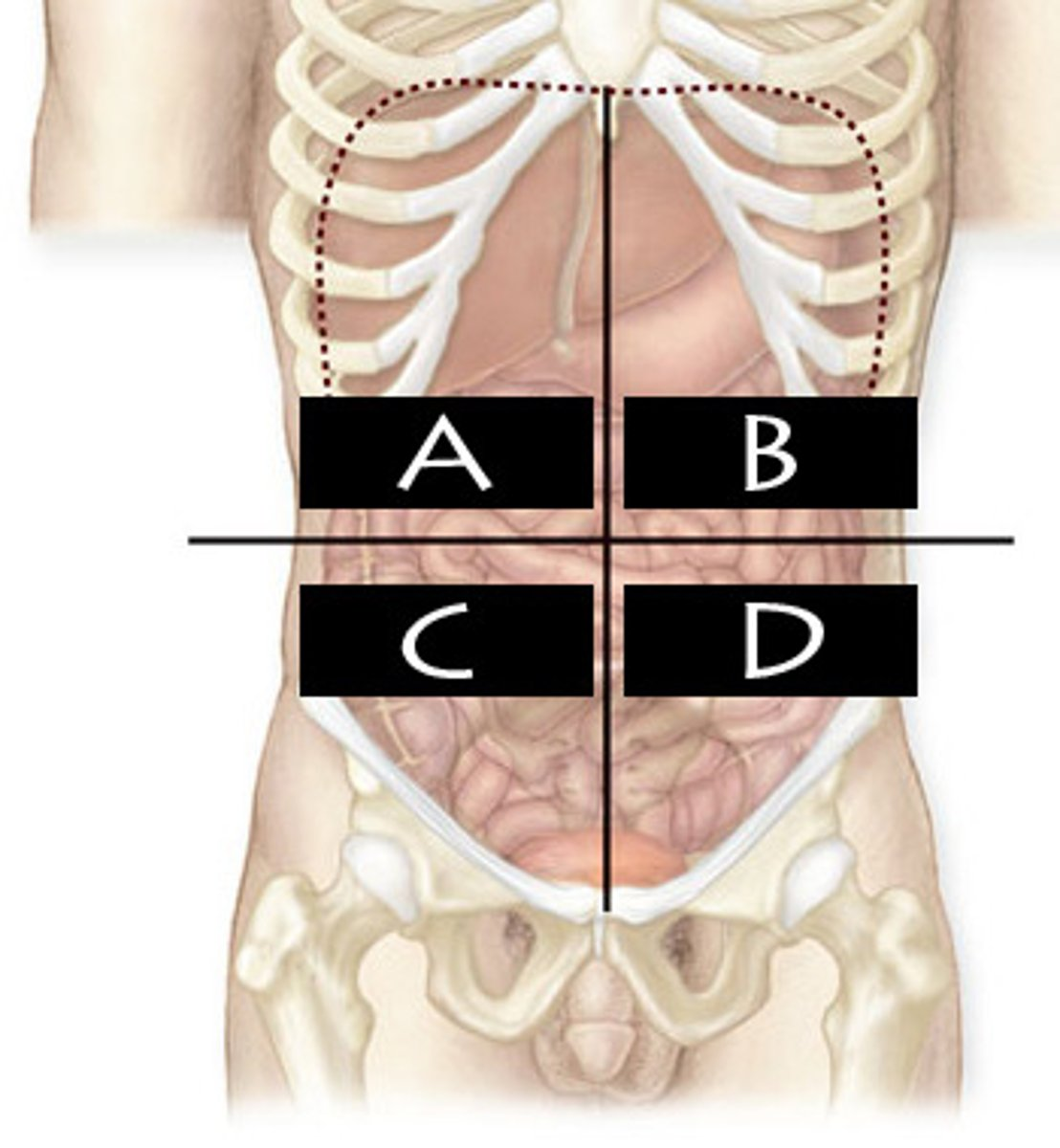
What abdominopelvic quadrant is A?
Right Upper Quadrant (RUQ)
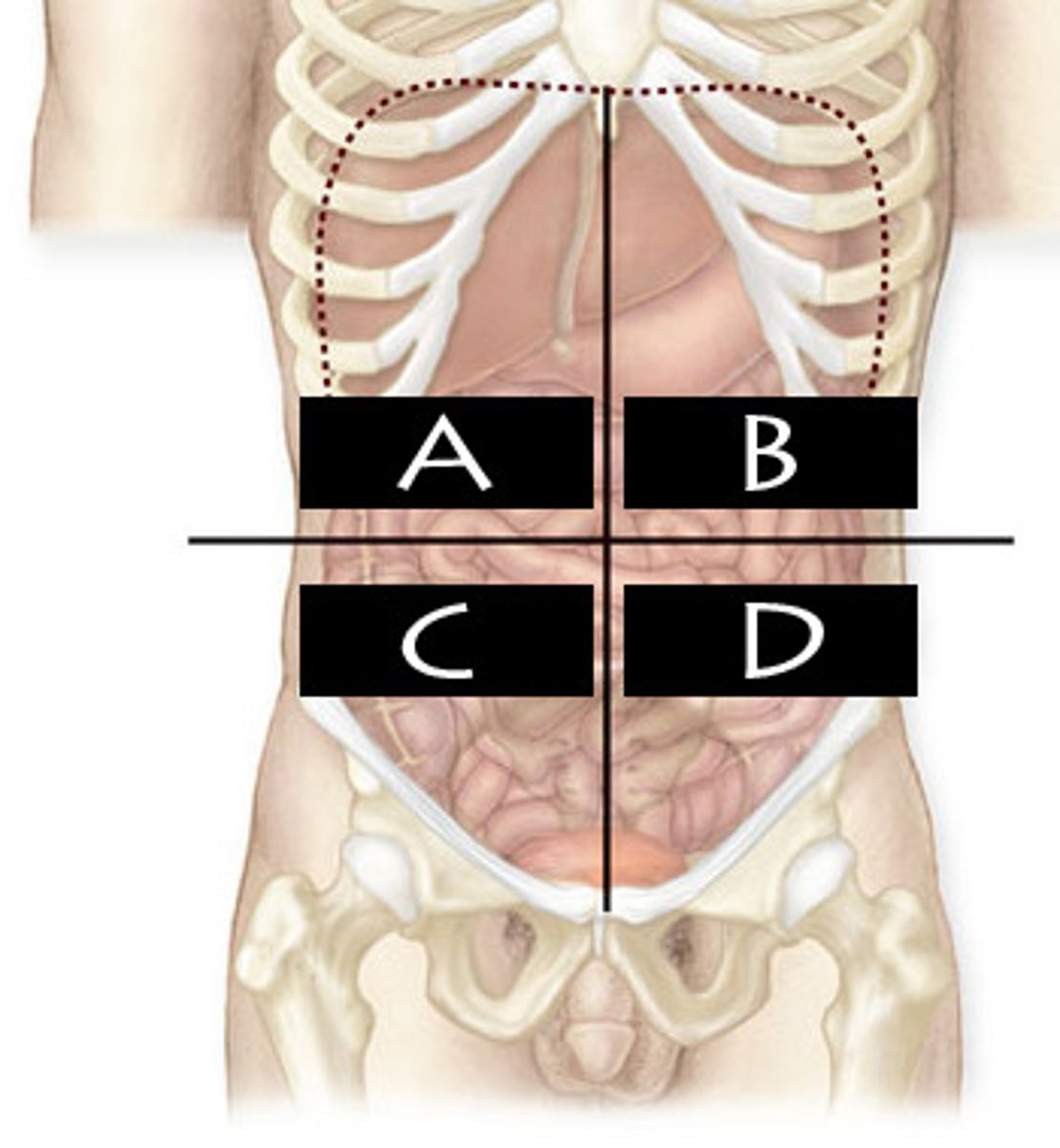
What abdominopelvic quadrant is B?
Left Upper Quadrant (LUQ)
What abdominopelvic quadrant is C?
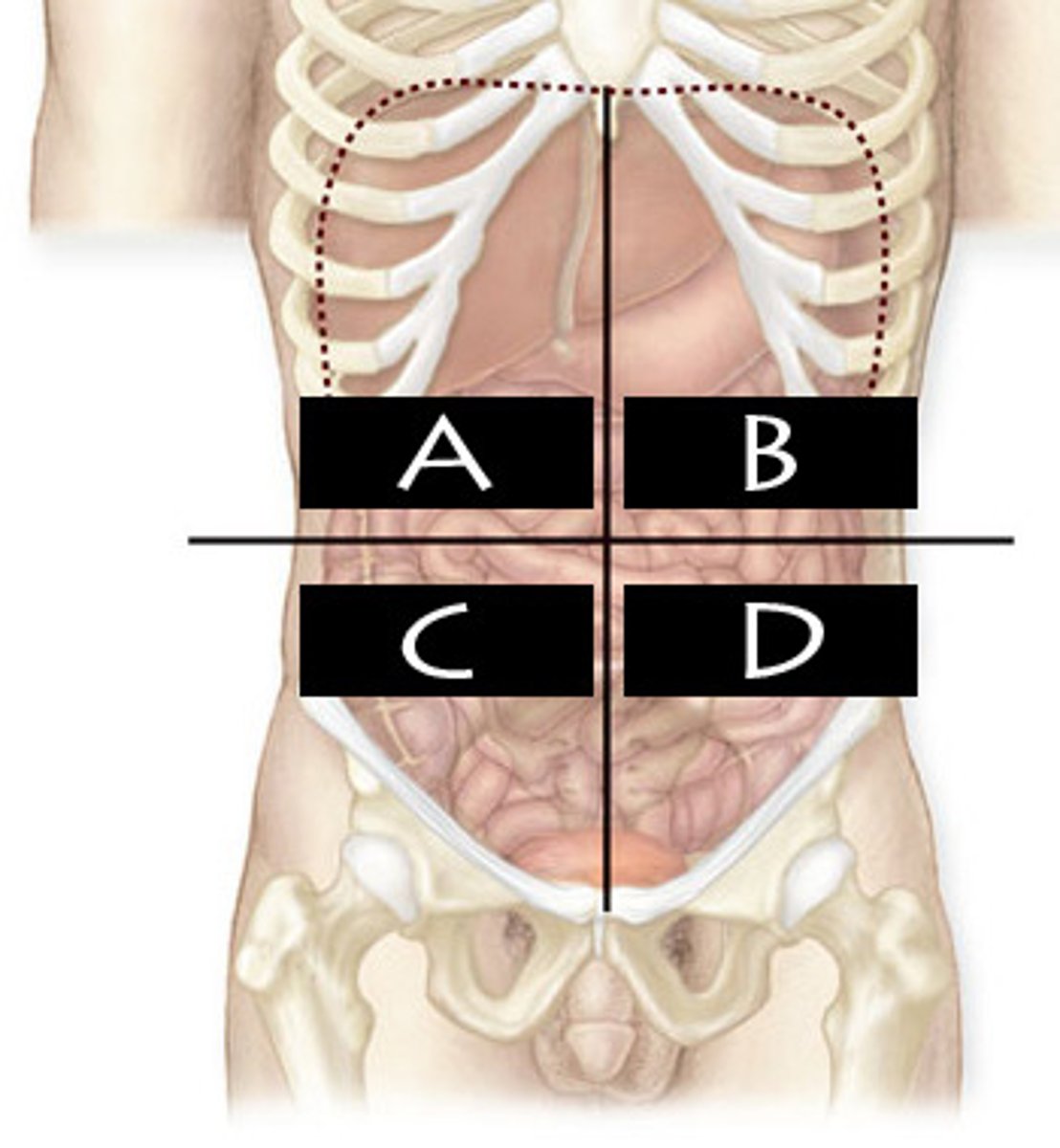
Righter Lower Quadrant (RLQ)
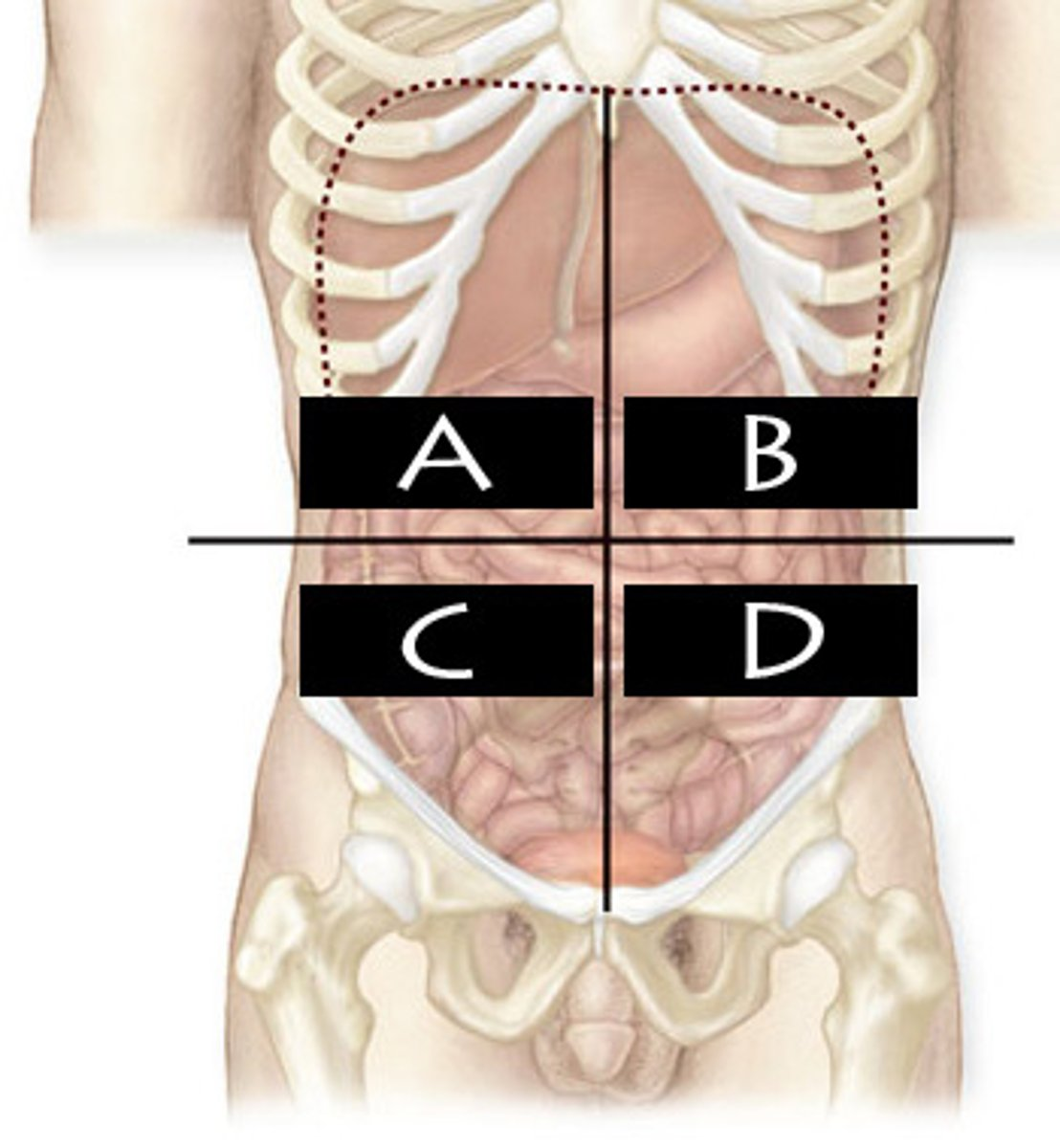
What abdominopelvic quadrant is D?
Left Lower Quadrant (LLQ)
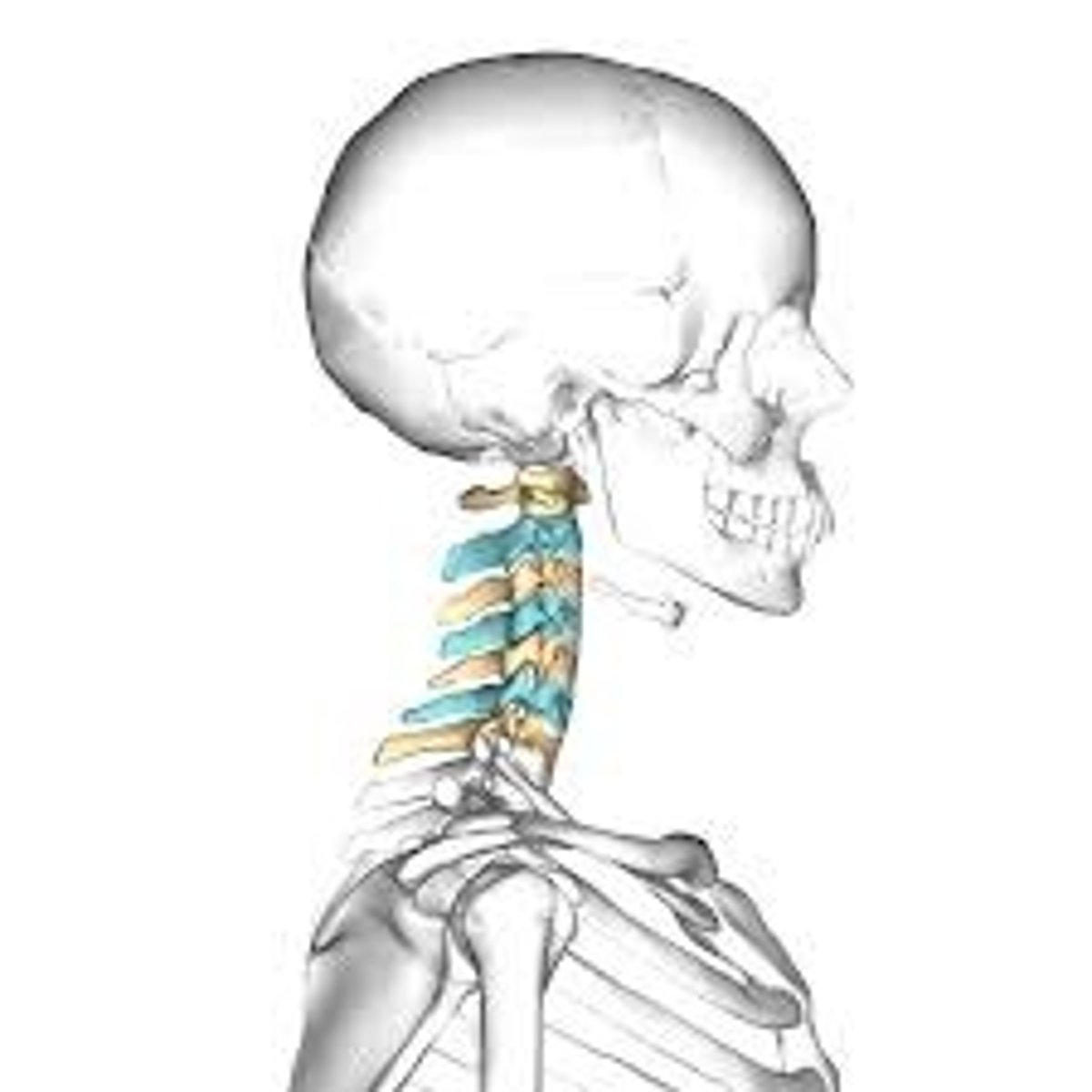
The 7 vertebrae found at the top of the vertebral column
Cervical Vertebrae
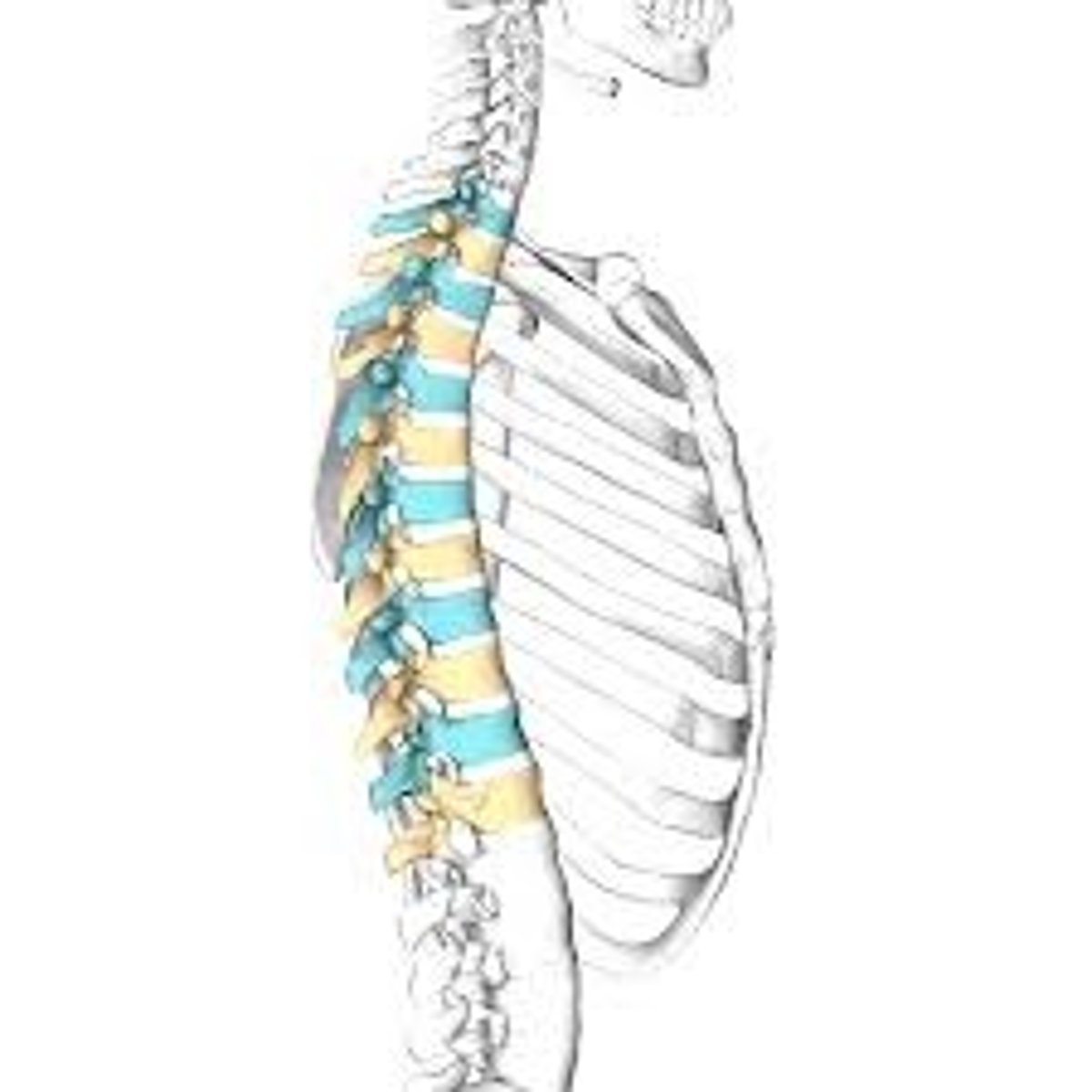
Thoracic Vertebrae
The 12 vertebrae found in the middle portion of the vertebral column.
Lumbar Vertebrae
The lower section of 5 vertebrae.
