Derm cumulative
1/281
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
282 Terms
_____ blanches with pressure because the lesion is due to vascular dilatation.
erythema
Which is thinning of the skin due to loss of connective tissue, associated w/ hypopigmentation, and most commonly secondary to overuse of steroids?
dermal atrophy
Which is thinning of the skin that becomes transparent, reveals papillary and sub papillary vessels, loses skin texture, and is common in older patients w/ cigarette paper like wrinkling?
epidermal atrophy
what is an exudate that involves the entire epidermis and is accompanied by necrosis of deeper tissues?
ecthyma
Which is a superficial, focal loss of part of the epidermis where the basement membrane remains intact and heals without a scar?
erosion
which is a focal loss of epidermis extending into dermis or SC tissue, typically heals w/ a scar, and is associated with pathologic tissue?
ulceration
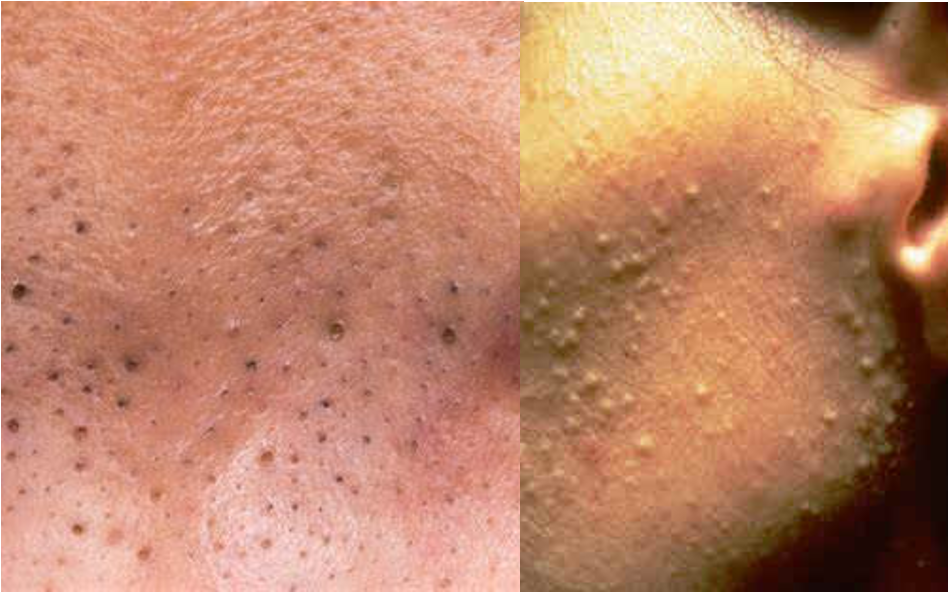
What is a plug of sebaceous and keratinous material w/in the opening of a hair follicle; may be dilated (blackhead) or narrowed (whitehead)?
comedone
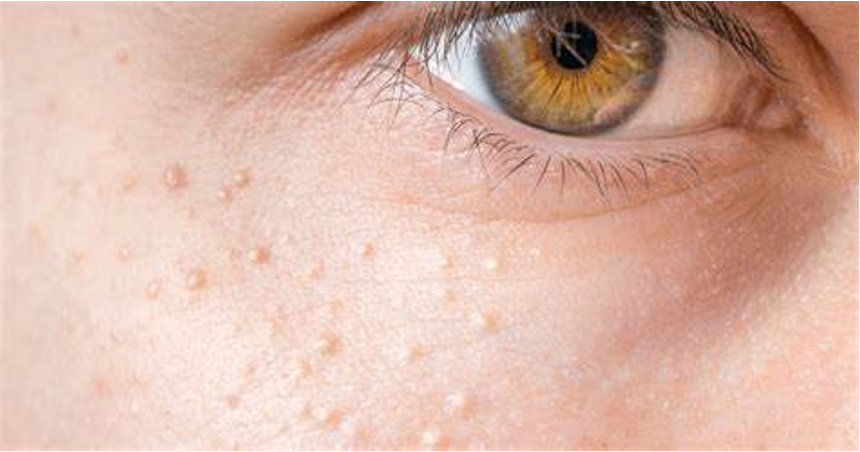
What is a small, 1-2mm sub epidermal keratin cyst that arises from pilosebaceous units or eccrine sweat ducts?
milia
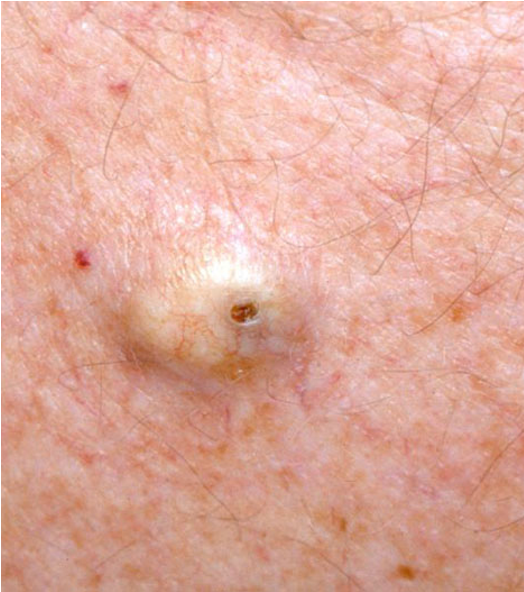
what is a circumscribed lesion with a wall and lumen that may contain liquid, solid, or semisolid material and may be superficial or deep?
cyst
Which are extensor surfaces?
elbow, knee
Which are flexor surfaces?
antecubital fossa, popliteal fossa
Dermatophytosis of a hair follicle will illuminate as _____ under a wood’s lamp.
yellow/green
Erythrasma will illuminate _____ under a wood’s lamp.
coral
Urine from a patient with porphyria will illuminate ____ under a wood’s lamp.
red/pink
______ will not blanch under pressure because it is an extravasation of blood.
purpura
What would multinucleate giant cells on a tzanck smear indicate?
herpes simplex or zoster
what would Henderson-patterson bodies on a tzanck smear indicate?
molluscum contagiosum
What is performed w/ colposcopy to detect subclinical HPV lesions?
acetowhitening (positive result = blanching/whitening of lesion)
The appearance of new skin lesions on previously unaffected skin secondary trauma is known as _______, and indicates psoriasis.
koebner phenomenon
Slight scratching or curetting of a scaly lesion that reveals punctate bleeding points is known as ______, and is seen in psoriasis.
auspitz sign
When the epidermis is dislodged from the dermis by shearing pressure with a finger, this is known as _____ and commonly associated w/ SSS or pemphigus vulgaris.
nikolsky phenomenon
Rubbing or scratching of skin affected by mastocytosis that results in redness, swelling, itching, and a palpable wheal is known as _____ and may indicate atopic dermatitis.
darier sign
What is the atopic triad?
atopic dermatitis, asthma, allergies
What is the strongest risk factor for atopic dermatitis?
FHx of atopic triad
What condition has the clinical presentation of pruritic, dry skin, the itch scratch cycle, lichenification and is most commonly on the flexor surfaces (expect in children under 2- extensor)?
atopic dermatitis
Diagnosis of atopic dermatitis?
clinical based on H&P
labs: CBC → eosinophilia
skin bx: spongiosis
what is the treatment for mild to moderate atopic dermatitis?
TCS and emollients
low potency (group 5/6- desonide, hydrocortisone)
Alt: topical calcineurin inhibitors
tacrolimus or pimecrolimus
what is the treatment for moderate-severe atopic dermatitis?
