Shafqat
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Where are antibodies found?
Free in serum
Free in secretions (mucous, milk, saliva, tears)
Surface of cells
Function of Antibodies
To binds to antigens with a complimentary shape and neutralise them.
Basic Antibody Structure
2 light chains
2 heavy chains
2 antigen binding sites
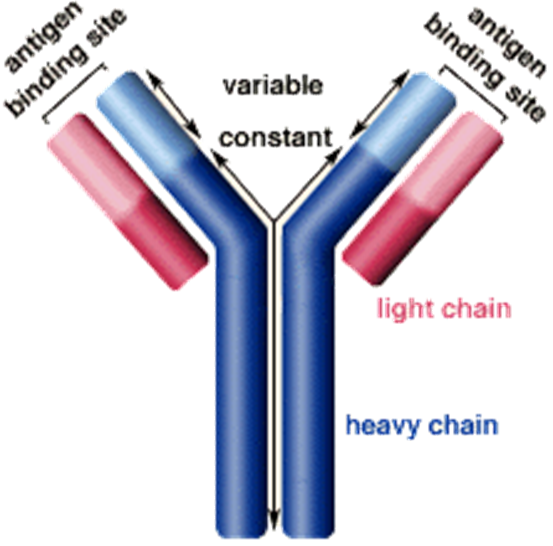
2 types of light chain
Kappa and Lambda
5 types of heavy chain
-Gamma
-Delta
-Epsilon
-Alpha
-Mu
How is diversity in an antibody produced
Through rearrangement of genes in the variable regionWhat
What binds chains together
disulphide bonds
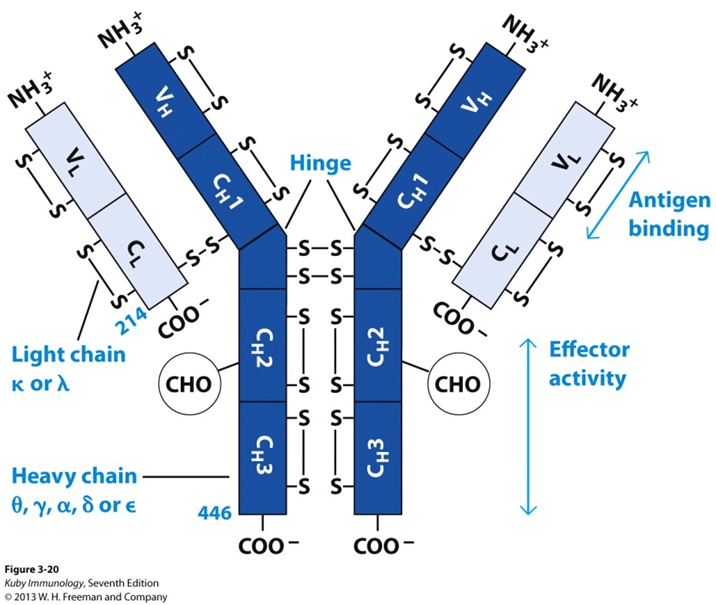
what is the function of the hinge region
provide flexibility when binding to the antigen
What is a CDR
Complimentary Determining Regions
-Binds to antigens
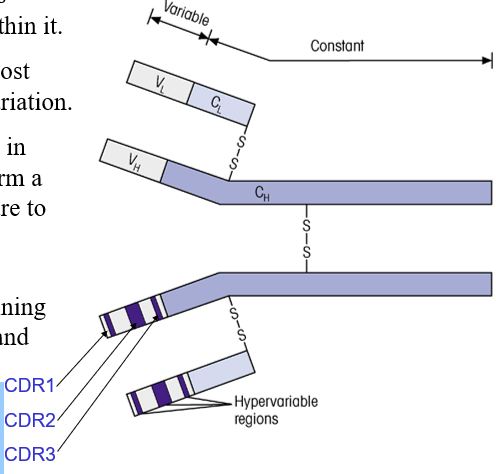
Structure of Variable Region
Forms a beta-sheet structure to hold hypervariable regions in place
Stability of variable region?
