Matter: Properties, Changes & Classification
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Solid, Liquid, Gas Elements, Mixture, Compound Particle Diagrams Homogeneous vs. Heterogeneous Mixtures Separation of Mixtures ● Filtration ● Evaporation ● Distillation Physical and Chemical Properties and Changes Intensive and Extensive Properties Law of multiple proportions Law of constant composition Law of conservation of mass
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
chemistry
the study of matter and its changes
chemical
a substance that always has the same composition and properties wherever it is found
e.g) water (H₂O), salt (NaCl), sugar (C₆H₁₂O₆)
matter
has mass and takes up space (volume)
made of atoms
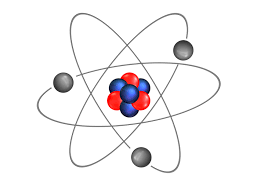
atom
the smallest part of a substance that cannot be broken down chemically
made up of subatomic particles
proton
neutron
electron
element
made of one single type of atom only.
cannot be broken down into simpler chemical substances by ordinary means.
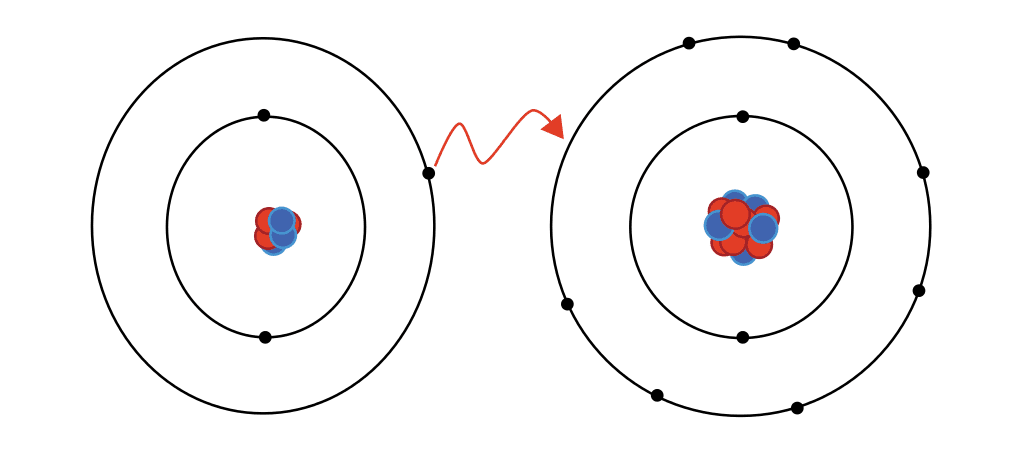
ionic bond
transfers electrons
between metal & nonmetal
e.g) NaCl = ionic
sodium is a metal
chlorine is a nonmetal
covalent bond
shares electrons
between two non metals
e.g ) H₂O = covalent
hydrogen is a nonmetal
oxygen is a nonmetal
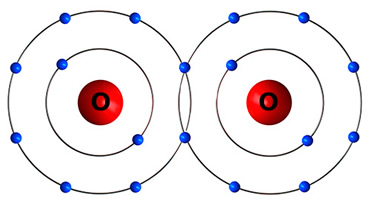
compound
two or more different elements chemically combined in a fixed ratio