TCS
medium-high potency (group 3-5, triamcinolone, etc)
systemic immunosuppressants
dupilumab/dupixent
alt: narrowband UVB phototherapy 2-3x/wk
What is non-pharmacologic management of atopic dermatitis?
oral antihistamine for pruritus
lukewarm baths, wet dressings
daily emollients and creams w/ ceramides
avoid fragrances, wool clothing, chemicals, etc
manage stress/anxiety
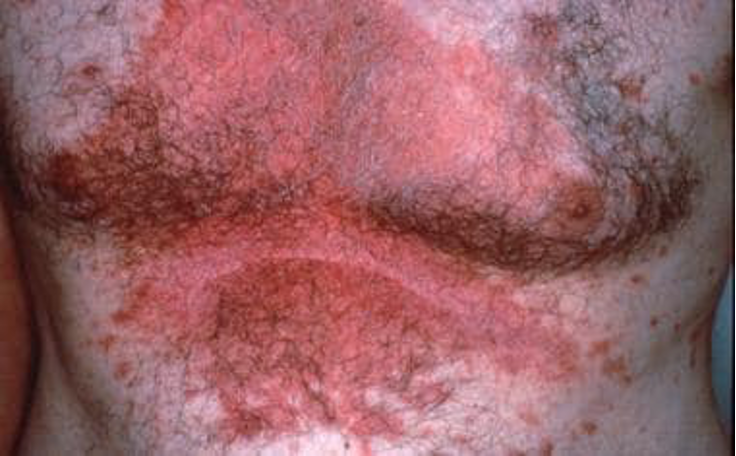
What condition?
sebum-rich areas of scalp, face, trunk, intertriginous
well demarcated, pruritic erythematous plaques w/ greasy appearing yellow scales
ranges from scalp dandruff (pityriasis sicca) to widespread
biphasic: infants 2-12 wks (cradle cap) and 4th decade
unknown cause but has been linked to malassezia furfur colonization
seborrheic dermatitis
what is the treatment for seborrheic dermatitis?
OTC scalp: selenium sulfide (selsun blue) or coal tar shampoo
cradle cap: mineral oil or baby shampoo
1st line:
topical antifungals (ketoconazole 2%)
TCS low potency (alt- tacrolimus)
severe/generalized: oral anti fungal (itraconazole)
What condition occurs when contact with a substance elicits a delayed type IV hypersensitivity reaction with a rash appearing w/in 48hrs?
allergic contact dermatitis
what is the treatment for allergic contact dermatitis?
1st line: TCS
alt: tacrolimus
if severe / involving >20% body: oral steroids, medrol dose pack
2nd line: UVA/UVB or immunomodulators (MTX, cyclosporine)
calamine lotion and oatmeal baths may help pruritus
why should you NOT perform a patch test on an individual w/ poison oak/ivy dermatitis?
can sensitize the individual
Exposure to what substance causes poison ivy/oak dermatitis?
olioresin- urushiol
Which is ALWAYS sharply marginated and NEVER spreads?
irritant contact dermatitis
what is the treatment for stasis dermatitis?
tx underlying → leg elevation, walking, exercise, weight reduction, compression socks
emollients
acute dz
TCS group 3-4 (long term use can cause ulceration)
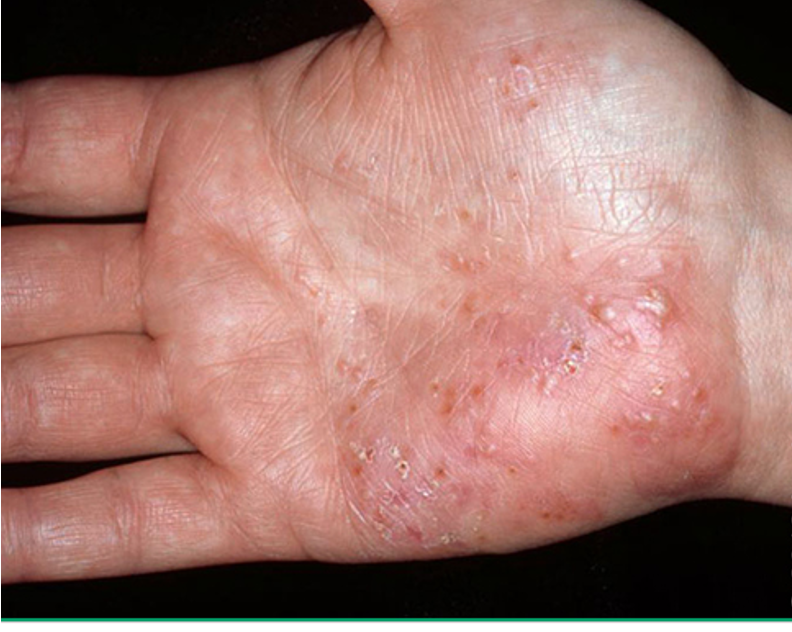
what condition?
intense pruritus
tapioca like vesicles that may coalesce to form bullae
lesions usually sterile
affects palms, soles, lateral aspects of digits
dyshidrotic eczema
what is the treatment for dyshidrotic eczema?
spontaneous remission occurs 2-3 wks
mild-mod: high potency TCS
severe: oral glucocorticoids
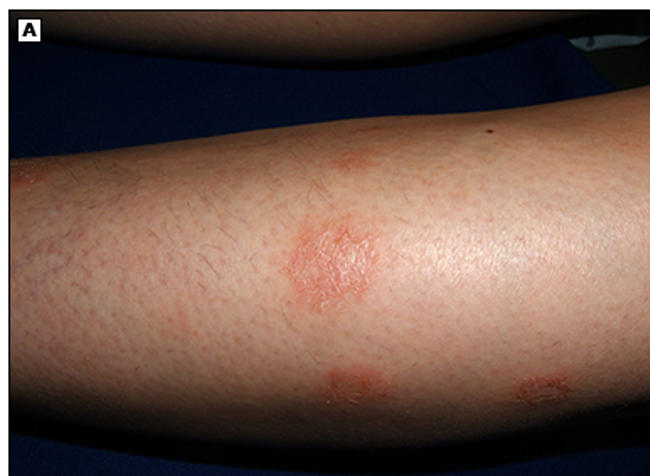
what condition?
highly pruritic round, coin shaped lesions (grouped small papules/vesicles on erythematous base)
excoriations/lichenification from scratching
acute: exudative, crusting; over time dry, scaly, w/ central clearing
M > F
extremities > trunk
nummular / discoid dermatitis
what is the treatment for nummular eczema?
1st line: high potency TCS
alt: PUVA/UVB
severe/refractory: systemic immunosuppressants (MTX, cyclosporine, dupixent)
what is the most potent topical corticosteroid (TCS)?
class 1- clobetasol propionate, halobetasol propionate
what is the least potent topical corticosteroid (TCS)?
class 7- hydrocortisone
what condition?
chronic inflammatory skin dz that involves hyperproliferation of keratinocytes in the epidermis
peaks 30-39 and 50-69
T lymphocytes, dendritic cells, cytokines play central roll; increased cell turnover
psoriasis
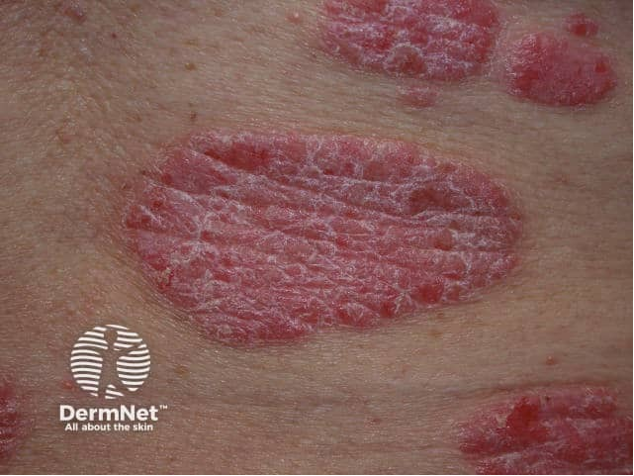
what subtype of psoriasis?
erythematous plaques w. silver scales
sharply defined well demarcated
± pruritus
positive auspitz, koebner
extensor surfaces, scalp, palms/soles (painful fissures)
chronic plaque psoriasis
what is the treatment for chronic plaque psoriasis?
limited:
high potency (1-3) TCS and emollients ± UVB
vit d analog- calcipotriene
topical retinoids- tazarotene
mod/severe:
phototherapy
retinoids
DMARDS- MTX, cyclosporine
anti-TNF- infliximab (Remicade), adalimumab (Humira)
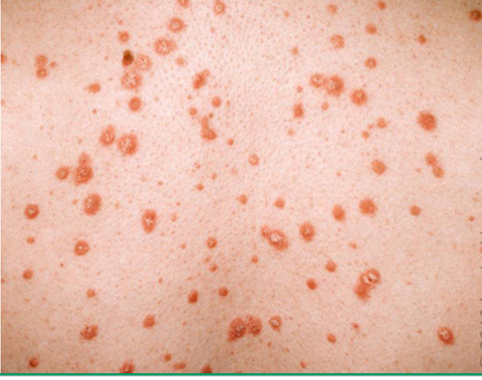
what subtype of psoriasis?
abrupt onset multiple small psoriatic papules and scales w/ raindrop appearance
may spontaneously remit
trunk, back, proximal extremities
children/young adult w/ recent strep infx
guttate psoriasis
what is the treatment for guttate psoriasis?