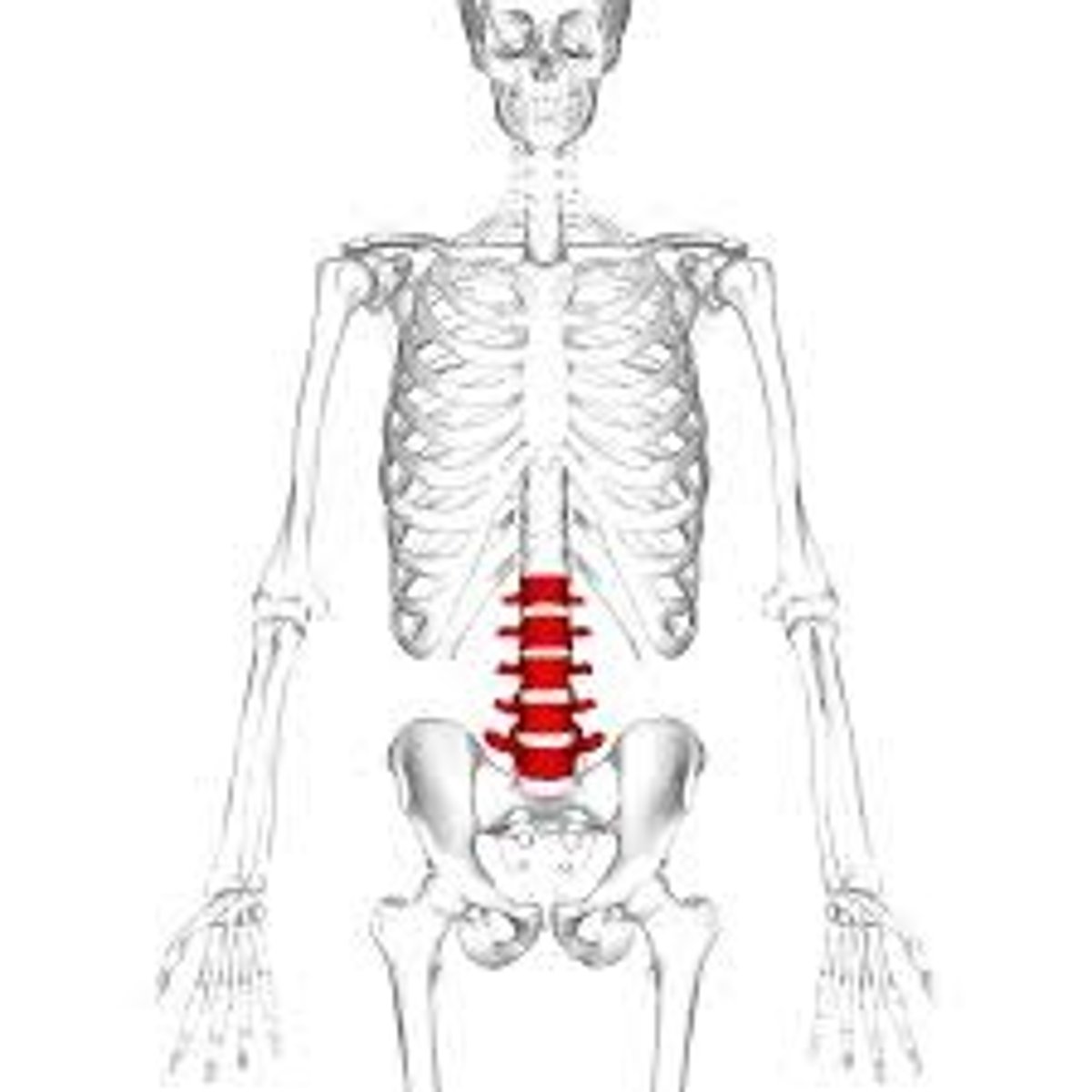
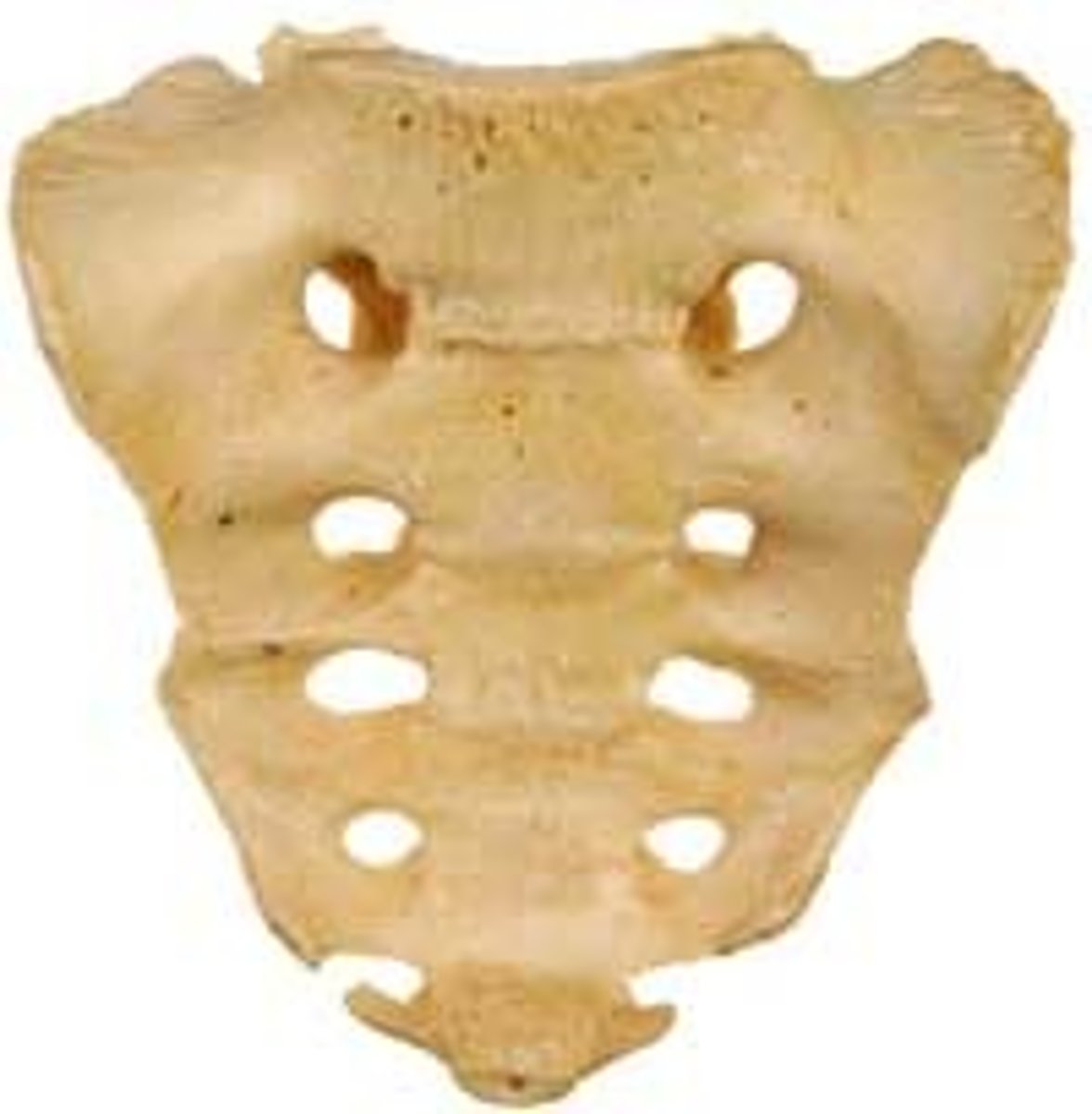
Sacrum
bone formed from five vertebrae fused together near the base of the spinal column
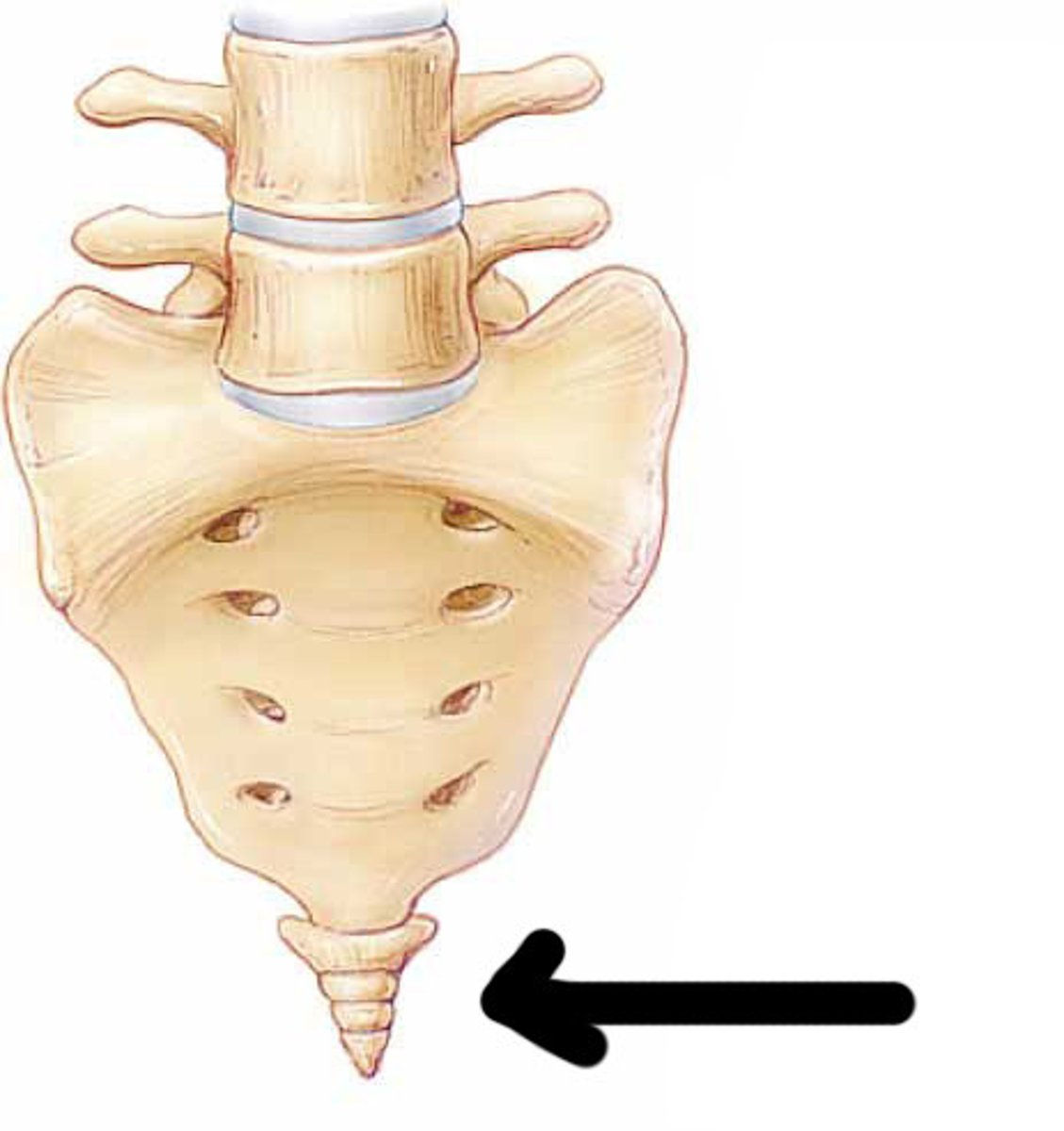
the tailbone, made up of the four fused vertebrae at the base of the spinal column
Coccyx
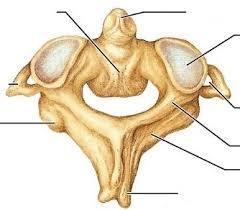
Body
The largest section of a vertebrae.
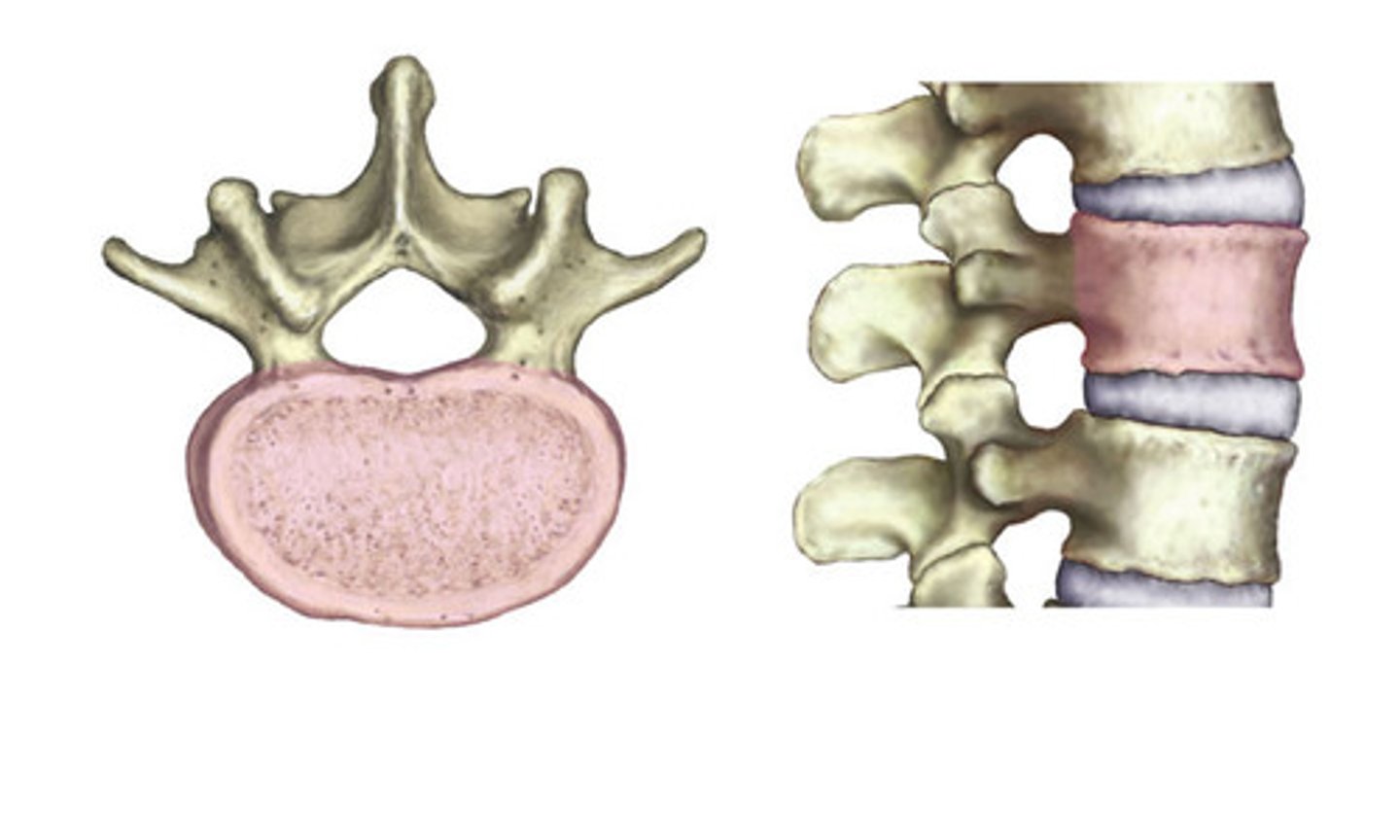
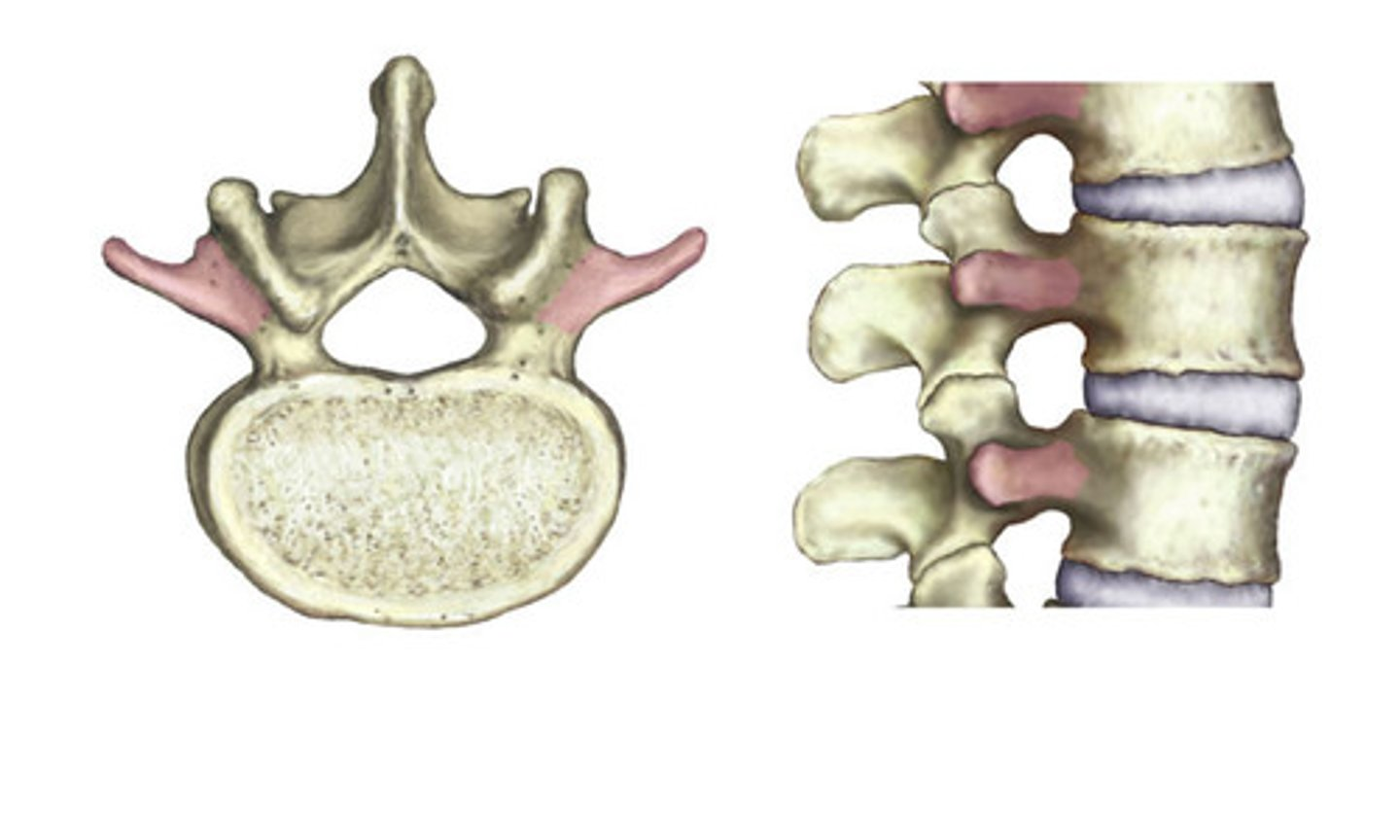
Projection on the sides of the vertebrae.
Transverse process
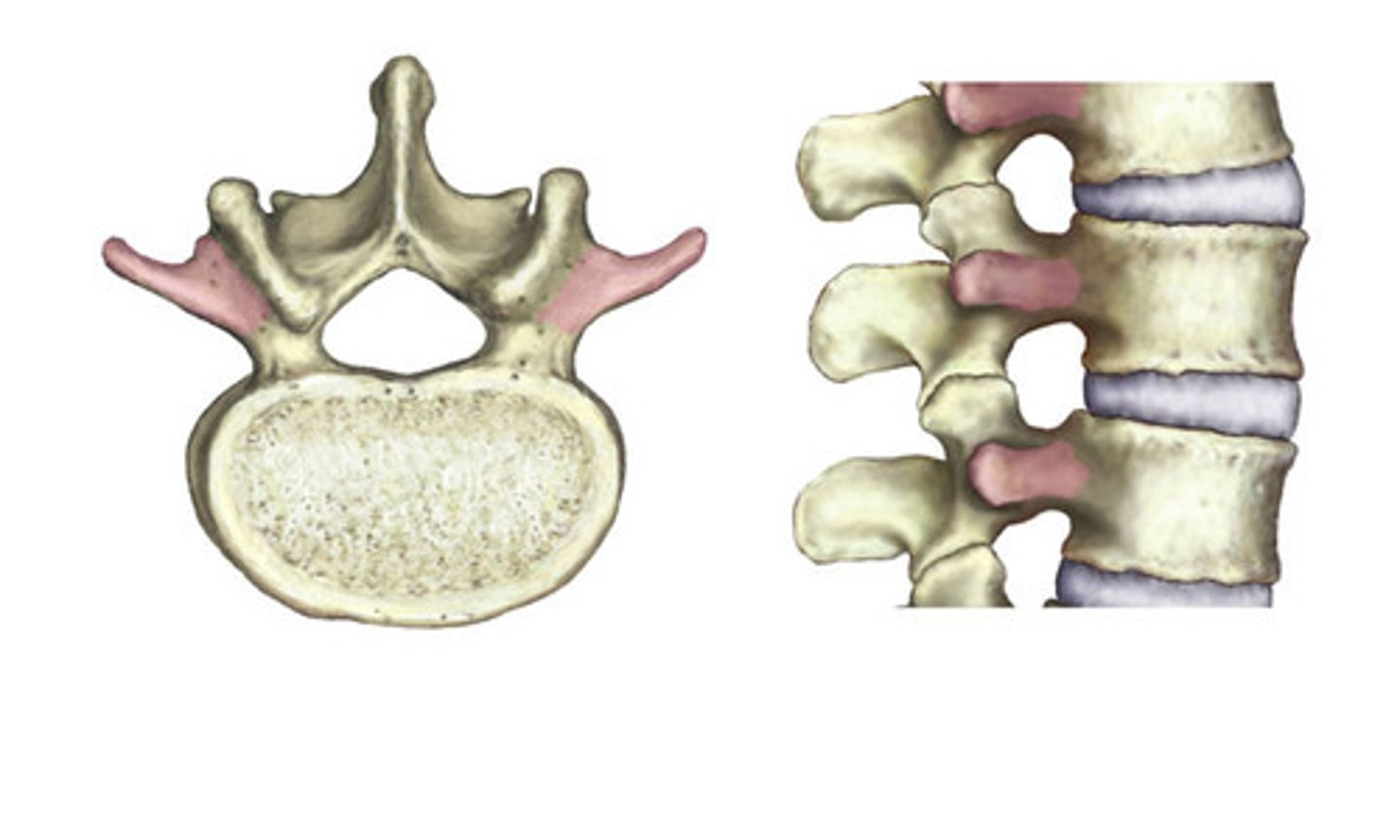
Spinous Process
Sharp, slender projection on back of vertebrae
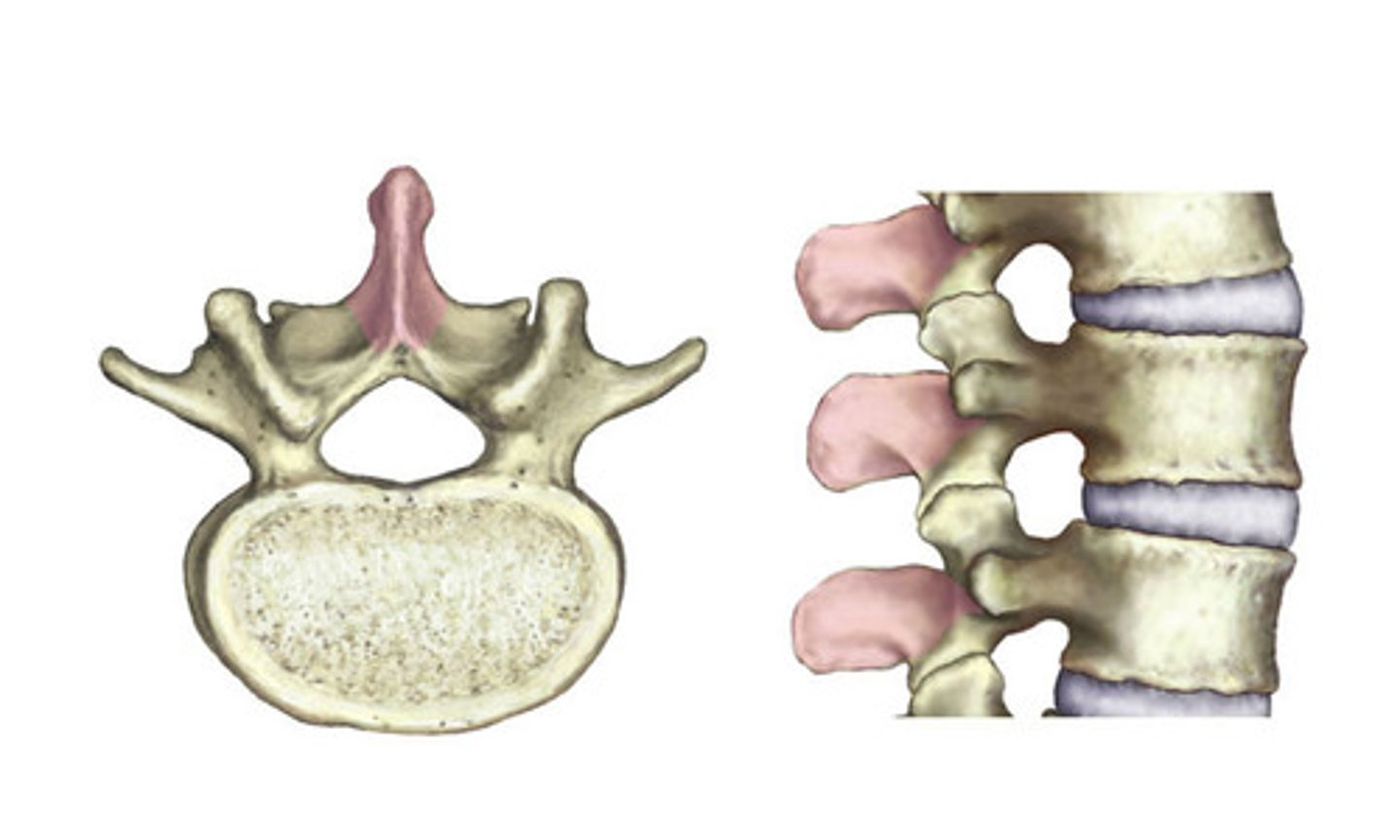
Hole for the spinal column.
Vertebral foramen
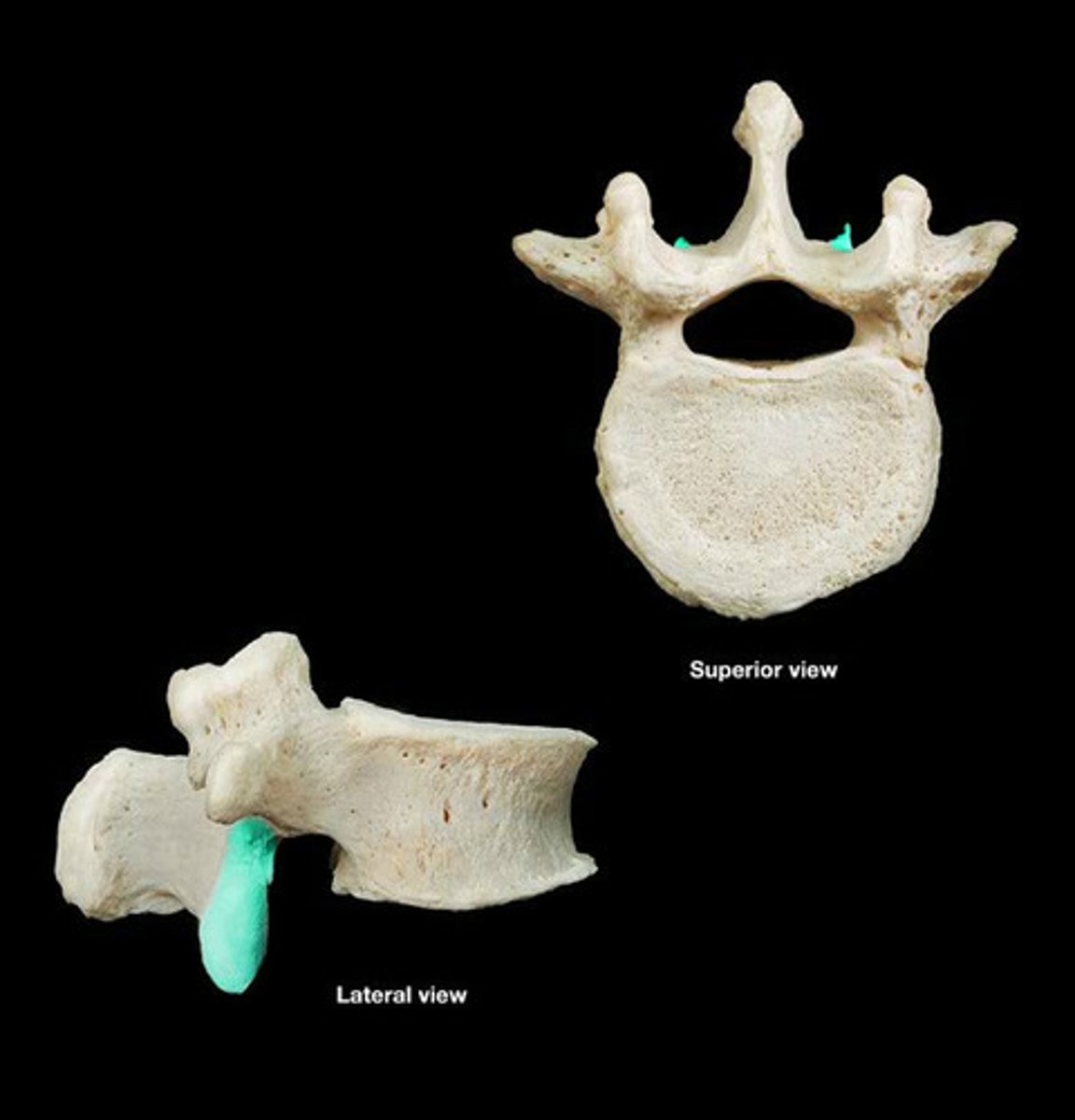
Superior articular facet
Location on top of vertebrae where it articulates with the vertebrae above it.