e.g) H₂O (water), C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁ (sugar), CO₂ (carbon dioxide)
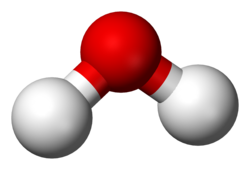
molecule
a group of atoms covalently bonded together
can be all different or same element
nonmetals
e.g) Ozone (O₃), water) H₂O
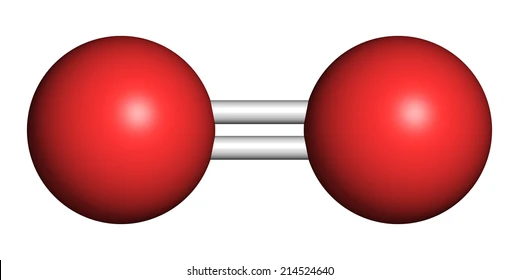
molecule vs compound
a molecule is any group of two or more atoms bonded together, while a compound is a type of molecule that contains at least two different elements
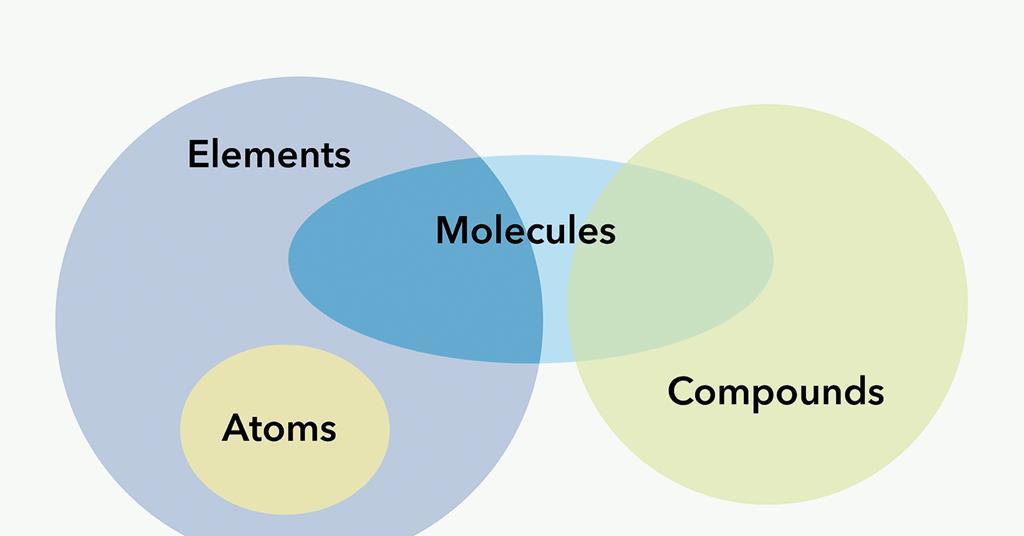
pure substance
matter with constant composition.
pure substances = only one type of element or compound
mixtures
two or more substances mixed together but not chemically joined.
proportions can vary.
homogeneous
heterogeneous
pure substance vs mixture
a pure substance has a fixed, uniform composition made of only one type of element or compound
while a mixture is a physical combination of two or more pure substances with a variable composition that can be separated by physical means.

homogeneous
one phase only.
parts of mixture are not distinguishable by naked eye.
often aqueous (dissolved in liquid).
a combination of substances that are evenly distributed and uniform composition.
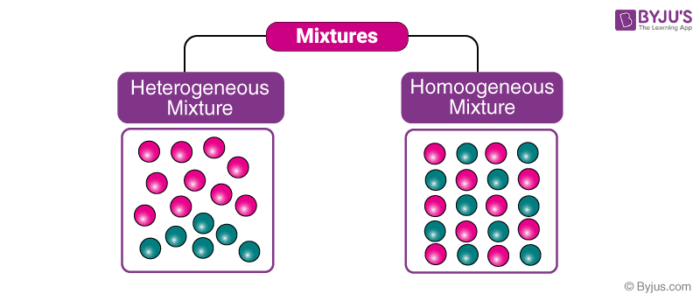
heterogenous
two or more phases.
components are not evenly distributed and remain physically separate.
parts distinguishable.

