12. temperature and heat
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
temperature
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. When particles move faster, they have higher kinetic energy and the substance is hotter. Conversely, when particles move slower, the substance is cooler.
temperature scales
Celsius: 0-> freezing point, 100—> boiling point Fahrenheit: ice melts at 32°F; boils at 212°F Kelvin: celsius+273
heat expansion of bodies
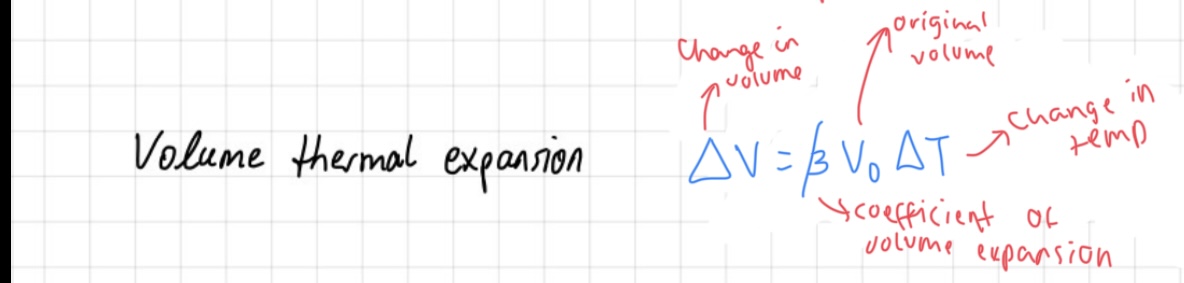
The heat expansion of bodies refers to the phenomenon where substances expand when heated. This expansion is proportional to the change in temperature (AT) and the original length (lo) of the substance, with the coefficient of linear expansion (B) representing the proportionality constant specific to the substance.
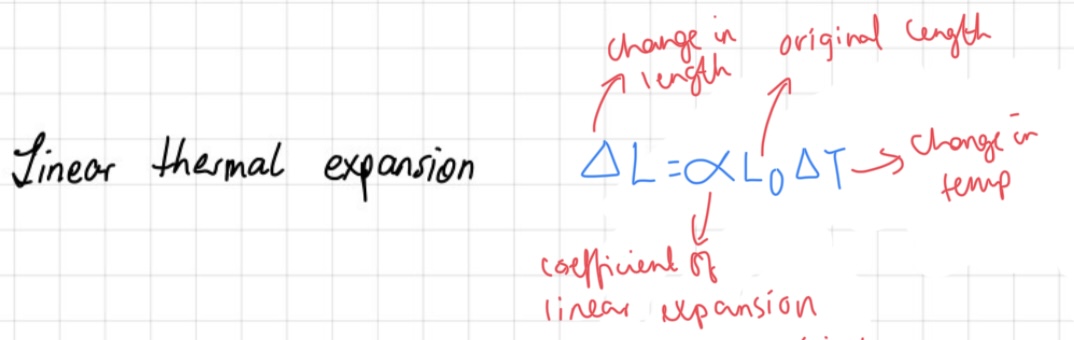
linear thermal expansion
volume thermal expansion
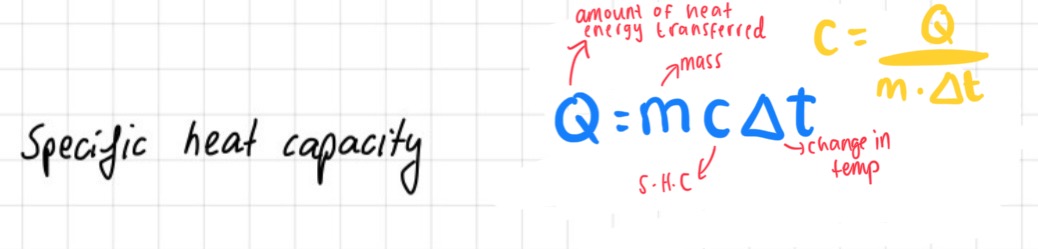
specific heat capacity
Specific heat capacity is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of one unit mass of a substance by one degree Celsius (or Kelvin)
calorimetry
Calorimetry is the science of measuring changes in the state variables of a body, typically its temperature, using a calorimeter. A calorimeter is a lightweight, insulated flask containing water. When an object is placed into the calorimeter, it transfers heat to or from the water, causing it to come to thermal equilibrium with the object.
The insulation of the calorimeter helps to prevent heat exchange with the surroundings, allowing for accurate measurement of the heat transferred.
water, properties and importance in living organisms
metabolite in condensation/hydrolysis/respiration. solvent so metabolic reactions can occur allowing transport of substances high SHC so buffers changes in temperature large latent heat of vapourisation so provides a cooling effect through vapourisation cohesion between H2O molecules so supports columns of H2O in plants cohesion between H2O molecules so produces surface tension supporting (small) organisms
thermostats, thermoregulators, sterilizers
Thermostats or thermoregulators are components of a system designed to maintain a constant temperature. They include a sensor that detects temperature variations and activates or deactivates an energy source, like a heater or air conditioner, to maintain the desired temperature.
A sterilizer is a device used to clean instruments by subjecting them to high temperature and pressure, effectively killing bacteria and other microorganisms.