Chapter 11 - Liquids and Intermolecular
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/39
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
1
New cards
Intermolecular means
forces between molecules
2
New cards
What breaks intermolecular forces
Boiling
3
New cards
Gases and Liquids
Fluids
4
New cards
Liquids and Solids
Condensed states
5
New cards
Dispersion forces or London forces
Only occurs in non-polar molecules. It is constantly shifting to a different set of temporary forces.
6
New cards
Polarizability
The tendency of an electron cloud to disort.
7
New cards
Tighter molecules
Lower surface area, lower boiling point
8
New cards
Dipole-dipole interactions
They form permanent dipoles. Occurs in polar molecules.
9
New cards
Bad interactions
2 positive or 2 negative banging into each other
10
New cards
Hydrogen bonding
Strongest force. It can only be formed with a hydrogen atom bonding with a nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine atom.
11
New cards
Crystalatus
Smallest defined unit that repeats inside a molecule.
12
New cards
Only liquid that freezes from the top
Water
13
New cards
Ion-dipole interactions
* Found in solutions of ions.
* Can only occur with polar compounds.
* Can only occur with polar compounds.
14
New cards
2 molecules with comparable moral masses and shapes
Dispersion forces are equal.
15
New cards
2 molecules have very different molar masses and there's no H-bonding
Dispersion force determines the substance with stronger attractions.
16
New cards
Viscosity
Resistance of a liquid to flow.
Increases with strong forces, decreases with higher temperature.
Increases with strong forces, decreases with higher temperature.
17
New cards
Surface tension
Water acts as if it has a skin be of the extra forces on the surface allowing water to bead up when in contact with nonpolar surfaces.
18
New cards
Capillary action
The rise of liquid up narrow tubes.
19
New cards
Cohesive forces
Intermolecular forces that bind similar molecules to one another.
20
New cards
Adhesive forces
Intermolecular forces that bind a substance to a surface.
21
New cards
Phase change
Conversion from one state to matter to another.
22
New cards
Melting / Fusion
Solid to liquid, endothermic.
23
New cards
Freezing
Liquid to solid, exothermic.
24
New cards
Vaporization
Liquid to gas, endothermic.
25
New cards
Condensation
Gas to liquid, exothermic.
26
New cards
Sublimation
Solid to gas, endothermic.
27
New cards
Deposition
Gas to solid, exothermic.
28
New cards
Heating curve
Graph of temperature (y) and the heat added (x).
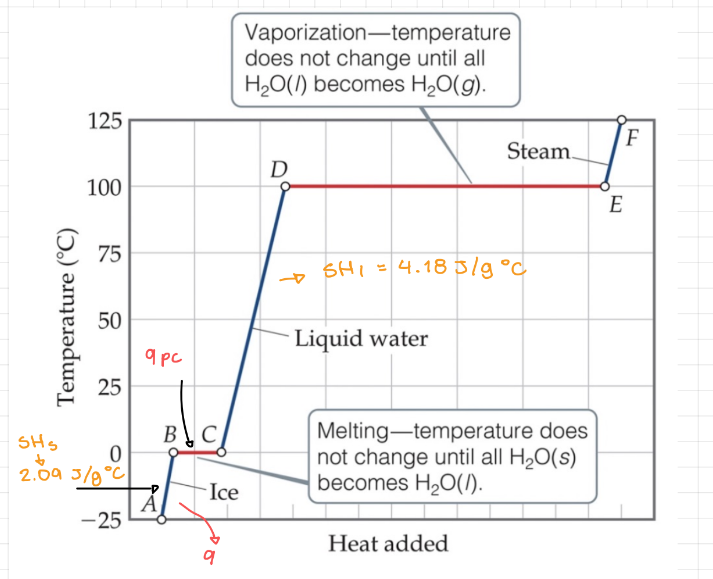
29
New cards
Vapor pressure formula
* **P = nRT/V**
* **P = MRT**
* M - molarity
* R - gas constant
* **P = MRT**
* M - molarity
* R - gas constant
30
New cards
Vapor pressure
How much of a liquid evaporates at a certain pressure.
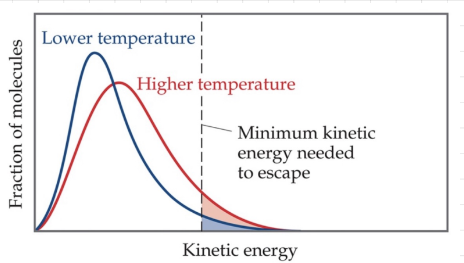
31
New cards
Vapor pressure at any temperature
__Some__ liquid molecules have enough energy to escape the surface and become a gas.
32
New cards
Vapor pressure while temperature increases
__More__ molecules are able to have enough energy to become a gas.
33
New cards
Natural log of the vapor pressure
It’s inversely proportional to its temperature.
34
New cards
Clausius-Clayperon equation

35
New cards
Clausius-Clayperon equation uses
* We can find **ΔH of vaporization** if we know the vapor pressure and the temperature at one point.
* We can find the **pressure at point 1** when we know the ΔH of vaporization and the temperature at point 2.
* We can find the **pressure at point 1** when we know the ΔH of vaporization and the temperature at point 2.
36
New cards
Phase diagram
A graph that shows the states of matter under conditions of temperature and pressure.
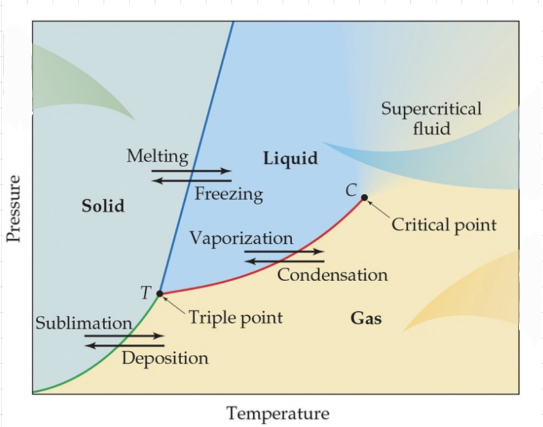
37
New cards
Triple point
The point where all three states of matter coexist.
38
New cards
between what are triple points
between the liquid and gas or between two solids
39
New cards
Critical point
* The point at which no amount of pressure alone can liquify the gas.
* Here you can’t tell the difference between a gas and a liquid.
* Here you can’t tell the difference between a gas and a liquid.
40
New cards
How many triple points does carbon has
2