1st line: UV phototherapy
alt: TCS and vit D analogs (not ideal due to widespread nature)
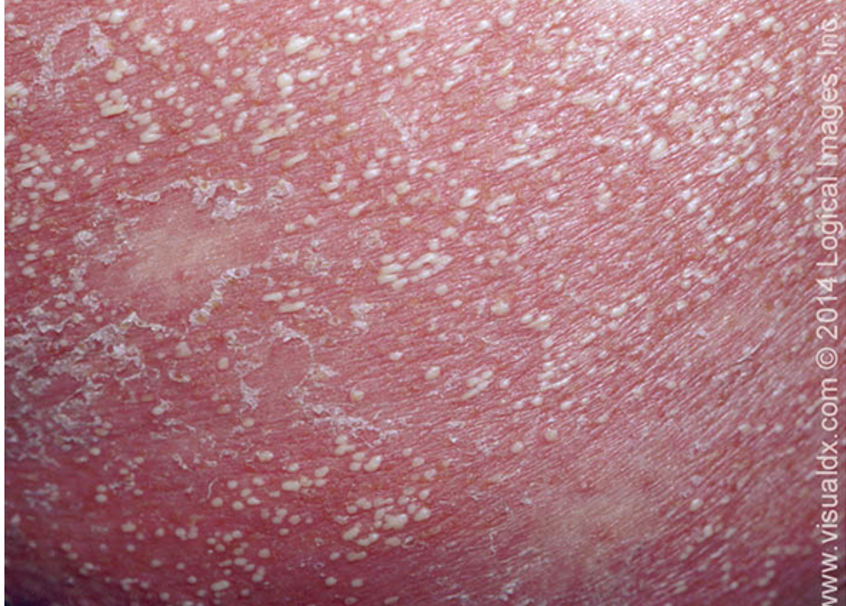
what subtype of psoriasis?
caused by pregnancy, infx, stress, withdrawal of steroids
acute onset of erythematous pustules, localized or generalized
assoc w/ malaise, fever, diarrhea, leukocytosis, hypocalcemia
can be life threatening
Von zumbusch (most severe), acrodermatitis continue of hallopeau (distal digits), palmoplantar pustulosis variants
pustular psoriasis
What would labs look like in pustular psoriasis?
elevated WBC
inc ESR
hypocalcemnia
hypoalbuminemia
what is the treatment for pustular psoriasis?
mild: acitretin and MTX
severe/acute: cyclosporine, infliximab
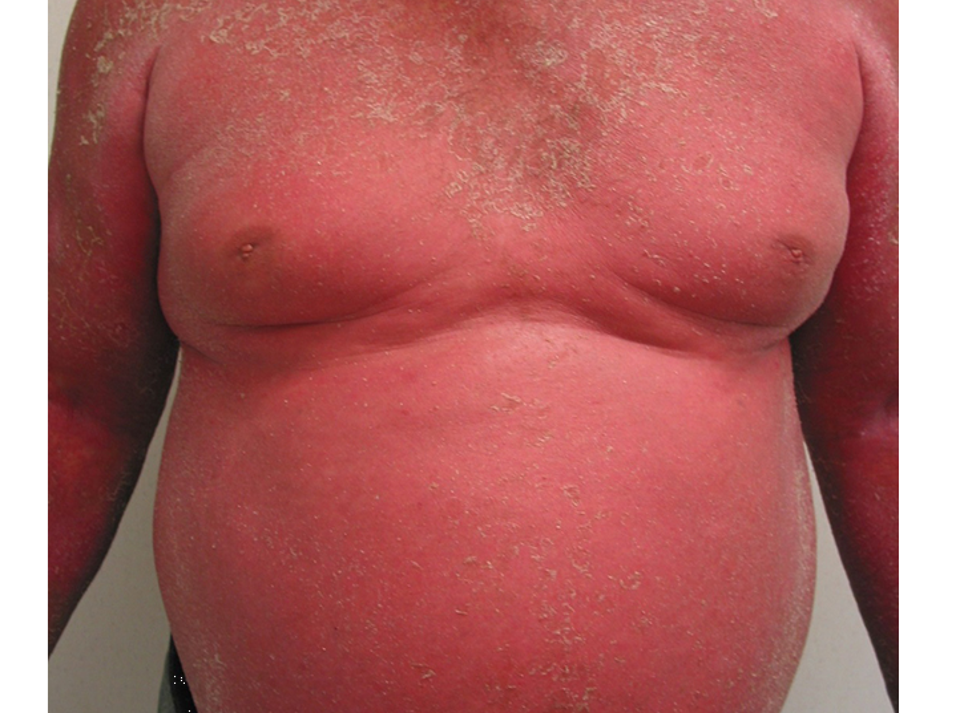
which subtype of psoriasis?
generalized erythema and exfoliation of ≥75% BSA
painful, pruritic scales
results from exacerbation of unstable plaque psoriasis
assoc w/ fevers, chills, malaise, arthralgias, LAD
leukocytosis w/ eosinophilia, anemia
erythrodermic psoriasis
what is the treatment for erythrodermic psoriasis?
stable: outpt, supportive care
TCS
systemic- cyclosporine or infliximab
unstable: admit ICU or inpt
fluid/elyte replacement
nutritional support
tx assoc infx
TCS and/or systemic immunomodulators
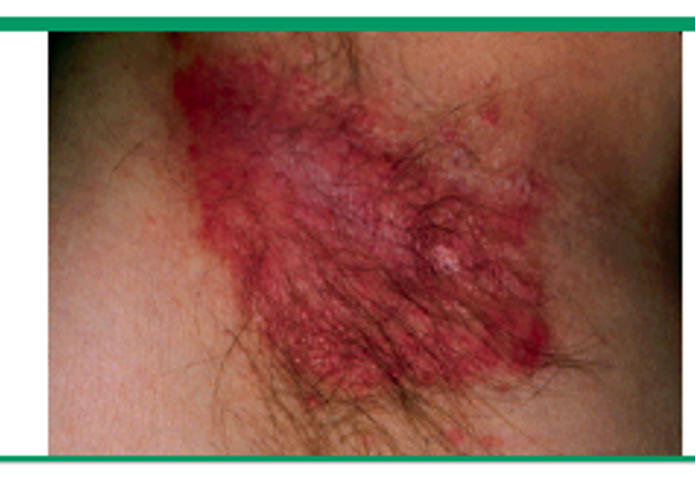
what manifestation of psoriasis?
well demarcated, smooth, shiny plaque w/ absent or minimal scale
often misdiagnosed as fungal or bacterial infx
intertriginous areas, inguinal, perianal, etc
inverse / intertriginous psoriasis
what is the tx for intertriginous psoriasis?
