Plant Reproduction - Biology 35
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/18
Earn XP
Last updated 11:31 PM on 5/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
1
New cards
Germination of Seeds
after seeds are formed, they dehydrate and enter a period of dormancy until favourable conditions exist, at which time germination will occur
2
New cards
Embryo
develops plant from within seed
3
New cards
Cotyledon
embryonic leaf in a seed (not a true lead); food storage site for developing embryo
4
New cards
Testa
seed coat; outer, productive layer covering the seeds
5
New cards
Micropyle
small pore in a seed allowing water to enter
6
New cards
embryo shoot(hypocotyl)
embryonic stem; above embryonic root
7
New cards
embryo shoot (radicle)
will become the root of the plant
8
New cards
Seed germination conditions
* water to rehydrate seed tissues
* warmth for biochemical reactions to occur
* oxygen to allow cellular respiration to occur producing atp for energy
* warmth for biochemical reactions to occur
* oxygen to allow cellular respiration to occur producing atp for energy
9
New cards
Angiosperm Growth
flowering plants; includes all plants except conifers, ferns, and mosses
angiosperms coevolved with insects and birds that pollinate them, making them co-dependent
* reproduction occurs in flowers making offspring of seeds
angiosperms coevolved with insects and birds that pollinate them, making them co-dependent
* reproduction occurs in flowers making offspring of seeds
10
New cards
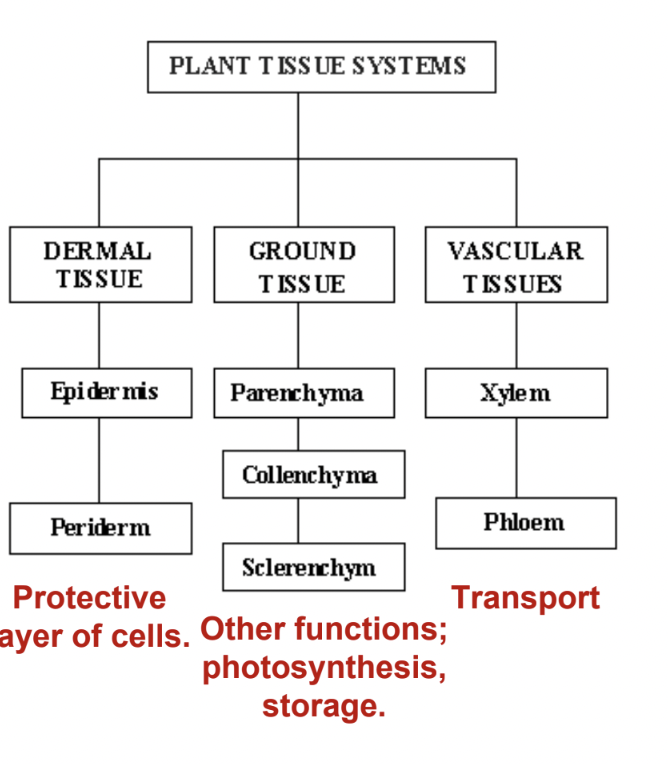
Tissues of Angiospermophytes
11
New cards
Mutualism
both species in a relationship benefit from an interaction
12
New cards
Example of mutualism
* animal pollinators get nectar and pollen from plant as food source