More stable amino acid sequence than CDR
CDR interactions with antigen
Hydrogen bonding
Electrostatic Forces
Van Der Waals Forces
Hydrophobic Forces
5 antibody classes
IgG
IgD
IgE
IgA
IgM
Type of chains in each
IgA has alpha chains, IgD has delta chains etc.
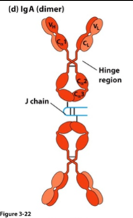
IgA Structure
Dimer of 2 antibodies joined by a J polypeptide chain
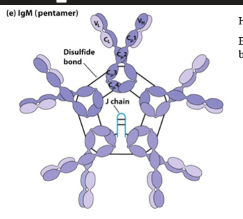
IgM Structure
Pentamer of 5 Ig molecules with Mu chains
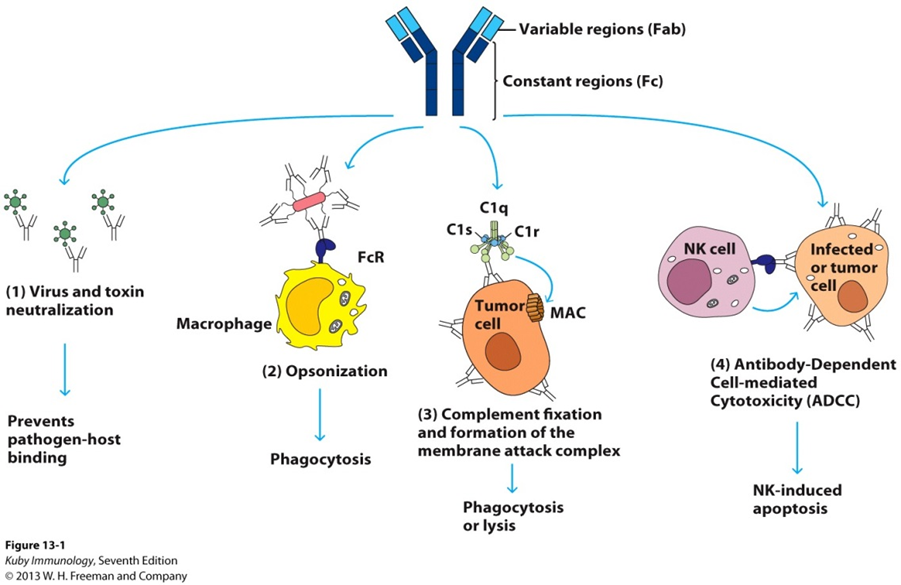
Functions of Antibodies
Immobilisation
Agglutination
Neutralisation
Opsonisation
Activation of Complement
Immobilisation of Bacteria (Antibodies)
Antibodies specific to flagella and cilia cause them to clump , preventing movement
What is agglutination?
The clumping of antibodies to antigens forming a large co
Benefits of agglutination? (2)
easier to dispose of antigens
antigen-antibody complexes are easily phagocytosed
What is the basis of blood group tests?
Haemagglutination
What is neutralisation (antibodies)
Bind to pathogens to disarm them and prevent toxins from entering the cell.
Disarmed pathogens are then phagocytosed
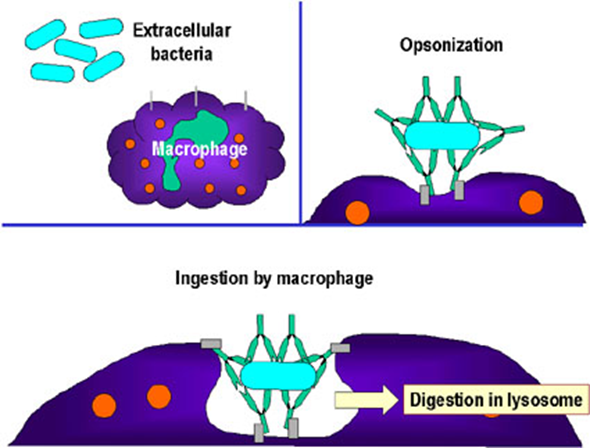
What is opsonisation?