TCS class 6, 7
topical vit D analog- calcitriol
tacrolimus, pimecrolimus
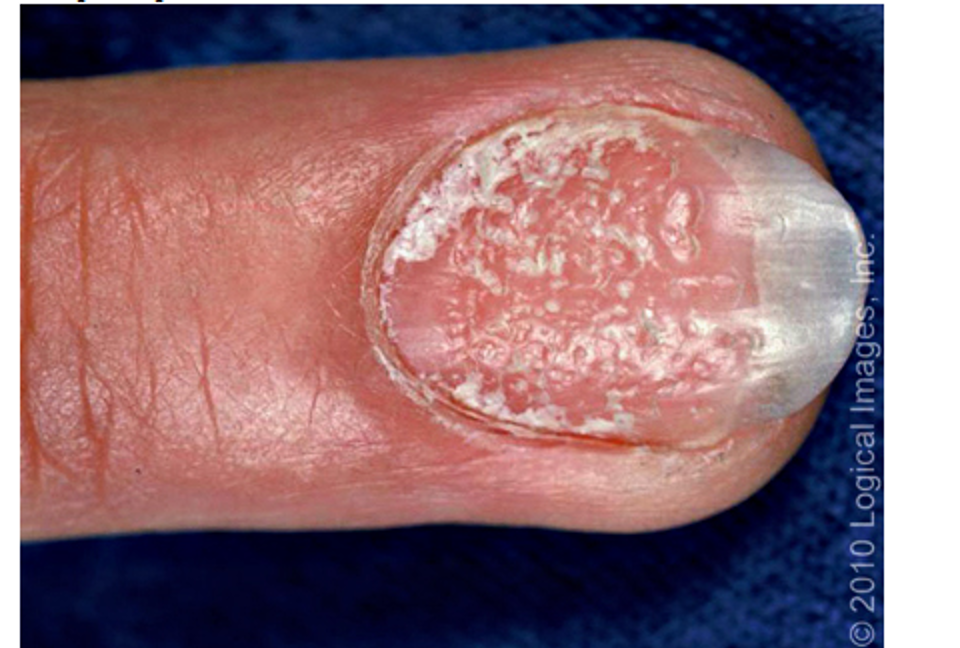
what condition?
pitting leukonychia, nail dystrophy, red spots on lunula and crumbling of nail plate; splinter hemorrhages
subungual hyperkeratosis
oil drop sign- changes in nailed to tan/brown
common w/ psoriatic arthritis
nail psoriasis
what is the treatment for nail psoriasis?
high potency TCS (betamethasone) and topical vit D analog (calipotriol)
what are clinical features of psoriatic arthritis?
joint pain, stiffness (morning), asymmetric back pain
dactylitis (sausage digits), tenosynovitis
nail involvement is common
arthritis mutilans- destruction of IP joints; “pencil in cup” deformity
asymmetric peripheral joint involvement of upper extremities; smaller joints
what is the treatment for psoriatic arthritis?
mild axial dz → NSAIDS (naproxen, celecoxib)
mod-severe axial dz → TNF inhibitors
1st line: adalimumab (Humira)
etanercept, infliximab
dactylitis: DMARDs (MTX + folic acid)
whitehead is _____, blackhead is _____
closed; open
acne vulgaris diagnosis?
comedones- required
labs- required if prescribing isotretinoin
LFTs, lipid panel, beta HCG
what is the treatment for mild acne vulgaris (few scattered comedones or small inflammatory papules w/o scarring)?
topical monotherapy of
benzoyl peroxide
tretinoin (Retin A)
salicylic acid
azelaic acid
resistant → topical dapsone (**Don’t apply w/ benzoyl peroxide)
what is the treatment for moderate acne (prominent comedones, large inflammatory pustules/papules)?
topical combo:
benzoyl peroxide + tretinoin + topical abx (erythromycin/clindamycin)
topical/oral combo:
benzoyl peroxide + tretinoin + oral abx (doxy, minocycline)
alt: intralesional triamcinolone (kenalog)
what is the treatment for severe acne (addition of nodules w/ scarring affecting multiple areas)?
oral abx + topical retinoid + benzoyl peroxide +/- topical abx
if refractory → oral isotretinoin (accutane)
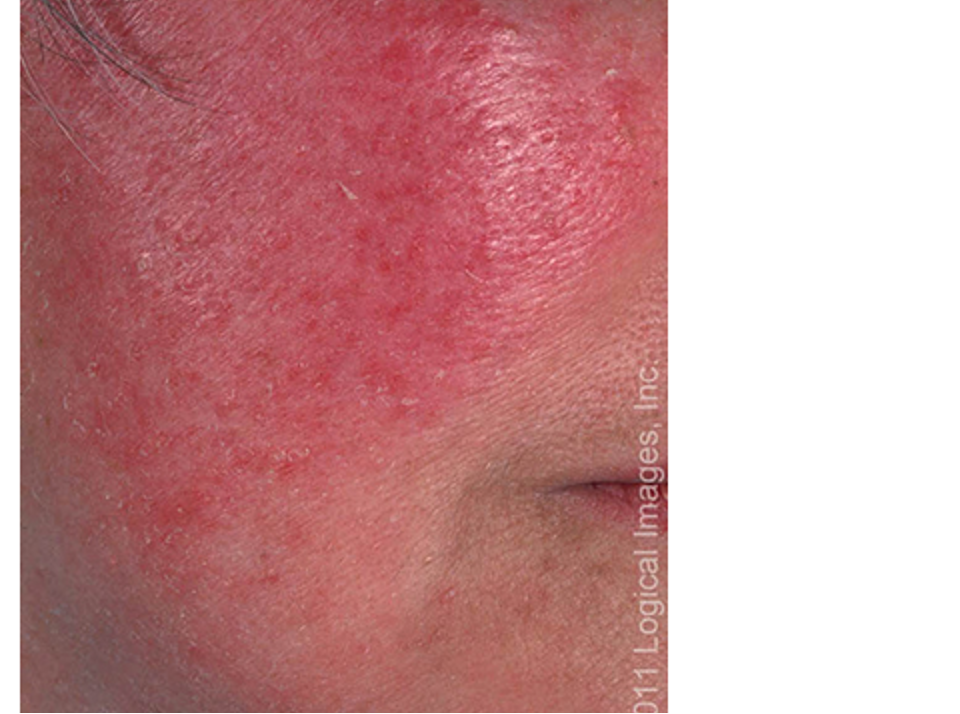
what condition?
inflammatory acneiform disorder of facial pilosebaceous units
facial flushing
papules/pustules localized to central face
telangiectasias
no comedones
+ /- burning, phymatous changes (tissue hypertrophy, nodules), ocular manifestations
rosacea
what is the treatment for rosacea?
mild-mod:
topical abx- metronidazole gel
alt: azelaic acid gel
oral abx: tetracyclines (DO NOT use w/ isotretinoin- risk pseudo tumor cerebri)
refractory: oral isotretinoin
non pharm: pulse dye laser
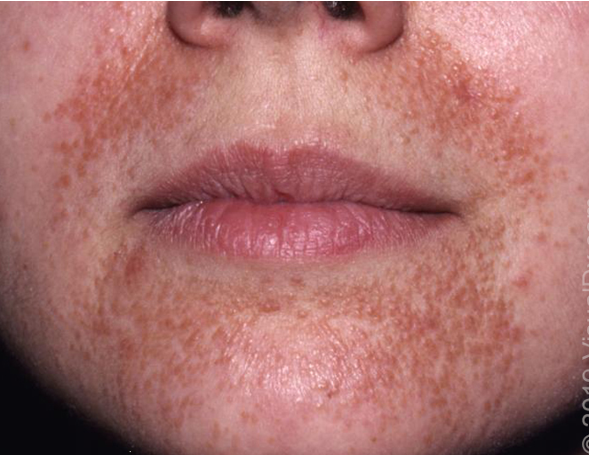
what condition?
discrete erythematous micropapules and microvesicles around mouth/nose/eyes
no comedones
assoc w/ atopy
spares narrow area around vermillion border
risk: F, age 16-45, TCS use
perioral dermatitis
what is the treatment for perioral dermatitis?
