Cellular Respiration
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
catabolic
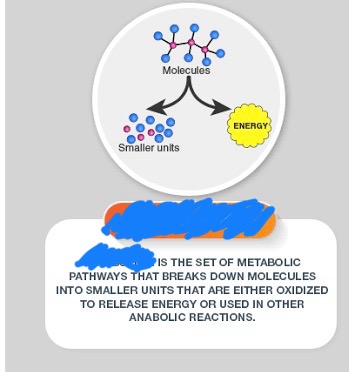
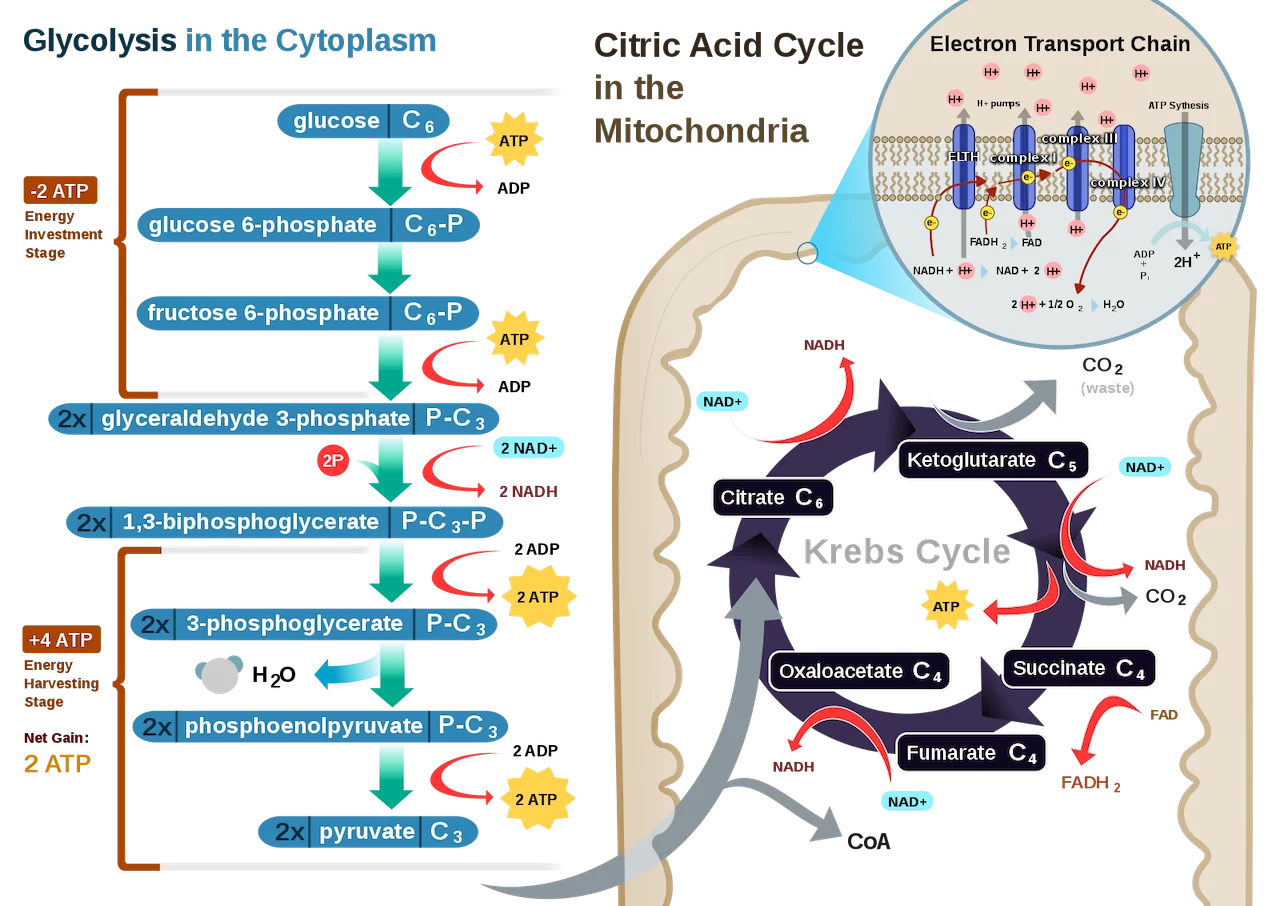
Cellular respiration is a _____ process. It means larger compounds are broken down resulting in the release of energy. Imagine chewing food on a molecular scale
around 30-32 ATP
How Much Energy Do We Gain Throughout Cellular Respiration?