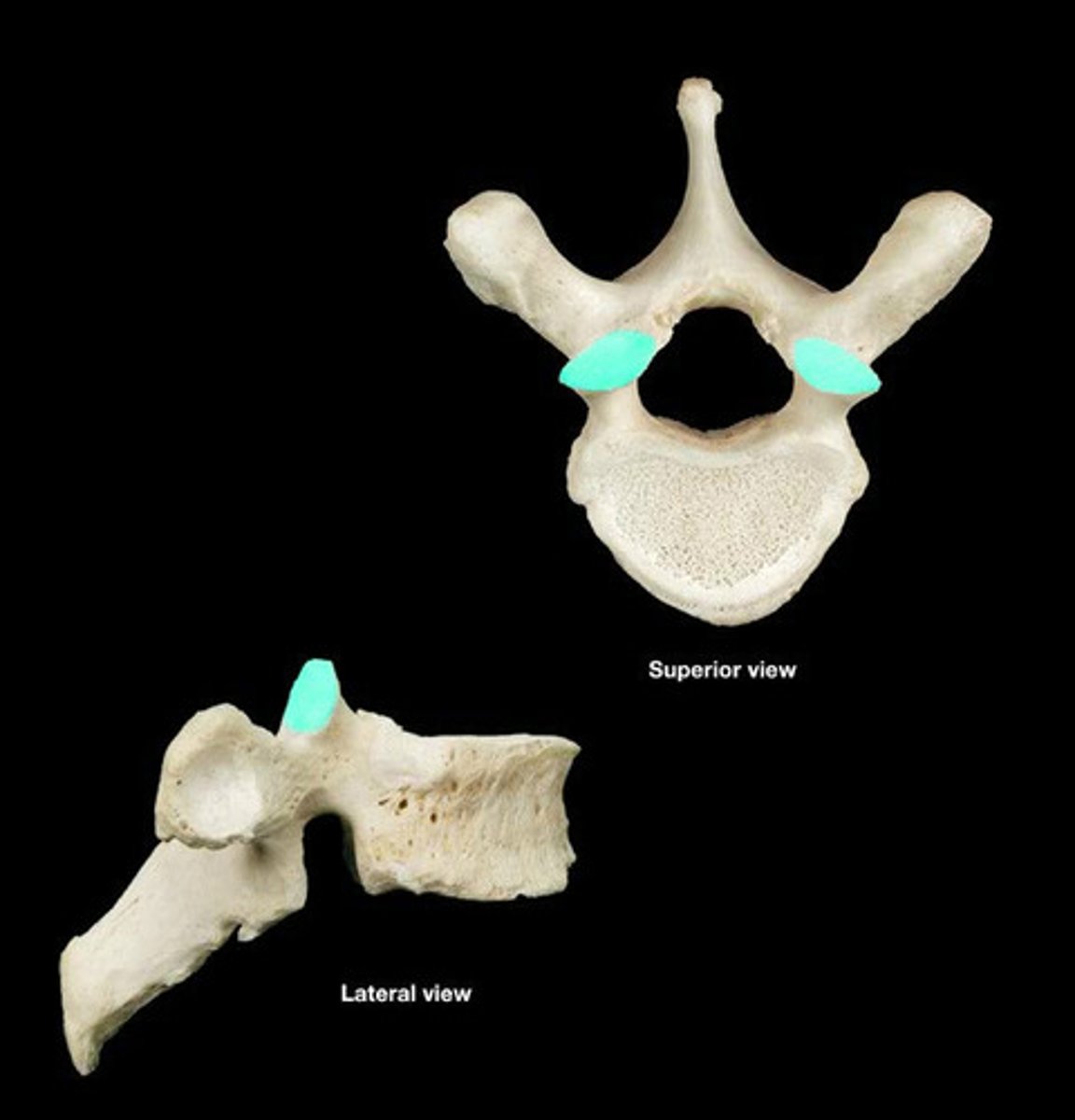
Inferior articular facet
Location on bottom of vertebrae where it articulates with the vertebrae below it.
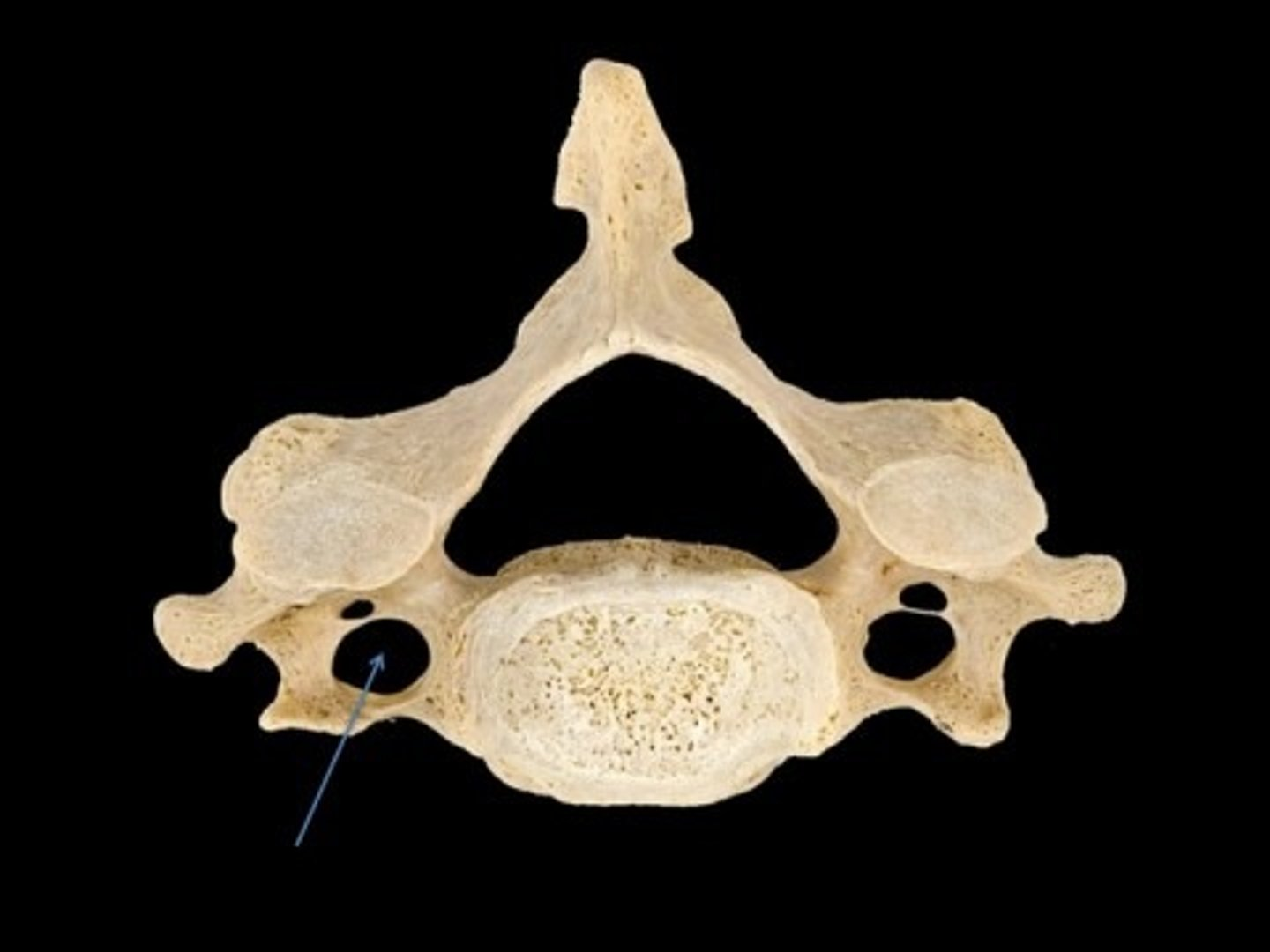
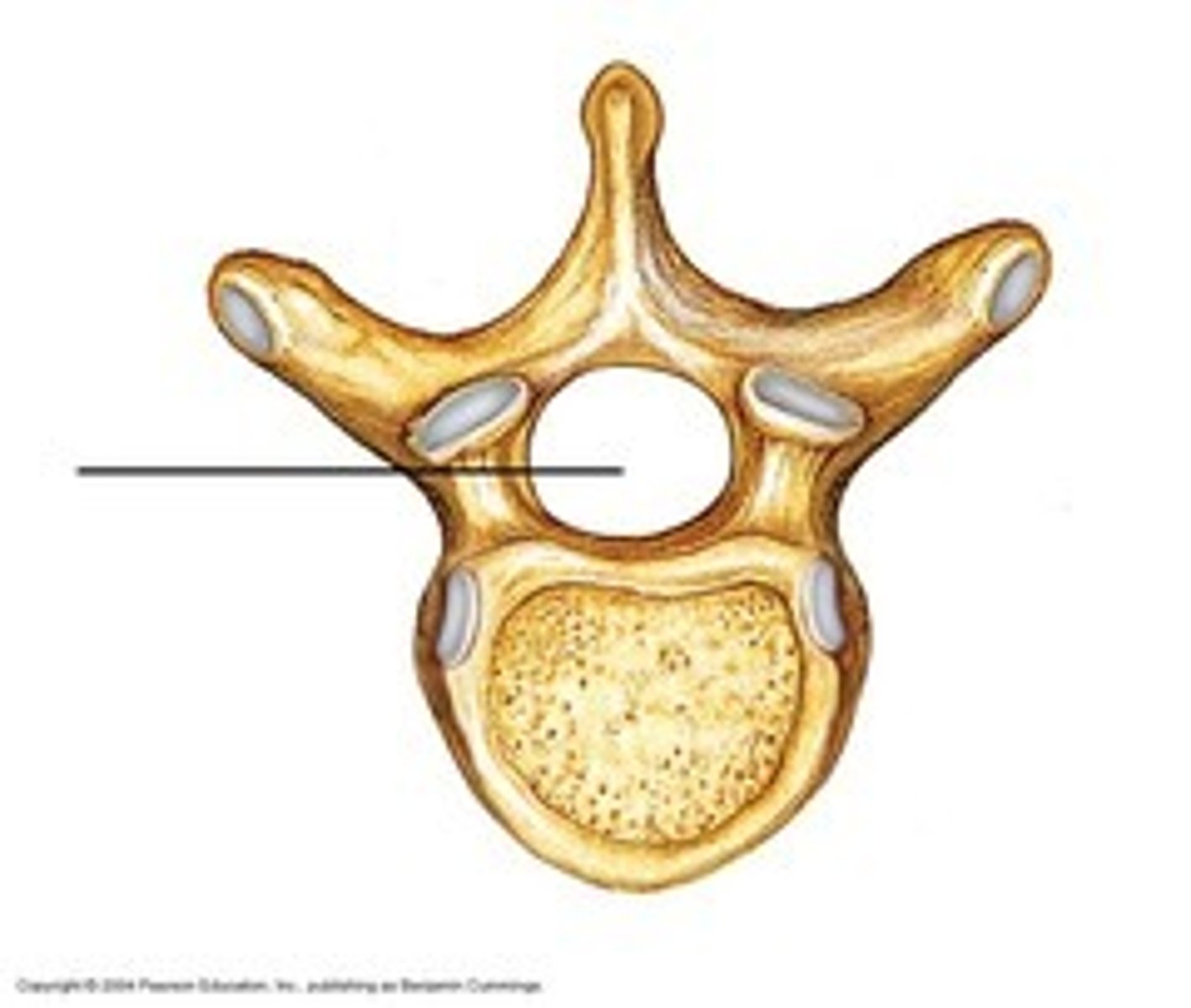
Holes located lateral of the transverse process.
Transverse Foramen
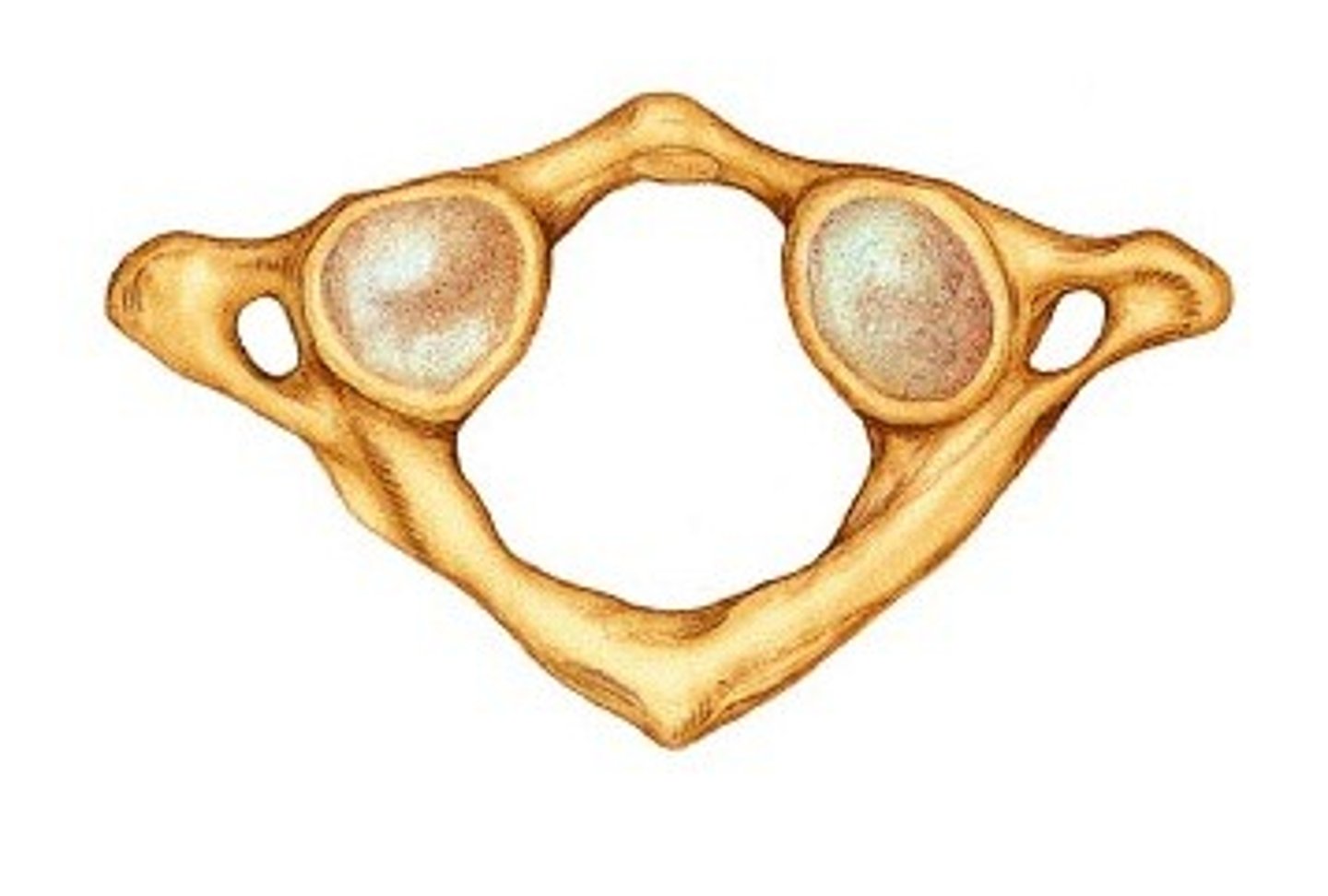
Atlas
C1 - First cervical vertebrae. Carries the skull.
C2, second cervical vertebrae
Axis
Prominent feature of the axis, allows the atlas and skull to rotate smoothly.