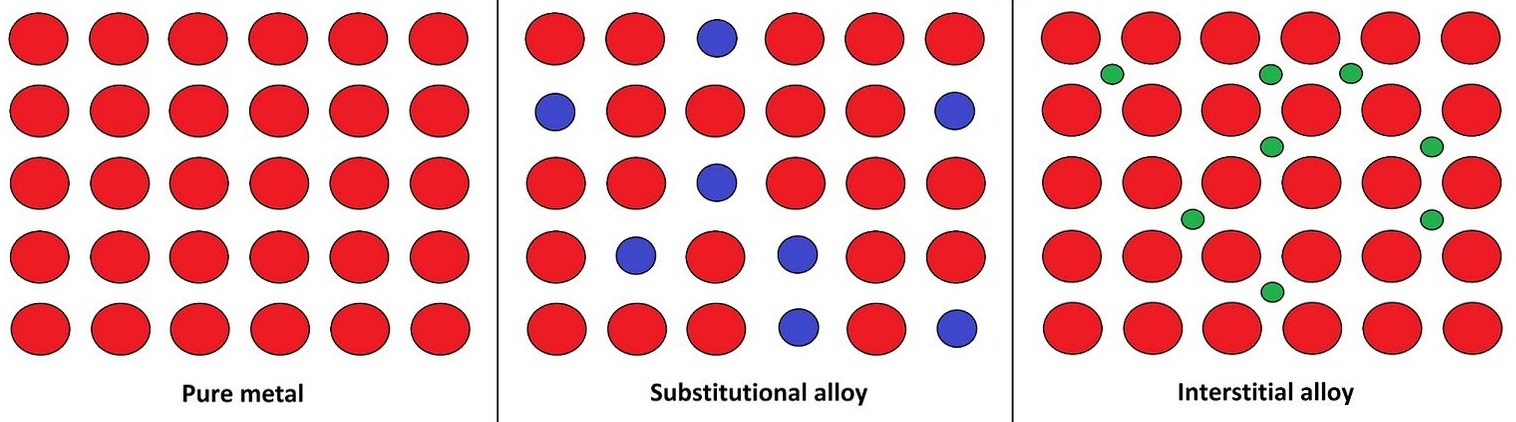
alloy
mixture of two or more metals, or a metal and one or more nonmetal.
pure metal - single type of atom.
substitutional - mixtures of metals where atoms of one metal replace atoms of another.
interstitial - in between spaces.
separation of mixtures
physical change is used to separate mixtures because there are no chemical interactions between the components.
filtration
the process of separating a mixture of a solid and a liquid.

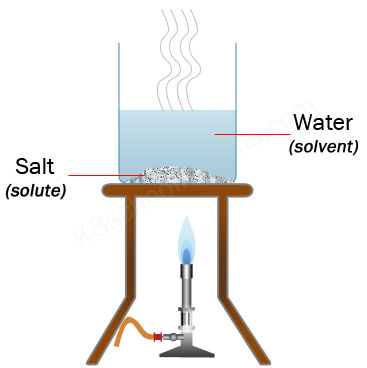
evaporation
the process of heating the mixture to turn the liquid into a gas (vapor) to leave the solid behind.
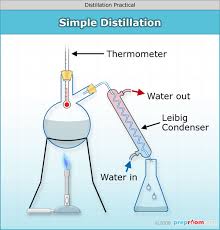
distillation
separates a liquid mixture based on different boiling points.