A mnemonic I found useful in remembering the products of each step is “_______________.” Each series of reactions release energy and is captured in molecules of NADH, ATP, and FADH2. Two turns will take place due to glycolysis producing two pyruvic acid molecules.
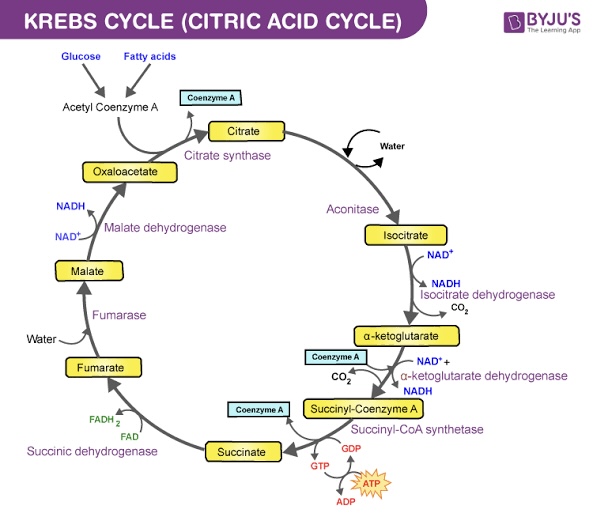
Citrate Is Kreb’s Starting Substrate For Making Oxaloacetate
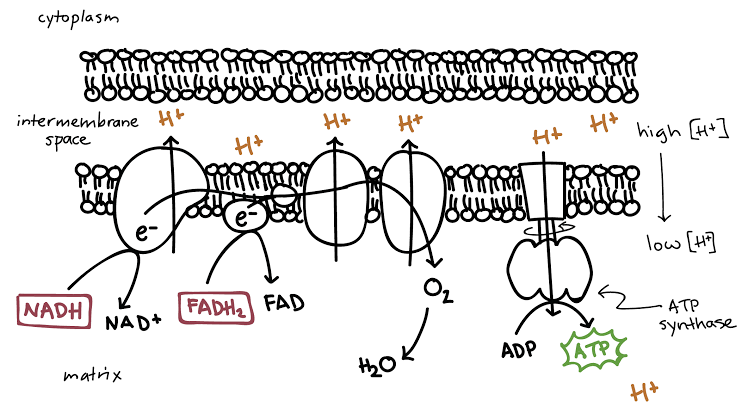
_______ _________ is the last step in cellular respiration and has two stages: the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis.
Oxidative phosphorylation
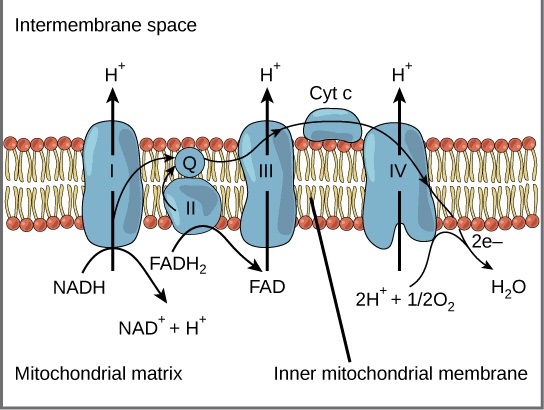
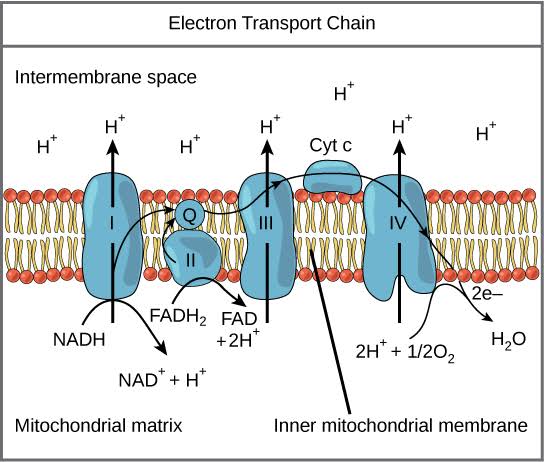
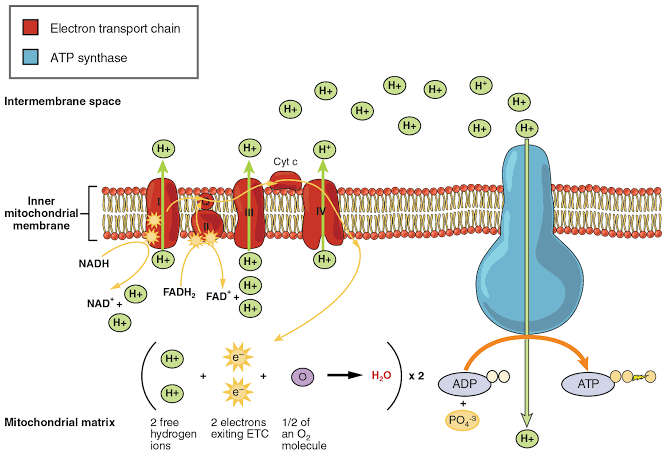
The inner membrane of the mitochondria is filled with proteins called complexes (4 main complexes, labeled “complex I” to “IV,” in the mitochondrion) which move electrons from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen. Energy from the carriers is also transferred to ATP. An ______ _______ ____ is a series of molecules that transfer electrons from one molecule to another by chemical reactions.
