Characteristics of Life & Biochemistry: Cell Structure, Chemical Compounds, and pH
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Science
We use science to answer questions we have about our world.
Biology
The study of life and the places and processes that support it.

Living things
All living things are made of cells and have organization.
Cells
The smallest unit of life; can be unicellular or multicellular.
Prokaryotic cells
Cells that do not have a nucleus.
Eukaryotic cells
Cells that have a nucleus.
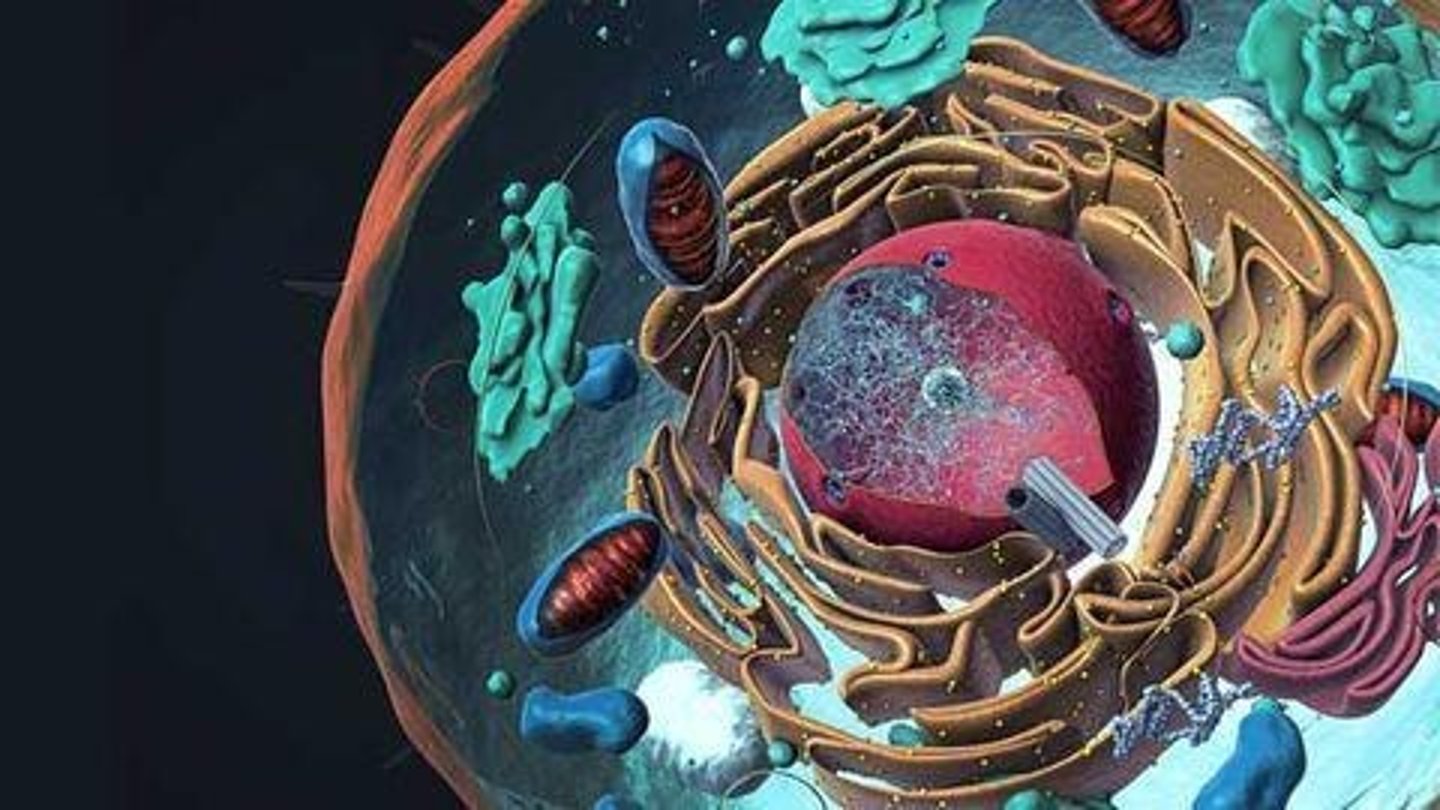
Homeostasis
The ability to maintain stable internal conditions.
Evolution
The capability of living things to change over time.
