physics - topic 1: matter
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What was John Dalton’s theory at the start of the 19th Century?
Atoms were ‘solid spheres’.
What was Thomson’s model called, and what did he conclude?
Plum Pudding Model: An atom contains smaller, negatively charged particles — electrons — distributed like a charged ‘soup’
What infamous experiment did Ernest Rutherford conduct and what did it conclude?
The Gold Foil Experiment: They were expecting the particles to pass through, although even though some went straight through, some were deflected at large angles. This concludes that there must be a positively charged nucleus at the centre, surrounded by a ‘cloud’ of electrons. He also concluded that most of the atom is empty space.
What did Rutherford’s model look like?

Who collaborated with Rutherford during the Gold Foil experiment?
Geiger and Marsden.
What did Neils Bohr propose?
Neils Bohr proposed that electrons orbit the nucleus in shells.
What did Bohr’s model look like?
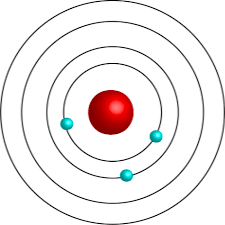
What is found in a nucleus?
Protons and neutrons.
What is the charge and relative mass of a proton, neutron, and electron?
Charge:
Proton: +1
Neutron: 0
Electron: -1
Relative Mass:
Proton: 1
Neutron: 1
Electron: 1/2000
What is the typical size of an atom?
1×10-10 metres
What is the typical size of an nucleus?
1×10-15 metres
What is the equation for density?
Density = Mass/Volume
What state of matter has the highest density?
Solid - Particles are closer together.
Typically liquids have a lower density than solids, but what’s the one exception?
Ice: Ice is less dense than water (solid is less dense than liquid).
Mass is ____ during a reaction.
Conserved.
What are some examples of a change of physical state?
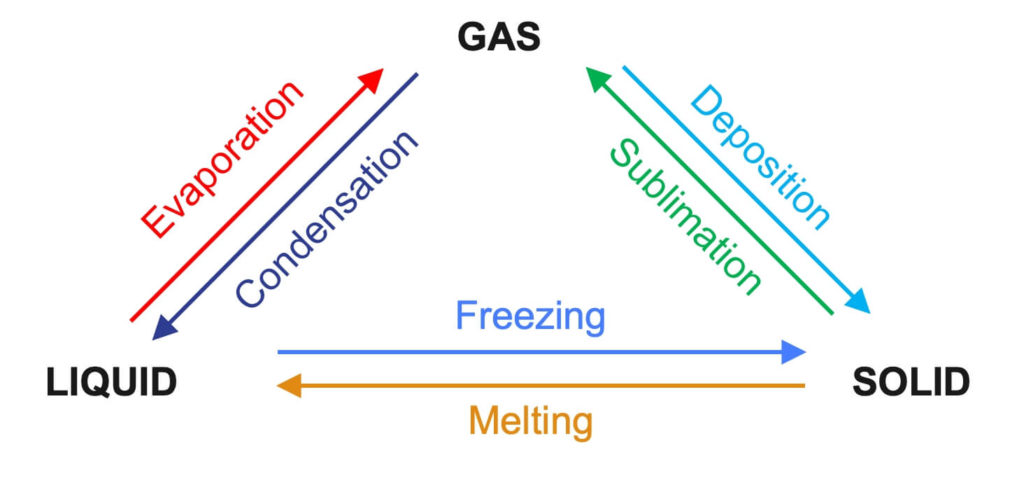
What is the difference between heat and temperature?
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of particles, while heat is a form of energy.
Temperature is measured on a relative scale, while heat is measured on an absolute scale.
What are 2 outcomes when a substance gains heat energy?
It could raise in temperature, but remain the same state.
It could remain the same temperature, but change state.
What is specific heat capacity?
The amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1 degree Celsius.
What is the symbol for specific heat capacity?
(c)
What is the formula —including SHC— for energy?
E = mcΔT
Where:
E = Energy (J)
m = Mass (kg)
c = Specific Heat Capacity
ΔT = Change in Temperature (°C)
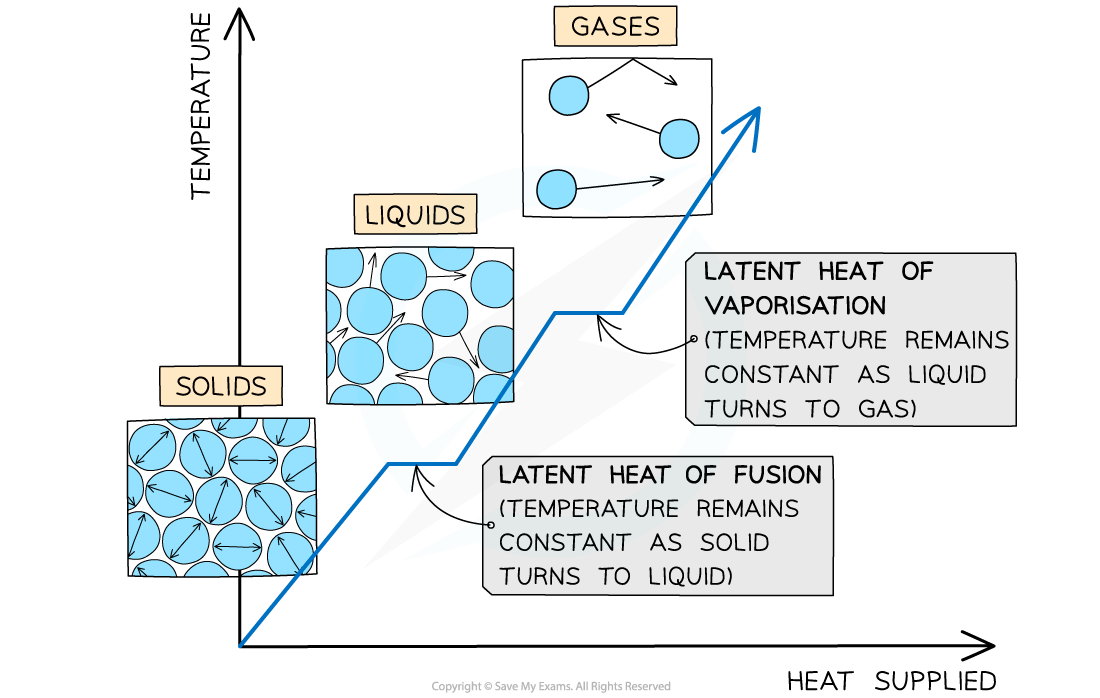
What is specific latent heat?
The amount of energy required to change the state of 1kg of a substance, without changing its temperature.
What is the symbol for specific latent heat?
(L)
What is the formula —including SLH— for energy?
E = mL
Where:
E = Energy (J)
m = Mass (kg)
L = Specific latent Heat (J/kg)
What is latent heat of fusion and vaporisation?
What is the formula for pressure?
Pressure = Force/Area
What is the formula for work done?
WD = Force × Distance
OR
WD = Pressure × Volume
The atmosphere is assumed to have ___ density.
Uniform density. (This means the Earth’s atmosphere is all the same temperature)
Atmospheric pressure ____ as the altitude above Earth’s surface increases.
Decreases. (With higher altitude, there’s less molecules in the air, decreasing weight and therefore pressure)
Why do some objects float?
An object will float if it’s weight is less than the fluid’s weight.
What is the equation for pressure due to a column of liquid?
Pressure = Height of column × Density of liquid × g
P = hρg
g= gravitational acceleration (10)