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
Some of the energy from the electrons pump the positively charged hydrogen ions (H+) from the matrix into the intermembrane space. NADH transfers electrons from complex I while FADH2 is only able to enter the chain starting at complex II. Thus, NADH yields more _____ compared with FADH2.
ATPs
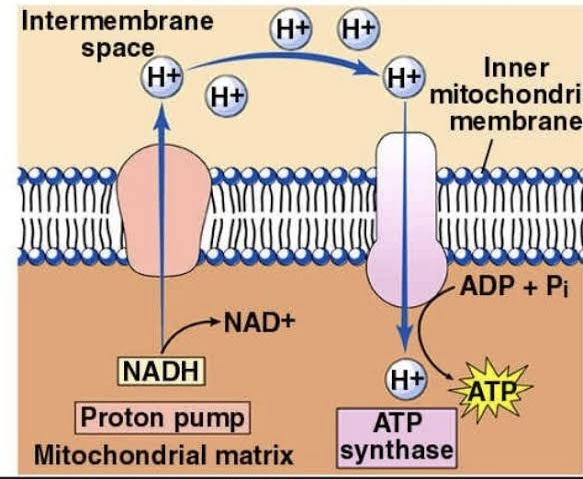
As more ions are pumped, this creates a difference in concentrations of charges, an electrochemical gradient, between the intermembrane space and the matrix. This gradient causes the ions to flow from high to low concentration, from the intermembrane space back into the matrix.
Chemiosmosis
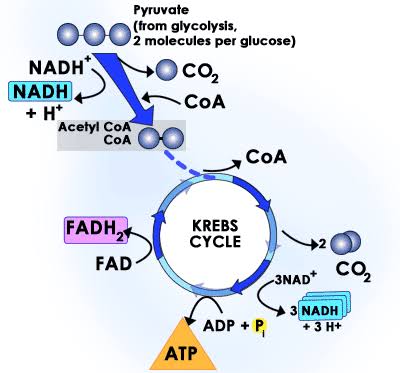
After the second turn of the cycle, the glucose molecule has been broken down completely with all six carbon atoms combined with oxygen to form carbon dioxide. This stage yields: 2 ATPs, 6 NADH, and 2 FADH2.
