A Level CIE Biology: 18 Classification, Biodiversity & Conservation
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
species (biological species concept)
a group or organisms with similar morphological and physiological features that able to breed together and produce fertile offspring
biological species concept
reliant on determining whether inbreeding produces fertile offspring - difficult and time consuming to determine in practice. other discriminating factors that scientists can use to group similar orgs together
morphological species concept
scientists described by physical features and group together orgs that share many physical features that distinguish them from other species.
ecological species concept
when there’s a population of similar orgs living in same area at the same time, they can be described as an ecological species
taxonomy
practice of biological classification involving placing orgs into series of categories/taxa to make it easier to see evolutionary relationshisp between orgs.
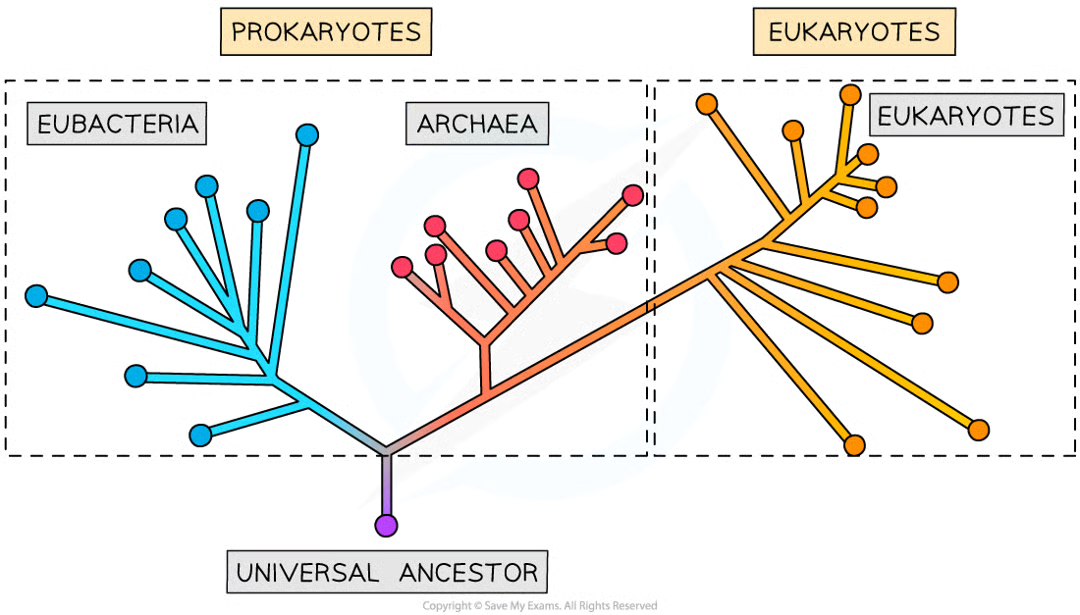
domain
highest rank of hierarchical classification
cell types (major) role in classification of orgs into the 3 domains
prok cells easily distinguishable in that they lack a nucleus
euk cells have compartmentalised structures, w at least their genetic material segregated from rest of cell in a nucleus
prok are divided into 2 separate groups based on molecular analysis of rna genes proving cell type insufficient classification
3 domains:
archaea (prok)
bacteria (prok)
eukarya (euk)
archaea features 9
single-celled/unicellular orgs
sometimes extremophile prokaryotes (live in extreme environments but not all)
no nucleus
not bacteria bc: 3
unique lipids in membranes of cells
no peptidoglycan in cell walls
ribosomal structure (particularly that of small subunit) more similar to euk ribosome than bac
similar size range
dna transcription similar to euk
e.g. haloboacterium salinarium (dead sea)
bacteria features 5
single-celled/unicellular
prok no nucleus
vary in size over wide range (smallest are bigger than alrgest known viruses and largest smaller than singlecelled euk
divide by binary fission
e.g. streptococcus pneumoniae
eukarya features
orgs w euk cells w nuclei and memb-bound organelles placed in this domain