non pharm: stop/taper TCS usage; gentle cleanser
pharm:
topical erythromycin/clindamycin, metronidazole gel
tacrolimus
mod-severe: oral tetracyclines
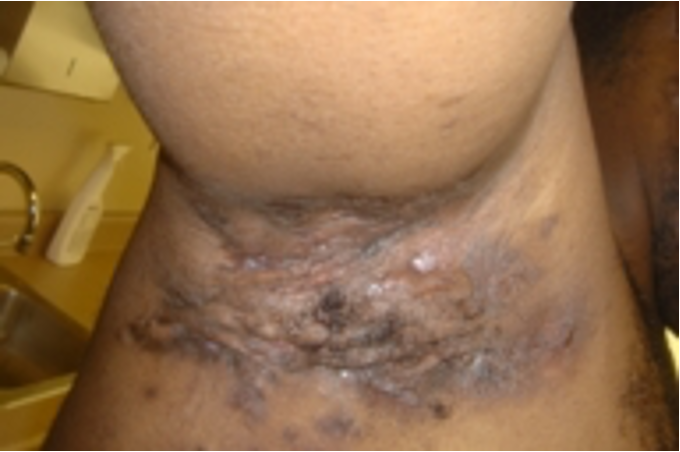
what condition?
recurrent inflamed, painful nodules/abscesses
malodorous draining sinus tracts/fistulas
follicular occlusion
progressive severe scars
open comadones
intertriginous areas
uses Hurley staging
hidradenitis suppurativa
what is the treatment for hidradenitis suppurativa?
that’s a lot to type lol

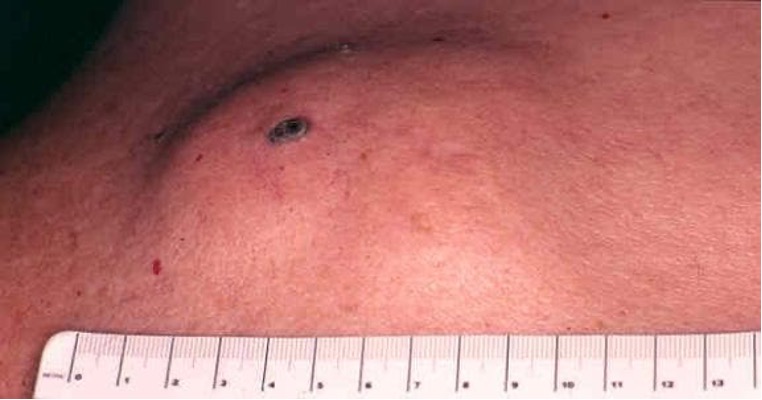
what is the most common type of cutaneous cyst that may result from trauma of follicular epithelium or comedones?
epidermoid cyst / epidermal inclusion cyst
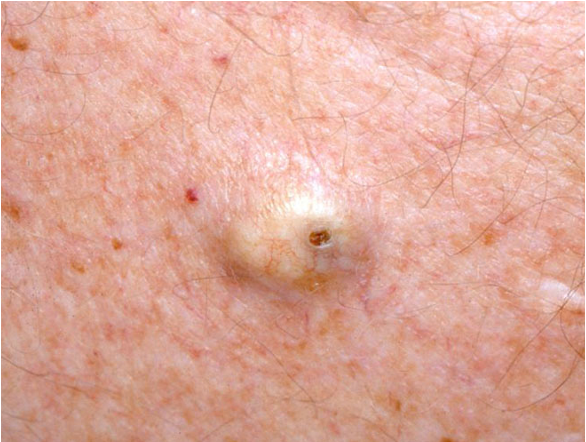
what condition?
skin colored benign dermal nodule often w/ visible central punctum
cyst wall made of normal stratified squamous epithelium
nontender, freely moveable
filled w/ thick malodorous keratin material
epidermal inclusion cyst
what is the treatment for milia?
asx- no tx necessary
neonatal- will spontaneously resolve
definitive tx- incision and expression of contents
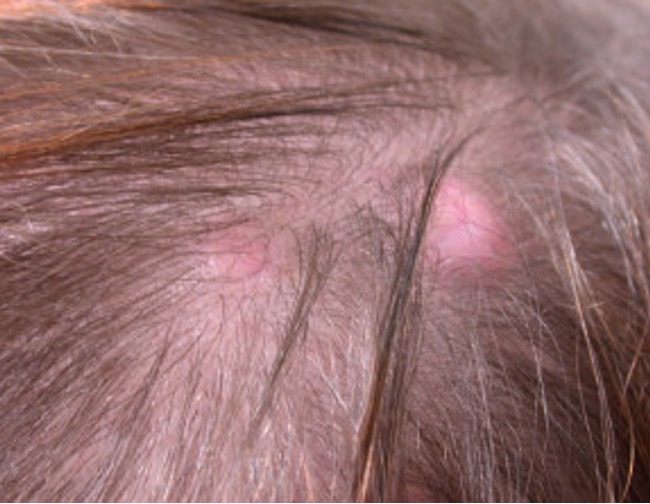
what condition?
derived from root sheath of hair follicle
firm, slow growing SC nodule filled w/ keratin
lacks central punctum
not connected to epidermis
can be painful
pilar / trichilemmal cyst
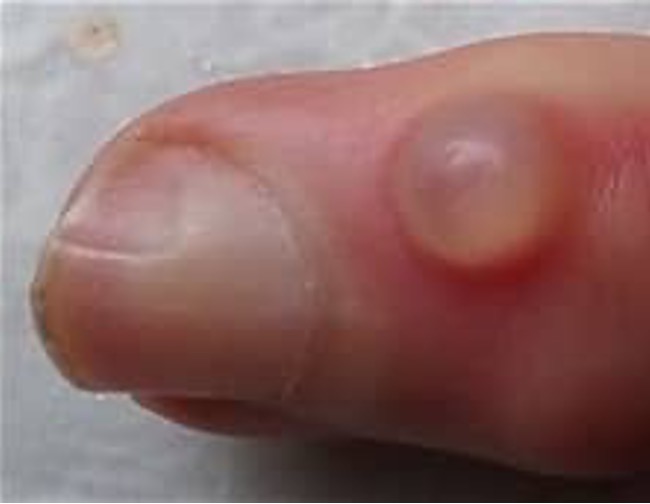
what condition?
translucent papule on dorsum of digit bt DIP and proximal nail fold
no capsule (pseudocyst)
caused by degeneration of connective tissue and/or joint fluid leaking from osteoarthritic DIP joint
mc > 60
digital myxoid cyst
what is the treatment for a digital myxoid cyst?