Fab region binds to antigen
Fc region binds to receptors on phagocytic cells
Activation of Compliment by antibodies
Antibodies bound to pathogen act as a receptor for the first protein of the compliment system
What is ADCC and ADCP?
ADCC = Antibody Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity
ADCP = Antibody Dependent Cell-Mediated Phagocytosis
Process of ADCC/ADCP?
Fab region binds to infected cell
NK cell binds to Fc region
Perforin released
Granzymes pass through pores and destroy cell cytoskeleton causing apoptosis
What type of antibody is produced first in the immune response?
IgM
4 phases of antibody response to infection?
Lag phase
Exponential phase
Steady State
Declining Phase
3 Facts about secondary immune response.
Lag phase is shorter due to presence of memory cells
Antibody levels are higher for longer
Less IgM and more IgG
What is class switching?
genetic rearrangement allowing B-cells to stop producing IgM and produce other types of antibodies.
DOES NOT CHANGE ANTIGEN SPECIFICITY
What is affinity maturation?
B-cells produce antibodies with progressively higher affinity for an antigen
Where dos affinity maturation occur?
Germinal centres
What is somatic hypermutation?
Rapid point mutations in the variable regions of immunoglobulin genes.
enhances antibody diversity and specificity
Where does somatic hypermutation occur
In B-cells within germinal centres after antigen exposure
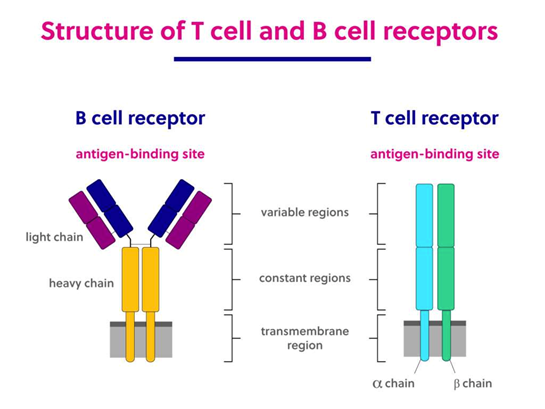
What is the function of a B-cell receptor?
binds to membrane bound and free-floating receptors
What is the function of a T-cell receptor?
Only binds to membrane bound receptor when antigen is attached
Shape of BCR and TCR
BCR is a Y shape, TCR is an I shape
What does MHC stand for?
Major Histocompatibility Complex
What does HLA stand for?
Human Leukocyte Antigen
What is the function of MHC?
Recognises foreign substances
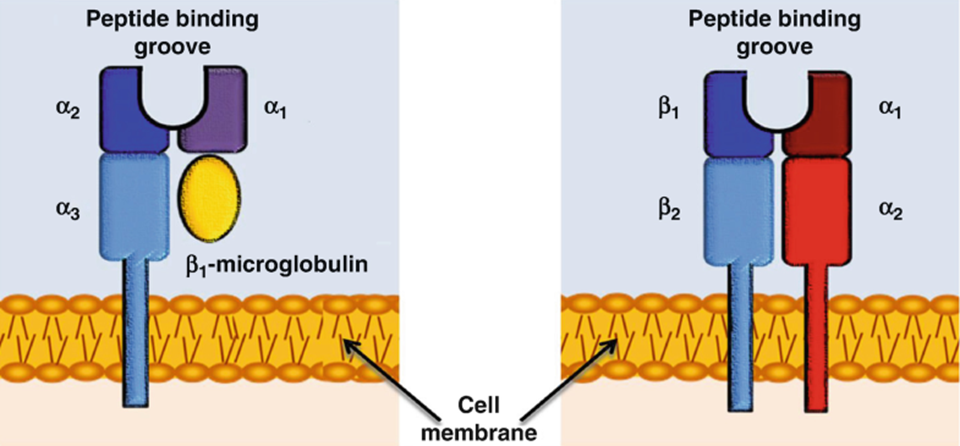
Difference between class1 and class2 MHC?
Class 1 has 1 heavy chain, class 2 has 2 heavy chains
What is an antigen?
Any substance that can elicit an immune response
What is a Complimentary Determining Region (CDR)?
Determine an antibodies specificity to an antigen an bind directly to it.