End of Krebs Cycle (after 2 turns)
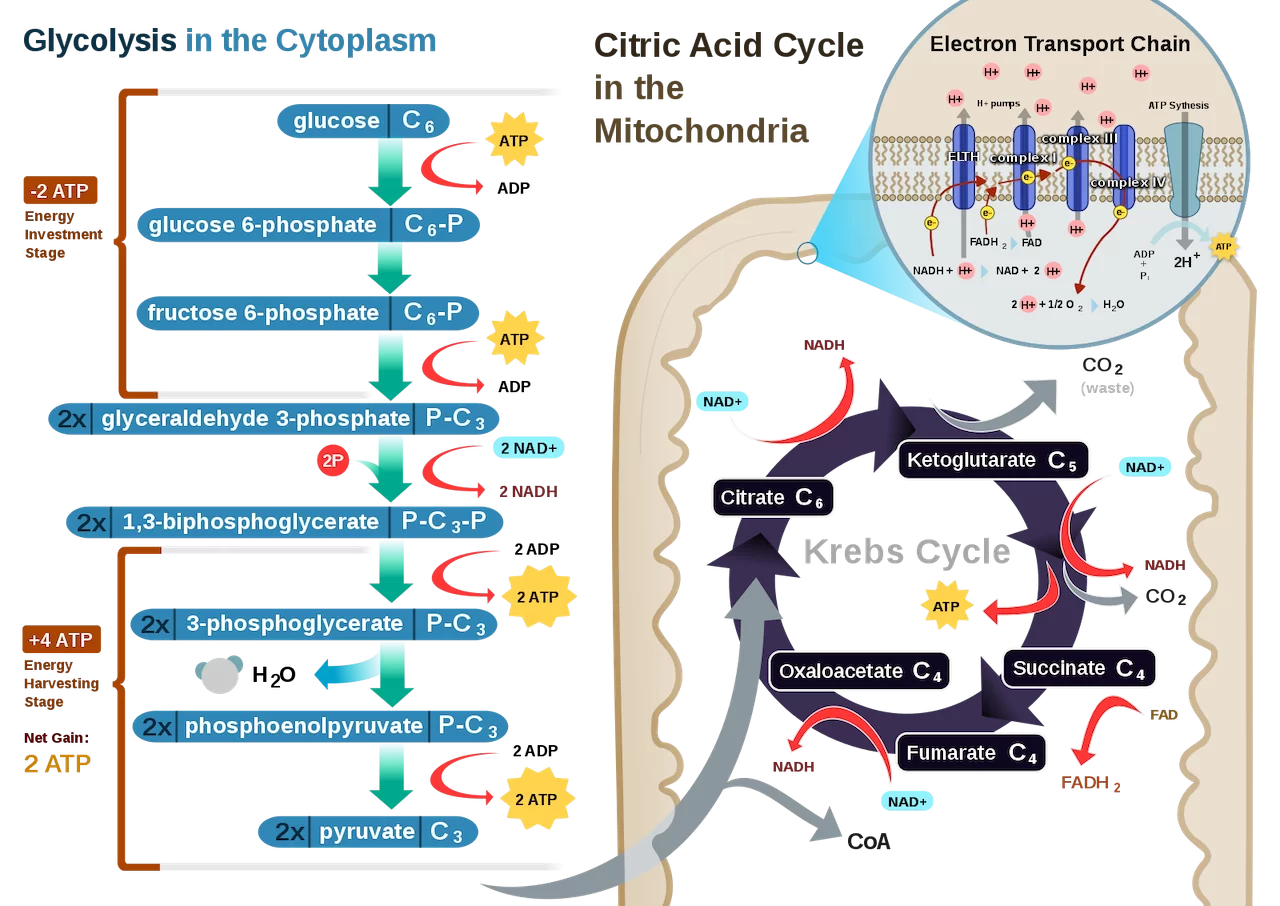
Still in the matrix, the Krebs cycle is a closed loop; this means the last part of the cycle reforms the molecule used to initiate the step. The cycle involves eight major steps resulting in citrate, isocitrate, ketoglutarate, succinyl-CoA, succinate, fumarate, malate, and oxaloacetate.
What is the third step of cellular respiration?
mitochondrial matrix
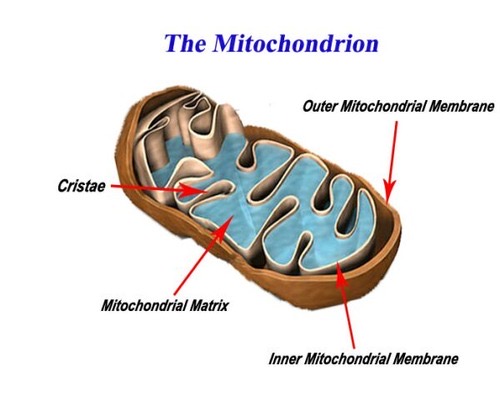
The pyruvic acid is able to diffuse past these membranes and into the _____ ______, the innermost compartment of the mitochondrion. Pyruvic acid is split and then chained to an enzyme resulting in the 2-carbon compound Acetyl Coenzyme A (Acetyl CoA). The cleaved carbon combines with oxygen to form carbon dioxide, a waste product. Acetyl CoA is then subjected to the next process.
