Cold War Study Guide
1/89
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
Cold War
A competition between the United States and the Soviet Union for power and influence worldwide after WWII.
Length of Cold War
around 44 years (1947-1991)
3 things the Cold War influenced
American domestic politics, foreign affairs, and the government’s role in the economy.
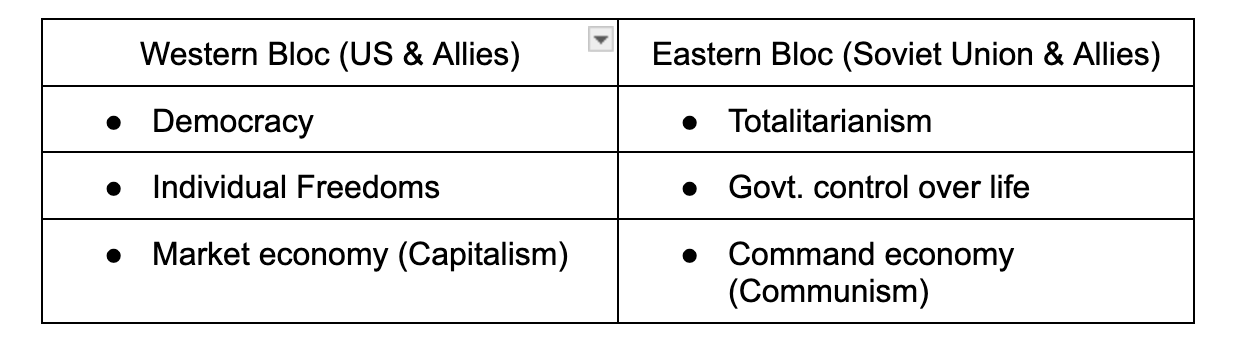
Differences between US vs. Soviet Union (govt., economy, & civil rights)
Events (3) causing tension between US and Soviet Union before WWII
Red Scare (1917–1920s): Fear of communism in the U.S. after the Russian Revolution.
Russia excluded from the peace conference after World War I.
Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact (1939): Increased distrust between the U.S. and the USSR
Aftermath of WWII and its impact on Soviet-US relations
U.S. & Soviet alliance during WWII was only temporary—deep mistrust remained.
Disagreements over battle strategies and postwar plans.
Potsdam Conference (1945) - Truman’s View of Stalin’s Expansionist Goals
President Harry Truman believed Joseph Stalin aimed for world domination; spreading communism possibly through revolution
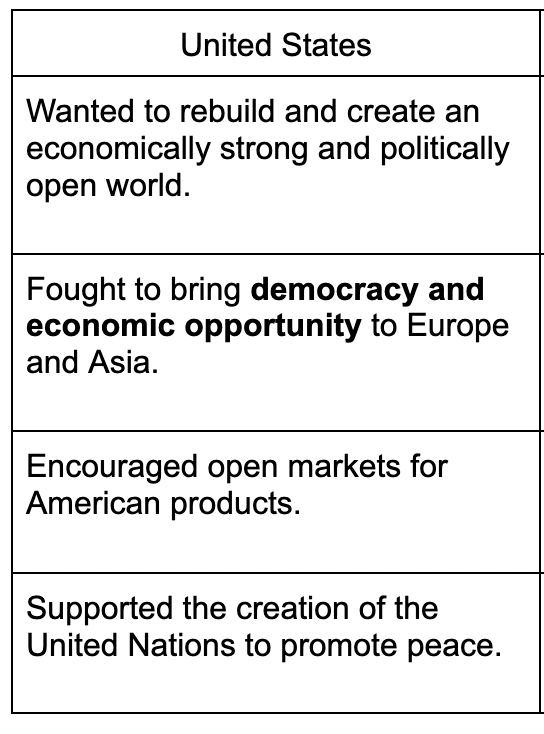
United States post-war goals
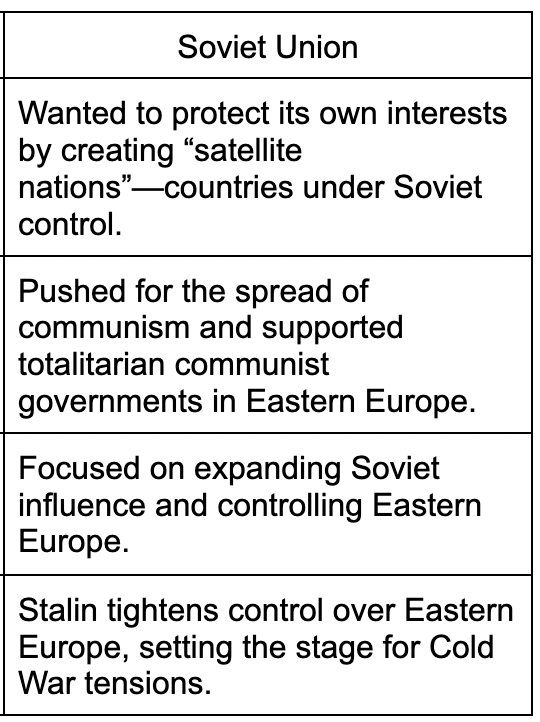
Soviet Union Post-war goals
3 Triggers to the Cold War
Iron Curtain speech, Truman Doctrine, Marshall Plan
Iron Curtain Speech (who, when, where)
Winston Churchill, 1946, Westminster College in Fulton, Missouri
Iron Curtain speech (3 key points)
Division of Eastern Europe 2. Threat of Soviet expansion 3. World War II + spread of communism could have been avoided if the right actions were taken earlier.