surgical excision; I&D
injection of sclerosis agent or triamcinolone
recurrence is high
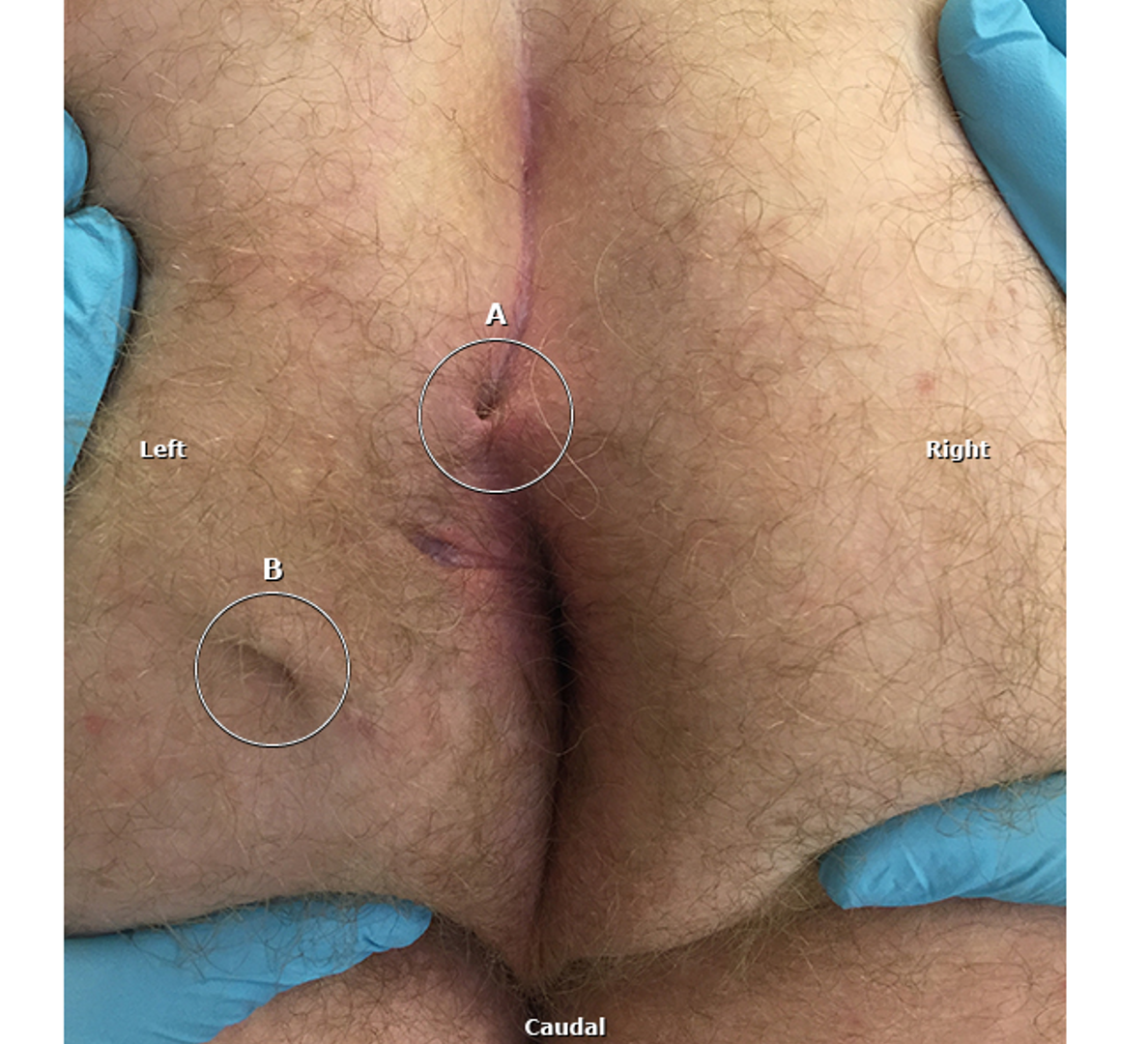
what condition?
painful, fluctuant mass in sacrococcygeal region
pain and purulent dc from sinus tract
person bends → damages hair follicle & opens pore/pit → collects debris, hair embeds → constant friction leads to sinus → infection & abscess develops
pilonidal cyst
what are risk factors for pilonidal cyst?
age 15-30
obesity
sedentary lifestyle
trauma/irritation
deep natal cleft
family hx
what is the tx for pilonidal cyst?
surgery
acute: I&D and curettage
chronic: excision w/ primary closure vs secondary closure or marsupialization
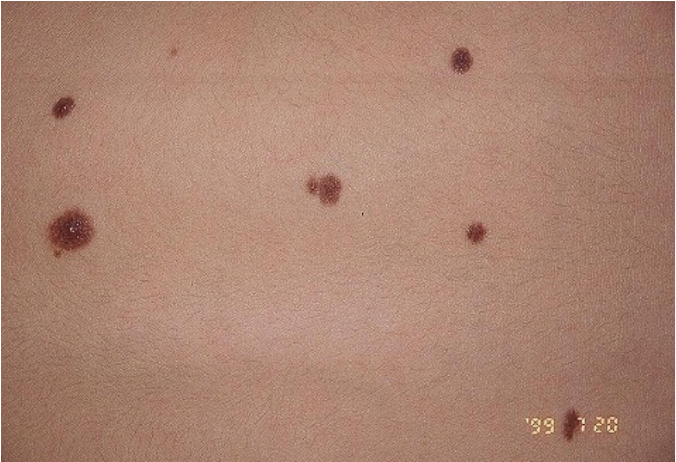
what condition?
asx, well circumscribed pigmented macule/papule/nodule
begin to appear after first 6 mos of life, can disappear w/ age
can itch w/ growth; can appear anywhere
acquired melanocytes nevi (mole)
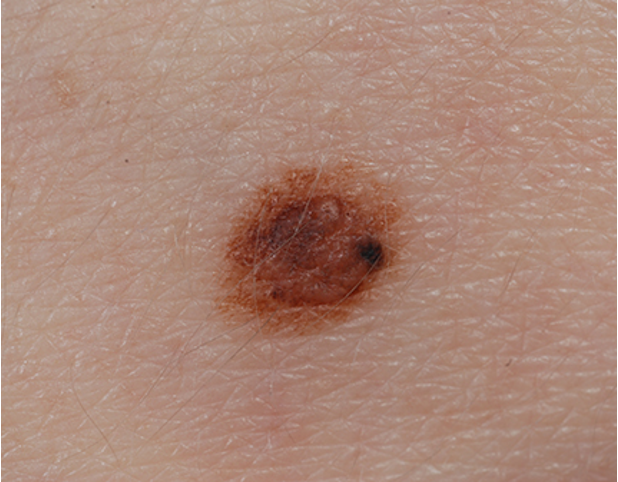
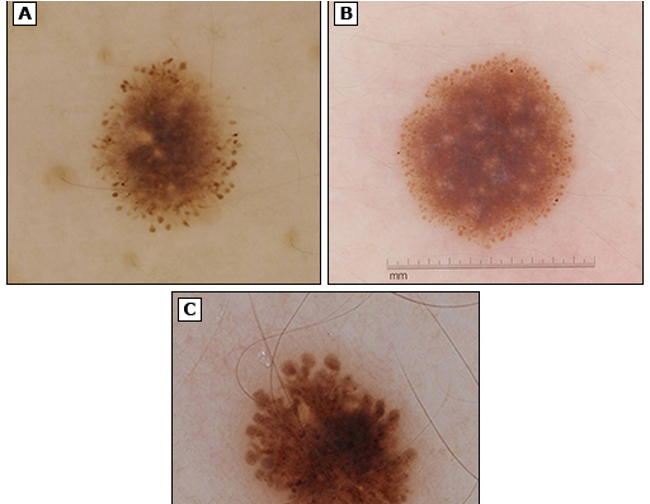
what condition?
precursor of malignant melanoma
benign AMN w/ asymmetric irregular borders,
variegated colors- pink, tan, brown
diameter > 5mm
macular component w/ papular center → fried egg appearance
atypical / dysplastic nevi
what is the rule of thumb for referring an atypical nevi to derm?
asymmetry + > 6 mm + irregular borders + abnormal color
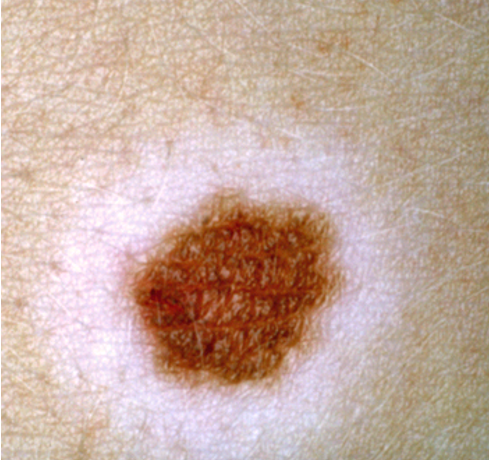
what condition?
melanocytic nevus surrounded by round/oval usually symmetric halo of depigmentation
common on back and trunk
occurs in 4 stages
common in children and young adults w/ FHx vitiligo
halo melanocytic nevus / Sutton’s nevus
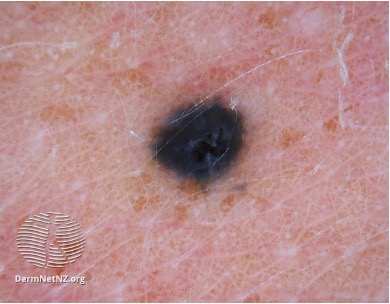
what condition?
