NUR 318 Exam 1
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
Main goal of U.S drug legislation?
protect the public by ensuring that drugs marketed are safe and effective
FDA
ensures public medication safety
Comprehensive Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act
enforces and regulates narcotics and substances of abuse
Controlled Substances Act
gives authority to the Drug Enforcement Agency to regulate the sale and use of drugs and places those drugs into a class schedule
Schedule I
most addicting, most strict
no accepted medical use and high abuse potential
ex. LSD, ecstasy, heroin
Schedule II
Used medically with a high abuse potential
requires a handwritten provider's prescription
Opioid analgesics, CNS stimulants, & barbituate sedative-hypnotics
ex. Morphine, Oxycodone
Schedule III
Less potential for abuse, but may lead to dependence
Androgens, steroids, some depressants
Schedule IV
Accepted medical use in US but has some potential for abuse
benzodiazepines
Schedule V
Less addicting, least strict
may be dispensed by pharmacist but some restrictions apply
Phase 1 of Research
New drug that is given to very few healthy people (guinea pigs)
Phase 2 of Research
drug given to a very small group of people who have the certain condition/disease trying to treat
Phase 3 of Research
drug given to different populations
Double Bind Research to test effectiveness
Placebo Effect
Phase 4 of Research
FDA approval
drug given to a large population
data still being collected
What are Black Box Warnings?
Warnings on the medications about serious side effects
Over the Counter Drugs
no prescription needed
gives more autonomy
Advantages to OTC drugs
easy access (autonomy)
helps decrease healthcare visits
Disadvantages to OTC drugs
People ignore S/S of illness with OTC (Masking symptoms rather than treating the problem)
Inaccurate self-diagnosis
Interaction with other medications
Are OTC drugs regulated?
YES, more highly regulated by FDA due to wrong reason/way
What are the Right’s to medication administration?
Right:
drug
dose
patient
route
time
reason
documentation
education
evaluation
to refuse
What is the organization “Quality and Safety Education for Nurses Project (QSEN” for?
Focused on the needed knowledge, skills, and attitudes required for the preparation of future nurses
What is the organization “Joint Commission” for?
targeted high risk activities
Contains the “Do Not Use’ list of abbreviations
What is Beers Criteria?
medications that should be avoided in older patients due to adverse effects
for older patients or patients with comorbidities
Herbal Supplements
can negatively interact with other drugs
most have not been studied, tested, or FDA approved
Most drugs are given for _____________ effect
systemic (travels through bloodstream)
What is pharmacokinetics?
The drug movements through the body
What are the four specific processes involved in pharmacokinetics?
Absorption - what route (PO vs. IV0
Distribution - where it’s going
Metabolism - How it’s broken down
Excretion - How does it leave
Absorption process
The time the medication enters the body to the time it enters the bloodstream
Onset of drug action is determined by the rate of drug absorption
What are some factors that affect the rate and extent of drug absorption?
Dosage form & route of administration
Administration site blood flow & GI function
The presence of food or other drgs
What route of drug takes longest to absorb?
PO drugs
Why do PO drugs take so long to absorb?
pass through stomach and small intestines
What drug/s has the highest bioavailability (100%)?
IV and Buccal (sublingual)
Why do IV/buccal drugs have highest bioavailability?
They go straight into the bloodstream - no first pass effect
What factors influence oral absorption?
food
stomach acidity
other drugs
What factor impacts IM/SubQ absorption?
Adequate blood circulation
Distribution Process
Drugs are carried by blood and tissues to:
action sites
metabolism sites
excretion sites
What does distribution depend on?
Adequacy of blood circulation
Distribution process affected by: Protein Binding
Some drugs are highly bound drugs which have a longer duration of action due to their size
albumin usually acts as a carrier for the drugs
Distribution process affected by: Blood Brain Barrier
acts as a guard to the brain and limits the movement and amount of drugs to the brain tissue
Metabolic Process
The method by which drugs are inactivated or biotransformed by the body
drugs are most often changed from active to inactive metabolites and then excreted
What are some locations metabolizing enzymes are located within?
Kidneys
Liver
RBC/plasma
Gastrointestinal mucosa
What organ is most commonly associated with drug metabolism?
liver
Factors affecting metabolsim
Age (very old/young)
Medication metabolizing enzymes (genetics affect the way meds are metabolized)
First pass (travel through kidneys)
nutritional status
First Pass Effect
Affects oral drugs that are carried to the liver to be metabolized, then go to the bloodstream and take effect
Travel through the kidney and then to the bloodstream leading to less concentration of the drug
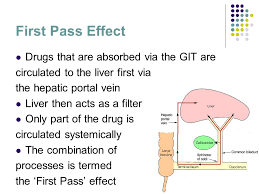
Excretion Process
Elimination of a medication from the body
Excretion requires adequate function of what organs?
circulatory system
Kidneys/Bowel
Lungs
Skin
What organ is most commonly associated with drug excretion?
kidneys
What will happen to the excretion process if a person has bad kidney function?
There will be decreased secretion from the kidneys = toxicity (due to not being able to fully excrete the drug)
What happens if drugs are not excreted from the body?
drug accumulation and toxicity
What is serum drug level?
A laboratory measurement of the amount of a drug in the blood at a particular time
What do serum drug levels determine?
bioavailability
half-life
dosages
pharmacokinetics
rates of metabolism & excretion
Minimum Effective Concentration
the minimum amount of drug required to produce a therapeutic effect
What is toxic concentration?