How Iron Curtain speech fueled the Cold war
highlighted the growing divide between the Western powers and the Soviet bloc. It increased anti-communist sentiment in the West.
Truman Doctrine (when)
1947
Truman Doctrine (what it states)
The U.S. would provide support—mainly military and economic aid—to countries that were threatened by communism
First 2 countries to be helped by truman doctrine
Greece and Turkey
How the Truman doctrine fueled the Cold War
established the U.S. policy of containment, which aimed to prevent the spread of communism globally, leading to increased tensions between the U.S. and the Soviet Union.
Providing help to countries at risk of communism fueled tensions between the U.S. and the Soviet Union
The Marshall plan (when)
1948
The marshall plan (what it is)
U.S. proposal to all European countries (including Soviet Union) to help rebuild Europe after World War II by giving $13 billion in aid to struggling countries
Idea behind the marshall plan
strong economies = stable governments, and poor economies could lead to communism
7 Steps for European reconstruction as per the Marshall plan
Upgrading factories and machines
Stabilizing currency and national budgets
Expanding trade and increasing exports
Encourage European countries to work together economically
Remove foreign trade restrictions
Boost production (ie. agriculture and energy)
Improve transportation systems
How the Marshall Plan fueled the Cold War (2 ways)
The U.S. was using money to fight communism by strengthening Western Europe.
The Soviet Union saw this as the U.S. trying to gain influence and stop communism from spreading in Europe.
containment (def)
US Cold War strategy of stopping the spread of Communism through the use of economic and military policies
Escalating tensions during the early cold war (3)
Berlin Crisis, China becomes a communist country, Korean War
Berlin Crisis (when)
1948-1949
Berlin Crisis (what)
An attempt by the Soviet Union to prevent allied forces from accessing West Berlin
Berlin Crisis (why + how)
The Soviets wanted to force the allied forces out of west berlin by cutting of all land and water access to this city
Effect of Berlin Crisis on West Berlin residents
Caused shortages of essential goods for 2.5 million people
Berlin Airlift
organized by the allied forces, over 200,000 flights were made to deliver necessary supplies to the residents of West Berlin.
End of berlin crisis (how) and its impact
The Soviets eventually lifted the blockade in May 1949, realizing it wasn’t working.
This event solidified the division of Germany and contributed to the growing East-West divide of the Cold War, with West Berlin becoming a symbol of freedom and resistance to Soviet control.
Chinese Civil War (when, who won, & what it resulted in)
1945-1949, CCP under Mao Zedong won, resulted in China becoming communist
People involved in Chinese Civil War
Chinese Communist Party (CCP), led by Mao Zedong, and the Nationalist Party (KMT), led by Chiang Kai-shek.
China’s government ideology before communism
Traditionally nationalist
United State’s role in the Chinese Civil War
provided aid to the Nationalists
Effect of the Chinese Civil War on U.S. & Cold War tensions (2 fears)
contributed to the U.S. fear of communism
fear of a “domino effect”, where one country’s shift to communism might lead to others following.