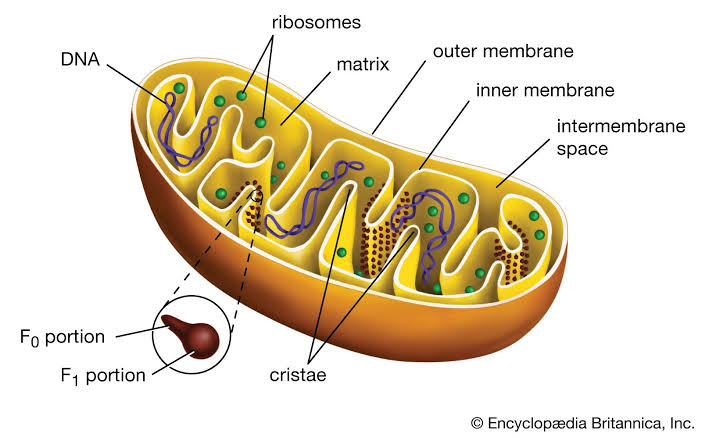
This is where the mitochondria and their importance in the process become apparent. The mitochondrion is a cellular unit called an organelle composed of two membranes, an inner and outer membrane.
What is the second step of cellular respiration?
reduction
In addition, high-energy electrons are also transferred to the electron carrier NAD+ (no charge) through ______ resulting in the electron carrier NADH with 2 NADH yielded in this step. These electron carriers are more important in the last step of cellular respiration.
nicotinamide, flavin
Chief of this is ______ adenine dinucleotide (NAD+/NADH) and then _____ adenine dinucleotide (FAD/FADH2). main electron carriers (aka the most important ones in cellular respiration)
Enzymes
In addition, proteins called ______, more specifically electron carriers, are essential in regulating and facilitating the process.
Adenosine Triphosphate
it is important to establish that the main goal of cellular respiration is to create energy (afer making/storing glucose from photosynthesis) that comes in the form of ATP (______ _______). Think of it as a currency in the cell.
Carbohydrate, compound of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