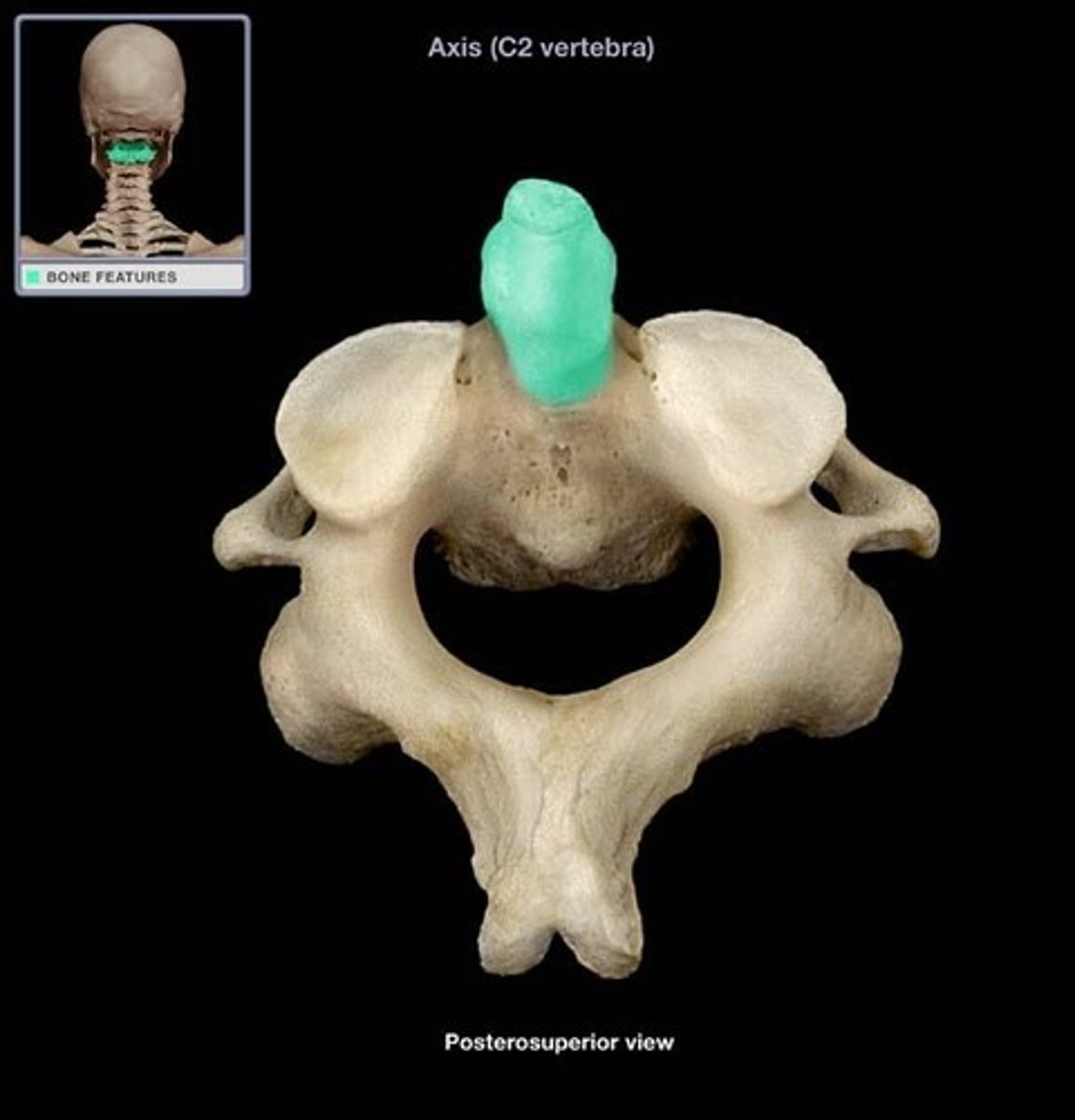
Dens
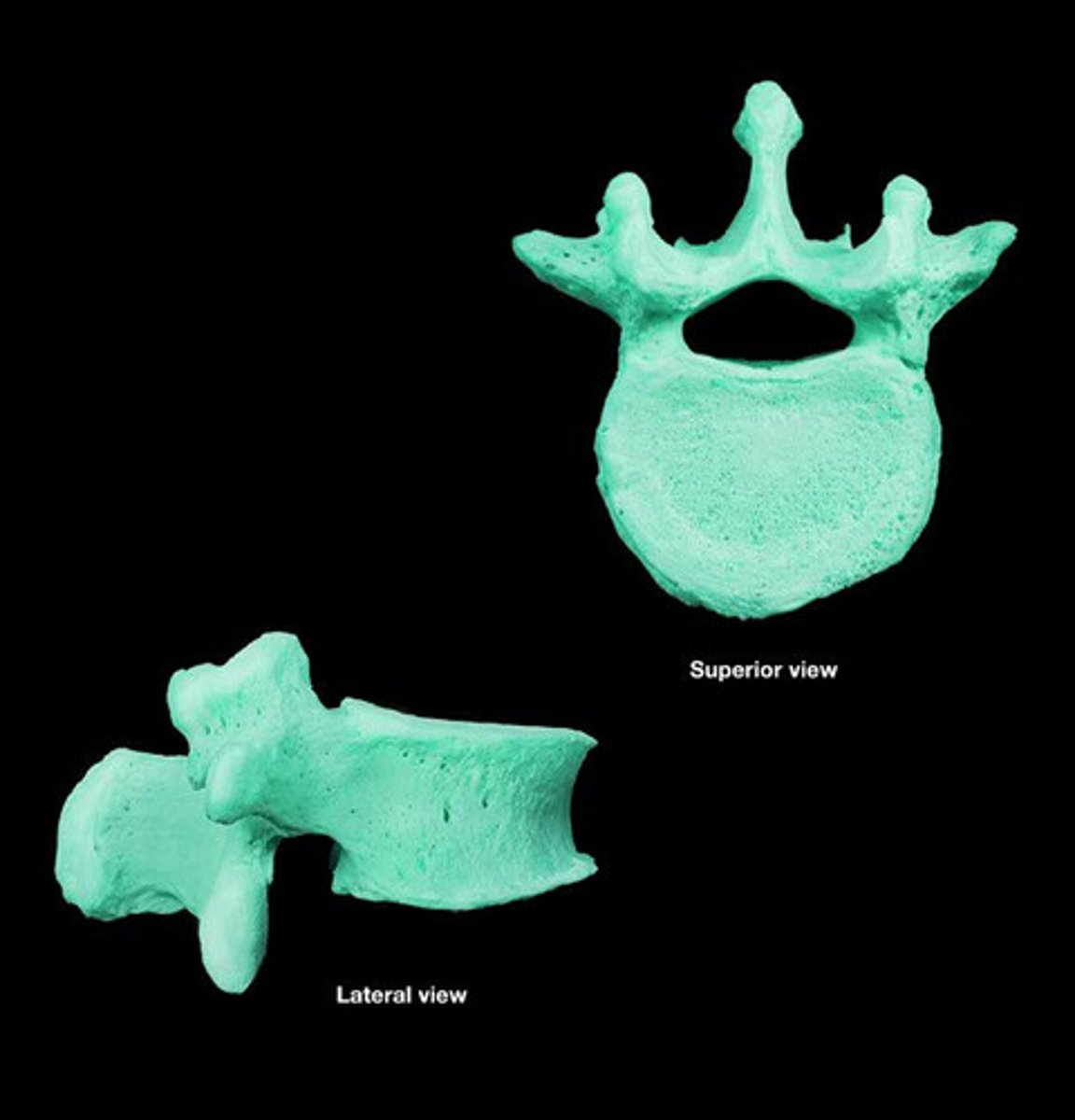
lumbar bone
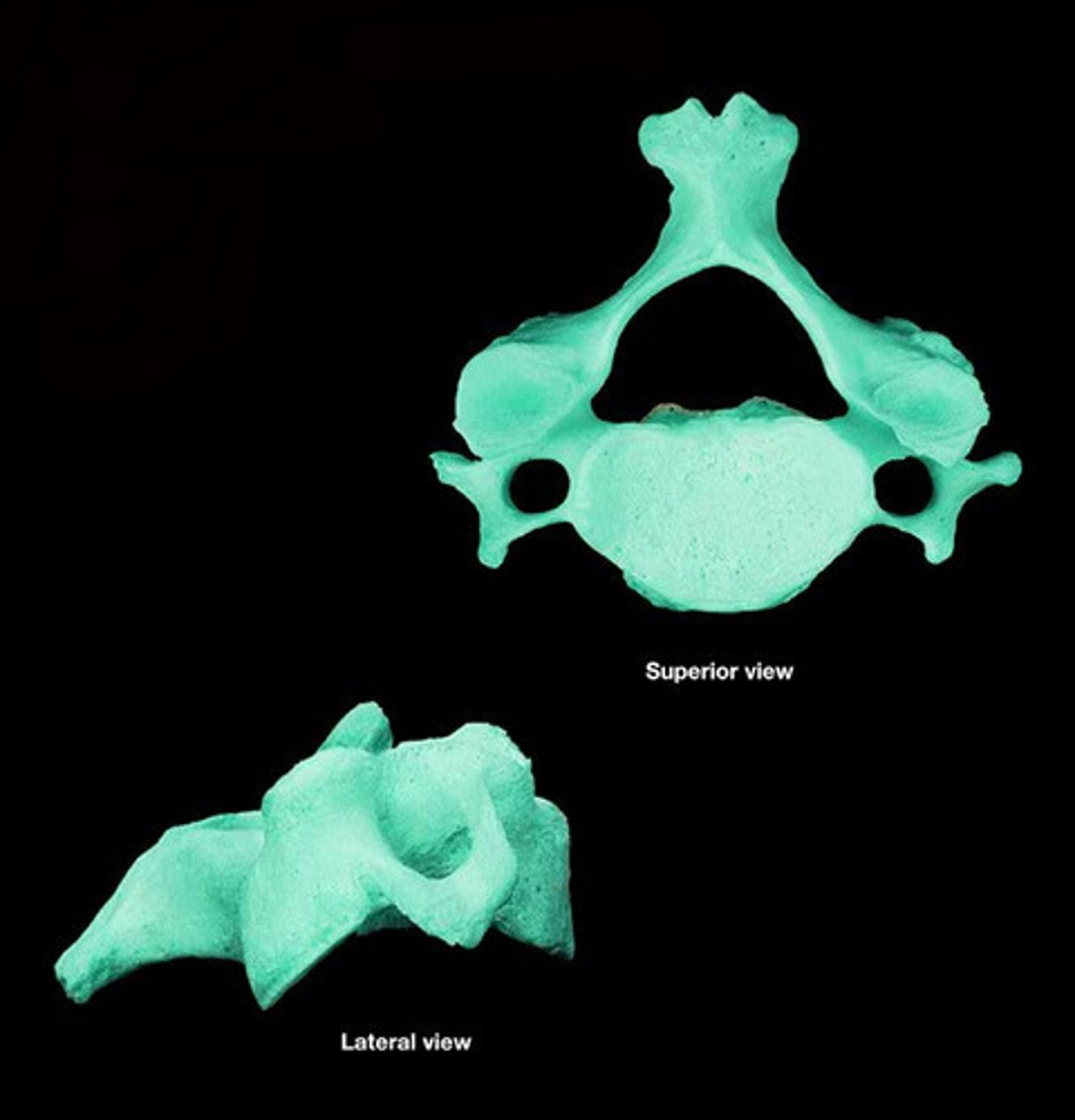
cervical bone
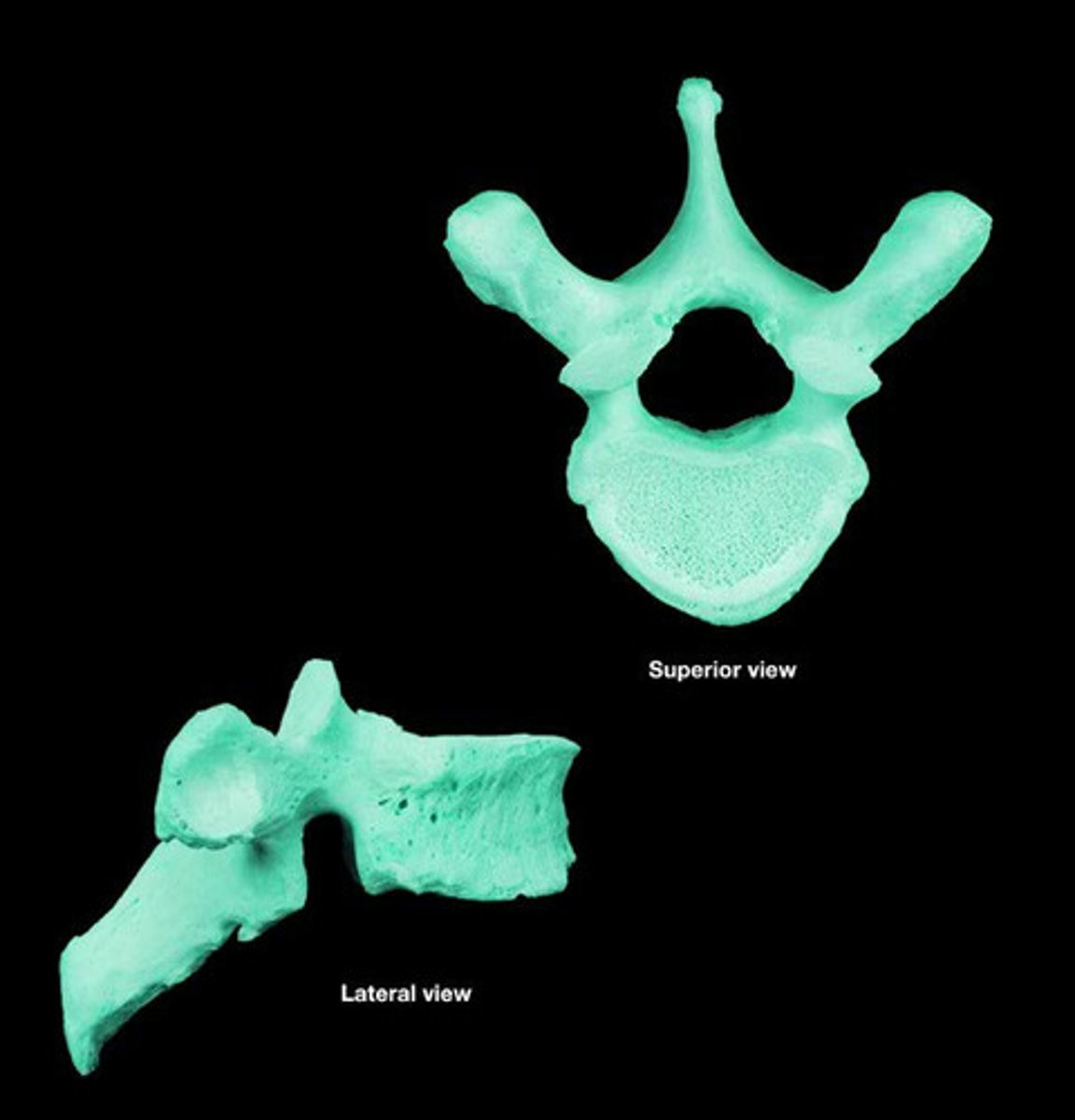
thoracic bone
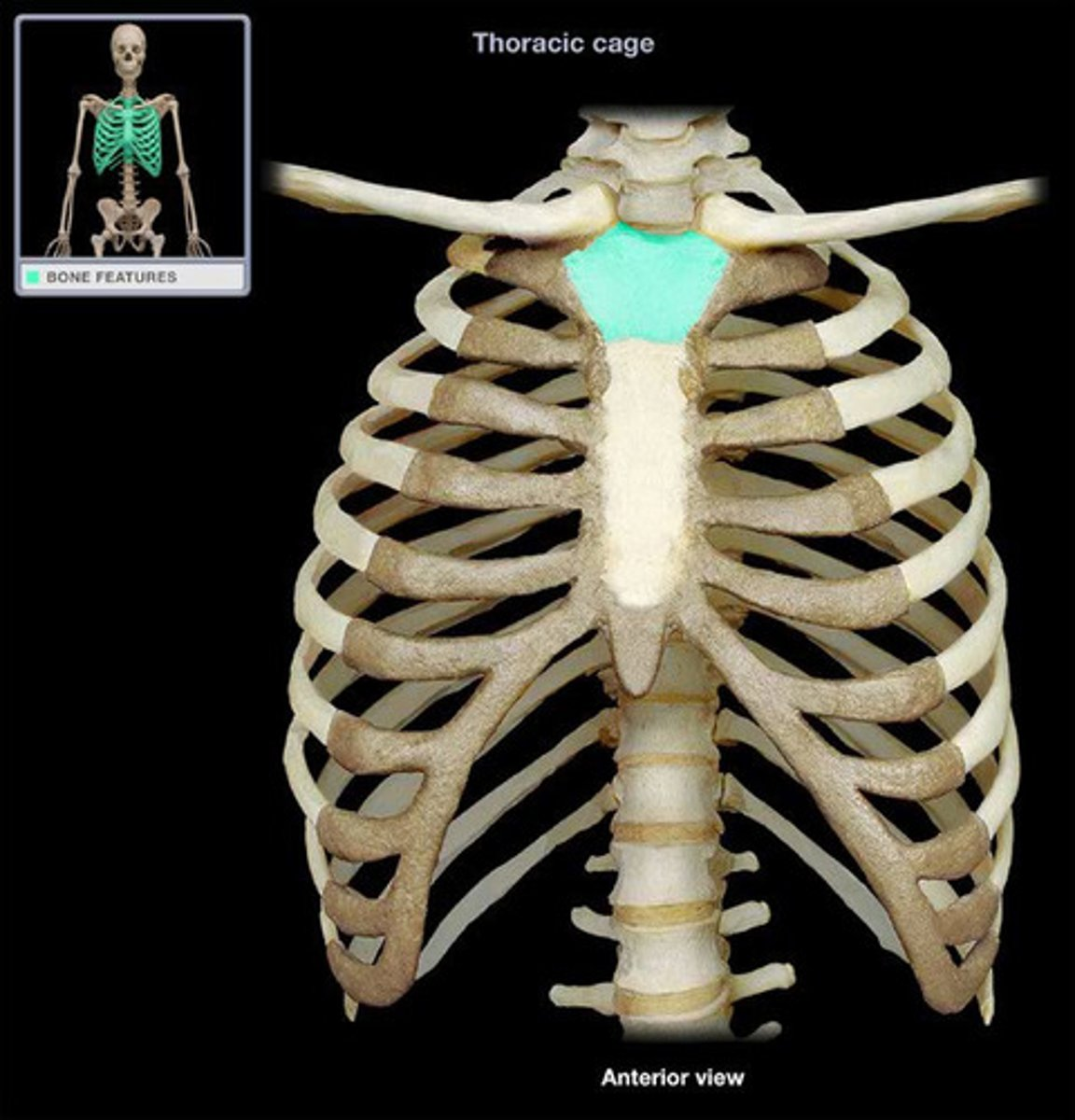
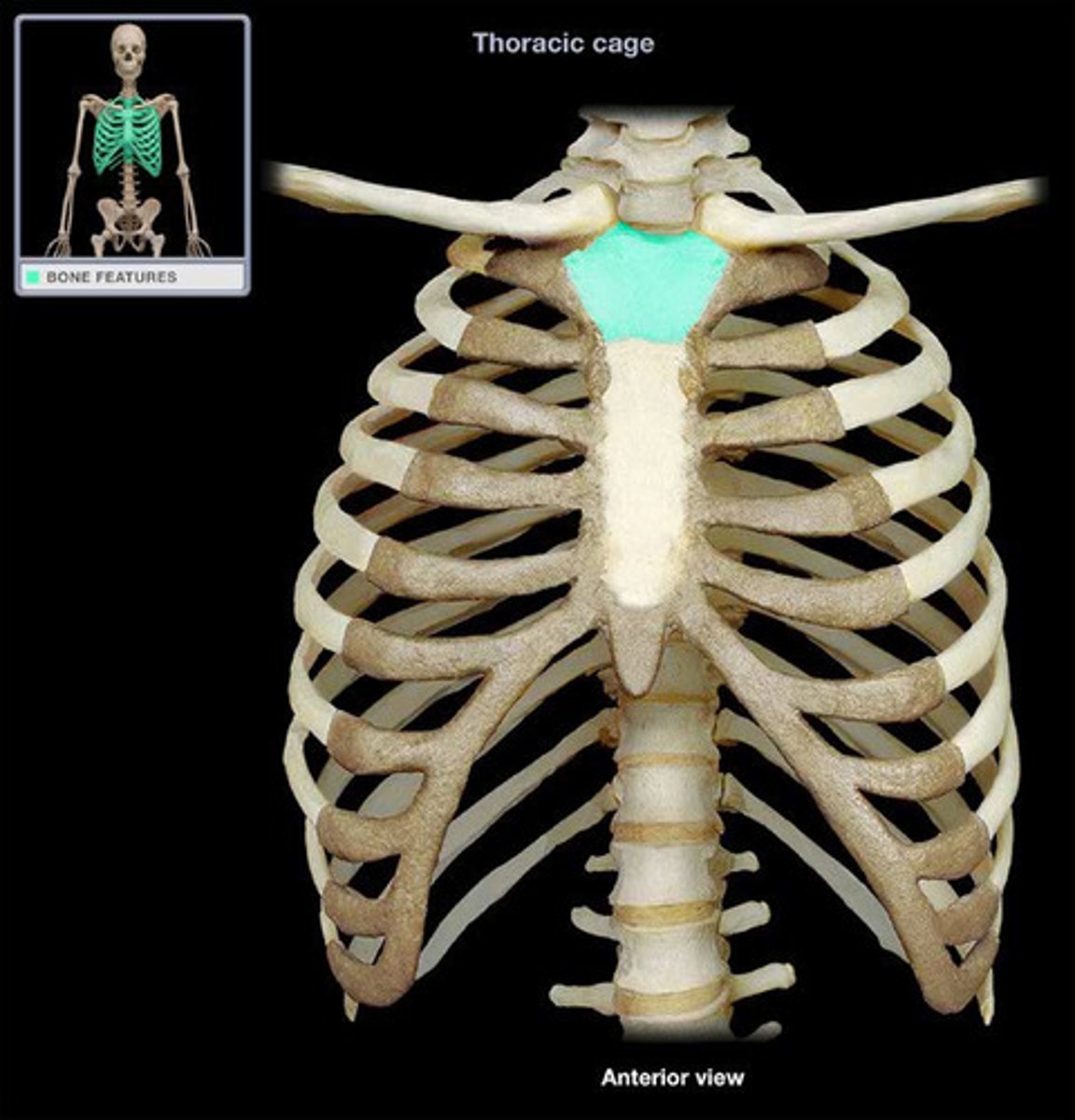
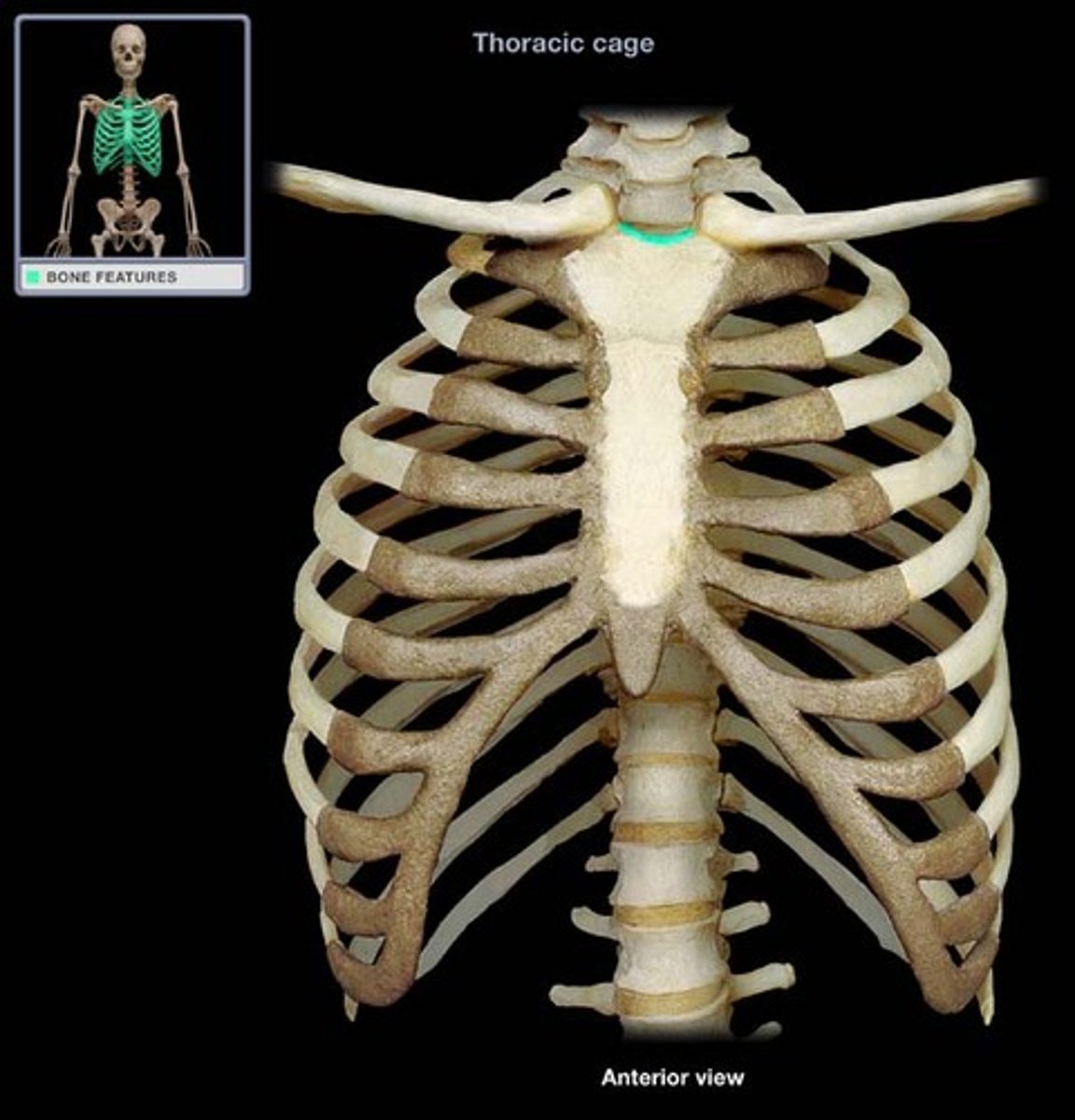
manubrium
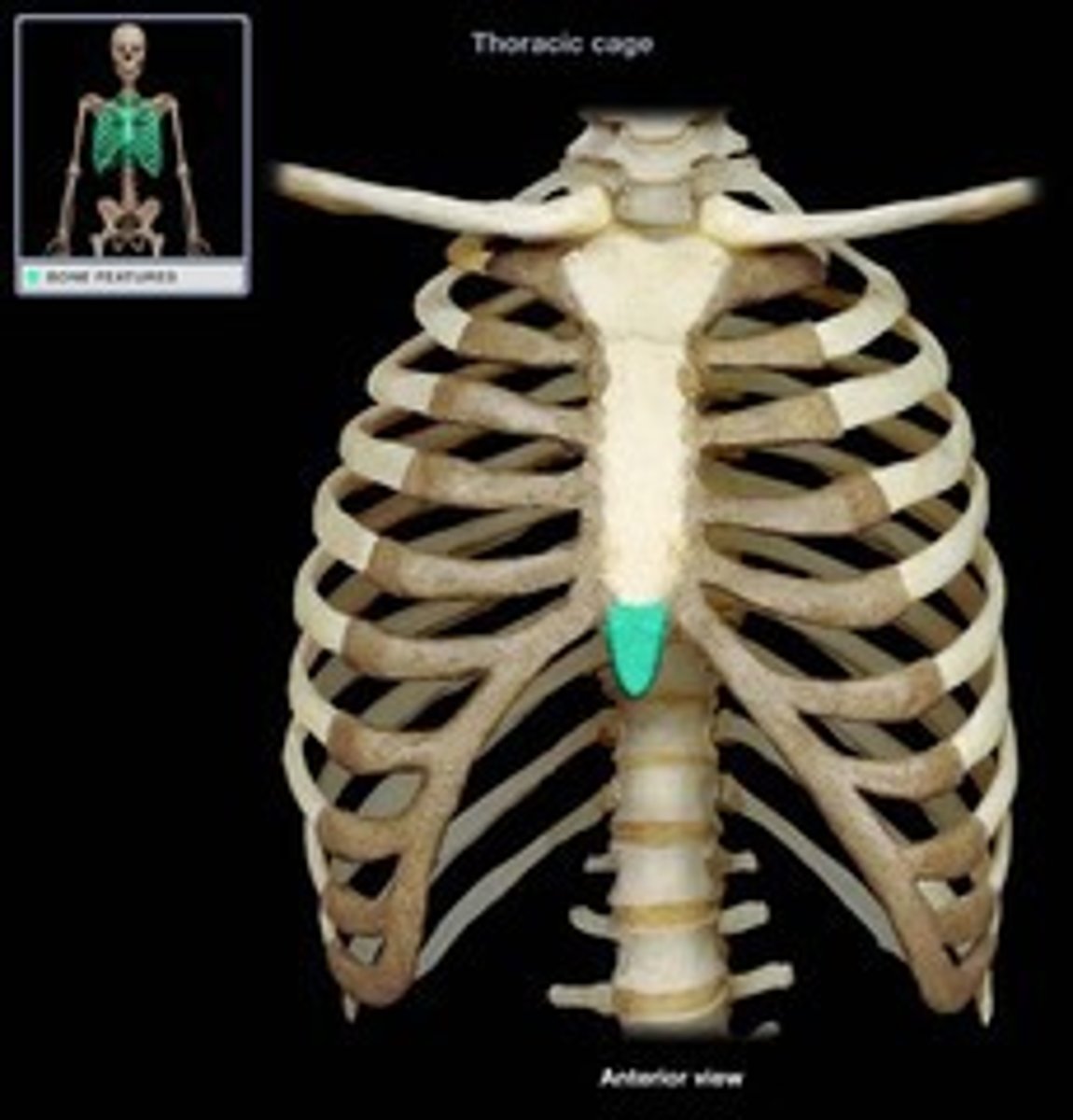
Xiphoid process of sternum
Name the portion of the bone.
