Chapter 11 - Liquids and Intermolecular
- Intermolecular - Forces between molecules.
- ==Boiling== breaks intermolecular forces.
Properties that reflect intermolecular forces
- Boiling point
- Melting point
- Viscosity
- Surface tension
- Capillary action
- Water has a ==high surface tension==.
States of matter
- Gas
- Liquid
- Solid
- ==Gases and liquids== are called fluids.
- ==Liquids and solids== are called condensed states, they have strong forces.
Intermolecular forces (Weakest to strongest)
- Dispersion forces or London forces - Only occurs in non-polar molecules. It is constantly shifting to a different set of temporary forces.
- The tighter the molecules, the lower the surface area they have, and the lower their boiling point is.
- Ex. Neopentane has a ==lower boiling point== than pentane because neopentane has a lower surface area.
- Dipole-dipole interactions - They form permanent dipoles. Occurs in polar molecules.
- Bad interactions - 2 positive or 2 negative banging into each other.
- Hydrogen bonding - Strongest force. It can only be formed with a hydrogen atom bonding with a nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine atom.
- Crystalatus - Smallest defined unit that repeats inside a molecule.
- Water is the only liquid that freezes from the top.
Ion-dipole interactions
- Found in solutions of ions.
- Can only occur with polar compounds.
Relative strengths of intermolecular forces
- When 2 molecules have comparable moral masses and shapes, dispersion forces are equal.
- When 2 molecules have very different molar masses and there's no H-bonding, dispersion force determines the substance with stronger attractions.
Properties affected by intermolecular forces
- Viscosity - Resistance of a liquid to flow. Increases with strong forces, decreases with higher temperature.
- Surface tension - Water acts as if it has a skin be of the extra forces on the surface allowing water to bead up when in contact with nonpolar surfaces.
- Capillary action - The rise of liquid up narrow tubes.
- Cohesive forces - Intermolecular forces that bind similar molecules to one another.
- Adhesive forces - Intermolecular forces that bind a substance to a surface.
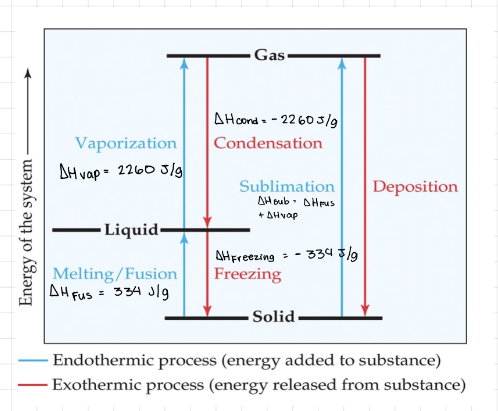
Phase changes
- Phase change - Conversion from one state to matter to another.
- Melting / Fusion - Solid to liquid, endothermic.
- Freezing - Liquid to solid, exothermic.
- Vaporization - Liquid to gas, endothermic.
- Condensation - Gas to liquid, exothermic.
- Sublimation - Solid to gas, endothermic.
- Deposition - Gas to solid, exothermic.
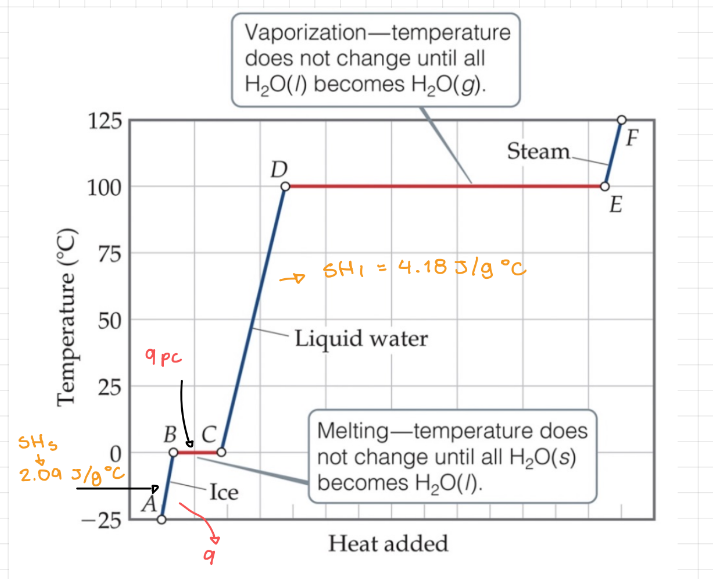
Heating Curves
- Heating curve - Graph of temperature (y) and the heat added (x).
Vapor pressure
- As temperature increases, more molecules are able to have enough energy to become a gas.
- P = nRT/V
- P = MRT
- M - molarity
- R - gas constant
- Vapor pressure - How much of a liquid evaporates at a certain pressure.
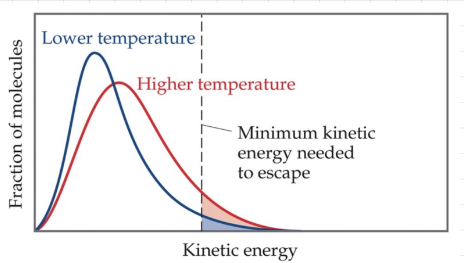
- At any temperature, some liquid molecules have enough energy to escape the surface and become a gas.
Vapor pressure curves

Natural log of the vapor pressure - It’s inversely proportional to its temperature.
Clausius-Clayperon equation

- We can find ΔH of vaporization if we know the vapor pressure and the temperature at one point.
- We can find the pressure at point 1 when we know the ΔH of vaporization and the temperature at point 2.
Formula simplification

Phase diagrams
- Phase diagram - A graph that shows the states of matter under conditions of temperature and pressure.
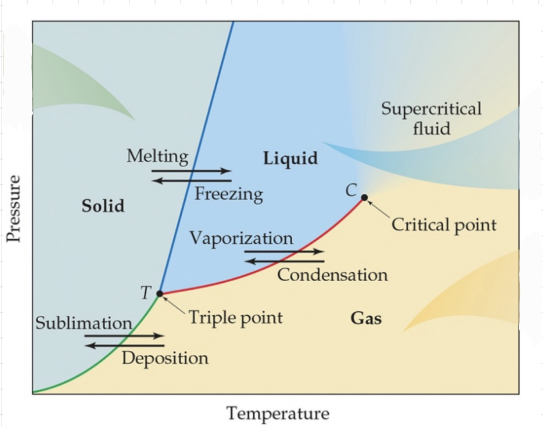
- Triple point - The point where all three states of matter coexist.
- Critical point - The point at which no amount of pressure alone can liquify the gas.
- Here you can’t tell the difference between a gas and a liquid.
- PHASE DIAGRAM OF WATER

- Water can melt only by pressure.
- The slope of the melting curve is negative, meaning that as the pressure goes up, the melting point goes down.
- CARBON PHASE DIAGRAM
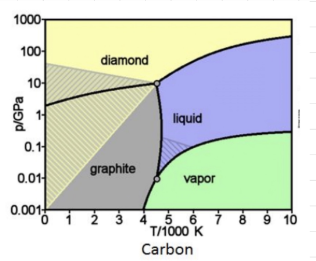
- Carbon has two triple points.
- Triple points are always between the liquid and gas or between two solids.