Among the food that are easier to digest and convert into energy are
Aerobic (air) Respiration
Uses oxygen and without it is (anaerobic).
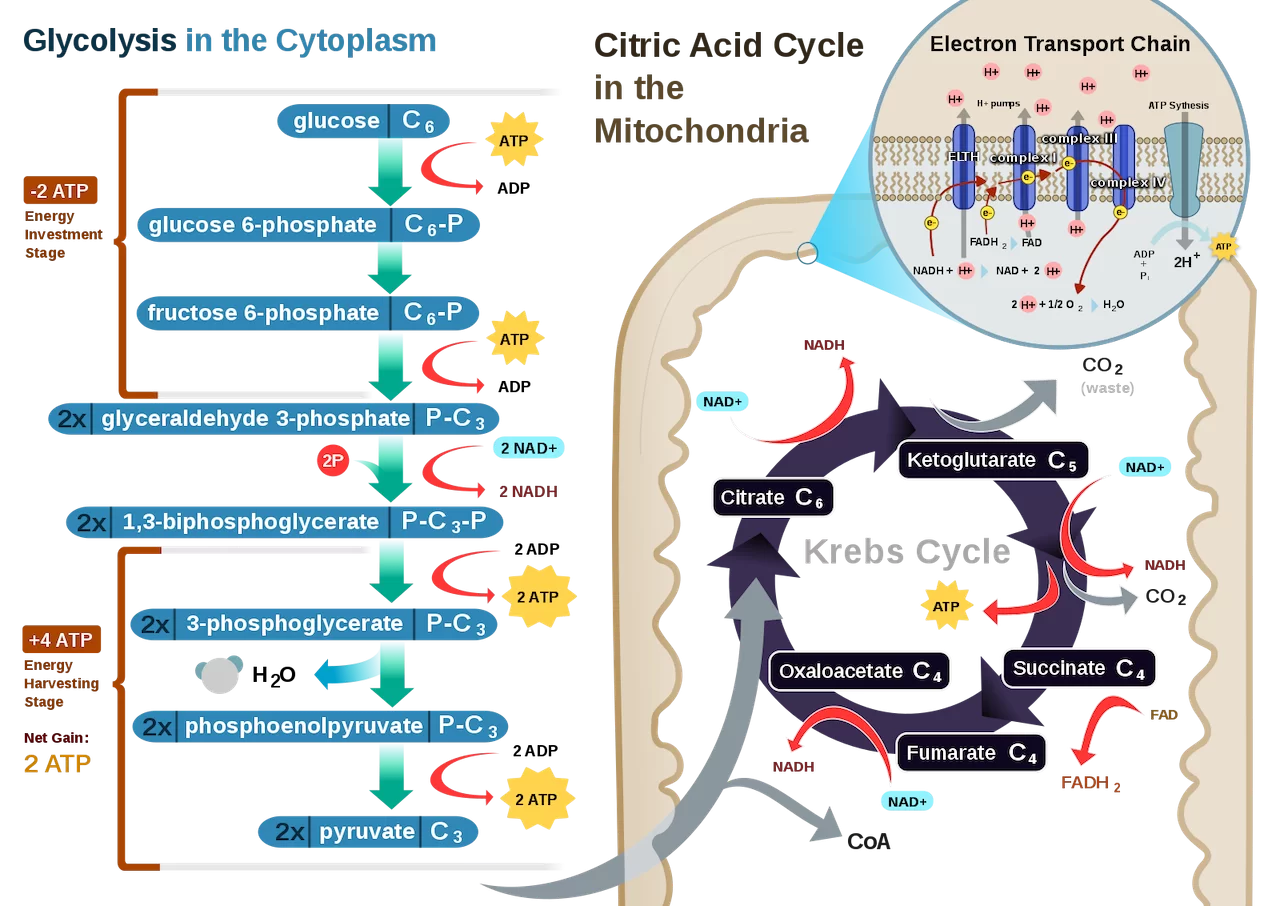
This step in cellular respiration is glycolysis = gly - bye, which simply means breaking up the glucose molecule which is suspended in the cytoplasm.
What is the first step of cellular respiration?
cytosol, pyruvic
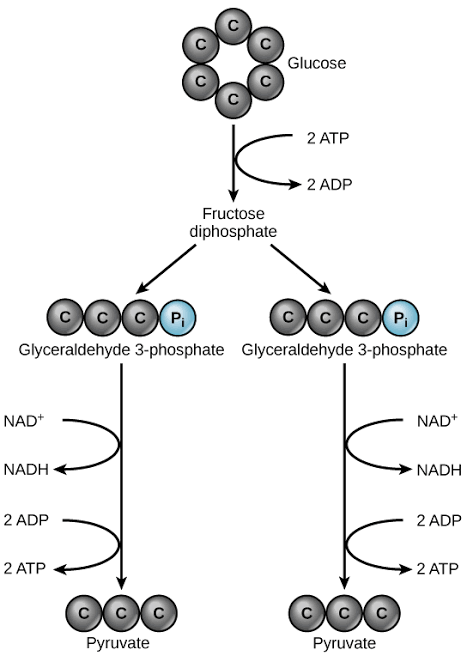
Within this cytoplasm is a fluid called _____ which also contains enzymes that aid the process. Once glucose enters this intracellular fluid, the enzymes break it into 2 _____ acid (or pyruvate, both used interchangeably) molecules. Step 1: Glycolysis
Electron Transport Chain
Occurs on the inner membrane of the mitochondria. All of the electrons (H) from glucose travel to the inner membrane of the mitochondria.
How many ATP are produced by the Kreb cycle for each molecule of glucose?
2
Which of the part of the cellular respiration process takes place in the cytoplasm?
Glycolysis
In what organelle would you find Kreb's cycle and the electron transport chain?
The Mitochondria
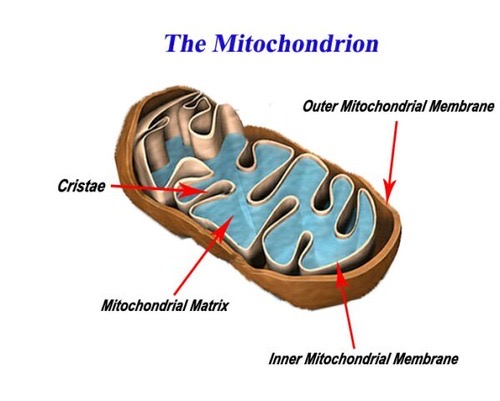
What is the main event that occurs in glycolysis?
