6.1.1 Aromatic compounds
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What is benzene?
Aromatic compound with a very stable planar ring structure with delocalised electrons
Name the different formulas of benzene

Displayed formula, kekule model, delocalised electron model
What 3 pieces of evidence proved the kekule model wrong?
Benzene favours substitution reactions (when functional group replaces without breaking double bond) when the kekule model suggests it would break bond for addition reactions
All C-C bonds in benzene are the same length but if kekule was correct the C=C bond would be shorter
Enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene is lower than the predicted kekule as more stable so proves there isn’t x3 C=C bonds but rather a more stable delocalised electron ring
What is the bond length of C-C and C=C according to the kekule model?
C-C is 154pm
C=C is 134 pm
What is the actual length of all bonds in benzene?
140pm
What was the expected enthalpy of hydrogenation from the kekule model?
3 × 120 = -360 as there are 3 C=C bonds in kekule
What is the actual enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene?
-208 Kj mol^-1
Describe the actual structure of benzene:
p-orbitals of all 6 carbon atoms overlap and donate 1 electron each to form a delocalised ring of electrons ABOVE and BELOW the plane of carbon atoms
What is this called?
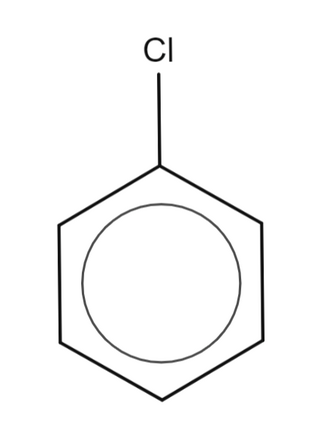
Chlorobenzene
What is this called?

Nitrobenzene
What is this?
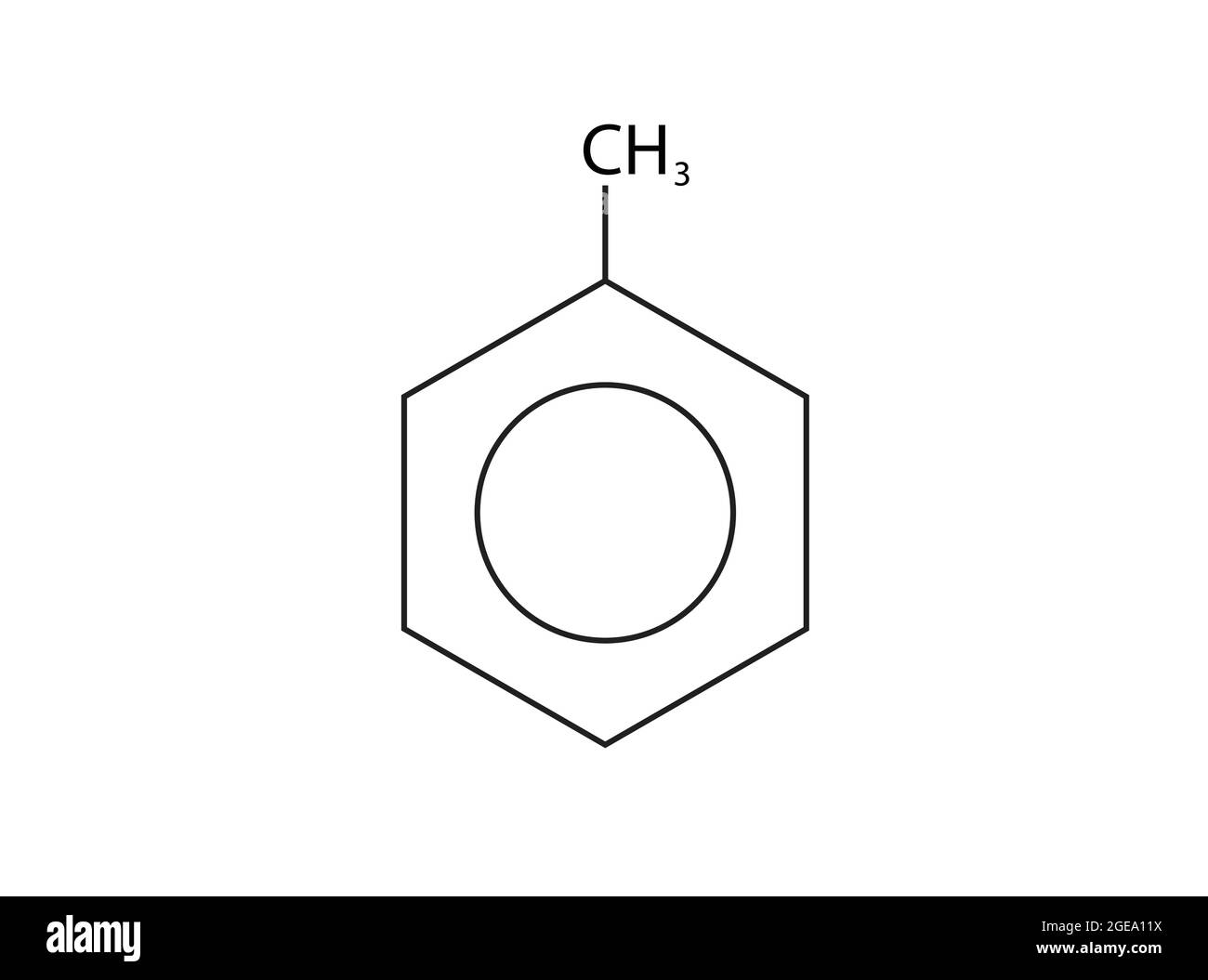
Methylbenzene
What is this?