jugular notch of sternum
ID the landmark and bone
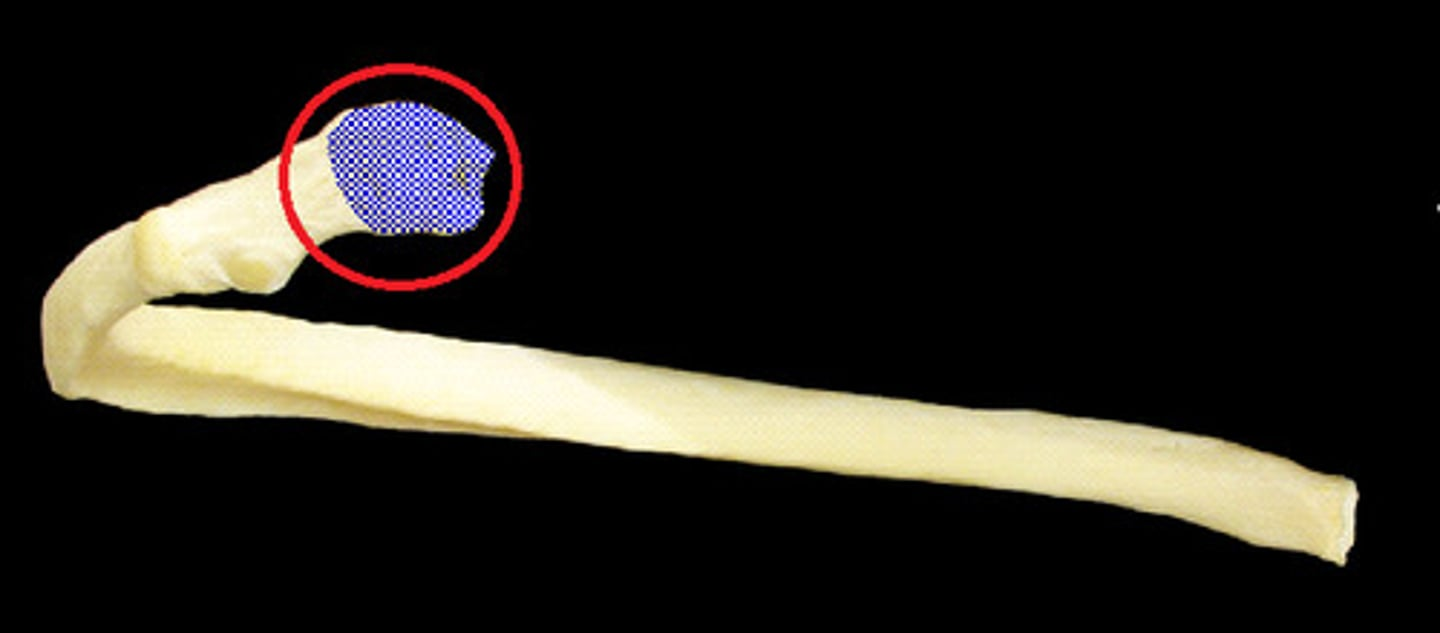
head of rib
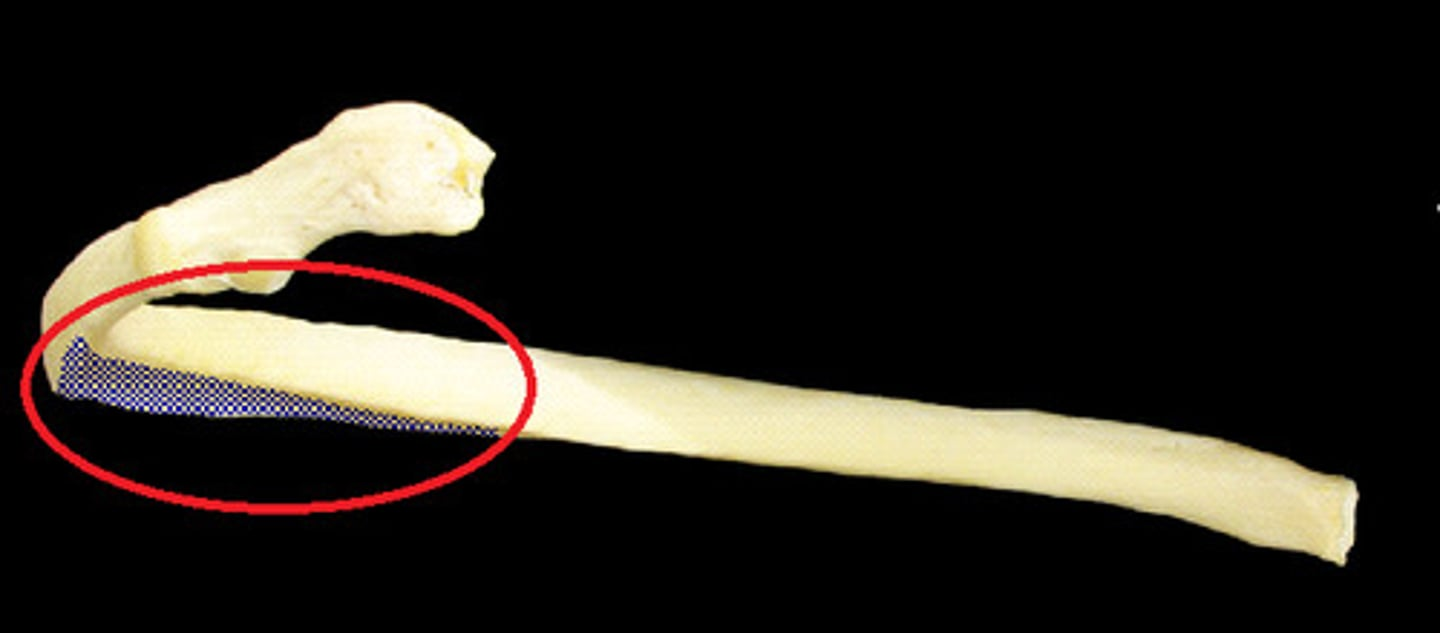
angle of rib
ilium (superior)
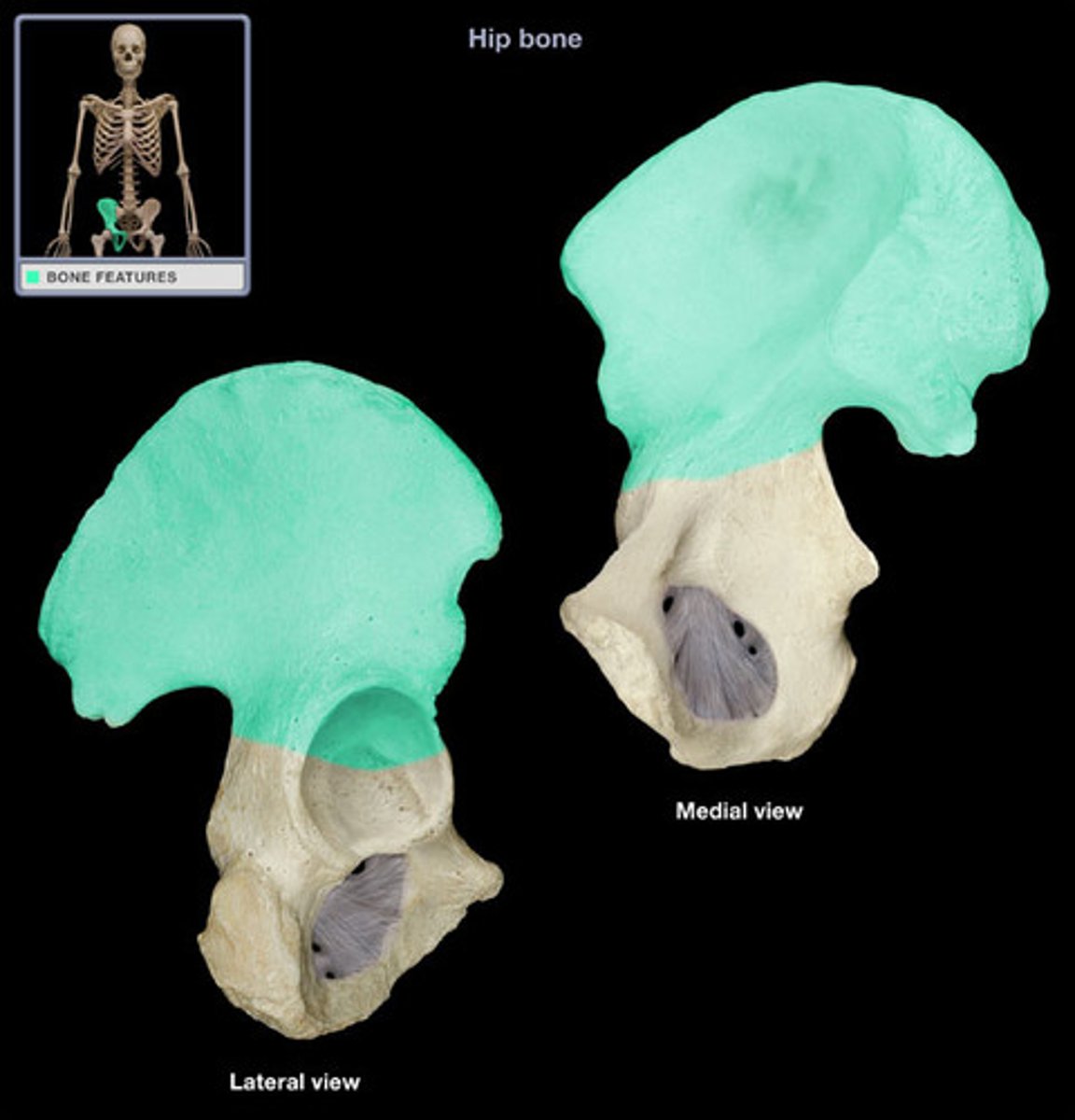
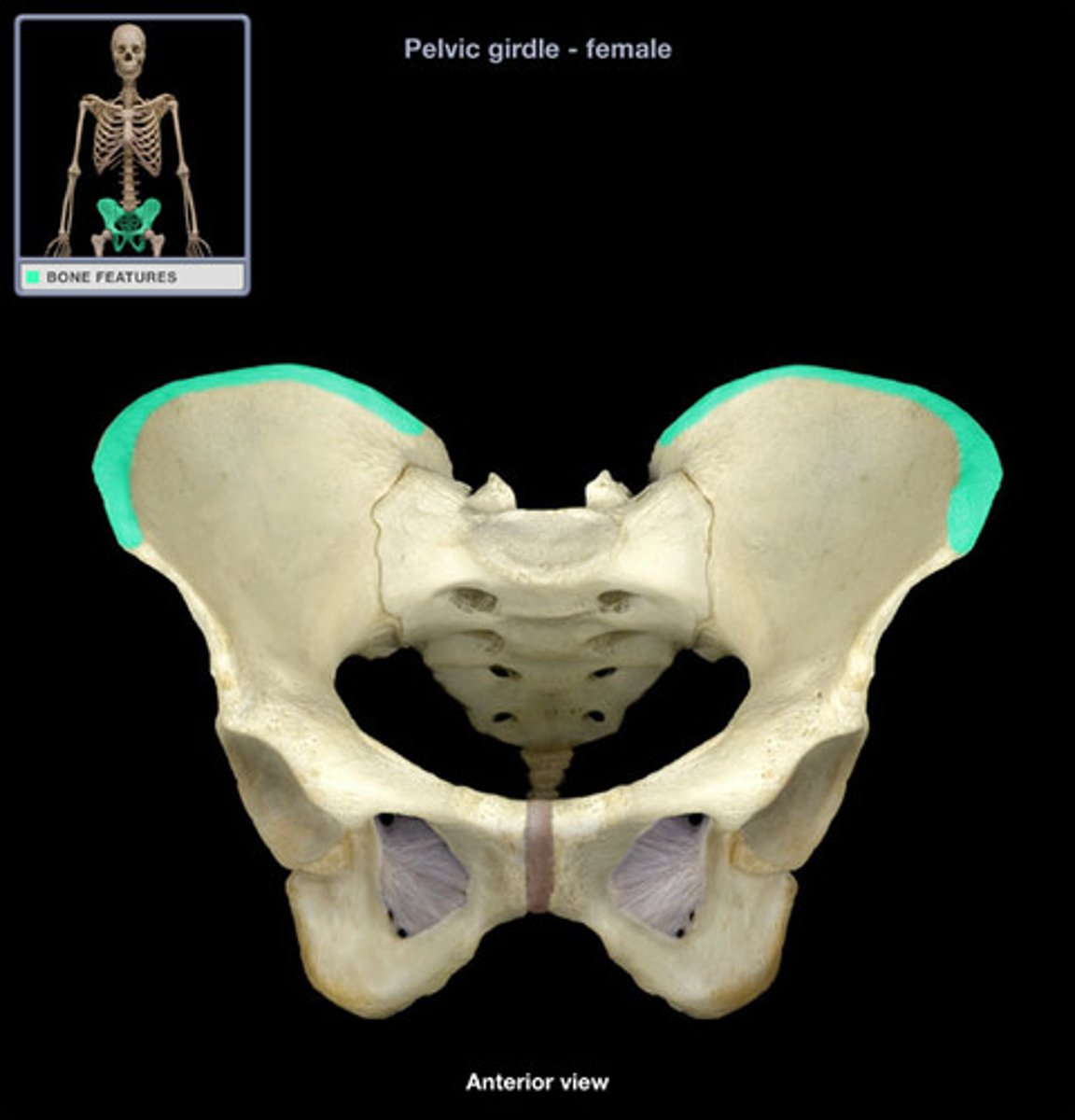
iliac crest
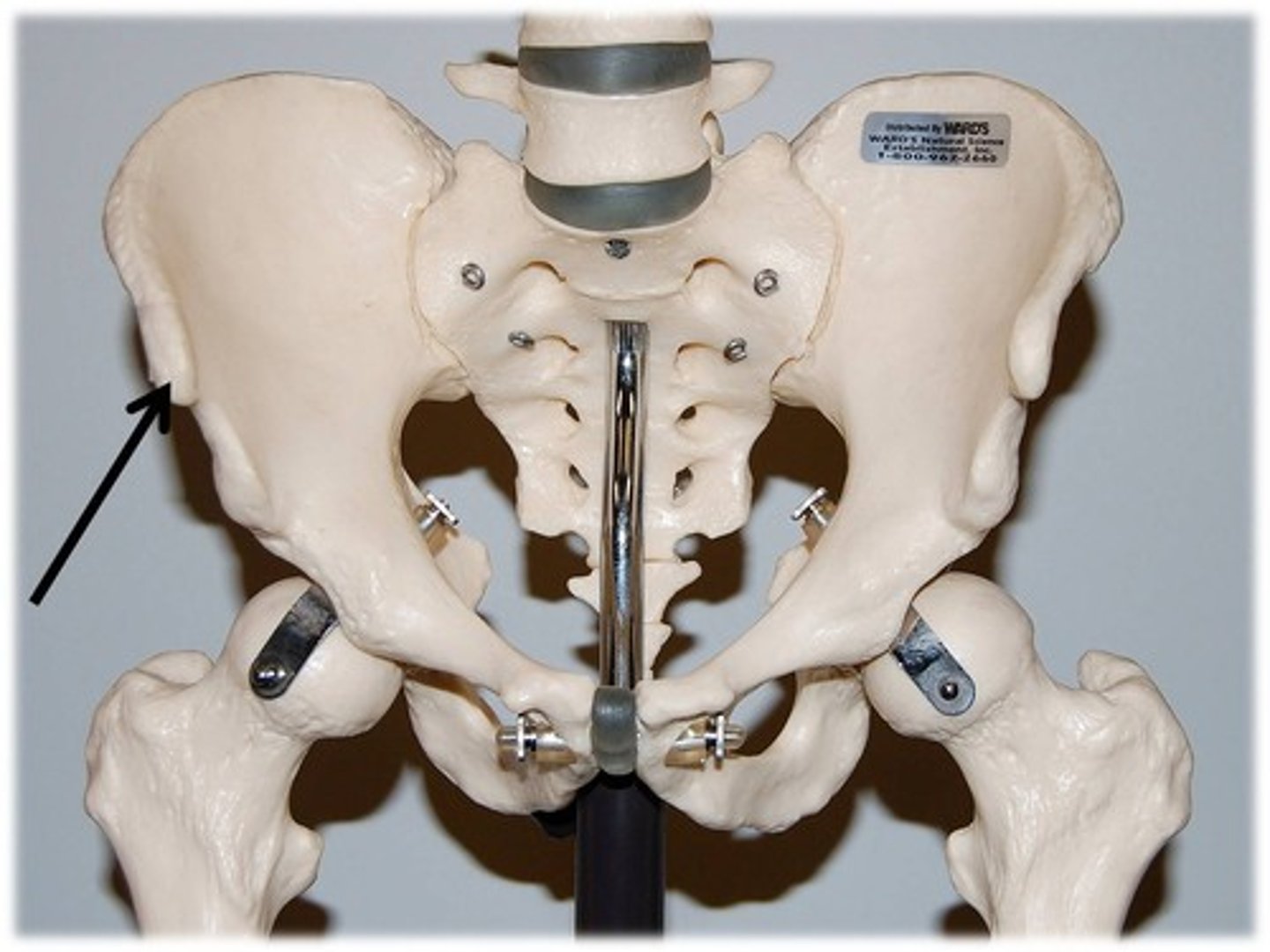
anterior superior iliac spine
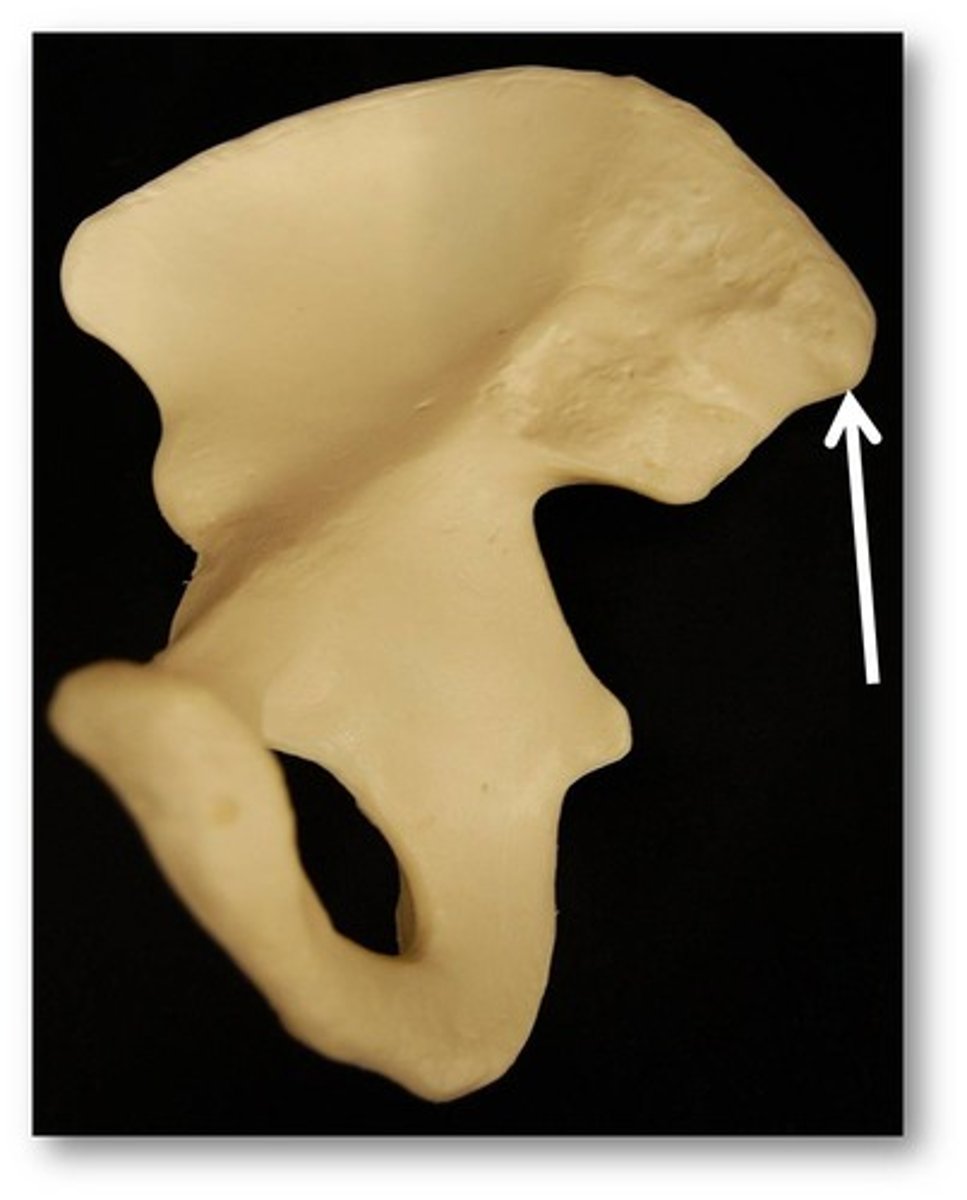
posterior superior iliac spine
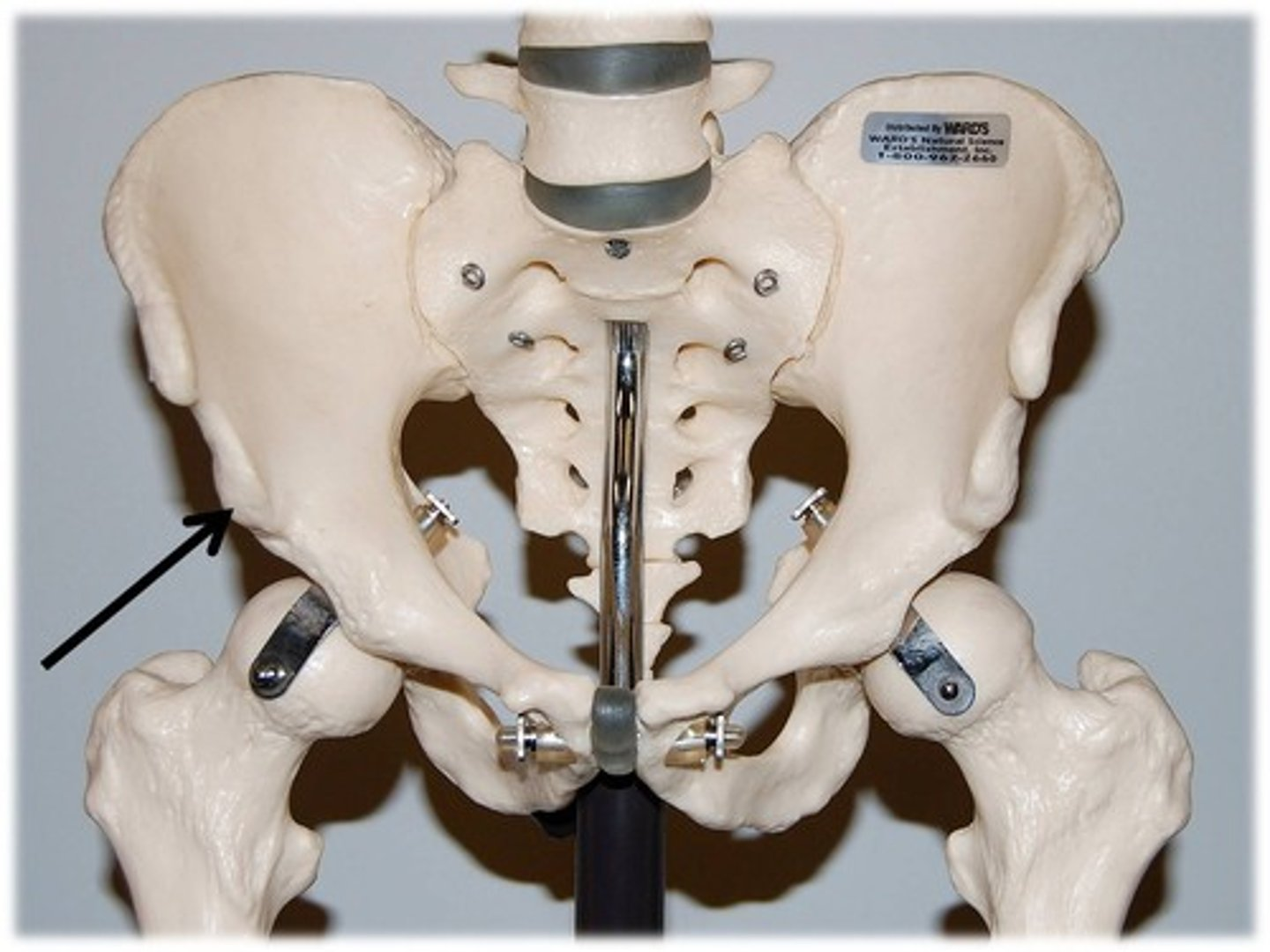
anterior inferior iliac spine
posterior inferior iliac spine