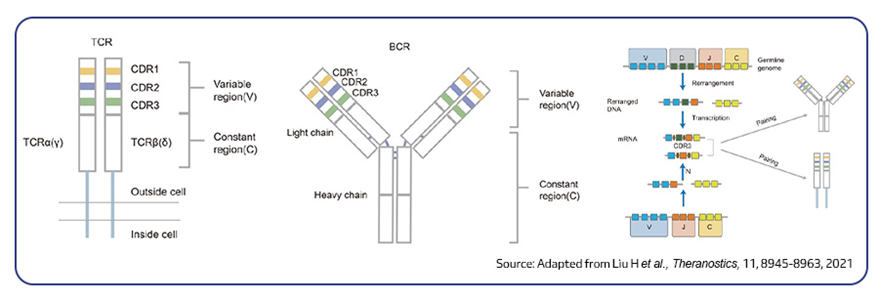
Sections of an immunoglobulin heavy chain (3)
Variable, Diversity, Joining segments
What are immunoglobulins?
hypervariable
T-cell rearrangement?
same as in B-cells as both are hypervariable
what is CD4?
T-helper cell
What is CD8?
cytotoxic T-cell
Where is MHC class 1 found?
on almost all nucleated cells
Where is MHC class 2 found?
B-cells
macrophages
dendritic cells
Differences of MHC classes
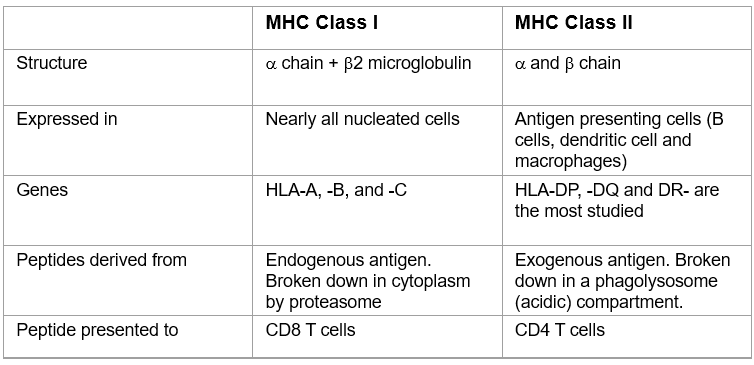
Function of MHC class 1

Function of MHC class 2

What marks a cell as self?
presence of MHC
What is the antigen presented on in an APC?
Antigen presented on MHC like a flagpole
Types of antigen presenting cell?
macrophages
Dendritic cells
B-cells
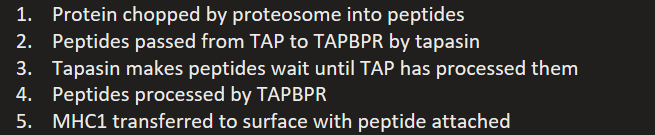
How is MHC1 presented?
Protein chopped by proteosome into peptides
Peptides passed from TAP to TAPBPR by tapasin
Tapasin makes peptides wait until TAP has processed them
Peptides processed by TAPBPR
MHC1 transferred to surface with peptide attached
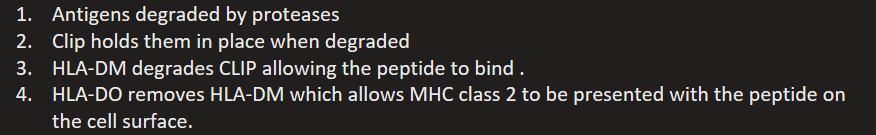
How is MHC2 presented?
Antigens degraded by proteases
Clip holds them in place when degraded
HLA-DM degrades CLIP allowing the peptide to bind .
HLA-DO removes HLA-DM which allows MHC class 2 to be presented with the peptide on the cell surface.
What do CD4 T-helper cells secrete to activate CD8 T-cells?
IL-2
How are T-cells activated?
MHC-peptide-TCR interaction
Co-stimulatory signals from CD80/86 with CD28
Cytokine signals
Inhibitory Signals via PD-L1-PD-1 OR CTLA-4 --CD80/86