Soviet-Sino Treaty (1950)
a formal alliance between China and the Soviet Union marked by friendship, alliance, and mutual assistance
Reason for the end of Soviet-Chinese relations
they eventually became rivals over territory disputes and global influence
Korean War (when)
1950-1953
38th parallel (what is it and how did it happen)
Created after WWII, Korea was divided at the 38th parallel:
The United States occupied the South.
The Soviet Union occupied the North.
North Korea’s invasion of South Korea (who, when, why)
led by Kim Il-sung (a communist) on June 25th, 1950, in an effort to unify the entire country under communist rule.
US involvement in Korean War (why)
became involved to stop the spread of communism in line with the Truman Doctrine (containment policy)
Truman’s role in the Korean War (what did he support)
supported military intervention through the United Nations
MacArthur’s role in the Korean War
leading the U.N. forces, was initially successful in pushing North Korean forces back but clashed with Truman over strategic goals and the possibility of escalating the war into China
End of the Korean War (peace talks)
Peace talks began in July, 1951, but fighting dragged on until 1953 when the armistice was signed.
Result of the Korean War on Korea’s division
The Korean War ended in a stalemate. No clear victory for either side, leaving Korea divided at the 38th parallel, just like before the war.
American Casualties during the Korean War
37,000 deaths + 103,000 wounded
Korean War’s impact on public perception of Truman and democrats
led to the perception that Truman and the Democrats were “soft on communism”
Results of presidential election of 1953 (who won and what they promised)
Eisenhower and the republicans in 1953; took a tougher stance on communism
3 Changes to National Security Post WWII
National Security Act of 1947
NATO
Arms Race
NATO (what it is and what it means + who)
a security pact between Western European nations + the US; a military attack against any of the members would be considered an attack on them all.
Warsaw Pact (created in response to what and why)
created to counter NATO and ensured Soviet control over member countries’ militaries
Warsaw Pact (what + when)
a military alliance formed in 1955 between the Soviet Union and its communist allies in Eastern Europe
Arms Race
a competition between the U.S. and the Soviet Union to develop and stockpile superior weapons, particularly nuclear weapons, during the Cold War.
deterrence
US policy of making its military so strong that no enemy would dare attack, fearing massive retaliation
1949 Nuclear Threat (who+what+impact)
The Soviet Union, successfully tested its first nuclear bomb, ended the U.S.’s monopoly on nuclear weapons and intensified Cold War tensions.
Mutually Assured Destruction (MAD
The idea that if one country launched nuclear weapons, the other would retaliate with equal force, leading to total destruction on both sides
What mutually assured destruction prevented
prevented US and USSR countries from using nuclear weapons
Yooks vs. Zooks (butter battle book)
Americans vs. Russians (butter battle book)
Butter side up vs Butter side down (butter battle book)
democracy vs communism (butter battle book)
wall (butter battle book)
iron curtain/berlin wall (butter battle book)
parades (butter battle book)
support of american people to contain communism (butter battle book)
building bigger and bigger weapons (butter battle book)
arms race (butter battle book)
Amount of nuclear weapons in US today
5044 nuclear weapons
Amount of nuclear weapons in UK today
225 nuclear weapons
Amount of nuclear weapons in Russia today
5580 nuclear weapons
Amount of nuclear weapons in North Korea today
50 nuclear weapons
Amount of nuclear weapons in France today
290 nuclear weapons
Amount of nuclear weapons in Israel today
90 nuclear weapons
Amount of nuclear weapons in Pakistan today
170 nuclear weapons
Amount of nuclear weapons in India today
172 nuclear weapons
Amount of nuclear weapons in China today
500 nuclear weapons
Sputnik I (when + what)
First artificial satellite launched by the Soviet Union on October 4, 1957
Impact of Sputnik I on the US (3 things)
Started the Space Race between the U.S. and the USSR
Showed Soviet technological/military advantage, worried the U.S.
Led to the creation of NASA (1958) and more focus on science & tech education
Apollo II (when, what, who)
First Moon landing by the U.S.
Astronauts: Neil Armstrong, Buzz Aldrin, Michael Collins
July 20, 1969
Apollo 11 (2 impacts)
Proved U.S. technological dominance, won the Space Race
Major Cold War victory for the U.S.
Berlin Wall (why it was built + when)
• Berlin, though located inside East Germany, was also divided into East Berlin (Soviet-controlled) and West Berlin (democratic).