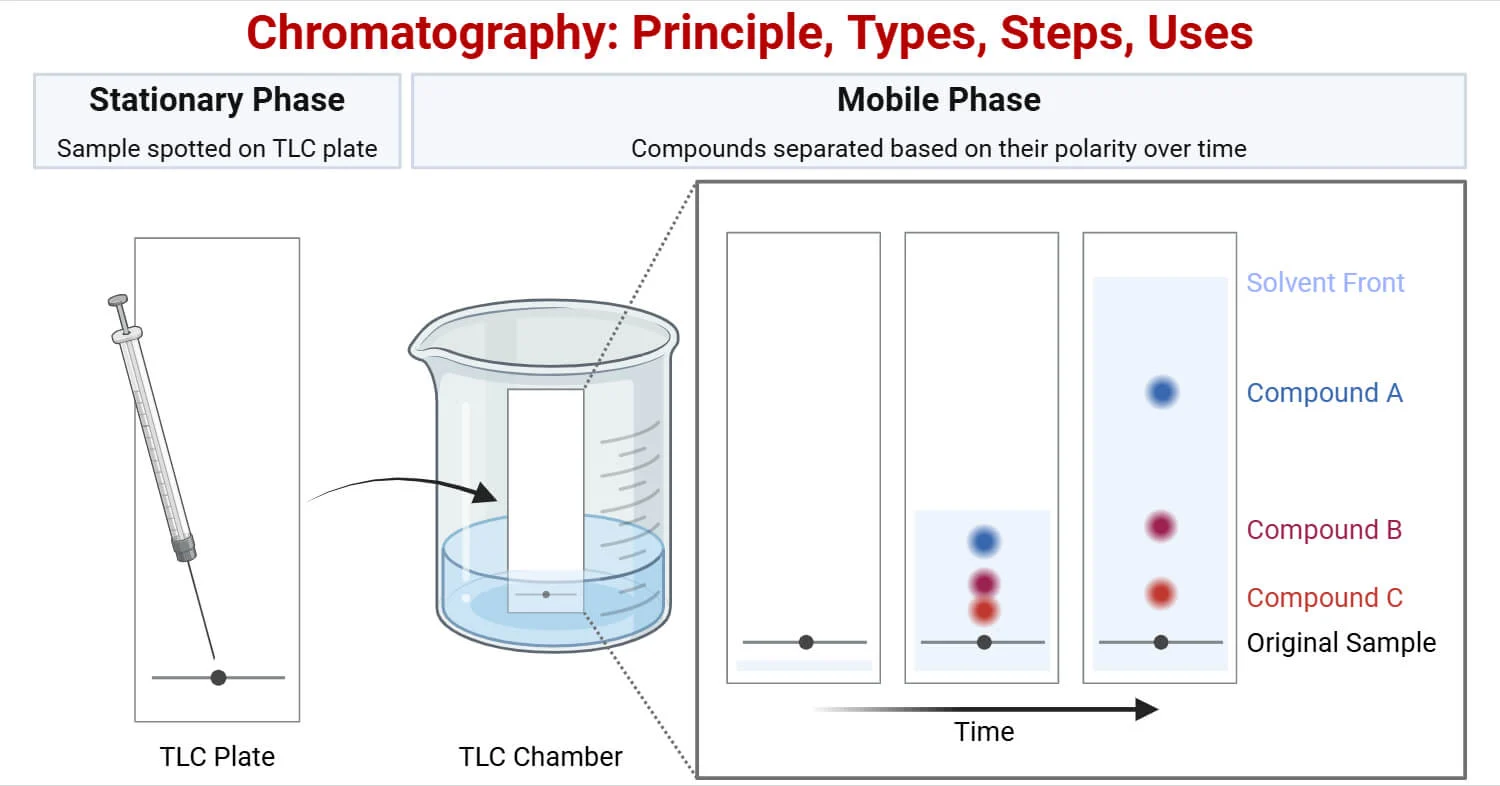
chromatography
separate a mixture by different solubility in a solvent.
solute = dissolved by solvent.
solvent = dissolves the solute.
physical change
alters the appearance, form, or state of a substance without changing its chemical composition.
e.g) state, volume, temperature.
chemical change
changes that result in new substances with their own set of properties.
changes the chemical composition.
e.g) combustion, oxidation, decomposition.
physical properties
characteristics of a substance that can be observed without changing identity.
e.g) melting point, mass, color, dissolubility.
chemical properties
characteristics of a substance that can be observed only by changing chemical composition.
e.g) flammability, reactivity, acidity.