vary massively in size from single-celled orgs several micrometres across to large multicellular orgs many metres in size e.g. blue whales
euk cells diivde by mitosis
euks can reprod sexually or asexually
e.g. canis lupus

3 main diffs between archaea and bacteria
membrane lipids
ribosomal rna
cell wall composition
membrane lipid differences 3
archaras are completely unique, memb lipids consist of brancched hydrocarbon chains bonded to glycerol by ether linkages
memb lipids of bacteria unbranched hydrocarbon chains bonded to glycerol by ester linkages
not in bacterial or euk cells
ribosomal rna differences 4
both archaea and bacteria posses 70s ribosomes
70s ribs in archaea possess a smaller subunit similar to subunit in euk rib than sub in bac
base sequences of ribosomal rna in archae more similar to rRNA of eukarya
prim structure of ribosome proteins in archae more sim to ribosome proteins in eukarya than bacteria
composition of cell walls differences
bacteria always peptidoglycan
archaea always cell walls but not peptidoglycan
archaea: cell type, chromosome, cell memb lip, ribosome, cell walls, histones, introns
prok
circular
glycerol - ether lipids
70s ribs but small subunit more similar to euk ribs
always present w/o peptidoglycan
yes
sometimes
bacteria: cell type, chromosome, cell memb lip, ribosome, cell walls, histones, introns
prok
circ
glycerol - ester lipids
70s ribs
always present w peptidoglycan
no
rarely
euk: cell type, chromosome, cell memb lip, ribosome, cell walls, histones, introns
euk
linear chromosomes + circular mtDNA and cpDNA
glycerol - ester lipids
large 80s ribosomes in cytosol and 70s ribosomes in mitoch and chloro
sometimes present w/o peptidoglycan
yes
yes
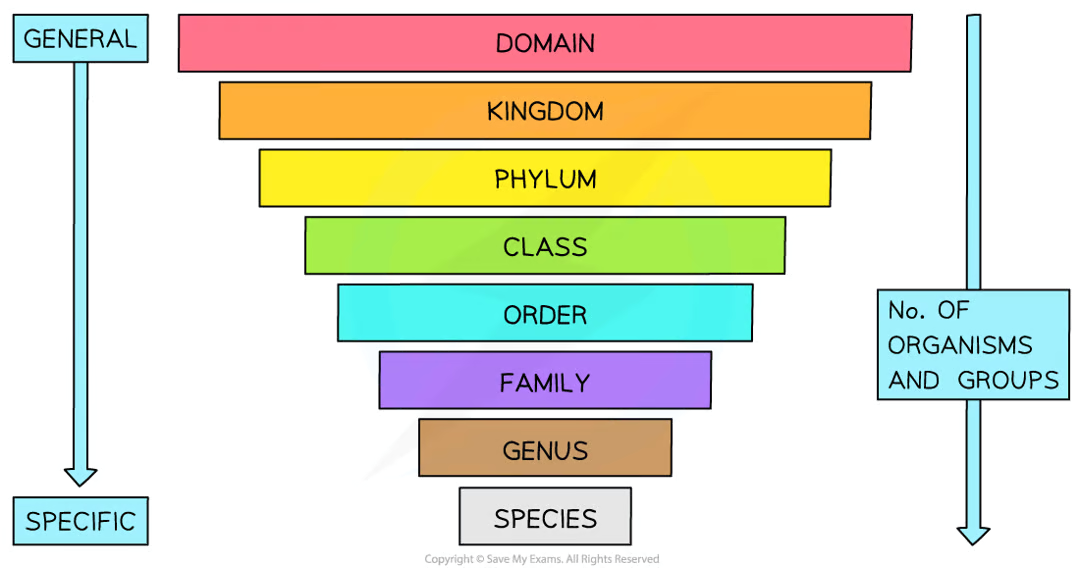
hierarchical classification system of organisms
used to organise and group similar organisms together so that evolutionary relationships between orgs more easily understood
7 taxonomic ranks (domain highest, species lowest)
similar species grouped in genus
similar genuses grouped in family
similar fams grouped in order
similar orders grouped into class
similar classes grouped into phylum
similar phyla can be grouped into kingdom
similar kingdoms can be grouped into domain
KINGS PLAY CHESS ON FANCY GOLD SQUARES