This process breaks glucose into pyruvate molecules. It produces 2 ATPs for each glucose.
How many ATP molecules are produced in the Kreb's cycle?
2
How would you describe the electron transport chain?
This process uses energy captured from electrons flowing to oxygen to produce most of the ATPs in cellular respiration
What is needed for aerobic respiration?
Oxygen
Which portion of cellular respiration produces the most ATP?
The Electron Transport Chain (32 ATP per glucose)
During respiration, the electron transport chain occurs in the....
inner membrane of the mitochondria.
Fermentation occurs....?
When oxygen is NOT present in anaerobic cellular respiration.
Where does glycolysis occur?
cytoplasm
What does the suffix -"lysis" mean?
To Break
Explain the Kreb Cycle. What happens?
This part of respiration occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria. It releases enough energy to make 2 ATP and 6 CO2.
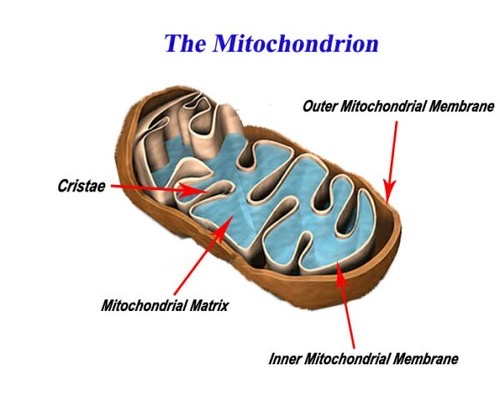
Where does the Kreb Cycle occur?
The matrix of the mitochondria.
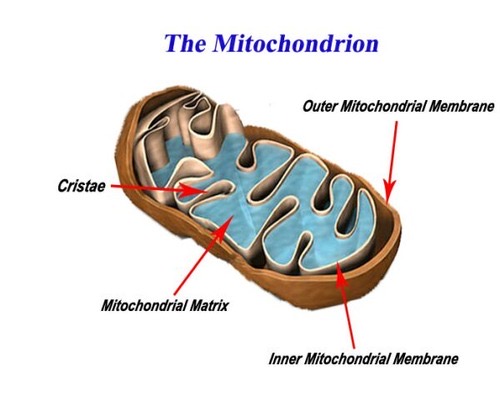
What is a pyruvate molecule?
1/2 of a glucose molecule.
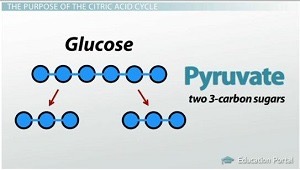
How many pyruvates - basically the end product of glucose metabolism before it moves on to the next stages of cellular respiration (3-carbon molecule) are produced from ONE glucose molecule?
2 (Since glucose has 6 carbon atoms, it’s split into 2 molecules of _____, each with 3 carbon atoms.)
How many carbons are in glucose? (C₆H₁₂O₆)
6
What is the storage form of energy called?
ATP
What is the name for the acronym ATP
adenosine triphosphate
what is the process of converting glucose into energy called?
cellular respiration
In which environment does a cell produce more ATP?
Aerobic
Steps of Anaerobic Cellular Respiration
Glycolysis, Fermentation
Steps of Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Glycolysis, Kreb's Cycle, Electron Chain Transport
Cellular Respiration Formula
C6H12O2 + 6O2 ------> 6CO2 + 6H20 + Energy (ATP)
Anaerobic Cellular Respiration occurs in ...
bacteria, yeast, or muscle cells.
Products of Aerobic Cellular Respiration
6CO2 +6H2O + Energy (ATP)
Reactants of Aerobic Cellular Respiration
C6H12O6 +6O2
Metabolic Rate
How quickly metabolism occurs. This affects how much food an organism needs to eat.
Definition of Cellular Respiration
The process of breaking the chemical bonds of glucose into energy. Breaking chemical bonds releases electrons.
ATP releases energy and becomes....
ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate)