L20 X-linked Traits & Recombination
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards based on lecture notes about X-linked traits and recombination.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Sex-linked Traits
Involving genes on the sex chromosomes (X or Y) rather than autosomes. Inheritance patterns differ between males (XY) and females (XX).
Autosomes
Chromosomes that are not sex chromosomes.
Drosophilia
Eye colour is sex linked, males cannot have red eyes because they inherited Y chromosome instead.
Hemizygous
Having only one copy of a gene, such as males for X-linked genes.
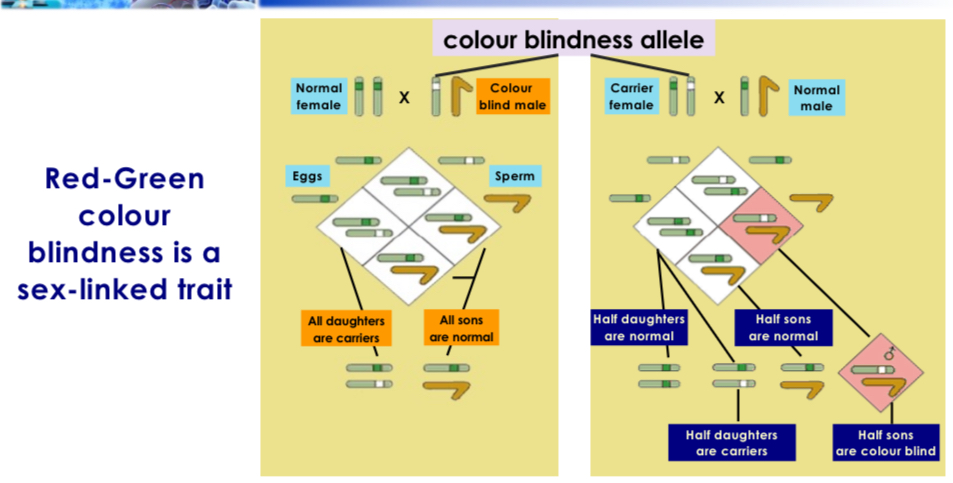
Red green colour blindness (X linked)
Normal female x colour blind male, all sons are normal and all daughters are carriers.
Linked Genes
Genes located on the same chromosome that tend to be inherited together. Closer on chromosome, more likely to be inherited together.
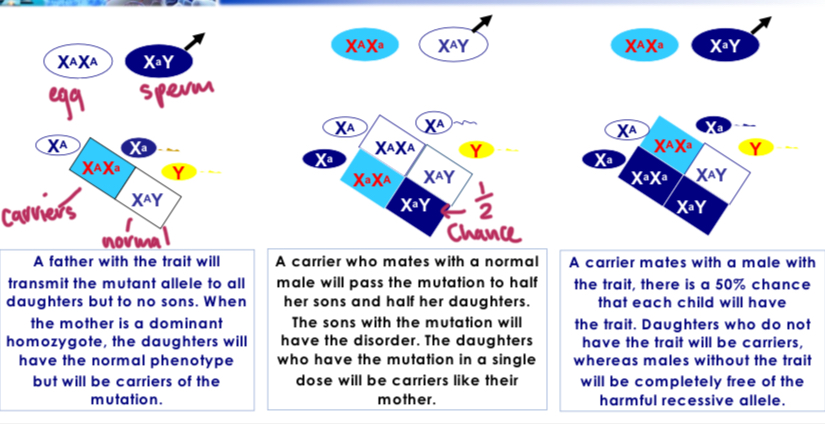
heamophilia allele ( cannot clot blood, X linked)
Father with trait= daughter carriers and normal sons. Mother carrier= ½ chance for sons and carrier daughters. Carrier mother and father with trait= ½ chance both daughter and sons affected, other daughter will be carrier, other son unaffected.
Recombination (crossing over)
The process by which genetic material is exchanged between homologous chromosomes during meiosis.
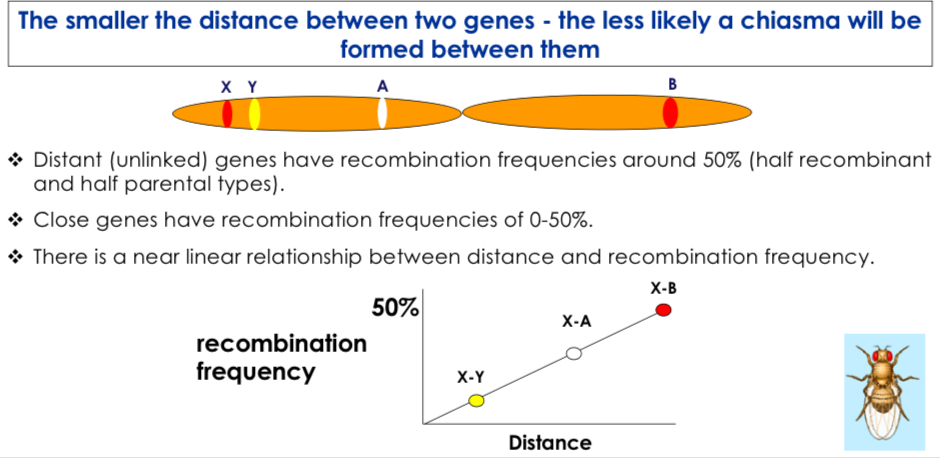
Recombination Frequency
The proportion of recombinant gametes, indicating the distance between two linked genes. RF= recombanants/total=chiasma between 2 genes. Reflects distance of allels on chromosome.
Centimorgan (cM)
A unit of distance on a genetic map, equal to a recombination frequency of 1%.
Carrier
An individual heterozygous for a recessive allele that does not express the trait but can pass it on to offspring.
Homozygous
Having two identical alleles for a particular gene.
Recombinant
An offspring with a different combination of genes from that of its parents, resulting from crossing over in meiosis.
Fewe recombanants show…
2 genes must be linked (on the same chromosome)this violates mendels 2nd law of independant assortment. Happens During crossing over.