AP Chemistry Unit 3
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
New
Card Sorting
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
1
New cards
Intermolecular Forces
attractions between entire molecules due to charge differences (positive or negative)
2
New cards
London Dispersion Forces
weakest typs of IMF and occur in all molecular samples (induced dipole)
3
New cards
Dipole-Dipole Forces
only occur in a sample of polar molecules and slightly stronger than LDFs
4
New cards
Hydrogen Bonding
strong dipole-dipole attraction between hydrogen directly bonded to F,O, or N in a molecule
5
New cards
Polarizability
ease with which the electron cloud of an atom or molecule is distorted
6
New cards
Ion-Dipole Attractions
only occur in a mixture of an ionic compound with polar molecules (strongest IMF)
7
New cards
Ion-Ion Attractions
occurs in a sample of ionic compounds; form a crystal lattice (salts)
8
New cards
Ionic Solids
held together by the mutual attraction between cations and anions
9
New cards
Covalent Network Solids
held together by an extended network of covalent bonds (diamonds/graphite)
10
New cards
Molecular Solids
held together by weak IMF
11
New cards
Metallic Solids
typically good conductors, malleable, and ductile (valence electrons are delocalized)
12
New cards
Crystal Lattice
a unit cell and the geometrical pattern of points on which the unit cells are arranged
13
New cards
Delocalized
when electric charge is spread over more than one atom (allows for conducting)
14
New cards
Substitutional Alloy
atoms of the minority element occupy positions normally occupied by atoms of the majority element (amongst)
15
New cards
Interstitial Alloy
atoms of the minority elements occupy interstitial positions that lie in the “holes” between atoms of the majority element (between)
16
New cards
Surface Tension
when molecules on a surface of a liquid experience a net inward force
17
New cards
Capillary Action
spontaneous rising of a liquid
18
New cards
Viscosity
measure of a liquid’s resistance to flow; stronger IMF, higher the viscosity (thickness)
19
New cards
Density
measures how compact a substance is (D = m / v)
20
New cards
Ideal Gas Law
PV = nRT
21
New cards
Combined Gas Law
P1V1 / T1 = P2V2 / T2
22
New cards
Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures
sum of all the partial pressures of each gas in a mixture of gasses is equal to the total pressure
23
New cards
Mole Fraction
denoted by Xa and equals moles A / total moles
24
New cards
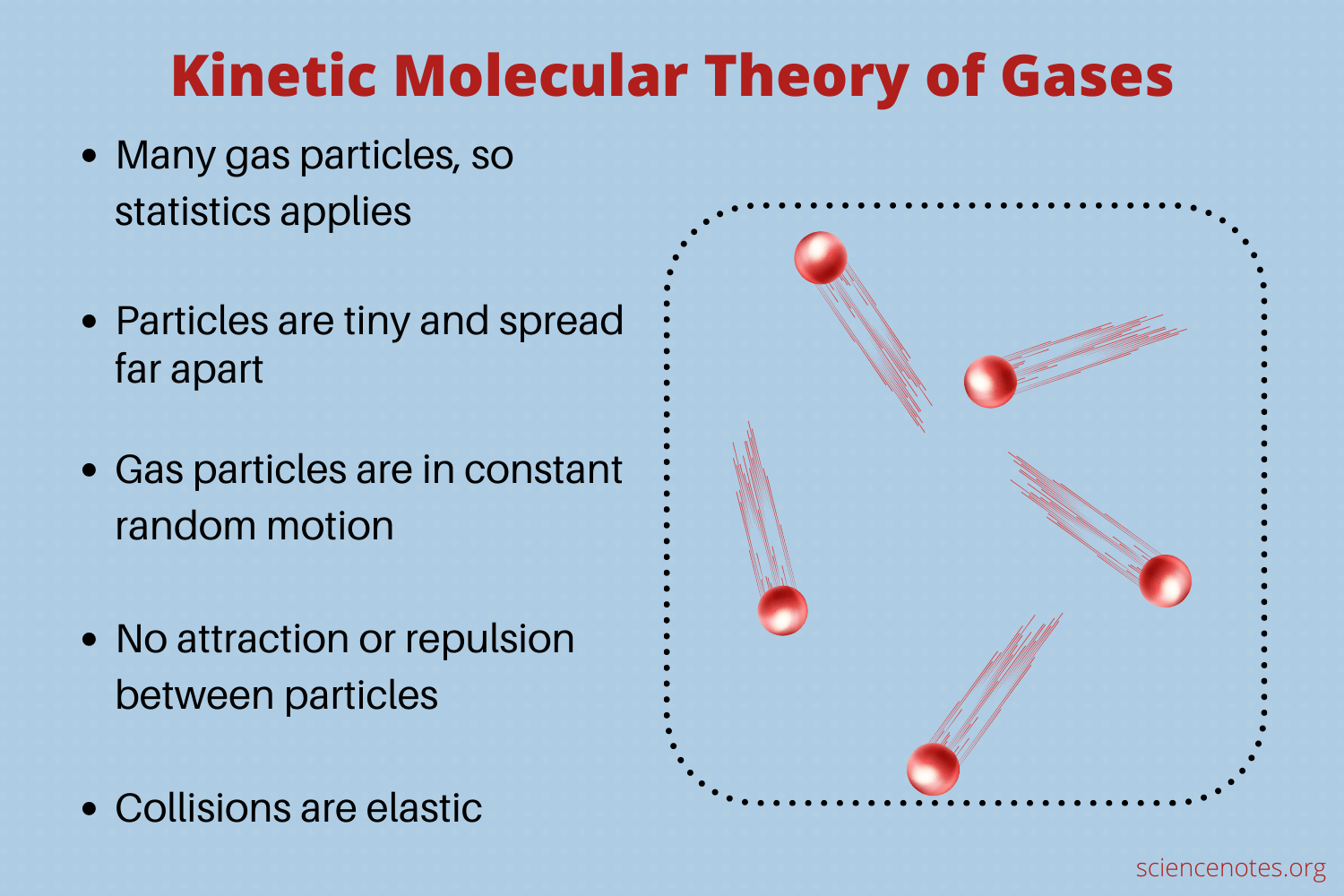
The Kinetic Molecular Theory
25
New cards
Maxwell-Boltzmann Distributions
display the distribution of energy at given temperatures for a gas
26
New cards
Effusion
describes the passage of gas through a tiny space into a vacuum space
27
New cards
Diffusion
describes the mixing of gases (temperature ↑, rate of diffusion ↑) (bigger molecules slower diffusion)
28
New cards
Molarity
numbers of moles of a solute dissolved in 1 liter of solvent; M = m / L
29
New cards
Diluting Solutions
decreasing the concentration of a solute in a solution by removing solute or adding solvent
30
New cards
Mixtures
in which the macroscopic properties depend upon the location in the mixture
31
New cards
Wavelength
the length of one period of a wave
32
New cards
Frequency
describes the number of waves that pass a fixed place in a given amount of time and is measured in per-seconds
33
New cards
Solubility
amount of solute needed to form a saturated solution at any particular temperature