<1 cm firm, blue-black sharply defined papule or nodule
benign proliferation of dendritic dermal melanocytes that actively produce melanin
arise in adolescence
found on dorsal hands and feet
benign and can be observed
common blue nevi
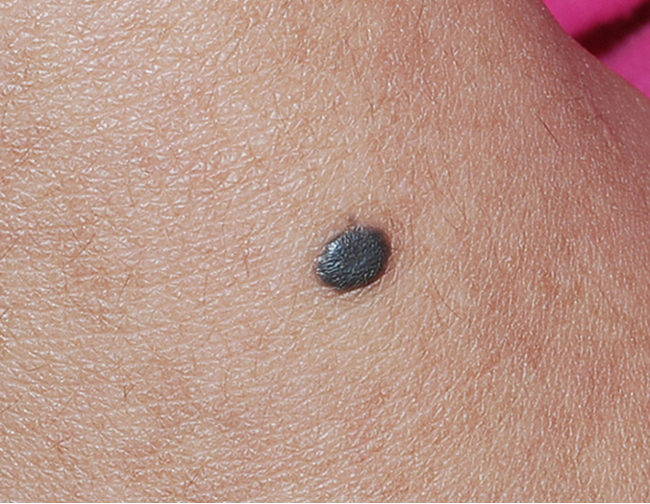
what condition?
> 1cm congenital or acquired elevated blue-black nodule or plaque
benign proliferation of dendritic dermal melanocytes that actively produce melanin
smooth or slightly irregular surface
found on scalp, buttocks, sacrum, face
can transform into melanoma, should be excised
cellular blue nevi
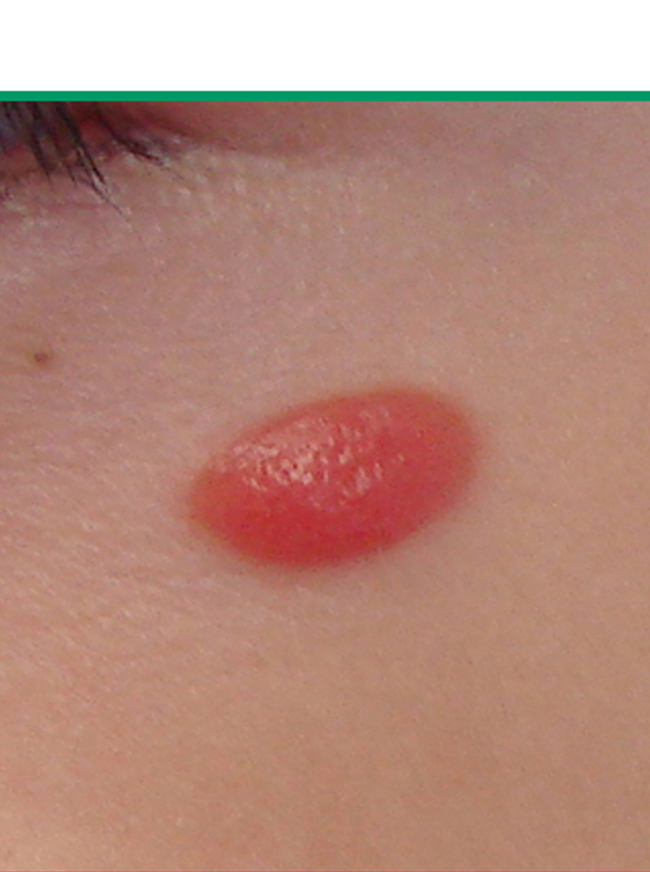
what condition?
uncommon melanocytic lesion of large epithelioid or spindled cells
rapid initial growth phase
dome shaped, red-brown or tan-brown papule/nodule
symmetric and sharply circumscribed
face, extremities
MC in children, adolescents, young adults
spitz nevus
what lesion has this appearance under a dermatoscope?
starburst / globular pattern of pigment
prominent punctate or rounded blood vessels
regularly distributed dottiest vascular pattern
spitz nevus
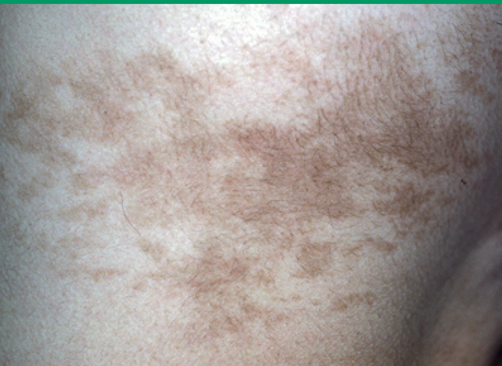
what condition?
common cutaneous hamartoma w/ epidermal or dermal elements
overgrowth of epidermis, melanocytes, and hair follicles
well-defined unilateral brown patch w/ sharply demarcated borders
macular w/ papular/verrucous surface
hypertrichosis in 50%
tx: laser therapy (q switch, pulse dye, fractional resurfacing)
Becker nevus
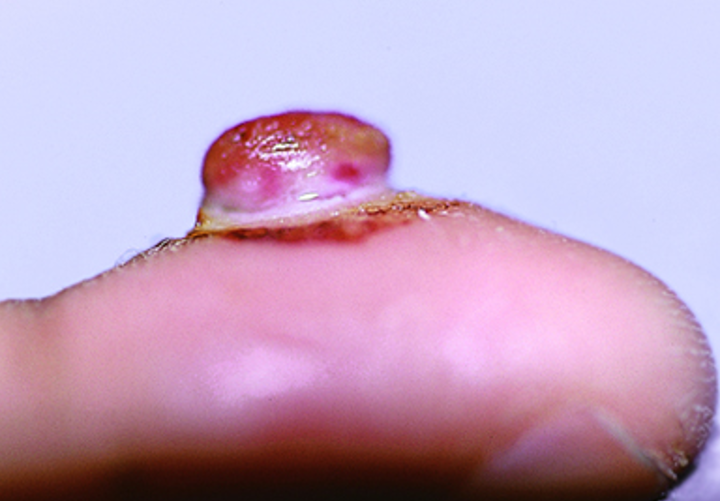
what condition?
benign vascular tumor of skin/mucus membranes
small, red papule that grows rapidly over wks-mos → pedunculated/sessil
friable + bleeds easily
+ /- collared scale at base
peaks in 6-10 y/o and 2-3rd decades
adults: trunk+extremities
children: head+neck
M > F
pyogenic granuloma (aka lobular capillary hemangioma)
what lesion has this appearance under a dermatoscope?
pink, homogenous papule w/ white septa
pyogenic granuloma
what is the treatment for pyogenic granulomas?
topical: imiquimod cream or timolol gel
procedural: elliptical excision w/ cautery, cryotherapy, pulse dye laser, CO2 laser
what is the most common vascular tumor characterized by proliferative phase (3-9 mos rapid growth) and involution phase (2-6 yrs regresses and resolves)?
infantile hemangioma
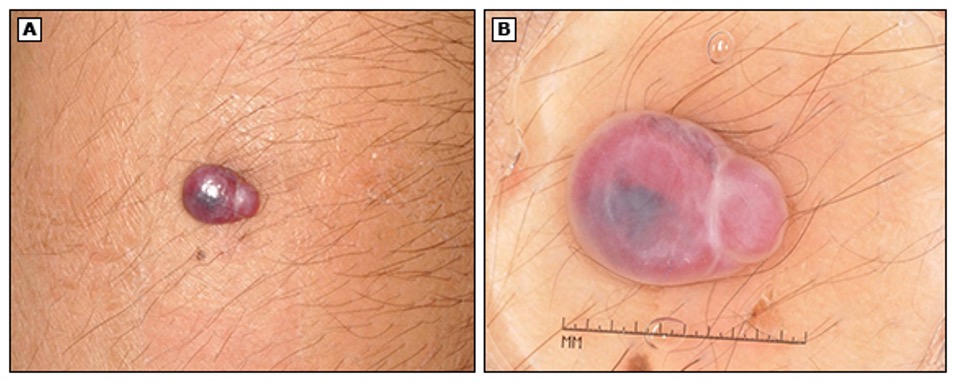
what condition?
superficial type: soft bright red papule or nodule
deep type: not visible to naked eye, may case proptosis, strabismus, dec VA if compressing optic nerve
mixed: combo of superficial and deep
located head and neck
risk: infants, low birth wt, advanced maternal age, placenta previa
Infantile Hemangioma
what is the treatment for infantile hemangiomas?
