Physics w/Calculus 2 - Resistance, Electromotive Force, and Direct-Current Circuits (Ch 25-26)
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
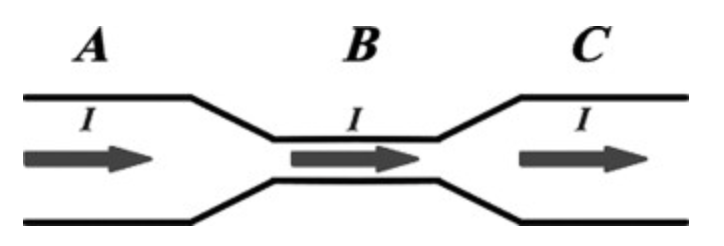
The figure shows a steady electric current passing through a wire with a narrow region. What happens to the drift velocity of the moving charges as they go from region A to region B and then to region C?
A. The drift velocity decreases from A to B and increases from B to C
B. The drift velocity remains constant
C. The drift velocity decreases all the time
D. The drift velocity increases from A to B and decreases from B to C
E. The drift velocity increases all the time
D
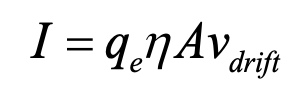
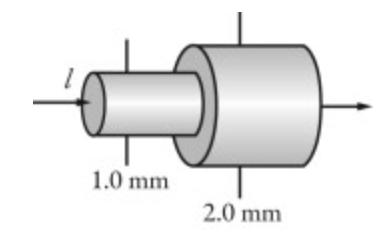
The figure shows two connected wires that are made of the same material. The current entering the wire on the left is 2.0 A and in that wire the electron drift speed is 𝑣 d. What is the electron drift speed in the wire on the right side?
𝑣 d/4
Which of the following statements are true?
A. By convention, the direction of a current is taken to be the direction of flow for negative charges
B. Current is the total amount of charge that passes through a conductor's full cross section at any point per unit of time
C. In a circuit, current is delivered by the positive terminal of a battery, and it is used up by the time it returns to the negative terminal of the battery
D. In order to maintain a steady flow of current in a conductor, a steady force must be maintained on the mobile charges
E. When an electric field is applied to a conductor, the free electrons move only in the direction opposite the applied electric field
B, D
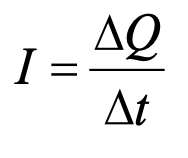
Which of the following will increase the resistance of a wire?
A. Increasing the cross-sectional area of the wire will increase the resistance of the wire
B. Increasing the resistivity of the material the wire is composed of will increase the resistance of the wire
C. Decreasing the cross-sectional area of the wire will increase the resistance of the wire
D. Increasing the length of the wire will increase the resistance of the wire
E. Decreasing the length of the wire will increase the resistance of the wire
F. Decreasing the resistivity of the material the wire is composed of will increase the resistance of the wire
B, C, D
Which of the following statements are true?
A. The resistance of a conductor is proportional to the conductivity of the material of which the conductor is composed
B. Good conductors of electricity have larger conductivity values than insulators
C. A material that obeys Ohm's law reasonably well is called an ohmic conductor or a linear conductor
D. The resistance of a conductor is proportional to the resistivity of the material of which the conductor is composed
E. Semiconductors have resistivity values that are larger than those of insulators
B, C, D
Consider two copper wires with the same cross-sectional area. Wire A is twice as long as wire B. How do the resistivities and resistances of the two wires compare?
A. Wire A has twice the resistivity of wire B
B. Wire A has twice the resistance of wire B
C. Wire A and wire B have the same resistivity
D. Wire B has twice the resistance of wire A
E. Wire B has twice the resistivity of wire A
F. Wire A and wire B have the same resistance
B, C
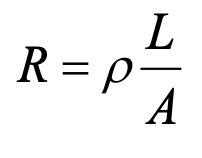
If the voltage across a circuit of constant resistance is doubled, how is the current in the circuit affected?