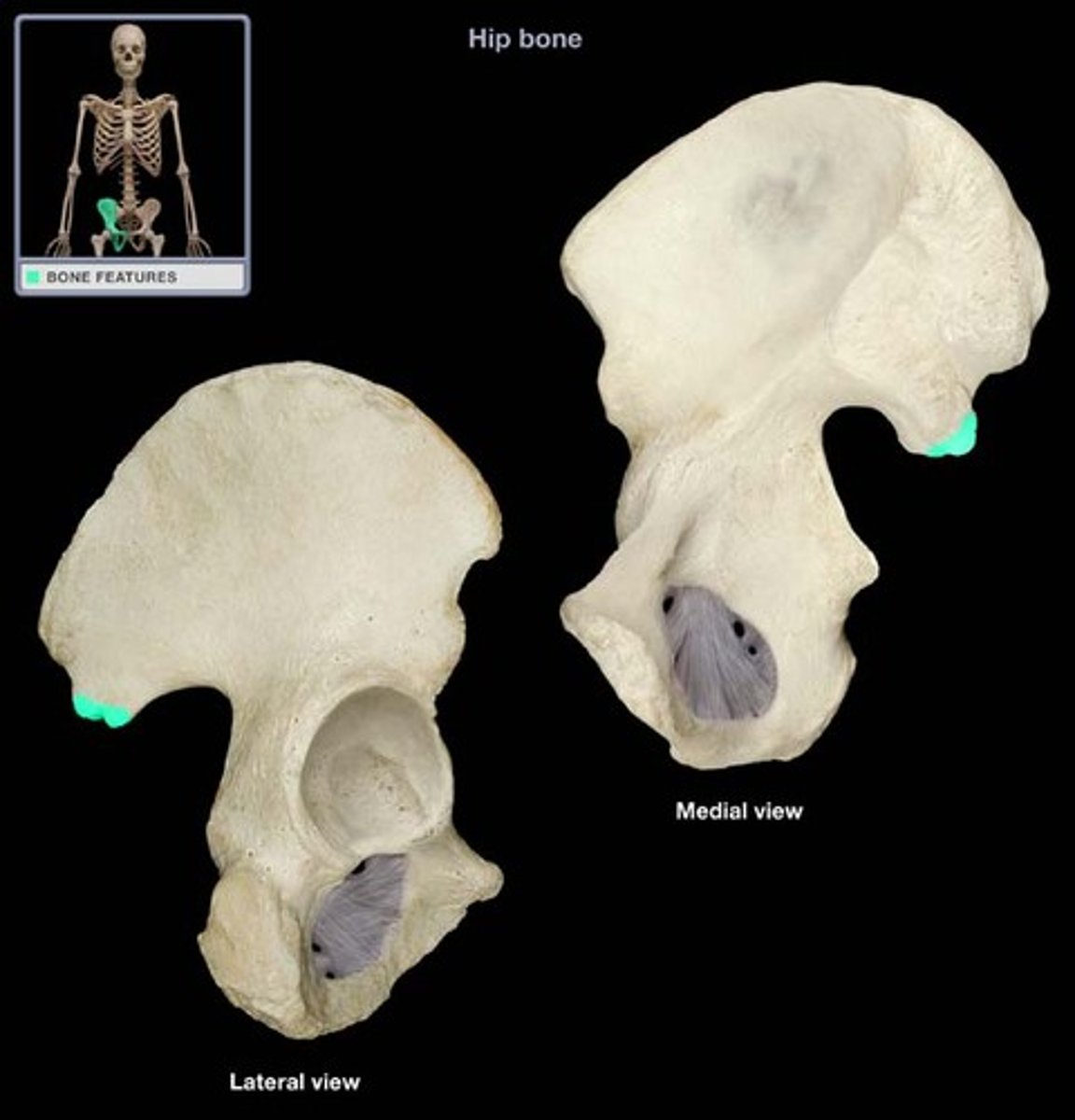
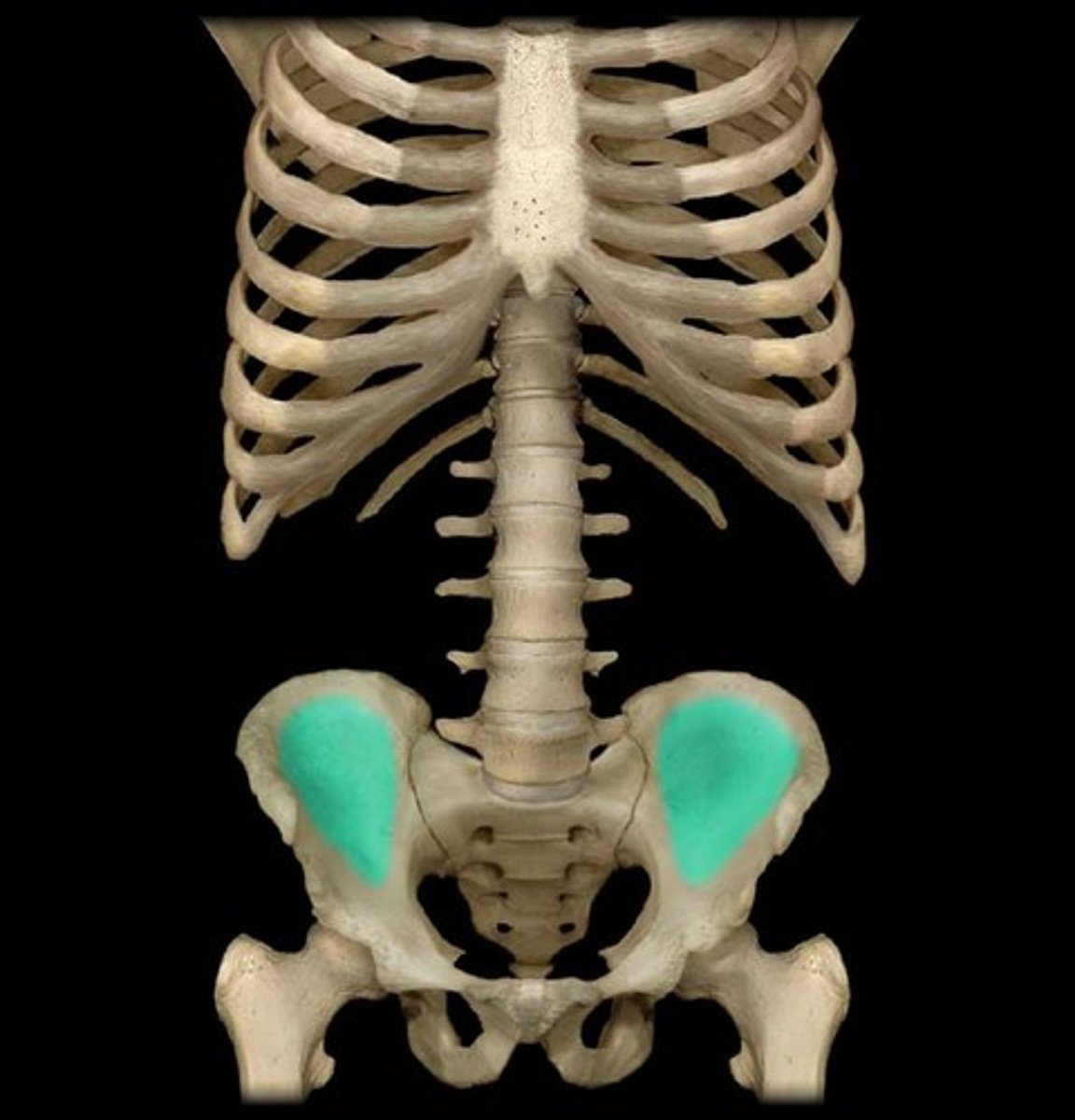
iliac fossa
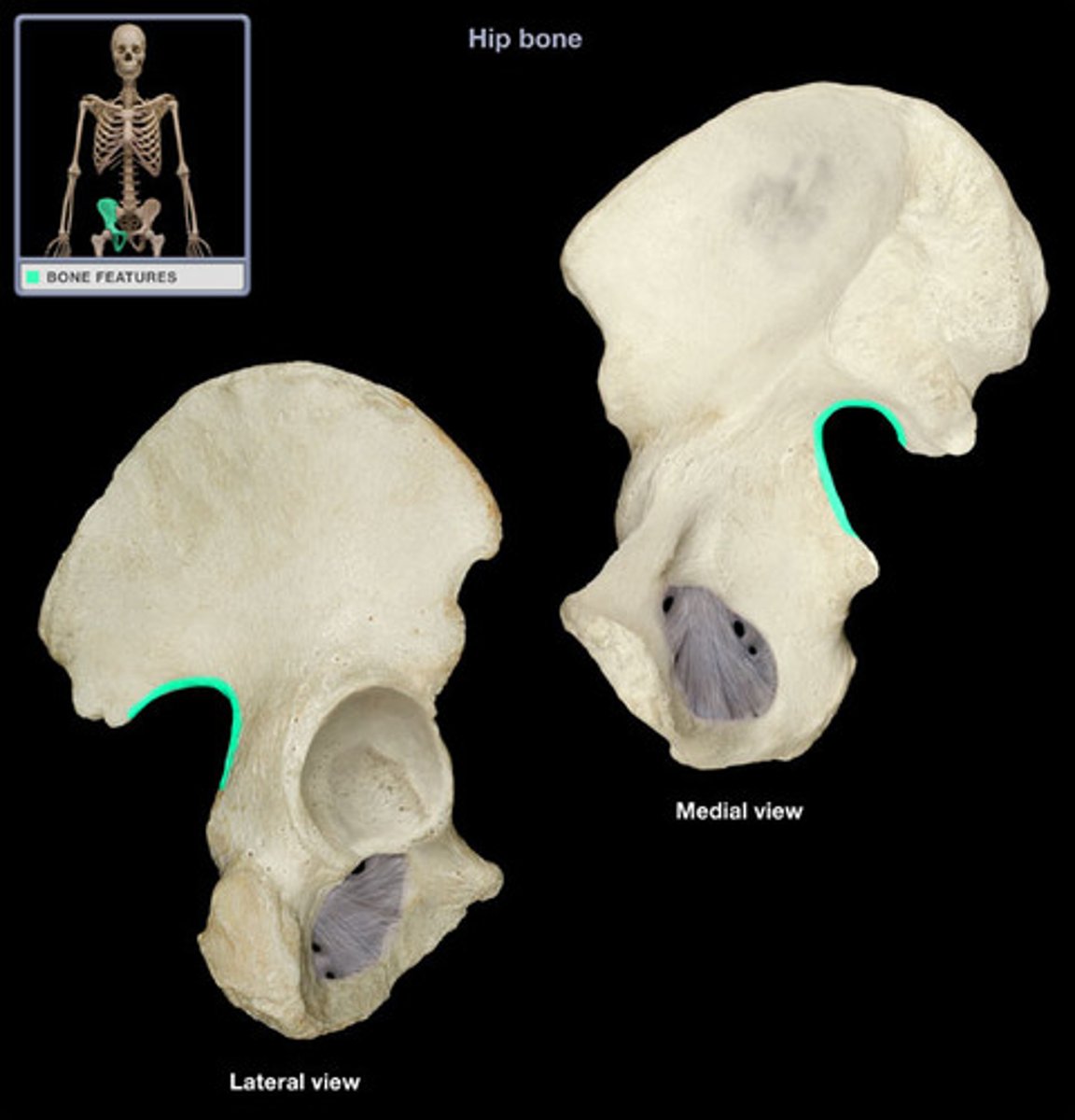
greater sciatic notch
pubis (inferior anterior)
acetabulum
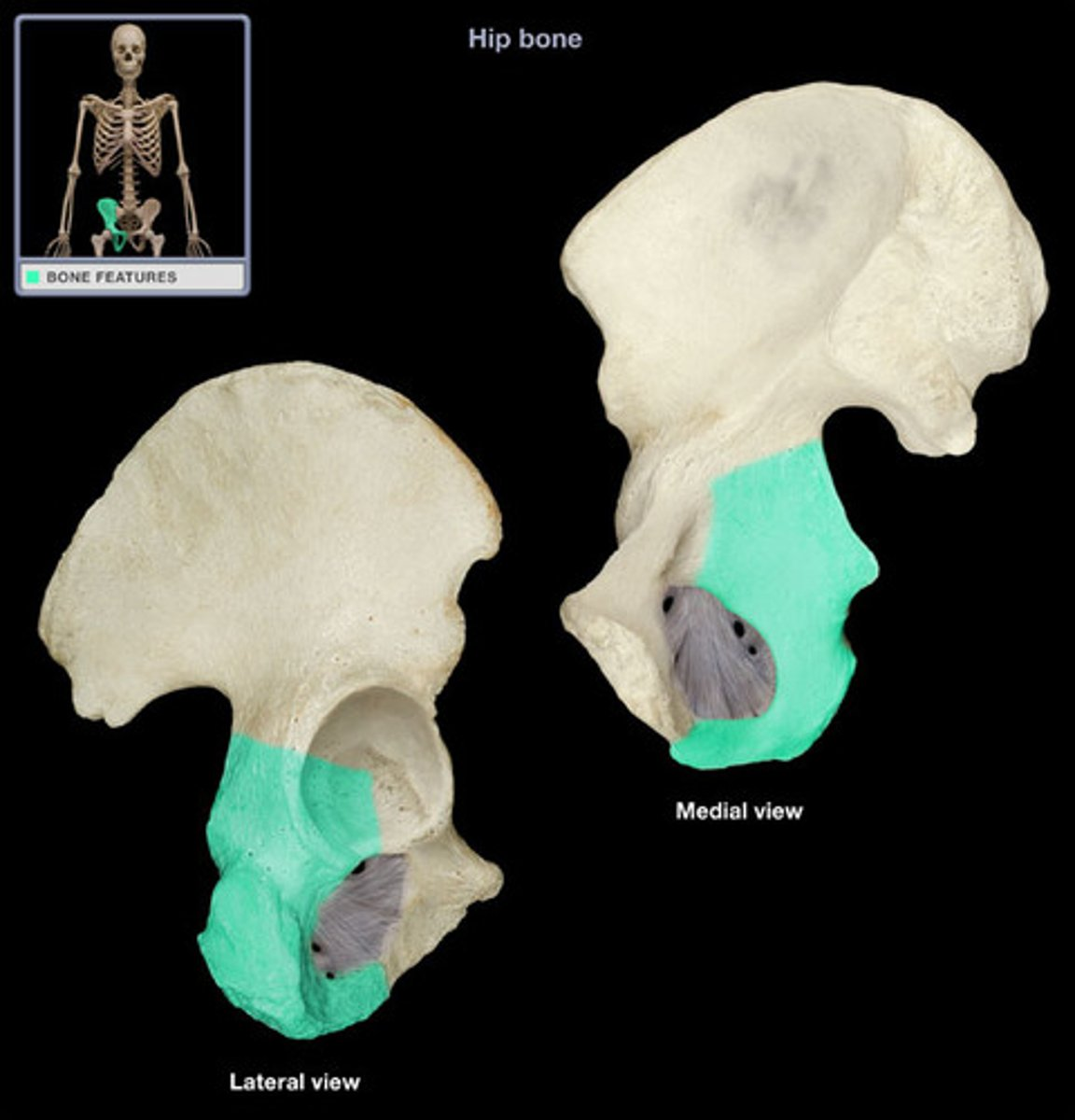
ischium (inferior posterior)
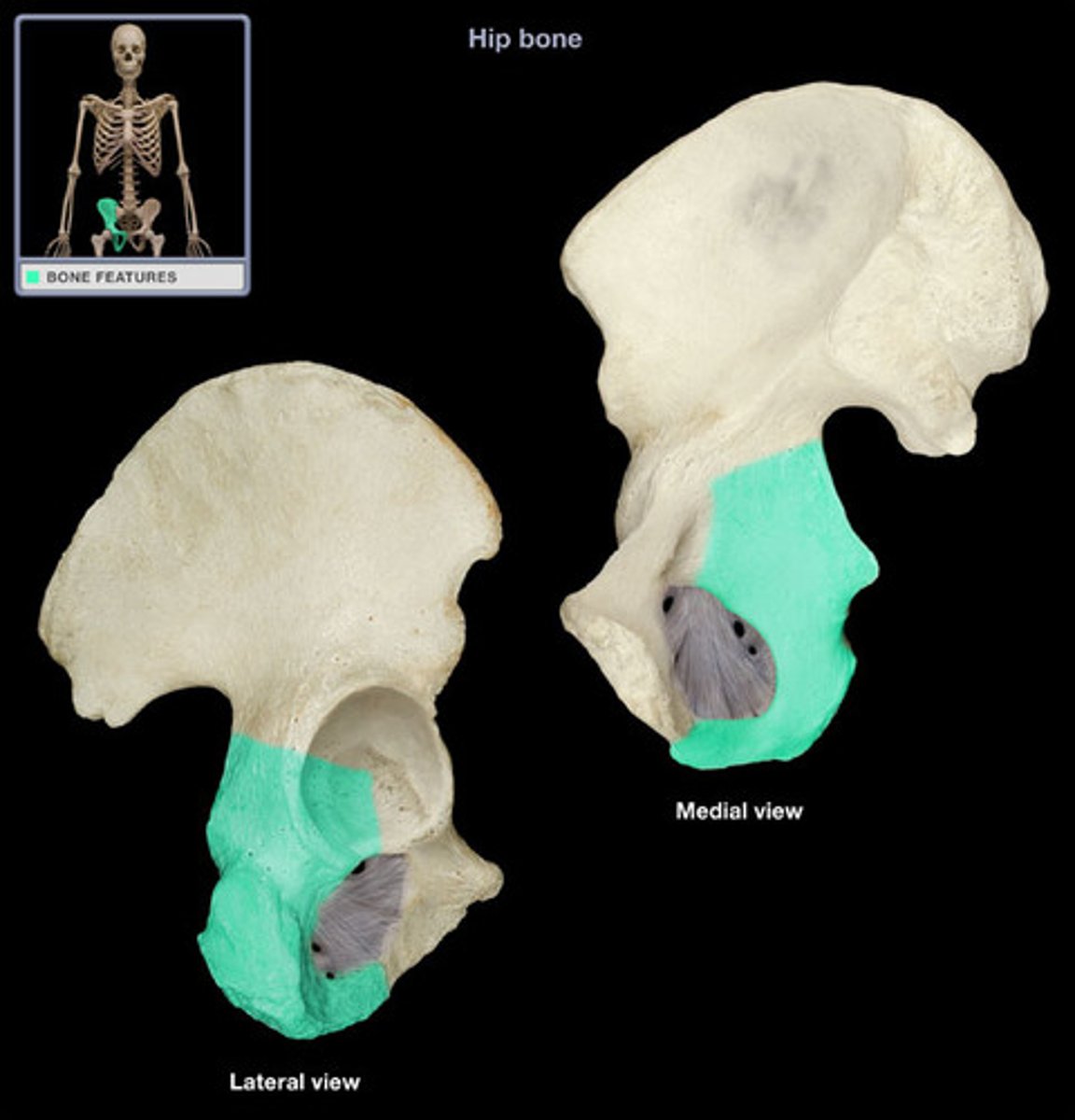
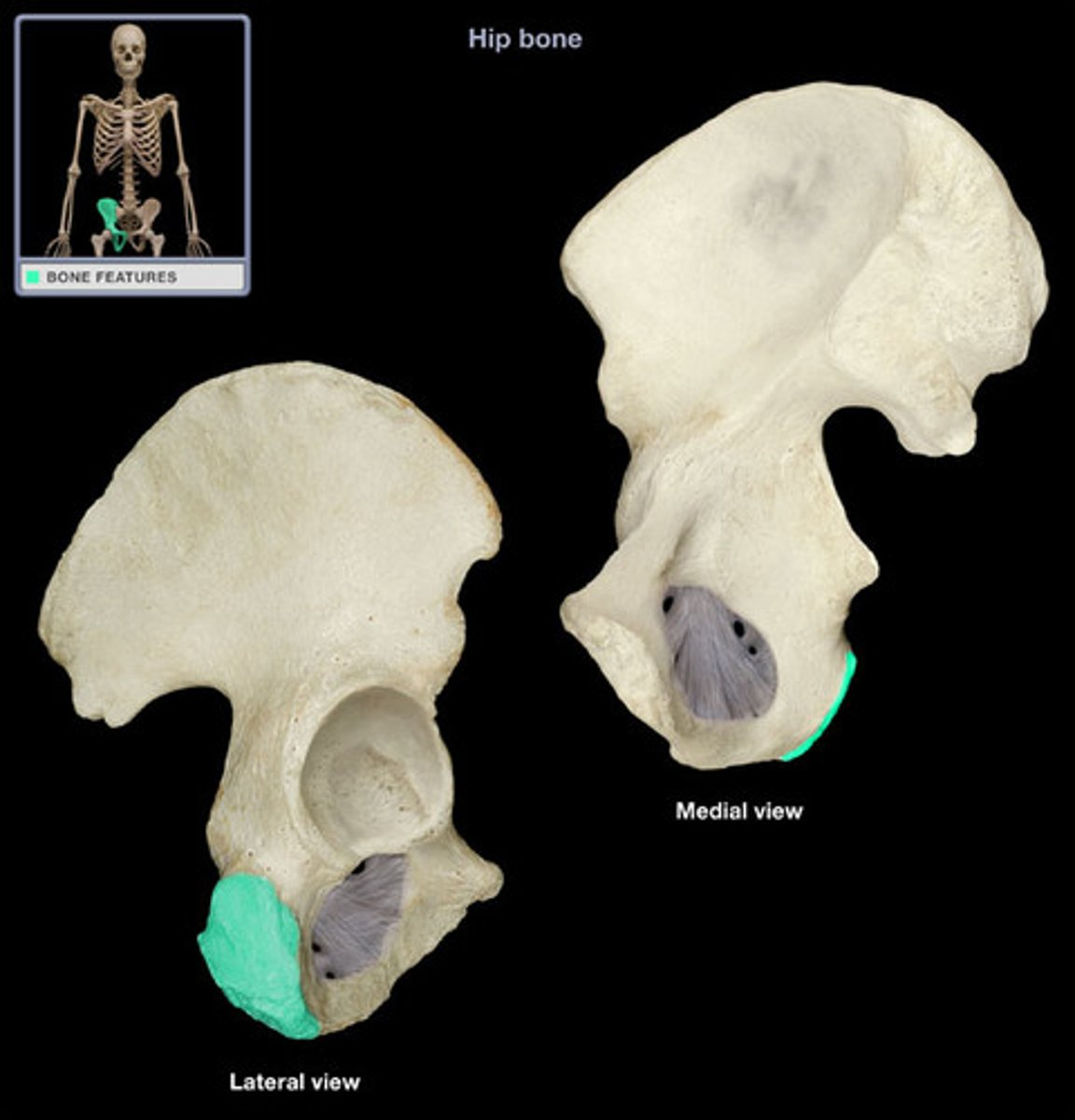
ischial tuberosity
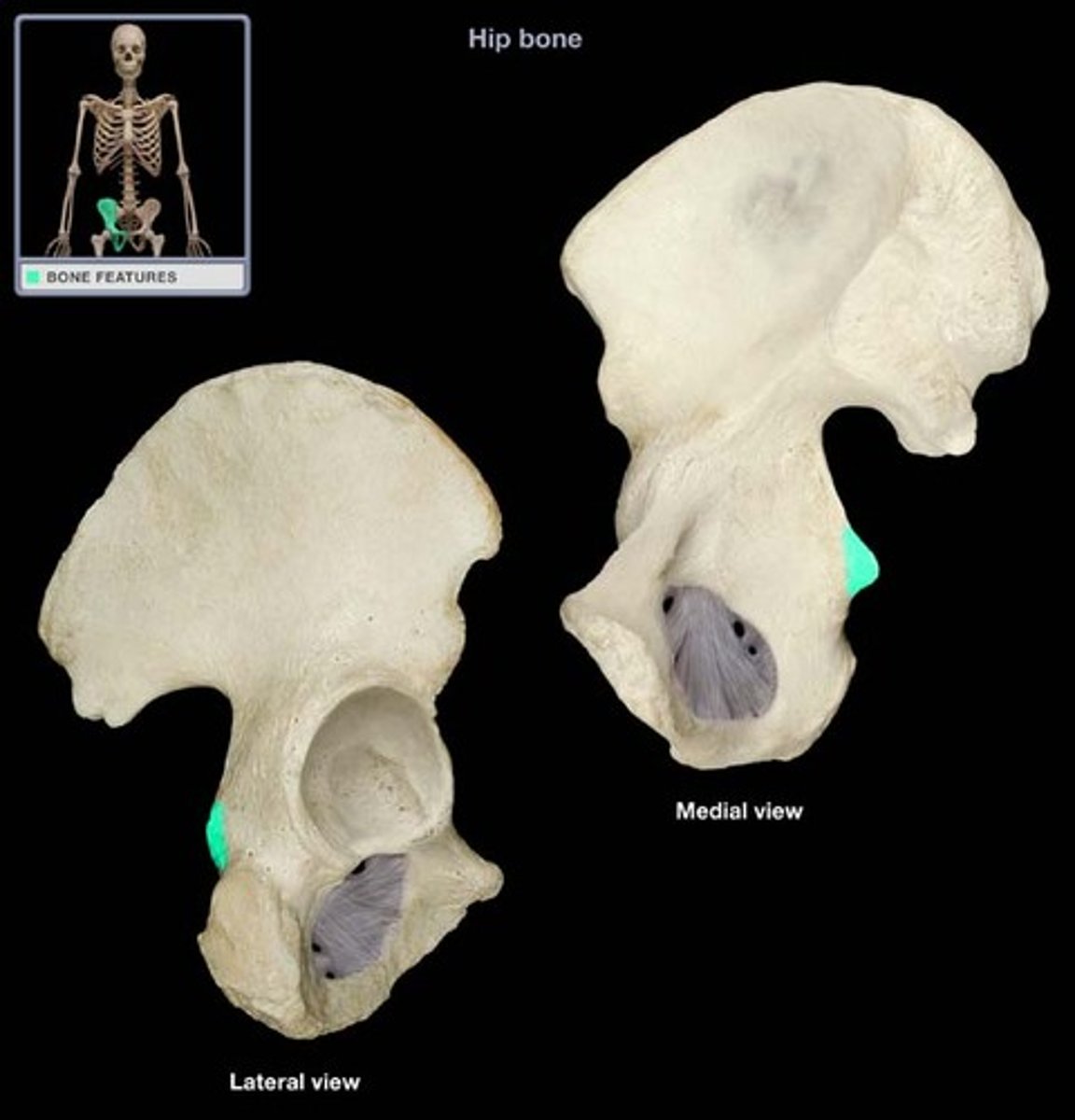
ischial spine
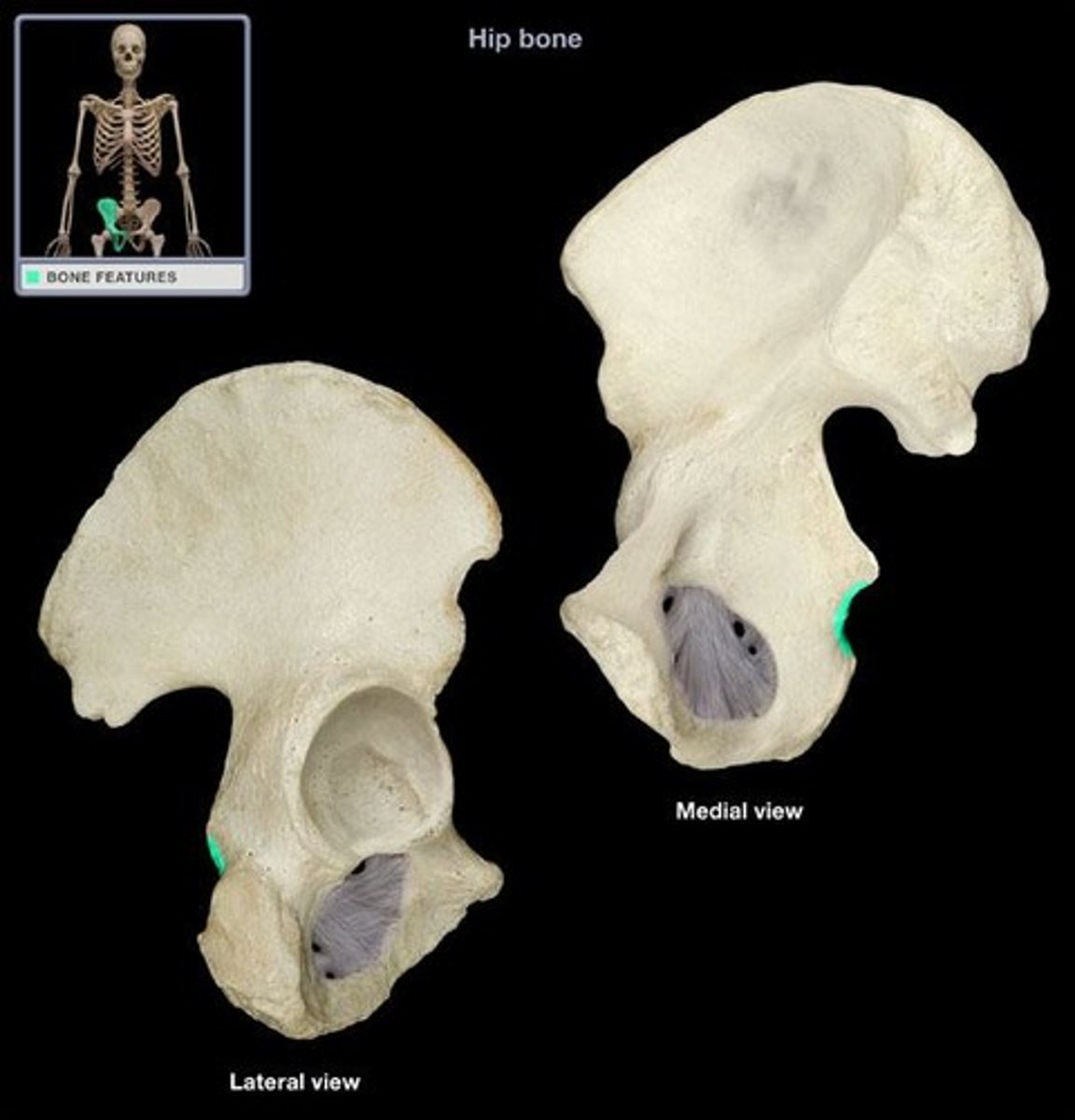
lesser sciatic notch
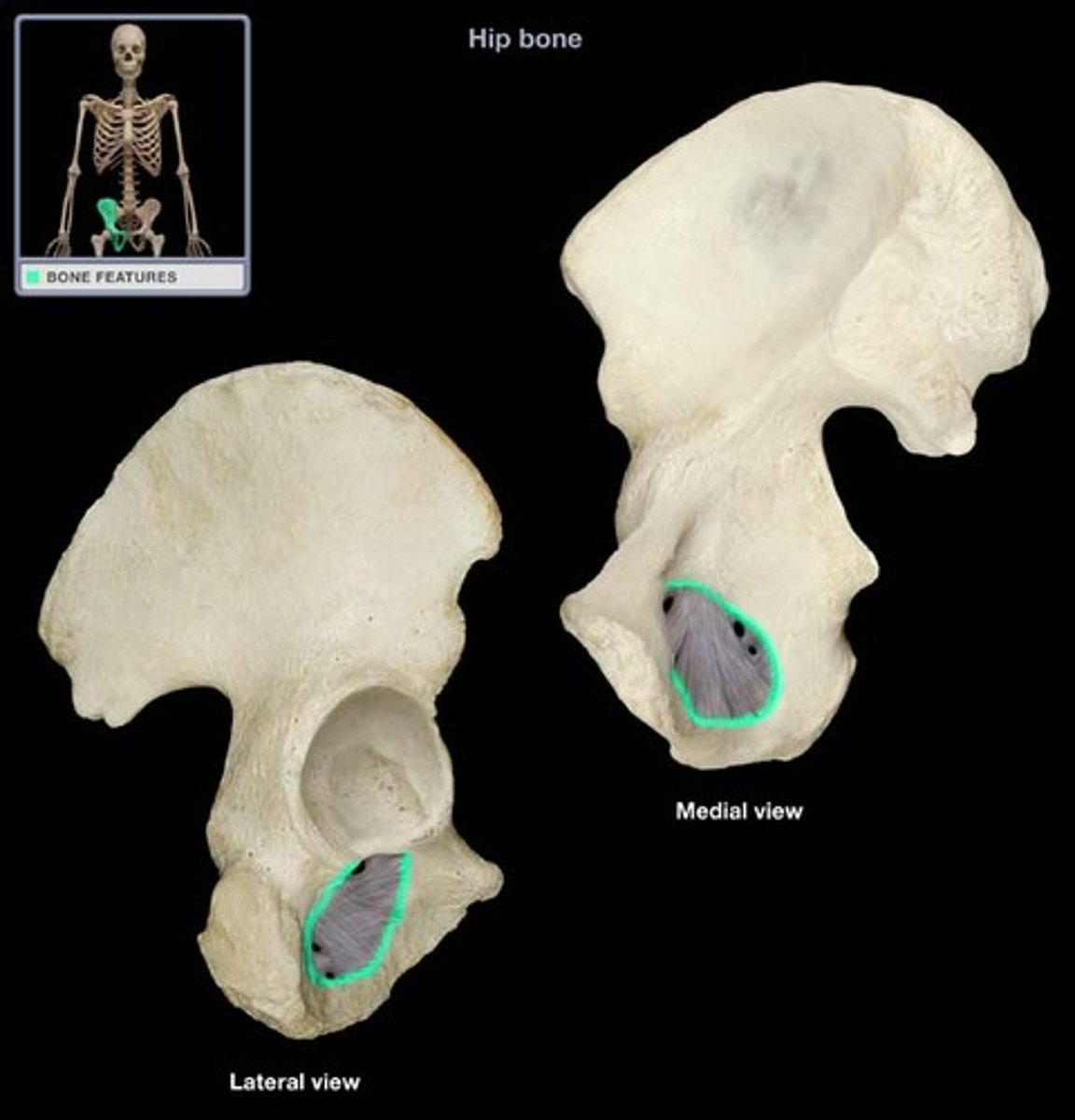
obturator foramen