1st line:
uncomplicated lesion: topical timolol gel
complicated: oral propranolol
2nd line:
pulsed dye laser
excisional surgery
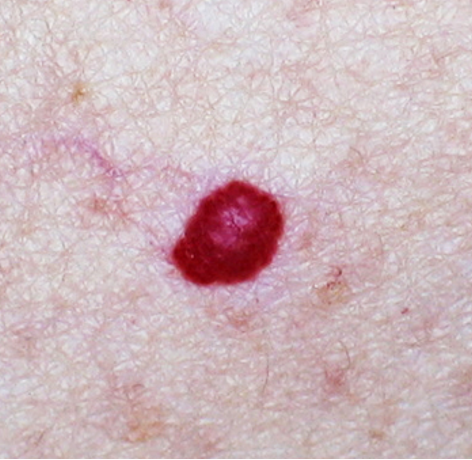
what condition?
dome shaped 1-4 mm red/purple/blue/black papule
can bleed w/ trauma
located on trunk
MC in middle age-older pts
cherry angioma / campbell de morgan spots
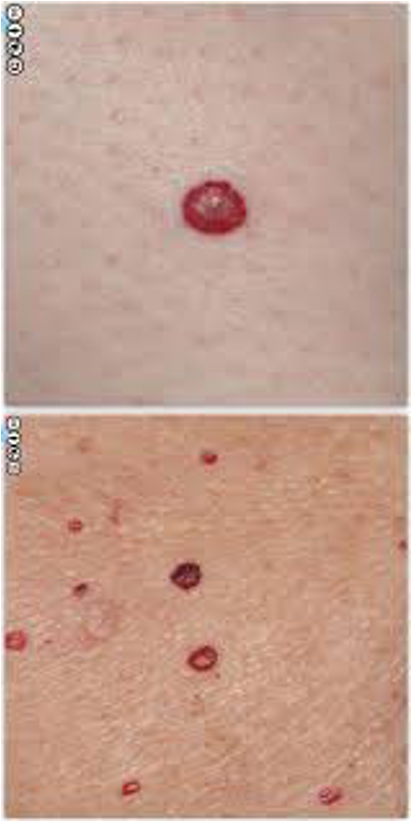
what lesion appears as red, purple, blue, or black lagoons under a dermatoscope?
cherry angioma
what are treatment options for cherry angiomas?
electrocautery, laser, shave excision, cryotherapy
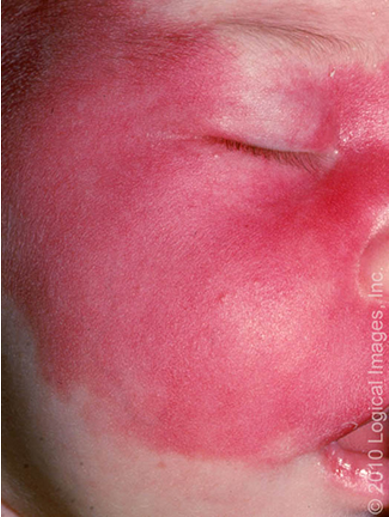
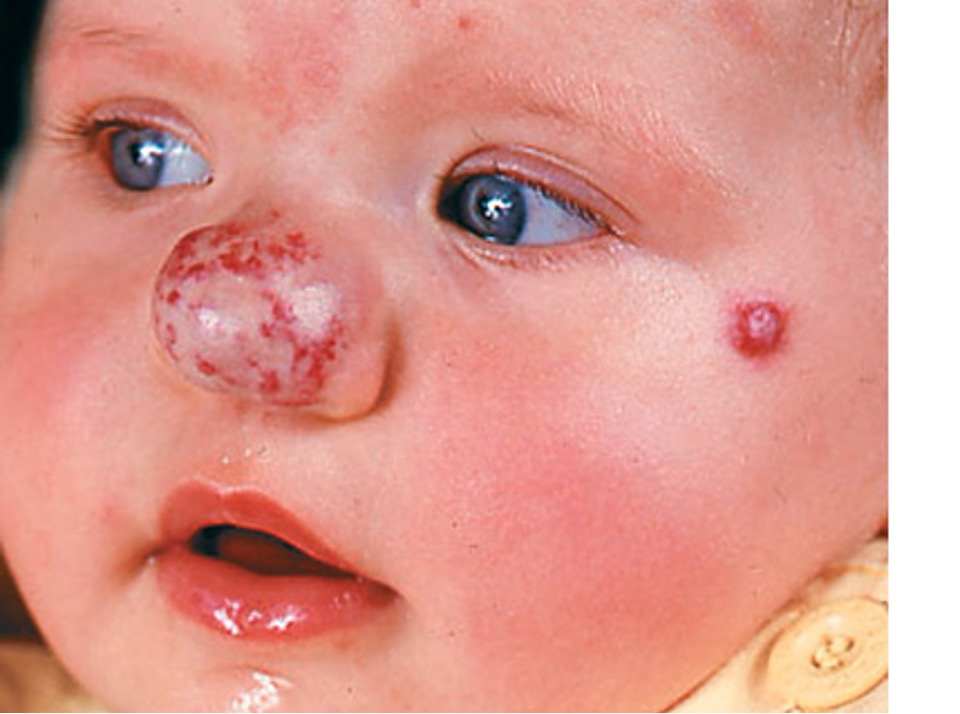
what condition?
irregularly shaped, painless red or violaceous patches that are present at birth and never disappear spontaneously
congenital low flow vascular malformation
blanchable
follows CN V and does not cross midline
assoc w/ sturge weber, klippel-trenaunay, CLOVES
treated w/ pulse dye laser
port wine stain
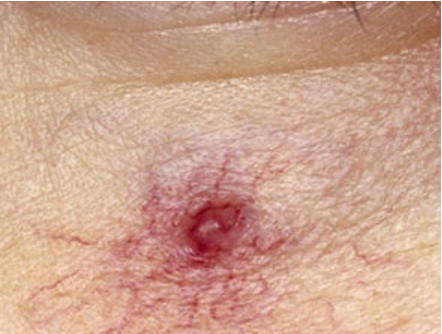
what lesion has this appearance under dermatoscope?
radiating telangiectasias
blanch
central arteriole may pulsate
spider angioma
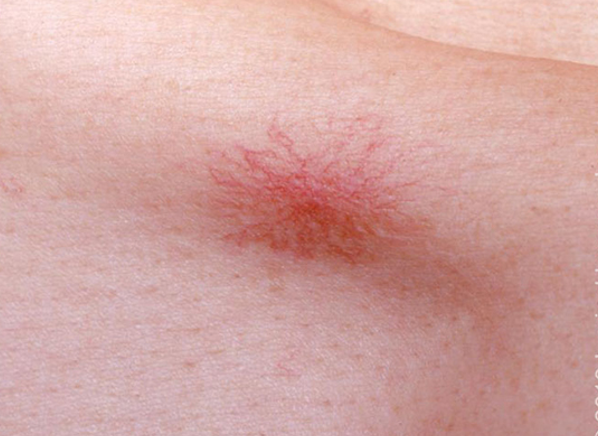
what lesion is an acquired vascular malformation of anomalous dilatation caused by failure of muscles involved in arteriole vasoconstriction? appear as:
central red papule w/ fine red lines that extend radially
face, forearms, hands
children, pregnancy, OCPs, cirrhosis
spider angionma / naevus / telangiectasia