Universal genetic code
All living things have DNA as their genetic material.
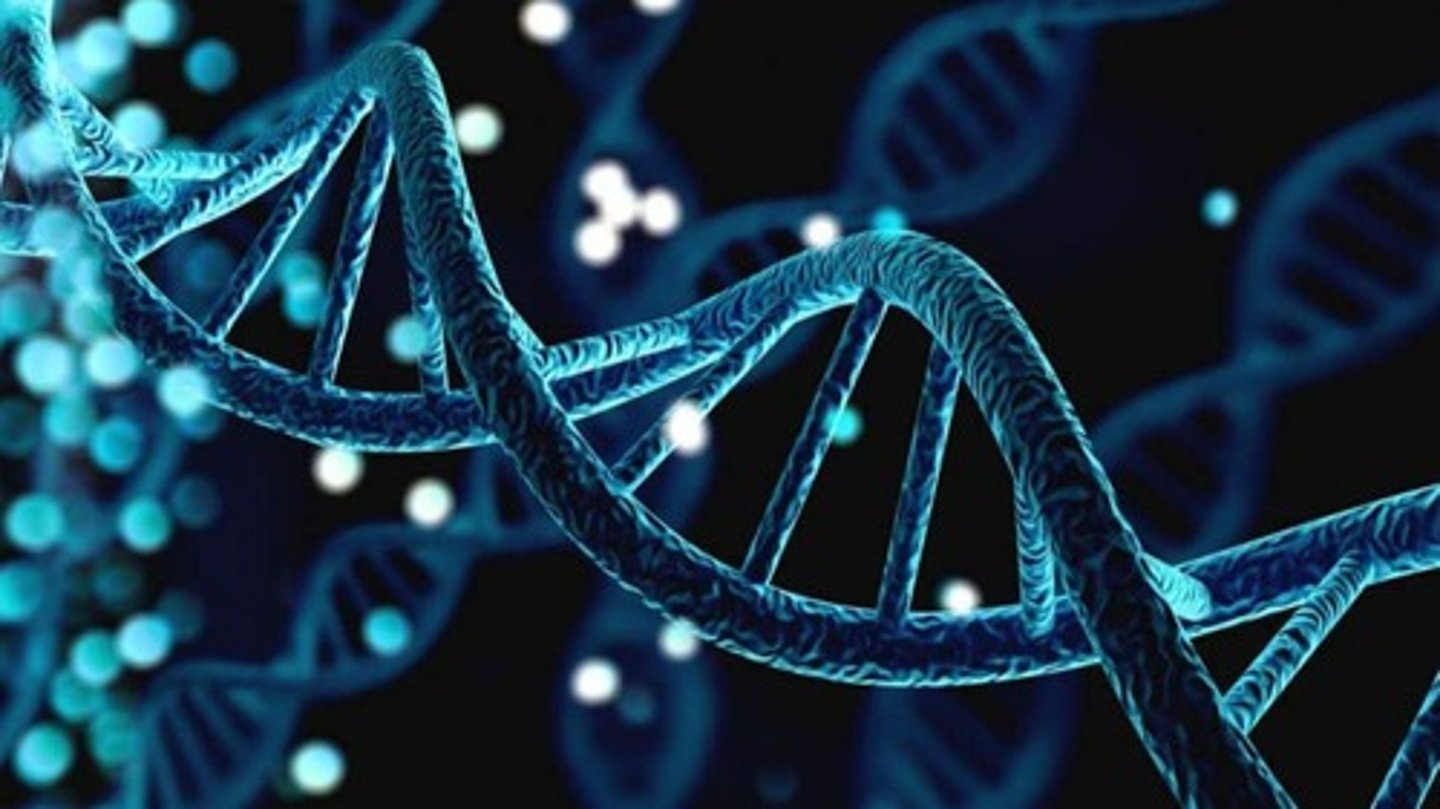

Metabolism
The process of obtaining and using materials and energy.
Autotrophs
Organisms that make their own food.
Heterotrophs
Organisms that consume other living things for food.
Phototropism
The response of plants to light.
Gravitropism
The response of plants to gravity.
Thigmotropism
The response of plants to touch.
Compound
A substance formed by two or more different elements.
Chemical formula
Shows the number of each element in a compound.
Mixture
When 2+ elements or compounds are physically mixed together but not chemically combined.
Suspension
A mixture of water and non-dissolved materials that will separate over time.