* plant gets safe and reliable transport of pollen from one flower to another
* plant gets safe and reliable transport of pollen from one flower to another
13
New cards
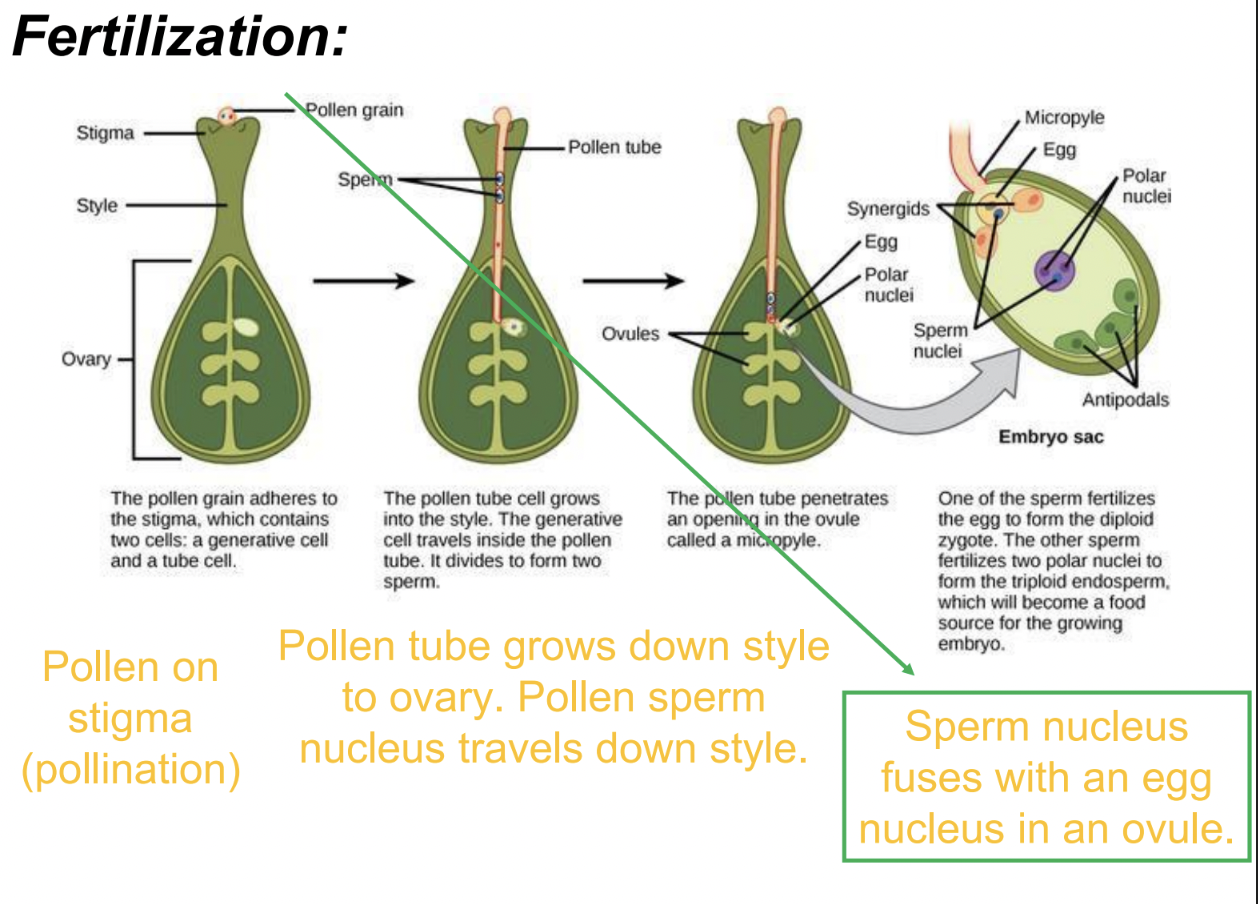
Fertilization
process by which sperm nucleus of pollen unites with ovule(egg) in ovary
14
New cards
seed dispersal (+examples)
embyro is dispersed to different locations
* through wind (milkweed, dandelion, maple)
* through animals (beggar0ticks, sandbur, blackberries)
* through water (lotus, cattail, coconut)
* by bursting (violet jewelweed, witch hazel)
* through humans (beans, wheat, cherries)
* through wind (milkweed, dandelion, maple)
* through animals (beggar0ticks, sandbur, blackberries)
* through water (lotus, cattail, coconut)
* by bursting (violet jewelweed, witch hazel)
* through humans (beans, wheat, cherries)
15
New cards
Photoperiodism
response of a plant to each amount of light or darkness it is exposed to each day; amount of uninterrupted darkness determines formation of flowers on most types of plants
16
New cards
Long-day plants
blooms in summer when nights are short (i.e. radish)
17
New cards
Short-day plants
blooms in early sprint and autumn when nights are long (i.e. chrysanthemum)
* when leaves are exposed to >12h of darkness, florigen-FT(a hormone) is stimulated to the shoot apex
* when leaves are exposed to >12h of darkness, florigen-FT(a hormone) is stimulated to the shoot apex
18
New cards
Day-neutral plants
Blooms without regard to light or darkness (i.e. dandelion)
19
New cards
Beginning of flower production
At the shoot apical meristem, the hormone enters the cells and activates floral genes. This induces the shoot to produce floral buds instead of leaves and lateral buds.