A. The current is reduced by a factor of 2
B. The current is quadrupled
C. The current is reduced by a factor of 4
D. The current remains constant
E. The current is doubled
E
If the resistance in a circuit connected to a constant current is halved, how is the voltage in the circuit affected?
A. The voltage remains constant
B. The voltage is reduced by a factor of 4
C. The voltage is reduced by a factor of 2
D. The voltage is doubled
E. The voltage is quadrupled
C
Which of the following statements are true?
A. A battery is a device that produces electricity by transforming chemical energy into electrical energy
B. The potential difference between the terminals of a battery, when no current flows to an external circuit, is referred to as the terminal voltage
C. A battery does work on electric charges to bring them to a position of higher electric potential energy so that they can flow through a circuit to a lower potential energy
D. The internal resistance of a battery decreases with decreasing temperature
C
A constant voltage is applied across a circuit. If the resistance in the circuit is doubled, what is the effect on the power dissipated by the circuit?
A. The power dissipated remains constant
B. The power dissipated is quadrupled
C. The power dissipated is reduced by a factor of 4
D. The power dissipated is reduced by a factor of 2
E. The power dissipated is doubled
D
A circuit maintains a constant resistance. If the current in the circuit is doubled, what is the effect on the power dissipated by the circuit?
A. The power dissipated is quadrupled
B. The power dissipated is doubled
C. The power dissipated is reduced by a factor of 2
D. The power dissipated remains constant
E. The power dissipated is reduced by a factor of 4
A
What happens to the resistance of most common metals as the temperature of the metal increases?
A. The resistance decreases as temperature increases
B. The resistance increases as temperature increases
C. Whether resistance increases or decreases as temperature increases depends on the type of metal
D. The resistance remains constant as temperature increases
B
Consider three resistors with unequal resistances connected in series to a battery. Which of the following statements are true?
A. The equivalent resistance of the combination of resistors is greater than the resistance of any one of the three resistors
B. The algebraic sum of the currents flowing through each of the three resistors is equal to the current supplied by the battery
C. The current flowing through each of the resistors is the same and is equal to the current supplied by the battery
D. The algebraic sum of the voltages across the three resistors is equal to the voltage supplied by the battery
E. The equivalent resistance of the combination of resistors is less than the resistance of any one of the three resistors
F. The voltage across each of the resistors is the same and is equal in magnitude to the voltage of the battery
A, C, D
Consider three resistors with unequal resistances connected in parallel to a battery. Which of the following statements are true?
A. The voltage across each of the resistors is the same and is equal in magnitude to the voltage of the battery
B. The equivalent resistance of the combination of resistors is less than the resistance of any one of the three resistors
C. The algebraic sum of the currents flowing through each of the three resistors is equal to the current supplied by the battery
D. The algebraic sum of the voltages across the three resistors is equal to the voltage supplied by the battery
E. The equivalent resistance of the combination of resistors is greater than the resistance of any one of the three resistors
F. The current flowing through each of the resistors is the same and is equal to the current supplied by the battery
A, B, C
As additional resistors are connected in series to a constant voltage source, how is the power supplied by the source affected?
A. The power supplied by the sources remains constant
B. The power supplied by the source decreases
C. The power supplied by the source increases
D. The effect on the power supplied by the source cannot be determined without knowing the voltage of the source
B
As additional resistors are connected in parallel to a constant voltage source, how is the power supplied by the source affected?
A. The power supplied by the sources remains constant
B. The effect on the power supplied by the source cannot be determined without knowing the voltage of the source
C. The power supplied by the source decreases
D. The power supplied by the source increases
D
Which of the following statements are true?
A. At any junction point in a circuit, the sum of all the currents entering the junction must equal the sum of all the currents leaving the junction
B. Kirchhoff's loop rule is based on the conservation of charge
C. The sum of the changes in potential around any closed loop of a circuit must equal zero
D. Kirchhoff's junction rule is based on the conservation of energy
A, C