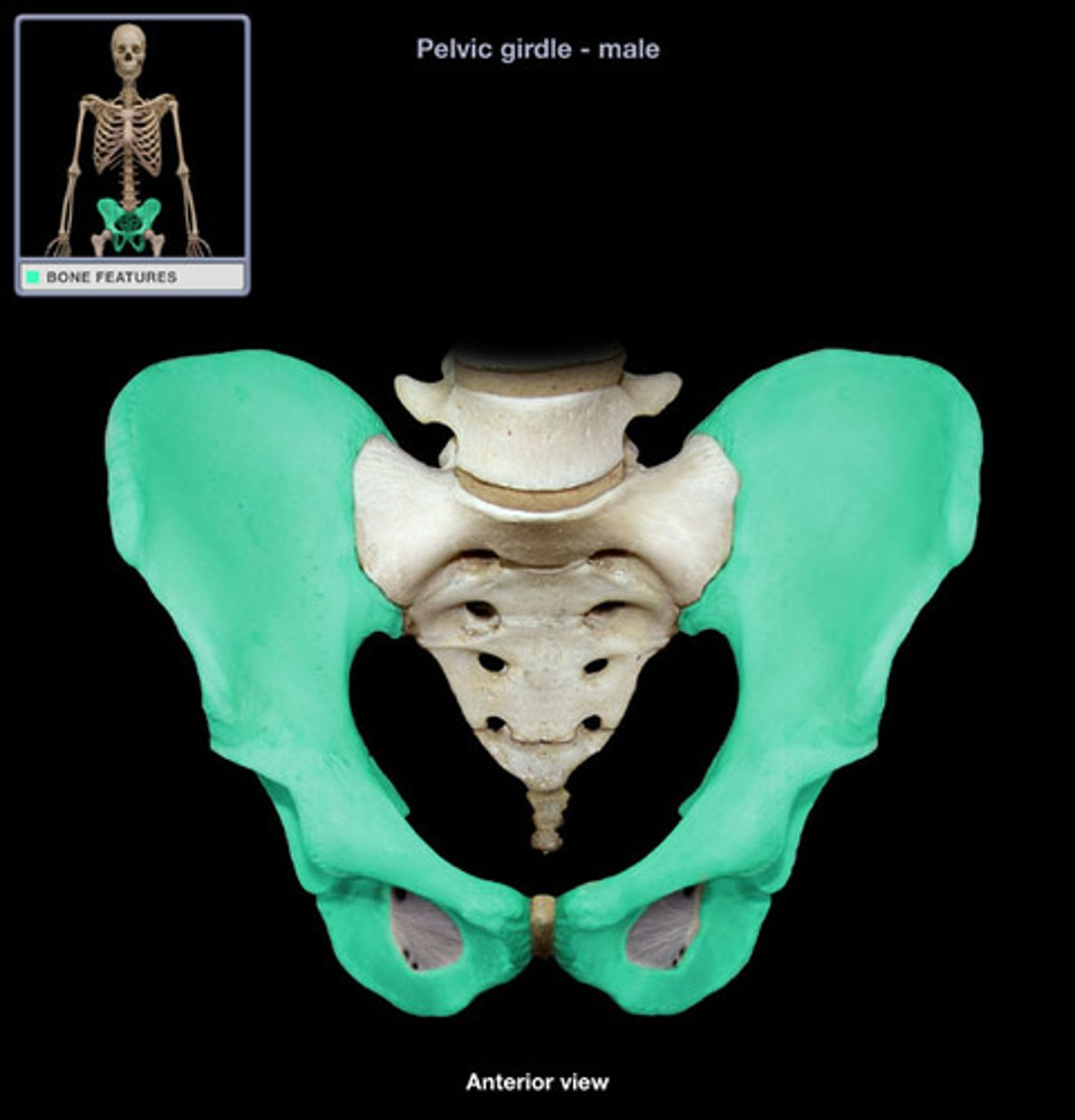
ossa coxae
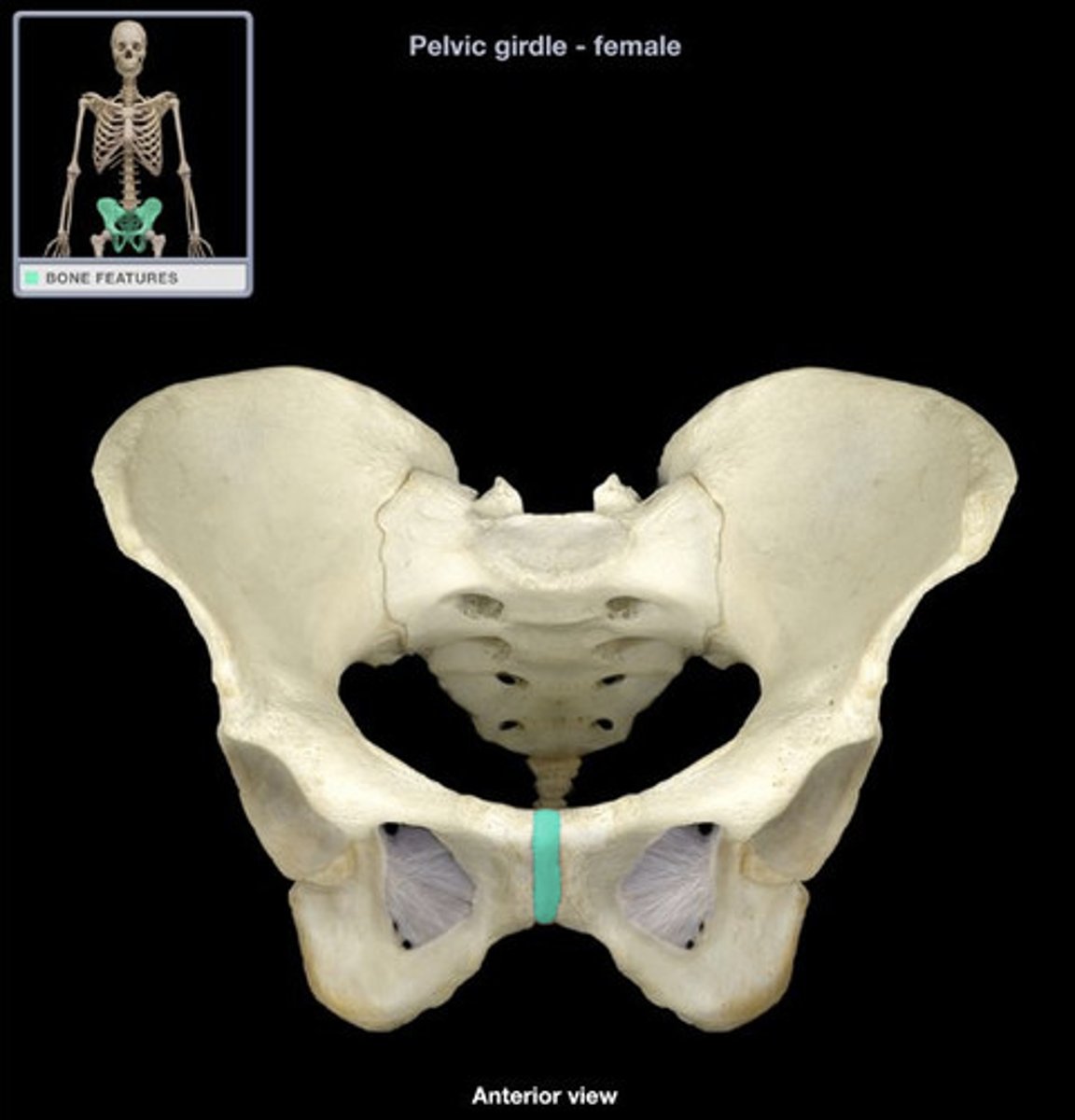
pubic symphysis
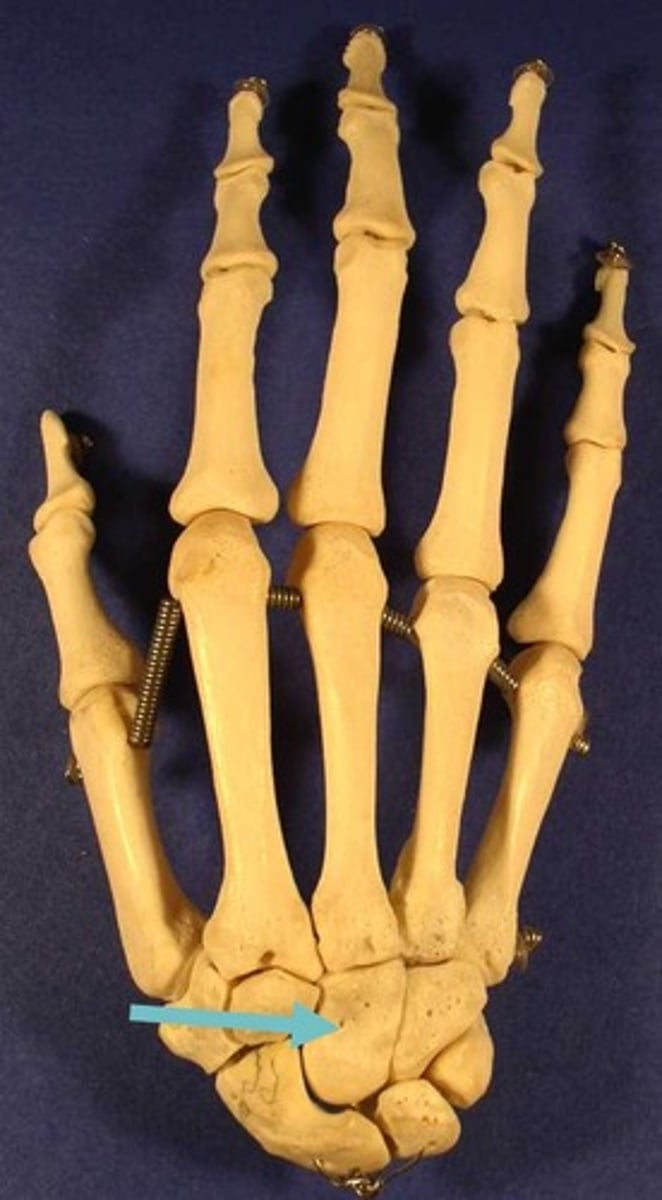
capitate
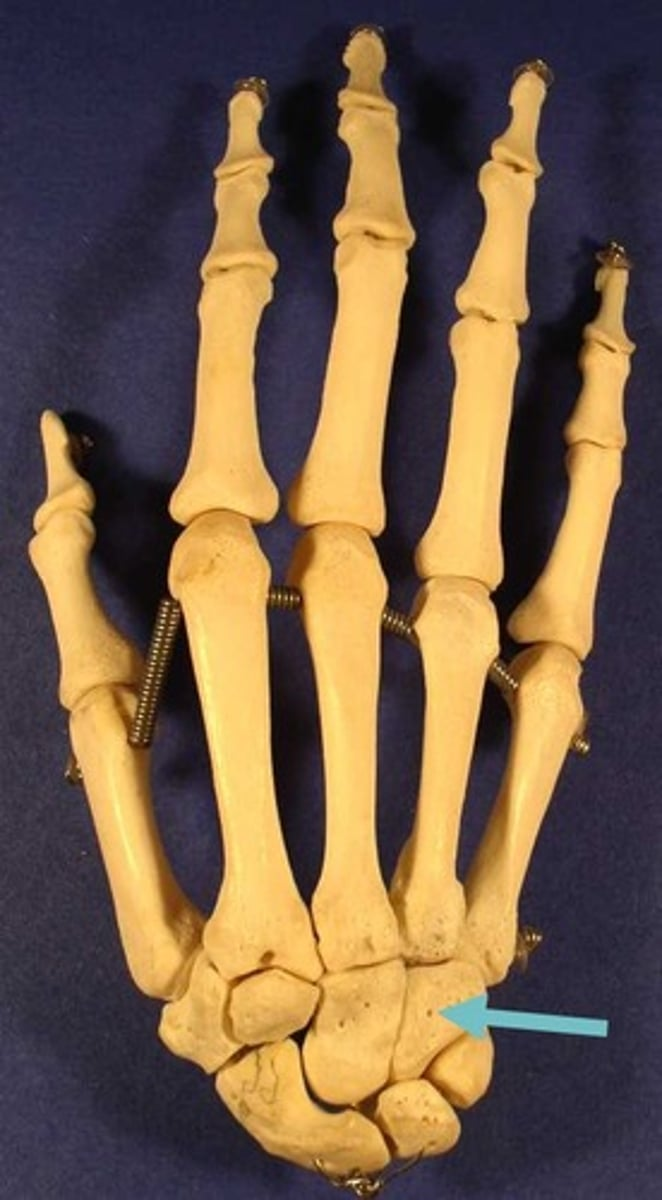
hamate
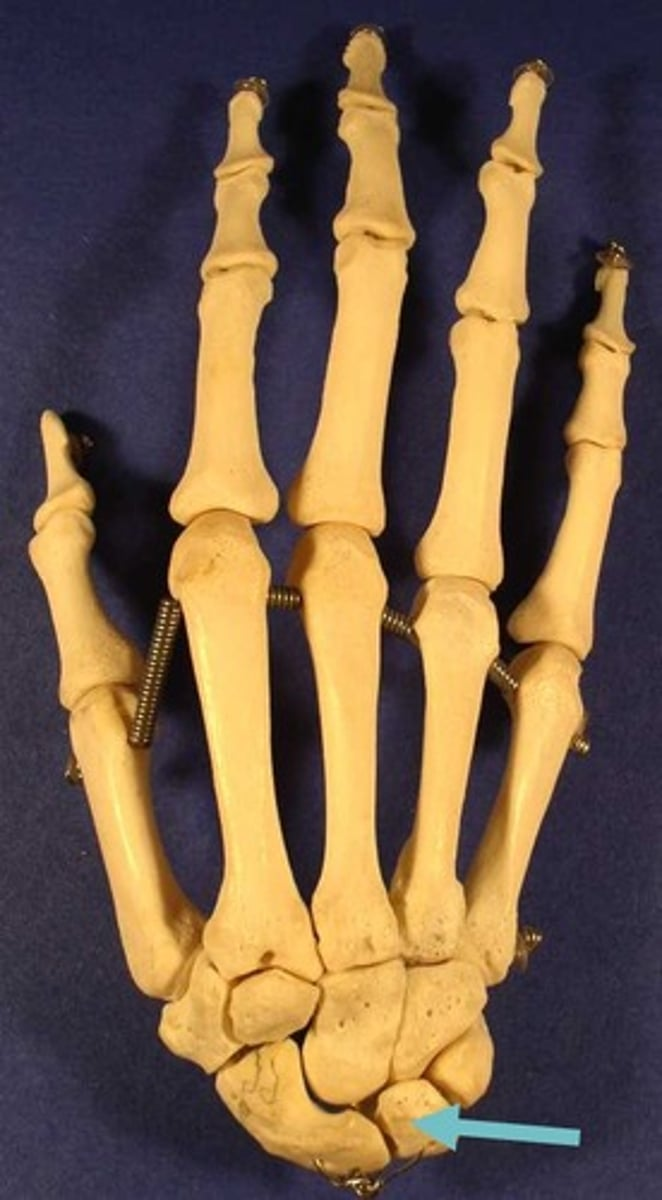
lunate
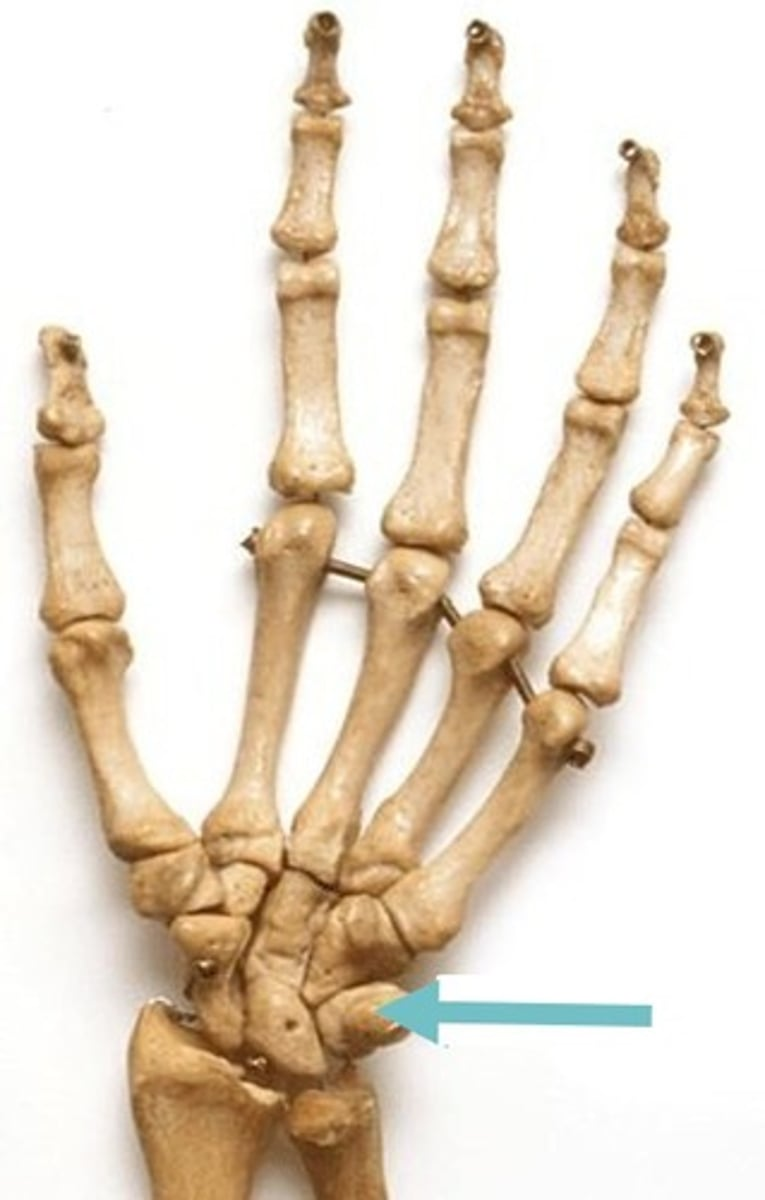
pisiform
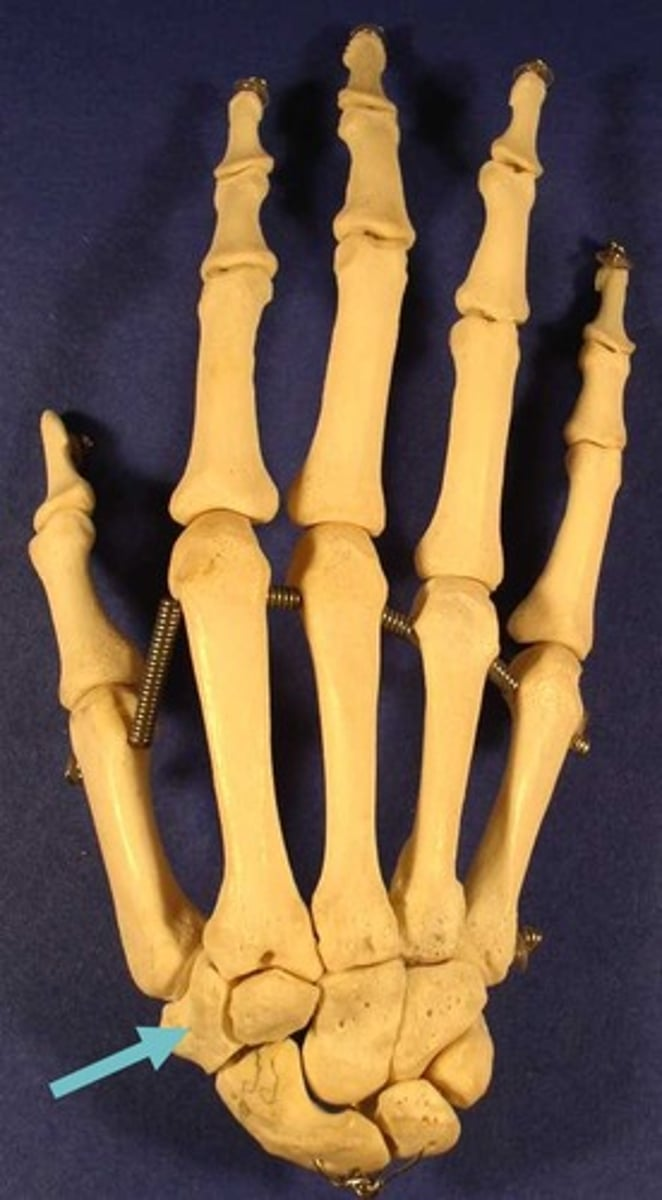
trapezium
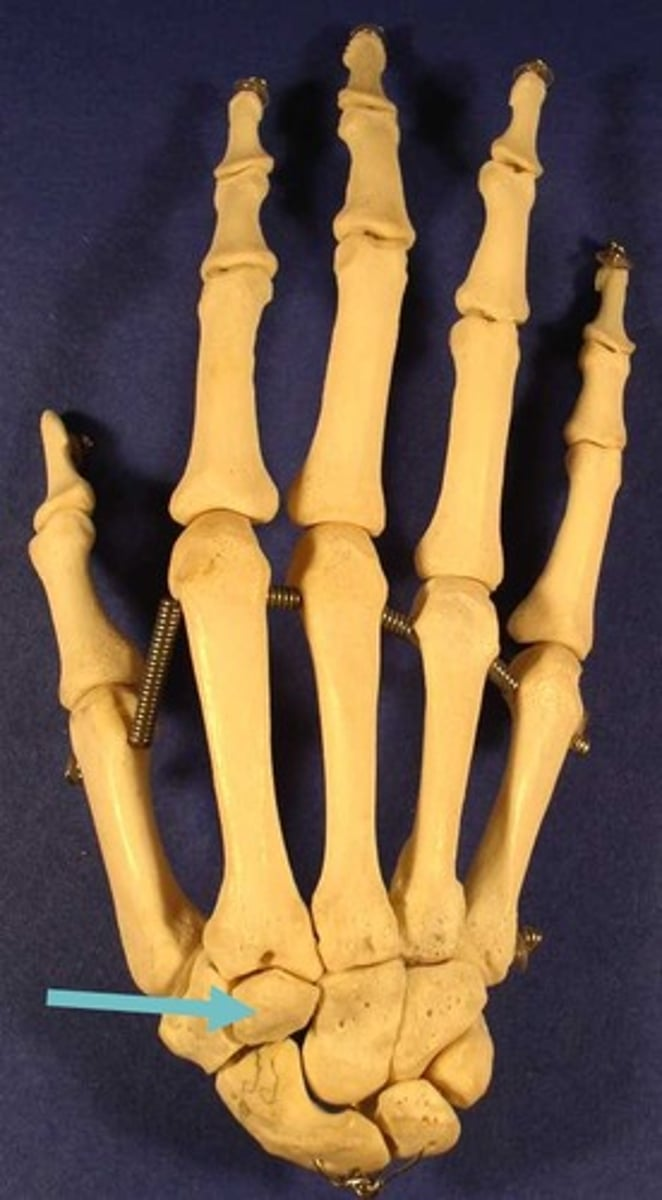
trapezoid
triquetrum
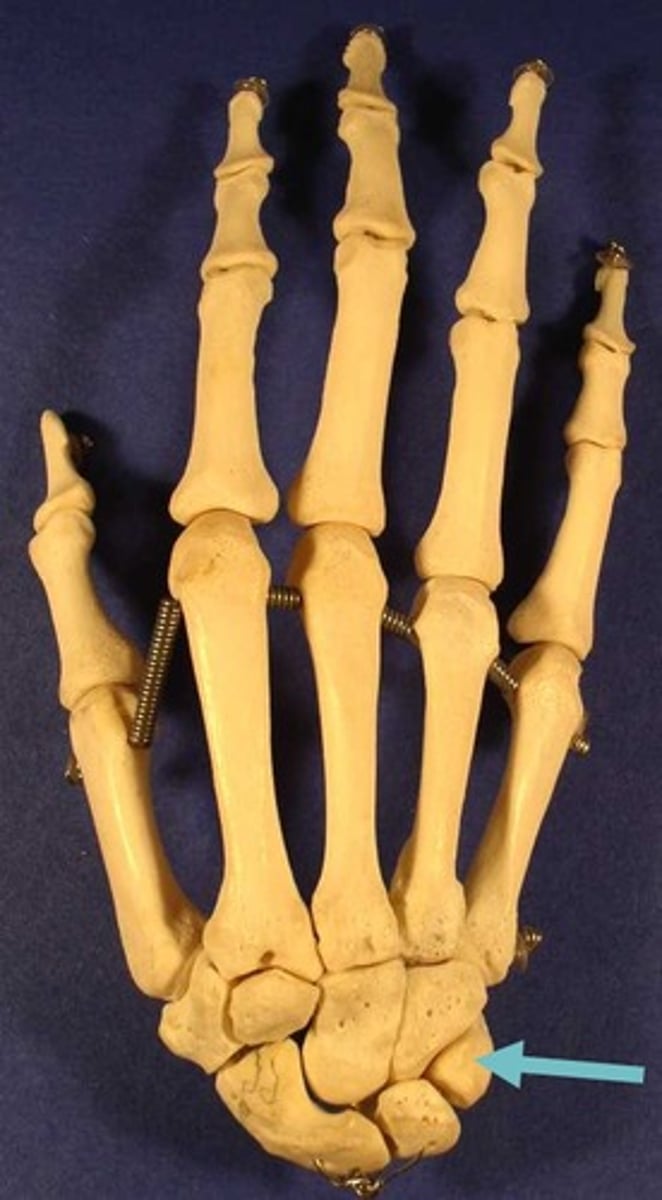
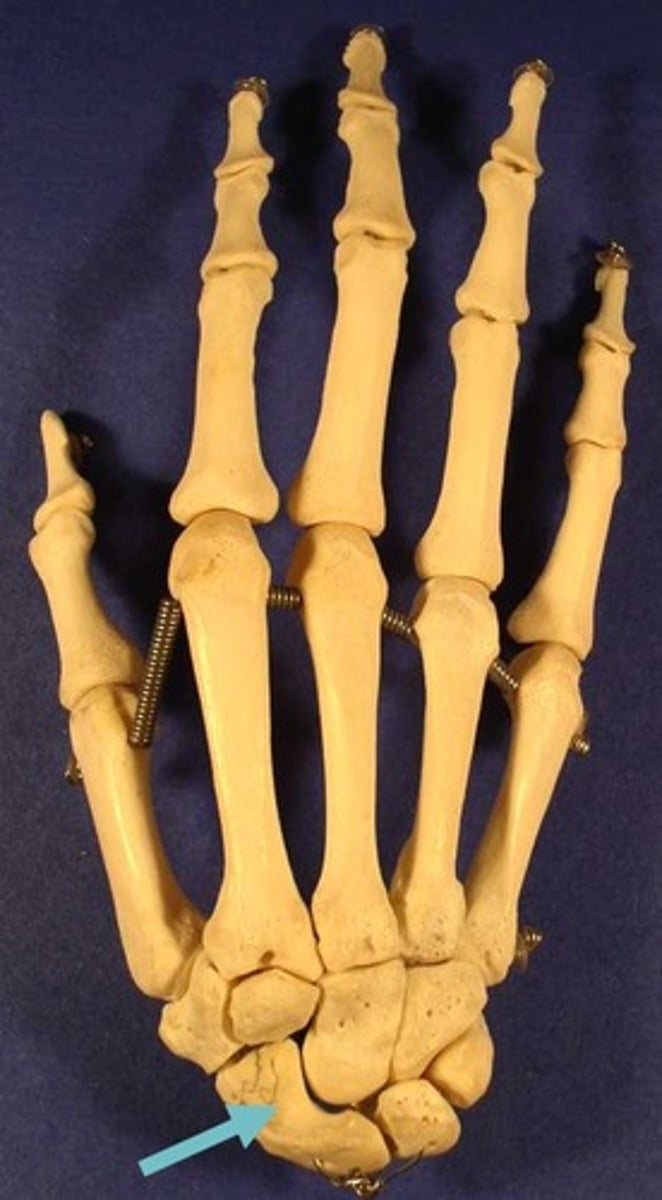
scaphoid
