C.3.1 - Integration of body systems
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Body systems for communication
Nervous system (receptors send signals to muscles) - electrical signals
Endocrine system (glands respond to chemical signalling and release hormones) - hormones signal chemically, transported in bloodstream
Negative feedback control
The body’s system of retaining homeostatic conditions (body temmperature, glucose levels, blood pressure, digestion, etc.)
Emergent properties
Properties that appear in a complete organism but aren’t present in its individual components
Autonomic nervous system (ANS)
Part of nervous system that communicates with the brain without conscious knowledge
Target tissue of a hormone
The body tissue where a certain hormone produces an effect
Exp. of the nervous and endocrine systems working together
Release of adrenaline hormone is triggered by information passed on by the nervous system. Sensory organs transmit information to the nervous system, indicating that adrenaline is needed as part of a fight-or-flight response. ANS then sends impulses to the adrenal glands (upper kidney) to release adrenaline.
Nervous system characteristics
Electrical impulses send messages
Neurons are used to transmit and recieve impulses
Parts control volontary actions, parts control involontary
Responses are quick and short-lived
Endocrine system characteristics
Hormones send messages
Hormones travel through bloodstream
Only involontary functions are controlled
Responses are slow but long-lasting
Brain receptors (conscious level) - Cerebrum
Photoreceptors - retina, process visual info
Chemoreceptors - tongue, process tastes
Thermoreceptors - skin, process temeperature changes
Mechanoreceptors - inner ear, process loud vibrations
Brain receptors (subconscious level)
Osmoreceptors - carotid artery, hypothalamus, regulate blood water levels and solute levels
Baroreceptors - carotid artery, aorta, sense blood pressure changes
Proprioceptors - muscles and joints, provide balance and coordination
How does the brain communicate with the body?
Spinal nerves (31 paired nerves emerging from spinal cord)
Cranial nerves (12 paired nerves connected to the brainstem)
Three main parts of the brain
Cerebrum
Cerebellum
Brainstem
Cerebrum
Divided into right and left cerebral hemispheres
Each hemisphere contains frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital lobes
Controls conscious activities
Frontal lobe coordinates memory & learning activities
Cerebellum
Coordinates volontary movements; controls balance + equilibrium
Brainstem
Relays impulses between cerebrum, cerebellum, and spinal cord
Controls subconscious functions neccessary for life (e.g. medulla regulates breathing and heart rate)
Spinal cord cell types
White matter (axons + neurons, carries neural impulses to and from the brain)
Grey matter (neurons + synapses)
Reflex arc
Pathway of an impulse
Hormone def
Produced in the glands
Secreted into the bloodstream
Acts on a target cell
Regions of spinal cord
Cranial nerves (facial movement)
Cervical region (head neck & upper body)
Thoracic region (torso, hands & fingers)
Lumbar region (legs)
Sacral region (bowel & bladder, sexual function)
Transduction
Conversion of specific physical stimulus to electrical impulse (action potential)
Motor cortex, motor neurons
Part of the cerebrum where action potetials are sent from, neurons that carry action potentials to muscle tissue
Neuromuscular junctions
Synapses formed by motor neurons and muscle fibres — release neurotransmitters (acethylcoline) that create muscle contractions
Types of neurons
Sensory: send sensory information to the brain via the CNS
Motor: send action potentials to muscles via the CNS
Inter: transport impulses through the CNS
Mixed nerves
Contain both sensory and motor neurons
Myelinated vs. unmyelinated neurons
Myelinated = have Schwann cells wrapped around the axon and “blank” areas in between called nodes of Ranvier — much faster transmission as impulses can skip between nodes of Ranvier.
Pain reflex arc
Nocireceptor - spinal nerve - interneuron
Resulting actions go directly to effector
Circadian rhythm
Pattern of behaviour or physiology based on a 24-hour cycle, controlled by the pineal gland
Adrenaline (epinephrine) effects
Raises heart rate
Dilates air passages to allow more oxygen to enter the lungs
Dilates pupils
Raises blood sugar: stimulates glycogen → glucose in the liver
Increases blood supply to muscles
Hypothalamus
Part of the brainstem that connects the nervous and endocrine systems. Composed of neuclei (group of neurons that recieve the same kind of sensory information) and glandular cells, produce hormones that stimulate or inhibit further hormone release by the pituitary glands. Associated with the ANS and recieves action potentials from other parts of the body with those receptors.
Pituitary glands
Two lobes: posterior and antererior, which secrete different hormones and communicate differently with the hypothalamus. Produces ADH (antidiuretic hormone) which regulates water levels in blood.
Posterior pituitary hormones
Oxytocin & ADH
Anterior pituitary hormones
LH, FSH, TSH, GH & Prolactin
Baroreceptors & chemoreceptors located
Baro: opening of aorta & sinus of carotid artery
Chemo: in tissues near baro outside the blood vessels, capillaries off major arteries
Action potentials transferred from baro- and chemoreceptors to…
Medulla
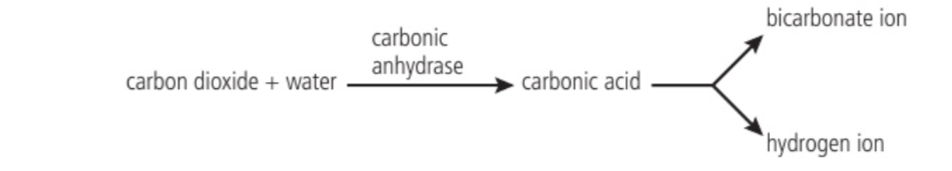
Chemoreceptors in blood sensitive to…
Oxygen levels
pH
Carbon dioxide levels
Resting ventilation rate controlled by…
Respiratory centres in the medulla, release spontaneous action potentials to diaphragm and intercostal muscles
Ventilation rate during exercise
Regulated by chemoreceptors in the medulla: blood is typically slightly alkaline, but exercise = higher rate of respiration = higher CO2 content in blood, which needs to be regulated
Nervous system & digestion
ENS (enteric nervous system) regulates peristaltic reflex (contractions moving food along alimentary canal) in an involuntary process.
Peristaltic reflex
Bolus (rounded mass of food) stimulates stretch receptors in the ENS. Stretch receptors synapse with relay neurons that synapse with two different types of motor neurons. One releases excitatory neurotransmitters, stimulating the muscle behind to contract, and one releases inhibitory neurotransmitters, stimulating the muscle ahead to relax.
How are hormones specialised to target cells/tissues?
Target cells/tissues have specialised receptors to recieve specific hormones
Heart rate control
Sinus node (pacemaker cells) generate action potentials stimulating the heart to contract
Adrenaline can stimulate the pacemaker cells to generate action potentials more frequently — causing an increase in heart rate
Feedback control of heart rate
Baroreceptors & chemoreceptors sense heightened blood pressure and fall in pH, causes an increase in the firing rate of nerves to the medulla.
Parasympathetic nerve signals to the SA node to decrease rate of depolarisation
During contiuous activation, sympathetic nerves signal to the adrenal gland to secrete adrenaline (epinephrine), which then acts on the SA node to keep heart rate up
Depolarisation
The passing of an action potential through a neuron