Solution
A mixture in which all the components are evenly distributed.
Solute
The substance that is dissolved in a solution.
Solvent
The substance in which the solute dissolves.
Chemical bonds
Atoms in compounds are held together by chemical bonds.
Valence electrons
Electrons that are available to form bonds.
Covalent bonds
Form when electrons are shared between atoms.
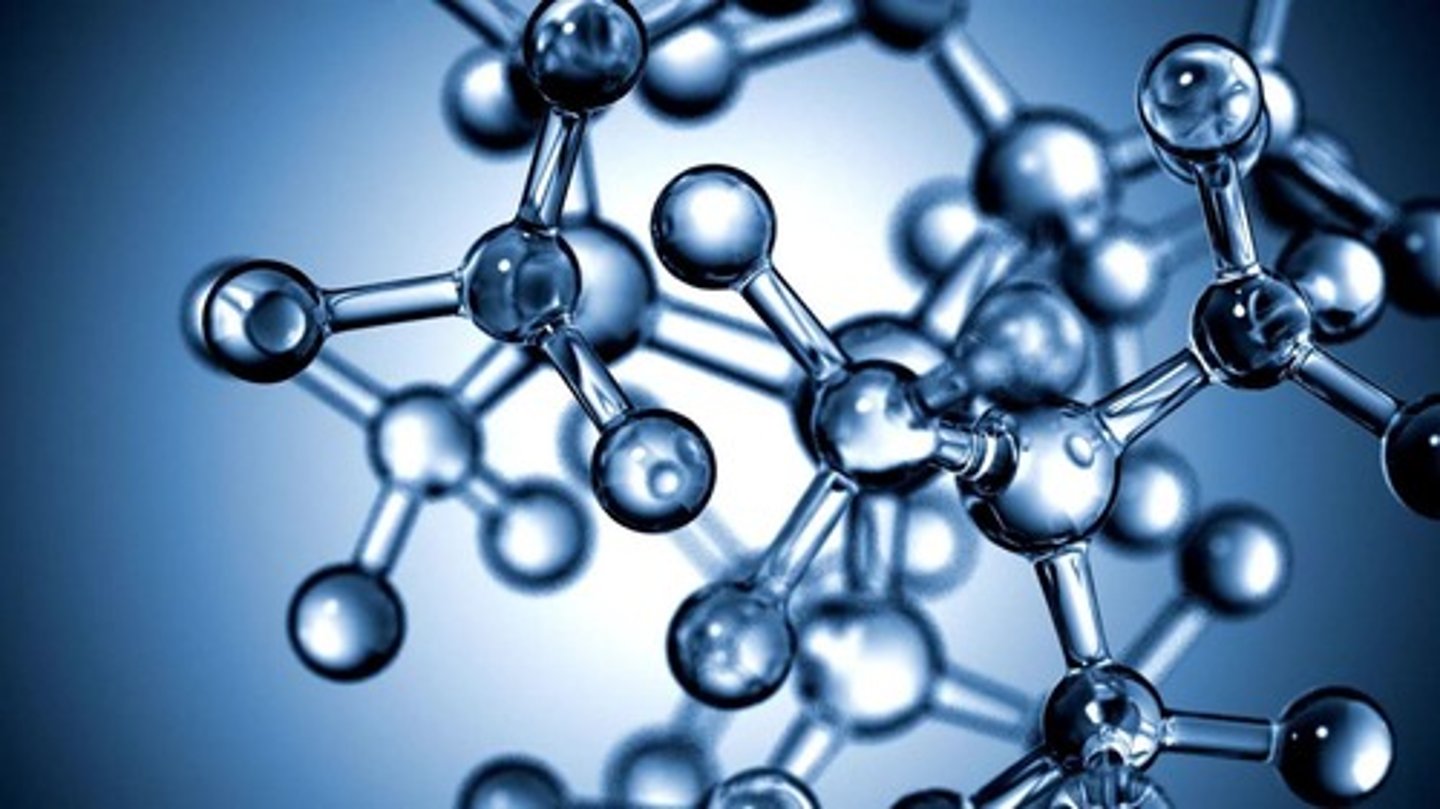

Molecule
When atoms are joined together by a covalent bond.