• Many East Germans were escaping to West Berlin to have better jobs, more freedom, and escape communism.
• The Soviet-backed East German government built the Berlin Wall (August 13, 1961) to stop people from leaving.
Berlin Wall (what it separated)
Completely sealed off West Berlin from East Berlin and East Germany.
Bay of Pigs Invasion (when + what)
April 17–19, 1961; The U.S. (under President John F. Kennedy) tried to overthrow Fidel Castro, the communist leader of Cuba.
Bay of Pigs Invasion (what happened; 3 things)
The CIA trained and armed Cuban exiles (people who had fled Cuba) to invade and start an uprising.
The exiles landed at the Bay of Pigs in Cuba, expecting local Cubans to join them against Castro.
The invasion failed—Castro’s forces quickly defeated them, and the U.S. did not provide enough support.
Bay of Pigs Invasion (end result)
Huge embarrassment for the U.S. and JFK.
Strengthened Castro’s power and pushed him closer to the Soviet Union.
Increased Cold War tensions, leading to the Cuban Missile Crisis (1962).
Cuban Missile Crisis (when + how long it lasted)
October 16–28, 1962 (13 days)
Cuban Missile Crisis (how it started)
The U.S. discovered Soviet nuclear missiles in Cuba, just 90 miles from Florida.
The U.S. saw this as a major threat since the missiles could reach American cities in minutes.
JFK’s response to Cuban Missile Crisis
• Setting up a naval blockade to stop more Soviet missiles from arriving.
• Demanding the removal of existing missiles.
• Warning of military action if the Soviets refused.
Results of Cuban Missile Crisis (2 things)
• Soviets agreed to remove the missiles from Cuba.
• In exchange, the U.S. secretly agreed to remove its missiles from Turkey (near the Soviet Union).
Impact of the Cuban Missile crisis
• Closest the Cold War ever came to nuclear war.
• Led to a hotline between the U.S. and Soviet Union to improve communication.
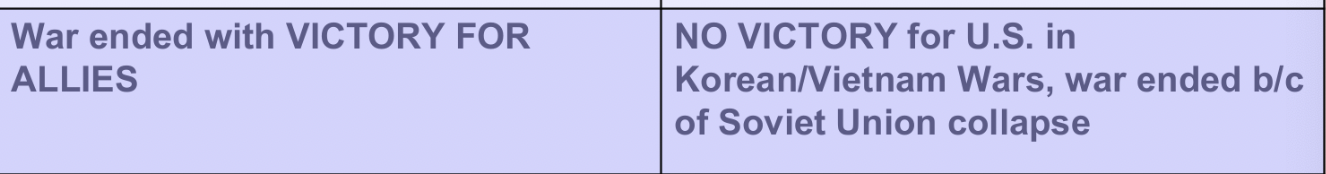
Differences between WWII and Cold War (countries involved)
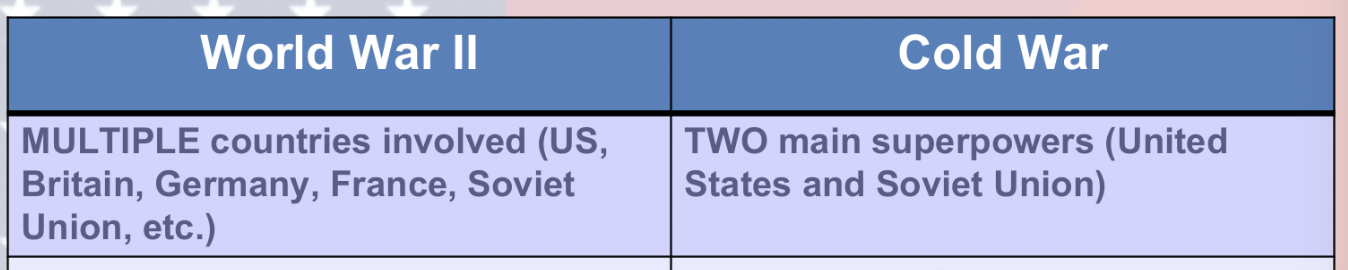
Differences between WWII and Cold War (who vs. who/ what vs. what)

Differences between WWII and Cold War (military engagement)

Differences between WWII and Cold War (nuclear weapons used)

Differences between WWII and Cold War (end result/who won)