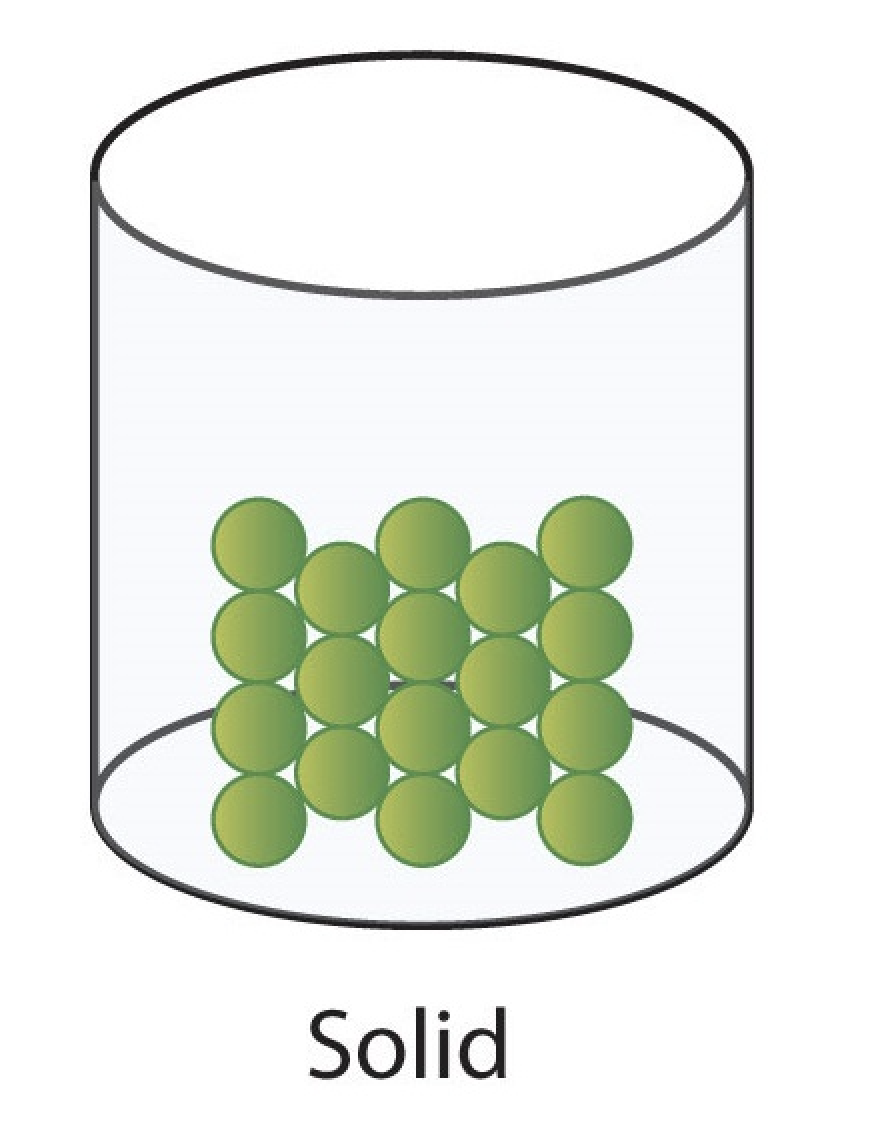
solid
definite volume.
holds its shape.
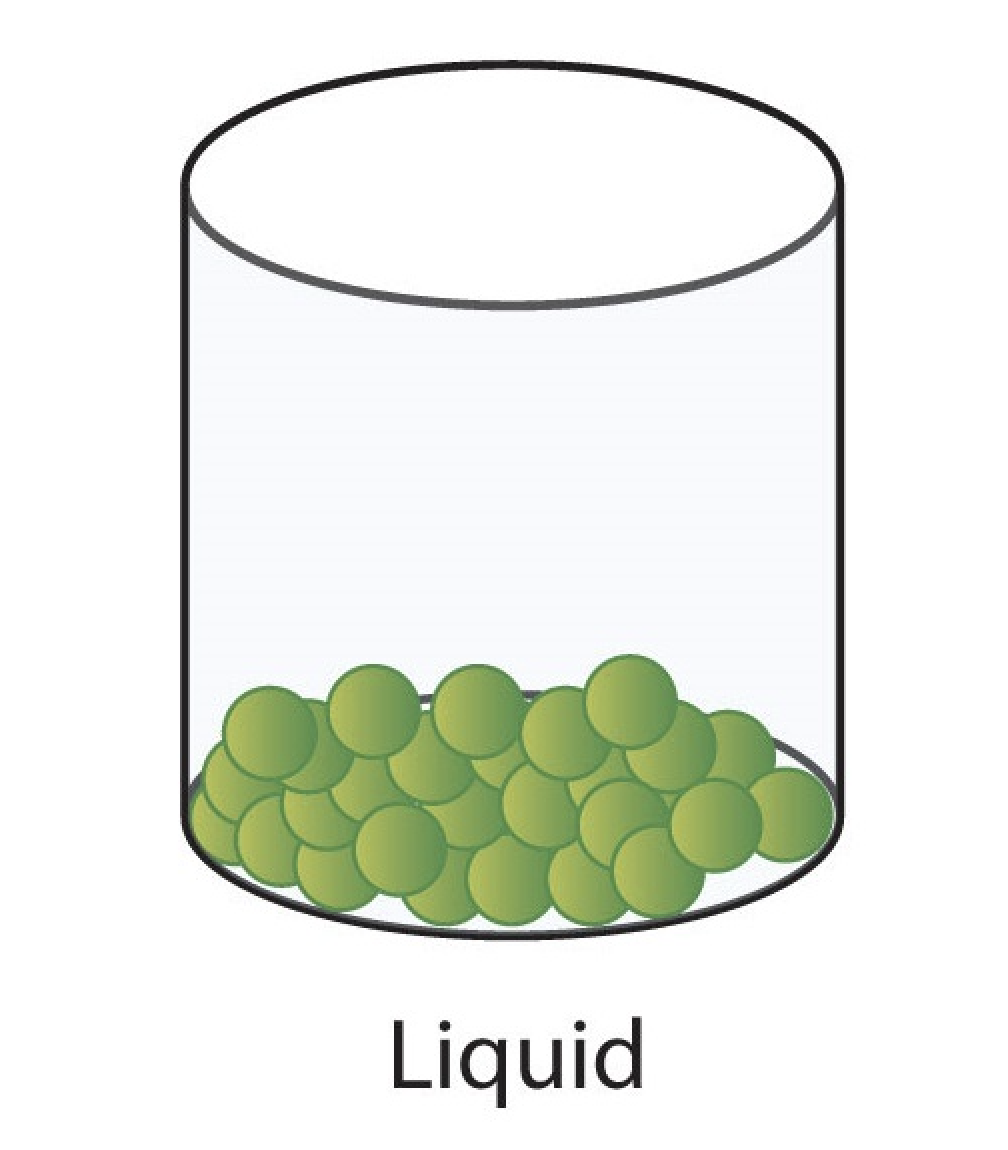
liquid
definite volume.
takes shape of container.
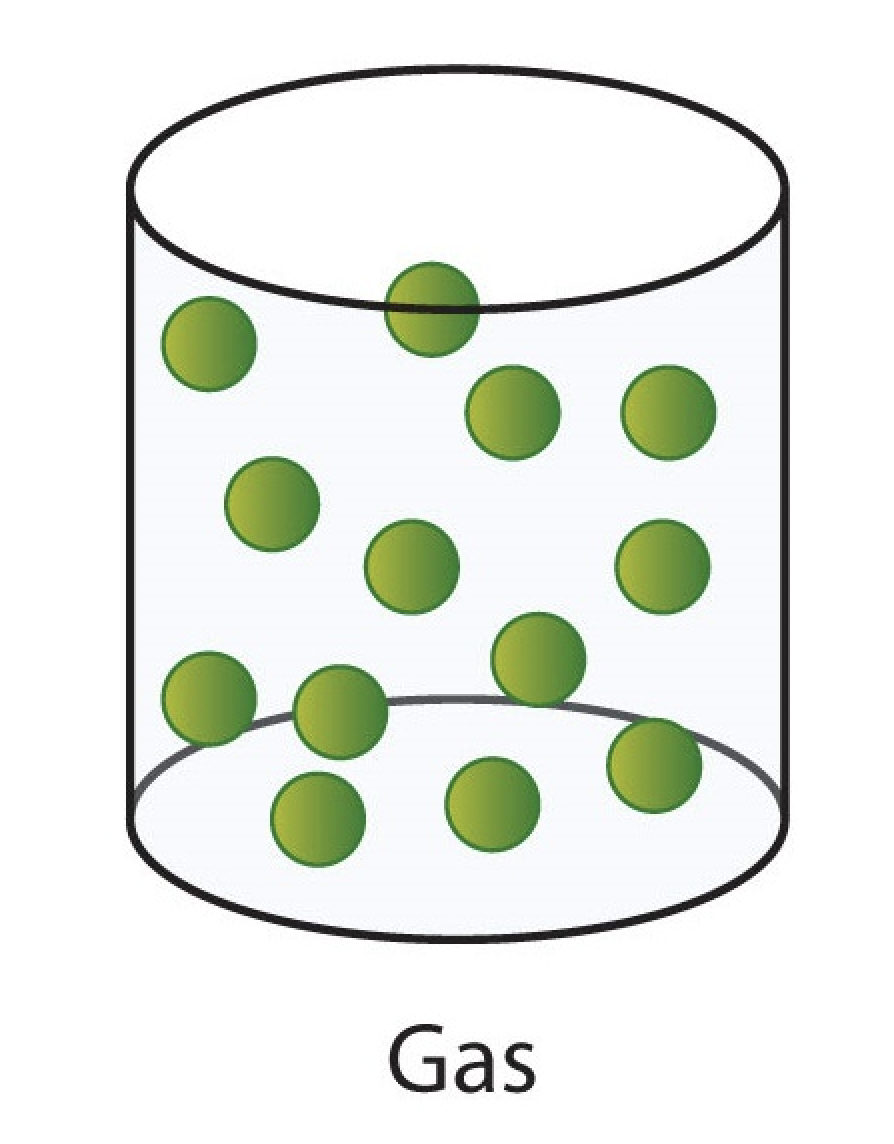
gas
indefinite volume (expandable/compressible).
takes shape of container.
intensive properties
depend on the type of substance, not on the amount of it
e.g) density, boiling point, color
extensive properties
