621 Lec 16 Clinical Relevance of Hepatic Function
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
FDA recommends PK studies in patients with hepatic impairment if…
\
- > 20% of elimination by hepatic metabolism and/or excretion
- < 20% of elimination is hepatic but drug has narrow therapeutic range
- Unknown contribution of hepatic elimination route
What are the 3 determinants of hepatic clearance ?
hepatic blood flow (QH ), protein binding (fu ), and intrinsic clearance (CL’int)
Facors that Impact Hepatic Clearance:
Hepatocellular Enzyme/Transporter Activity
Protein Binding
Hepatic Perfusion
Determinants of Hepatic Clearance
1) Intrinsic clearance
2)Unbound (free) fraction of drug
3)Hepatic Blood flow
1) Intrinsic clearnace
•Enzyme or transporter activity
→Induction: increased number of enzymes
→Inhibition: Decreased number of enzyme molecules or inhibition of function
- Enzymes and pumps only act on free (unbound) drug
- Cirrhosis, diet, drug-drug interactions, genetic polymorphisms
2)Unbound (free) fraction of drug
•Unbound drug is pharmacologically active
•Unbound drug is form that is cleared
•Increased Fu when a drug with higher affinity for the protein is given, displacing the other
•Increased fu when plasma protein production decreases
•Increased fu can also increase drug distribution (Vd)
When Drug B with higher affinity for protein is given →
Drug A is displaced and fu increases
When plasma protein decreases (hypoalbuminemia) →
fu increases
When fu (fraction unbound) increases, Vd…
increases
3)Hepatic Blood flow
•Combination of portal vein (2/3) and hepatic artery (1/3)
•Flow impairment:
→Primary:Cirrhosis (liver scarring)
→Primary: Budd chiari syndrome
→Secondary: Heart failure
→Secondary: Hypotension/Hypoperfusion
Primary causes of flow impairment
cirrhosis, Budd Chiari Syndrome
Secondary causes of flow impairment
heart failure, hypotension, hypoperfusion, sepsis, volume depletion
Extraction Ratio
Ratio of the rate of drug elimination over the rate of drug entry for an organ of elimination
Hepatic Clearance equation
QH x ER
High extraction ratio IV Clearnace Hepatic
CLh = Qh
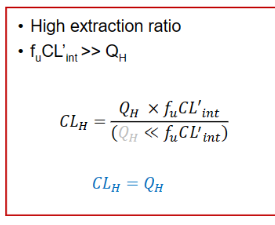
High extraction ratio for IV drugs
CLh = Qh
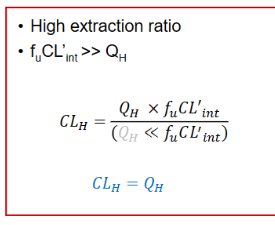
Low Extraction Ratio for IV drugs CL equation
CL = fu CLint
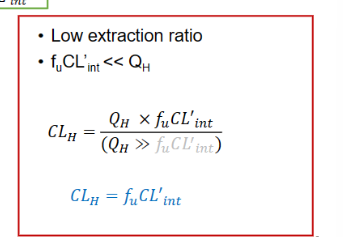
For IV drugs with low extraction ratio, what factors affect Css unbound
Cl int
For IV drugs with high extraction ratio, what factors affect Css unbound
Fu and Qh
For oral drugs, what factors affect Css unbound at high and low ER?
only CLint