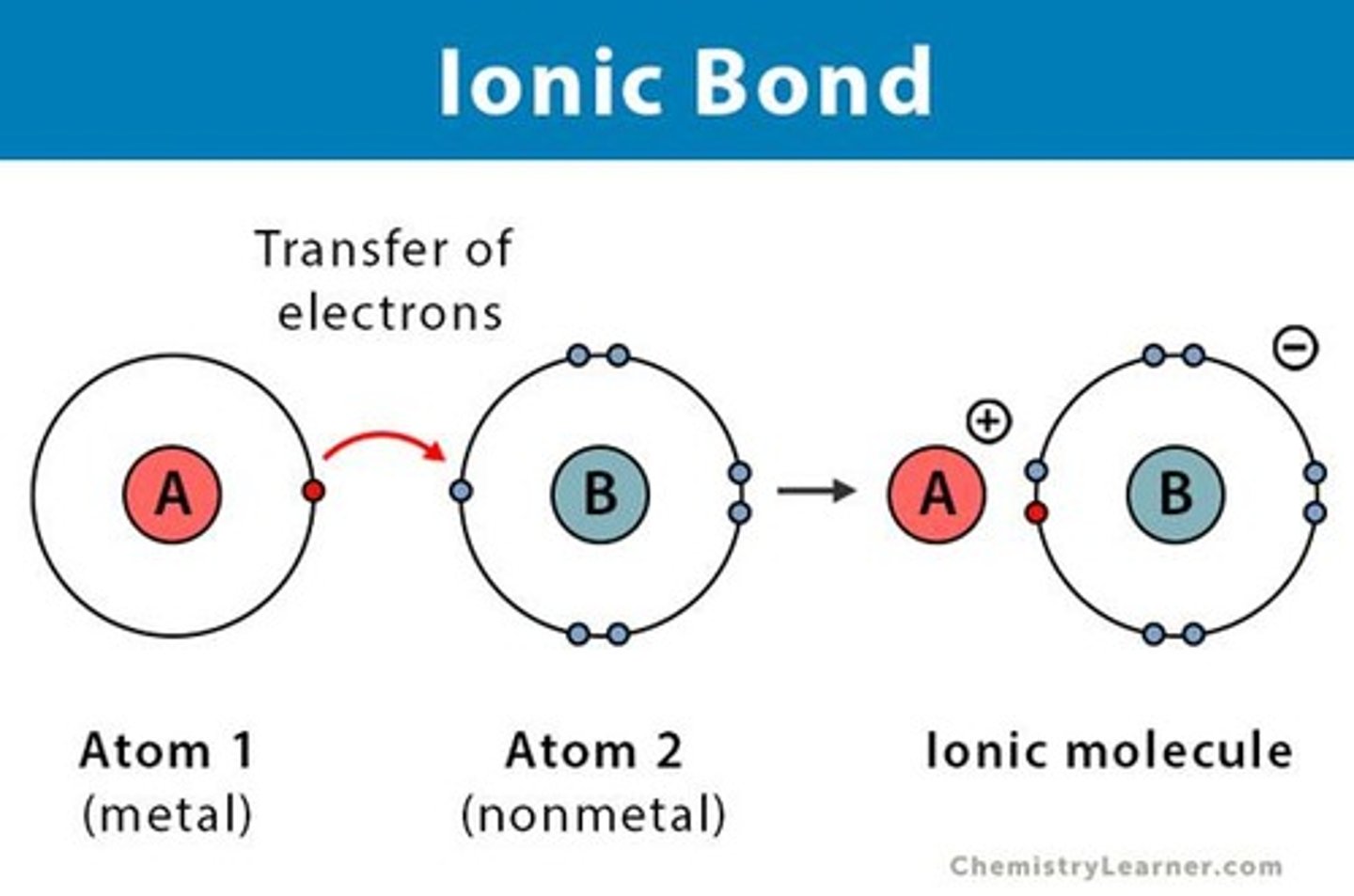
Ionic bonds
Form when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another.
Acid
Any compound that forms H+ ions in solution (pH less than 7).
Base
Any compound that forms OH- ions in solution (pH greater than 7).
Neutral
Any compound that has an equal concentration of H+ and OH- ions.
pH scale
A measurement system that indicates the concentration of H+ ions in a solution (0-14).

Buffer
Weak acids or bases that react with strong acids or bases to prevent sudden changes in pH.
Water dissociation
Water naturally dissociates into H+ and OH- ions.