dependent upon the amount of substance given
e.g) mass, length, energy
law of conservation of matter
matter can neither be created nor destroyed, only changed in form, through chemical or physical changes
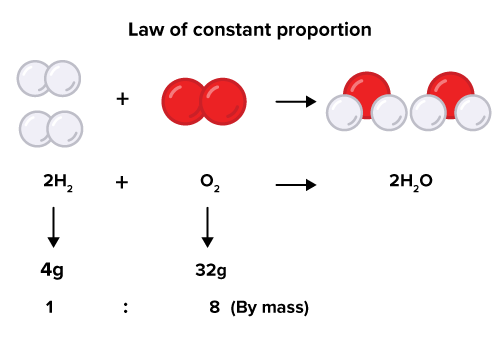
law of definite proportions
a given compound will always contain exactly the same proportions of element by mass.
e.g) H₂O is always 11% hydrogen and 89% oxygen by mass.
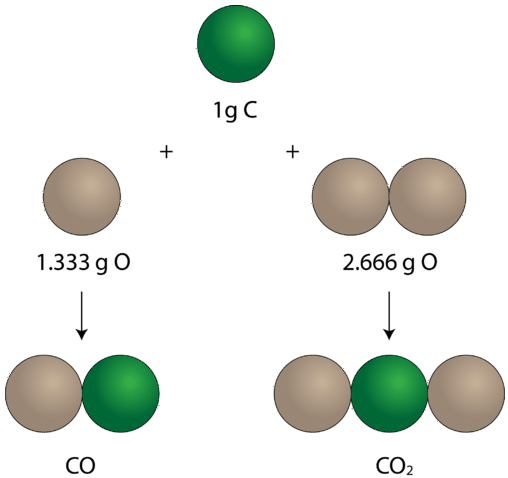
law of multiple proportions
when different compounds are formed by a combination of the same elements, different masses of one element combine with the same fixed mass of the other in a ratio of small whole numbers.
e.g) CO (carbon monoxide) 12 grams of carbon and 16 grams of oxygen
CO₂ (carbon dioxide) 12 grams of carbon and 32 grams of oxygen
oxygen mass ratio - 16:32 = 1:2