Chloromethylbenzene
What is this called?
1-Bromo 2-methyl benzene
What is this called?
Phenyl amine
What is this called?
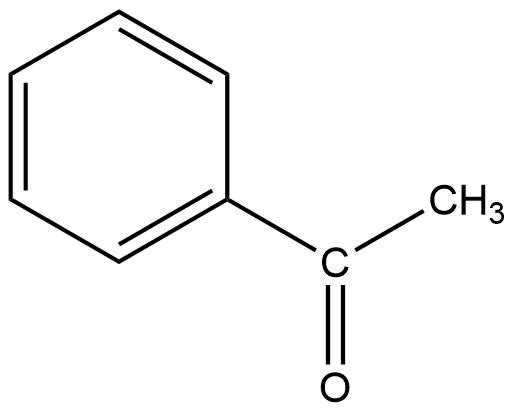
Phenyl ethanone
What is this called?
Phenyl ethene
What is this?

Phenol
What is this?

2,4 dichlorophenol
What is the formula for a phenyl group?
C6H5
Why are electrophiles attracted to benzene / phenol?
hgih density electron ring which attracts electrophiles
Describe the steps of electrophilic substitution to a benzene ring?
Electrophile attracted
Electrons transfer to electrophile to form bond
Ring broken
Electrons in C-H bond is donated to ring
Ring reform and H+ is released
What does adding a halogen require?
Requires a halogen carrier to make an electrophile as it’s not polar therefore an electrophile
Give examples of halogen carriers:
AlX3 and FeX3
Give the equation when Cl2 (halogen) is added to AlCl3 (halogen carrier):
Cl2 + AlCl3 → AlCl4- + Cl+
What will happen to the H+ that was released from the benzene?
React with AlX4 or FeX4 to produce the halogen carrier again as a catalyst and HX
What is nitration?
Adding NO2
What are the specific conditions for nitration?
warm benzene with HNO3 and concentrated H2SO4 catalyst at 55 degrees if one substitution
What is alkylation?
Adding an alkyl chain
What first has to be added before the alkyl or acyl can join to the benzene?
Halogen carrier has to be added as alkyl / acyl is not an electrophile to make the alkyl / acylelectrophile
What is acylation?
Adding an acylchloride to add an acyl group
What is this and why?

2-ethyl phenol as the OH has more priority than benzene