Excessive levels of drug in the bloodstream - causes adverse effects on the body
What is toxic concentration (toxiology) caused by?
single large dose
repeated small doses to frequently
slow metabolism of medication
How does excretion play a part in toxicology?
If a drug is not properly excreted, it can accumulate in the body causing overdose
What are some treatments to toxicity (AKA overdose)?
stabilization efforts
activated charcoal (can interfere with PO absorption)
Antidotes for IV
Common antidote: Narcan for opioid overdose
Onset
initial concentration needed for the drug to start working
Peak
highest concentration of drug in the body - has the most effect on the body
Duration
How long the drug is working in the body for
Trough
lowest concentration of a drug in the patients bloodstream
When should we collect a trough level?
right before giving the next dose of drug when the previous dose is at its lowest concentration
small therapeutic level
a small window where a drug works without becoming toxic and without losing its therapeutic effect
What is a serum half-life?
Length of time required for a drug's concentration to drop by 50%
AKA: elimination of half-life
Short half-life
Medications that leave the body quickly
Short dosing intervals to ensure constant blood levels
drugs leave the body quickly
can be given more frequently (multiple doses/day)
Long half life
Take more time to breakdown
drug remains in the body longer (24+ hours)
given less frequently
Greater risk of toxicity and accumulation
Pharmacodynamics (think mechanism)
How the drug works & what it does to the body
AKA mechanism of action
What are the two ways medications interact with cells?
Agonist and Antagonist
Agonist
Mimics receptor activity (makes it better to activate receptors)
Example of Agonist
Morphine:
Activates the receptors that produce analgesia, sedation, constipation, etc.
Antagonist
Blocks normal receptor activity
Example of Antagonist
Losartan:
works by blocking angiotensin II receptors on blood vessels to prevent vasoconstriction
What are some patient-related affects of pharmacodynamics (mechanism of action)?
Age/body weight (may need to increase dose)
Genetics/ethnicity/sex
Pathologic conditions (ex. GI disorders)
Psychological considerations (ex. placebo effect)
Tolerance and cross-tolerance
What is tolerance?
decreased response to a drug
What are adverse effects?
Undesired response to drug administration
Adverse effects are more likely to occur/more severe with…
higher doses (more med = more at risk for SE)
Older age
Polypharmacy (multiple meds)
What is cumulative effect?
Poor excretion of drugs
can lead to toxcicity
What are some common medication errors?
wrong medication
incorrect dose
wrong client, route, or time
administration of known allergic medication
omission of dose
incorrect discontinuation of medication
similar medication names getting mixed up
What are some ways to prevent med errors?
Bar coding
limiting the use of abbreviations
Med reconciliation
correct dosage calculation
prepare 1 patient’s med at a time
don’t leave meds at the bedside
What information is required for medication orders?
Full patient name
Name of the drug (preferably generic)
Dose
Route
Frequency
Date, time, and signature of provider
Routes of administration
Oral
GI (NG or gastrstomy)
Topical
Injections
SubQ
IM
IV
Assessment
gather data
physical assessment
subjective - what pt says
objective - observed
Diagnosis
Describes patient problems or needs
ND specific to drug therapy [y:
deficient knowledge r/t drug thera[y regimen
risk for injury r/t adverse drug effects
noncompliance rt overuse/underuse
Planning
Expected goals/outcomes of prescribed drug therapy
must be measured and observable
stated in terms of patient behavior
Example: Pt will self-administer morning insulin dosage per protocol
Intervention
Implementing planned activities (teaching)
example: teaching a patient how to administer insulin dosage
Evaluation
Determining the patient’s response to drug
observe for therapeutic and adverse effects
reassess with subjective and objective data
Why do we use evidence based practice?
maximize outcomes in an efficient, effective, and ethical manner using backed RESEARCH
How might absorption be impacted by young age?
decreased gastric emptying and intestinal motility
Increased Skin permeability:
skin is thinner = increased absorption = increased risk for toxicity
How might metabolism/excretion be impacted by young age?
immature liver and kidney function
reduced GFR
Slow renal clearance
How might drugs negatively impact older adults?
Reduced amount of receptor sites leads to increased adverse effects
watch for polypharmacy
How might older age impact absorption?
Changes in the GI tract:
Increased PH = stomach acid is more alkaline & meds don’t get broken down as much
decreased muscle mass and increased body fat
decreased blood flow
How might older age impact distribution?
decreased blood circulation and cardiac output
DRUGS STAY IN SYSTEM LONGER = TOXCICITY
How might older age impact metabolism/excretion?
Decreased liver and kidney function (assess BUN and creatinine clearance)
How might pregnancy impact drug use?
drugs can reach fetus through the maternal-placental-fetal circulation
Teratogenic drugs
cause abnormal embryonic/fetal development and should never be used during pregnancy
What should pregnant women avoid?
Live vaccines
Herbals
Alcohol
Smoking
Caffeine
Drug classification pregnancy risk categories (5 categories)
Categorized A (safest) to x (known danger)
A drugs
B drugs
C drugs
D drugs
X drugs
D and X are known to cause risk to the fetus (teratogenic)
Category A drugs
well-controlled studies have shown these have no risk to the fetus
Category B drugs
animal studies show these have no risk to the fetus
Category C drugs
animal studies show these can have adverse effects on the fetus
Category D drugs
there is evidence of human risk to the fetus
The benefits may outweigh the risks in certain situations
Category X drugs
there is strong evidence of fetal abnormalities with these drugs, and should not be taken while pregnant