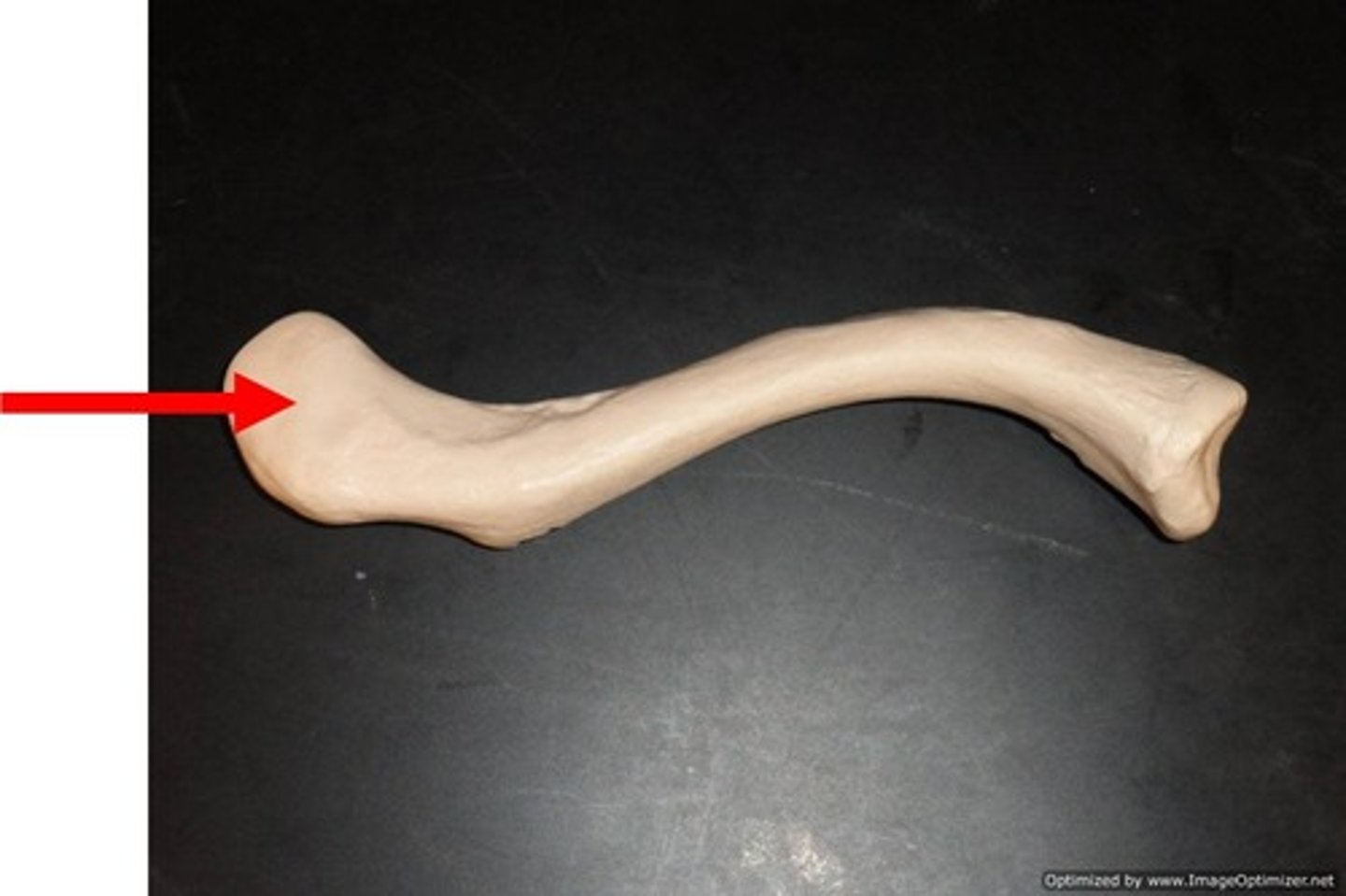
acromial end of clavicle
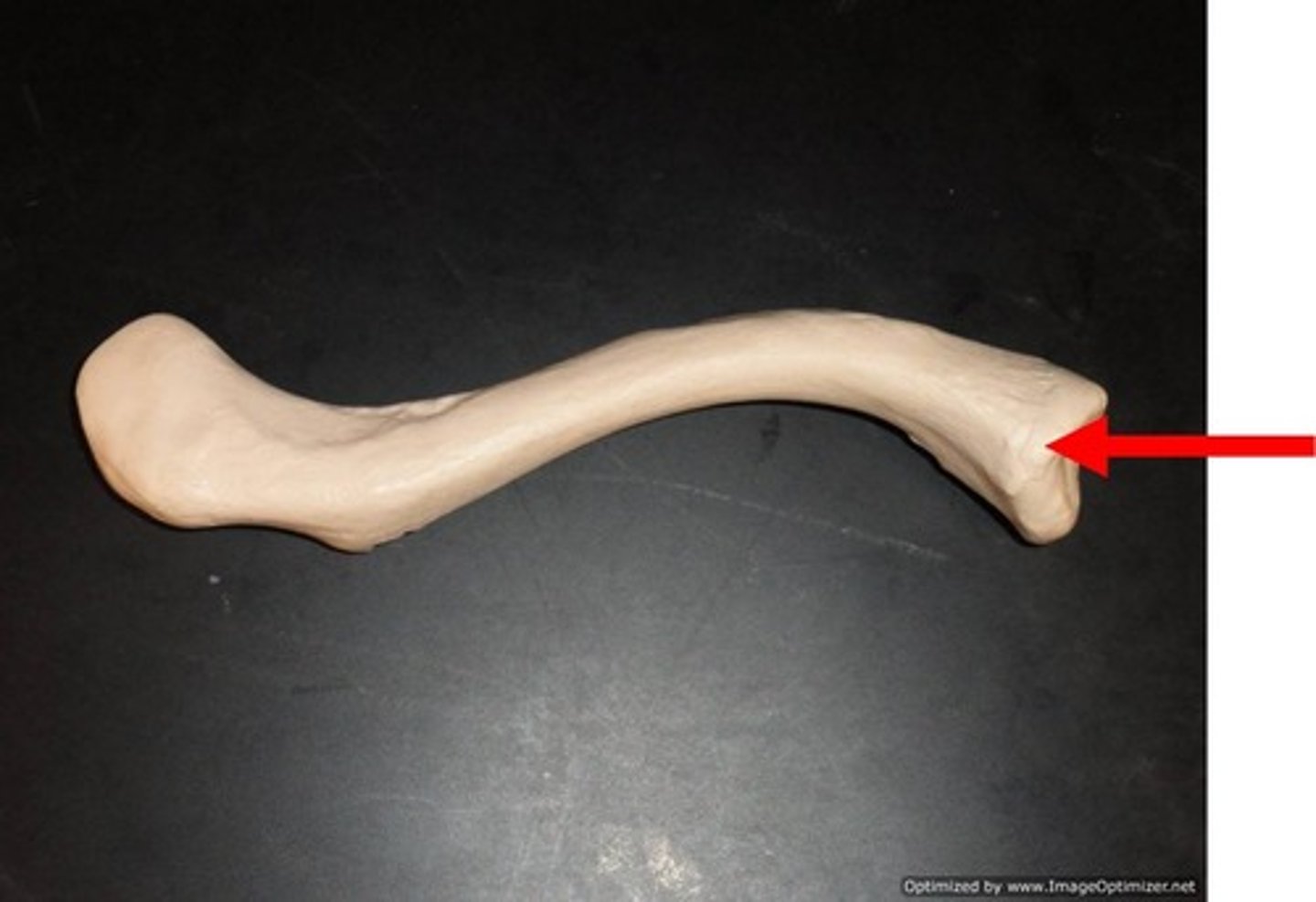
sternal end of clavicle
distal phalanx of foot
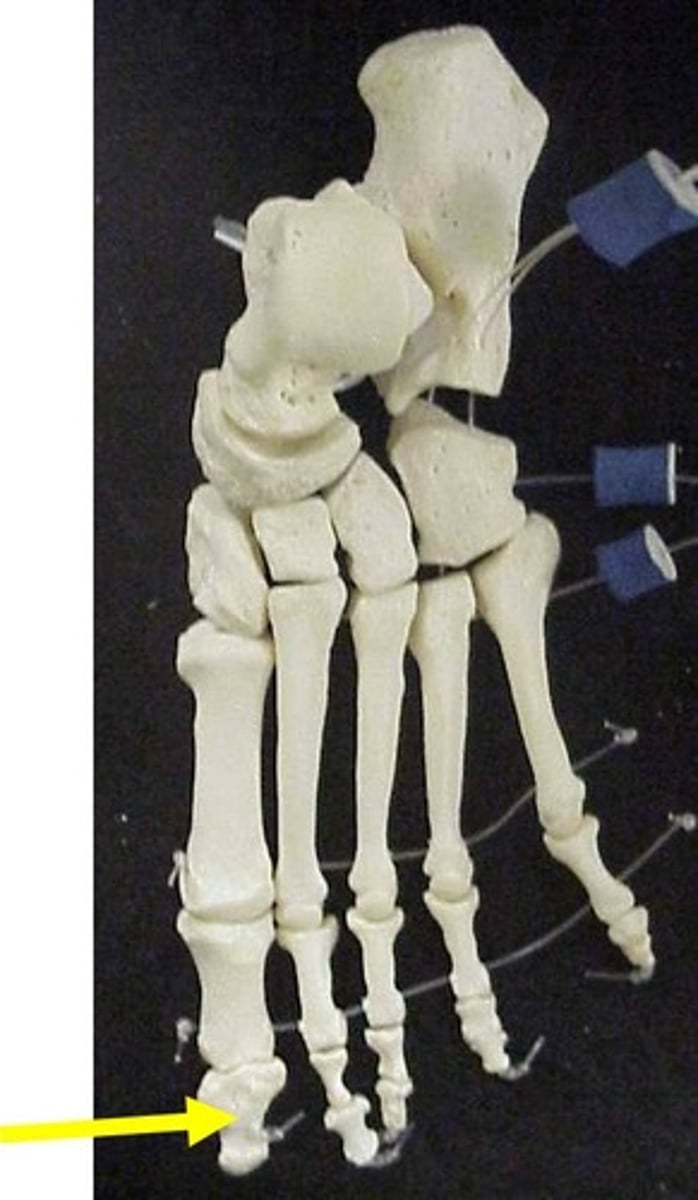
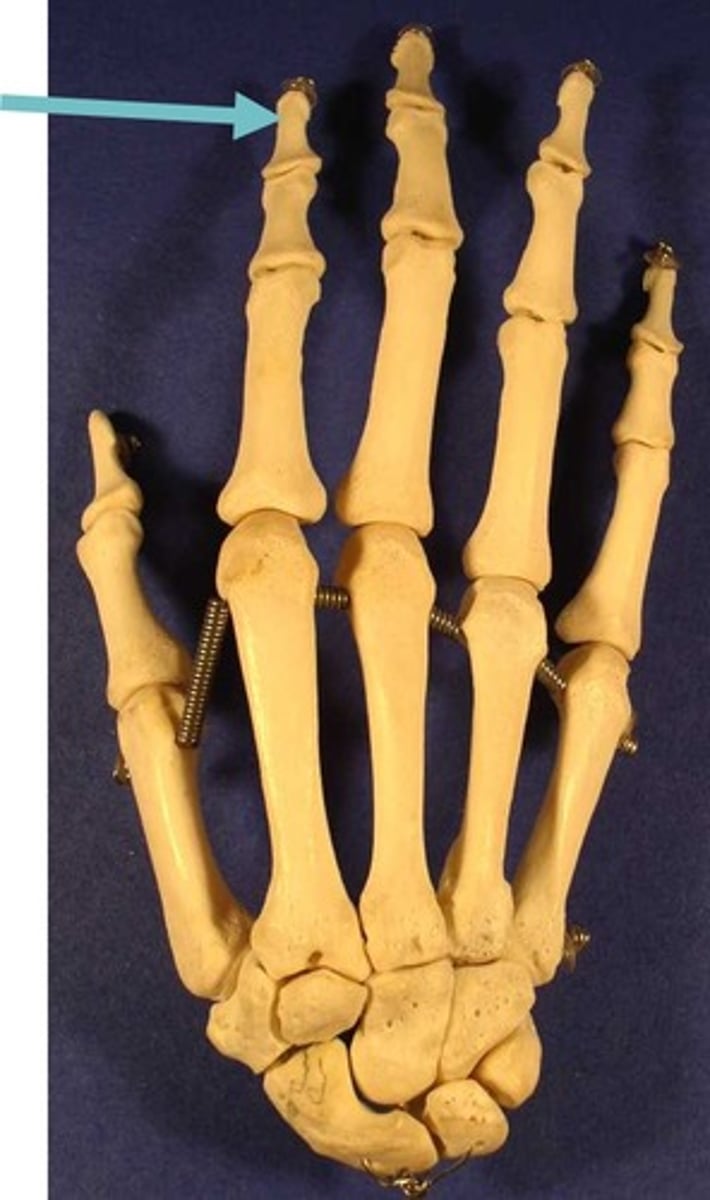
distal phalanx of hand
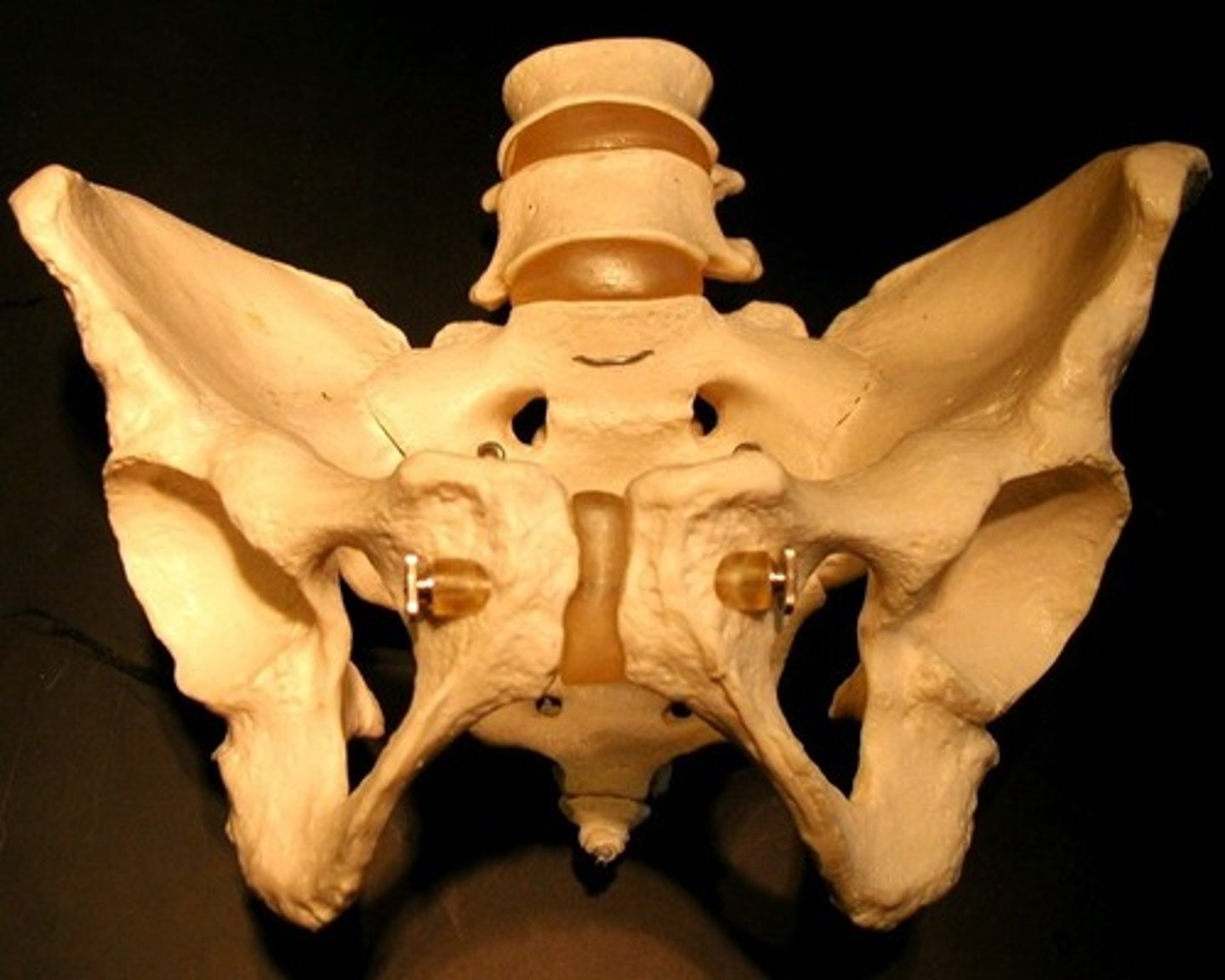
Identify the sex of this pelvis
female
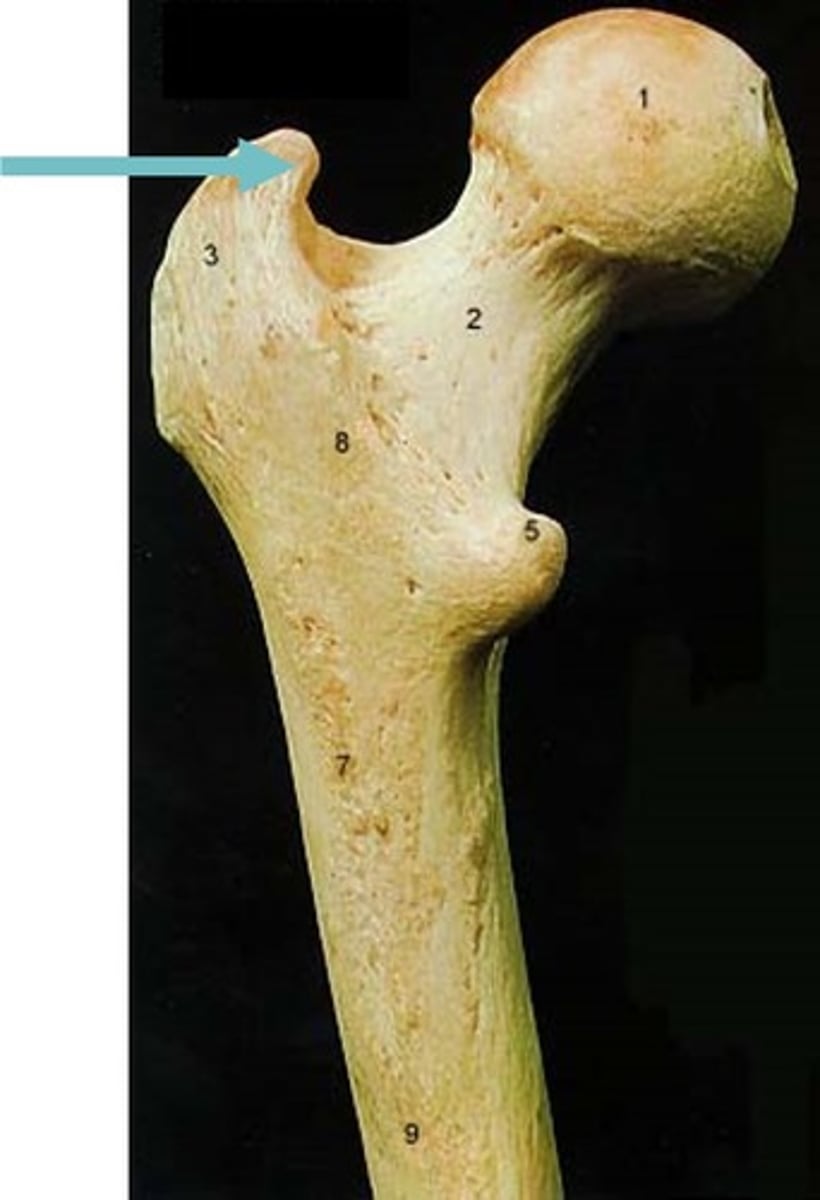
greater trochanter of femur
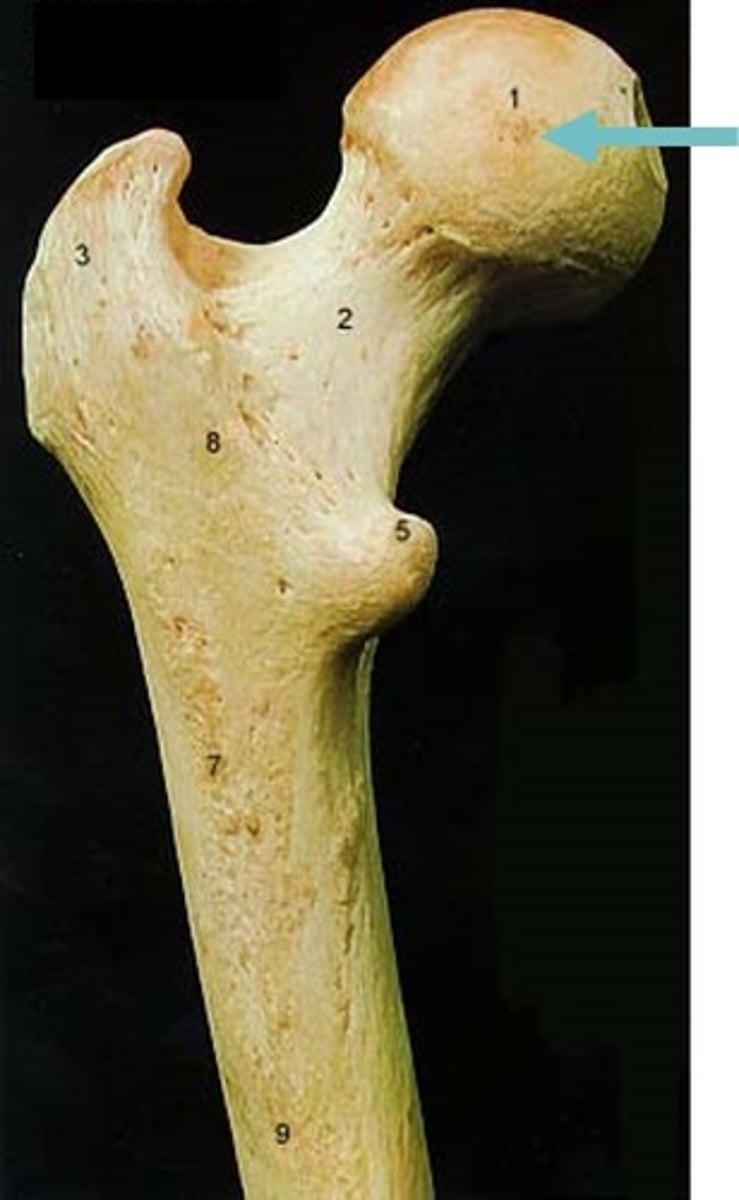
head of femur
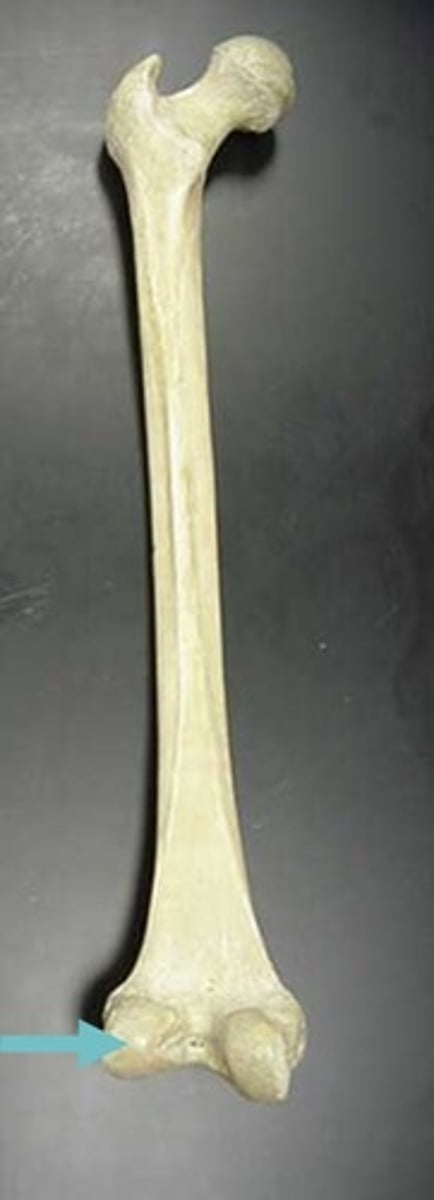

lateral condyle of femur
