P5 - Electricity in the Home
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
What current is used in a torch?
A direct current (DC).
What does a DC current mean?
The current is in one direction only.
What current is used in a light at home?
An alternating current (AC) because the mains electricity is an AC supply.
What does an AC current mean?
The current repeatedly reverses its direction, flowing one way then the opposite way in successive cycles.
What is the frequency of a current?
The number of cycles it passes through each second.
What is the mains frequency in the UK?
50Hz
How many wires does every single mains circuit have?
Two - a live wire and a neutral wire.
Why does the current through a mains appliance alternate?
Because the mains supply provides an alternating potential difference between the two wires (the polarity of the PD repeatedly reverses its direction).
Where is the neutral wire earthed?
At your local electricity substation.
What is the PD of the live wire in other words?
The potential difference between the live wire and the earth.
Why is the live wire dangerous?
Because its potential repeatedly changes from + to - and back every cycle.
What is the voltage of the live wire in UK homes?
About 325V.
Where does electricity get supplied from in mains appliances?
From power stations to homes and buildings through the national grid.
What’s the National Grid?
A nationwide network of cables and transformers.
How much alternating voltage does a typical power station generate?
About 25000V
What are step-up transformers?
Step-up transformers are used at power stations to make the size of the alternating potential difference much bigger to transfer electricity to the National Grid.
What is the increase in PD from a step-up transformer?
Typically 25,000V to 132,000V.
What are step-down transformers?
Step-down transformers are used to supply electricity from the national grid to consumers and decrease the voltage before being sent to homes/buildings.
What is the UK mains PD for homes and offices?
The same power as a 230V DC supply.
What is the UK mains PD for factories?
100kV or 33kV.
Why is the grid PD very high?
Because the higher the PD, the less current is needed to transfer the same amount of power. This means that power loss due to the resistance heating in the cables is much reduced.
What does the Earth Wire do?
Connects the metal case to earth. This stops the metal case becoming live if the live wire breaks and touches the case.
What would happen if you touched a live case?
You would be electrocuted.
When is an earth wire unnecessary?
If the plastic case is double-insulated.
Plastic materials are good insulators.
What are the outer casings of plugs, sockets, and cables of all mains appliances made from? Why?
Electrical insulators because they contain live wires.
How are most mains appliances connected?
By a wall socket using a cable and a three-pin plug.
What are sockets made of?
Stiff plastic materials with the wires inside them.
Explain earth wires in sockets.
The Earth wire is connected to the ground.
The longest pin of a three-pin plug is designed to make contact with the earth wire, automatically earthing the case of an appliance after plugging.
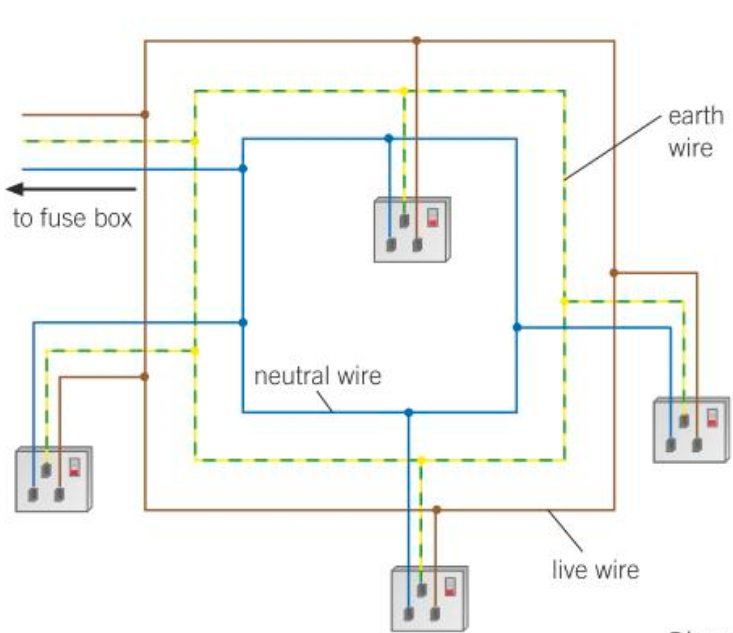
What is the PD and current of the earth wire?
0V, and only carries a current if there’s a fault.
What are plug pins made of? Why?
Brass because it’s a good conductor and doesn’t rust or oxidise.
Why not copper?
Copper isn’t as hard as brass although it conducts better.
Describe the shape and material of the case of a plug.
Made of an electrical insulator. It is shaped so that the wires and pins can’t touch each other inside the plug.
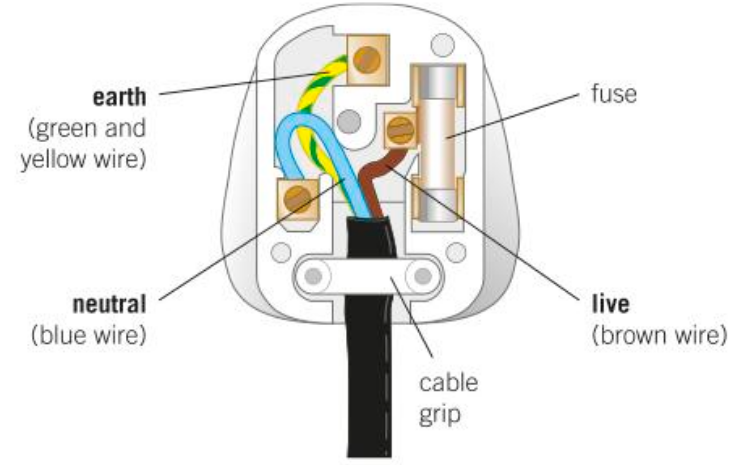
Why does a plug contain a fuse? Where is it located?
The fuse between the live pin and the live wire melts and cuts the live wire off if too much current passes through it.
What pin is the brown wire connected to?
The live pin.
What pin is the blue wire connected to?
The neutral pin.
What pin is the green and yellow striped wire connected to?
The earth pin.
What sort of cable doesn’t have an earth wire in the plug?
A two-core cable.
What are cables of mains appliances made of? Why?
Two or three insulated copper wires surrounded by an outer layer of rubber or flexible plastic.
Copper is a good electrical conductor and it bends easily.
Plastic is a good electrical insulator.
What are two-core cables used for?
Appliances that have plastic cases (hairdryers, radios, charges, etc.).
What are thicker cables used for? Why?
Cables that join together the wall sockets in your house. This is because more current passes along wall socket cables than along lightning circuits, so the wires must be thicker to have less resistance. This stops the current making the wires too hot.
What does the structure of a plug look like?
Explain a short circuit.
A short circuit occurs if a live wire touches a neutral wire. A very big current passes between the two wires at the point of contact. The current is cut off if the fuse blows.
Why should a person never touch the wires inside a supply cable, even if it’s switched off?
Because people’s bodies are at zero volts, if someone touches a live wire, a big PD will act across their body, causing a current o flow through them. This electric shock could be lethal.
What is the equation involving power, energy transferred, and time?
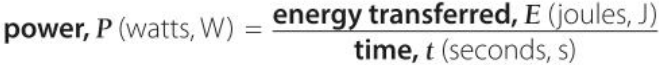
What is power the same as?
Energy transferred in joules per second.
What is current the same as?
The charge that flows each second.
What is PD the same as?
The energy transferred by each coulomb of charge.
What is the equation involving power, current, and PD?

What are the common fuses?
3A, 5A, or 13A.
What is the equation involving power, current, and resistance?
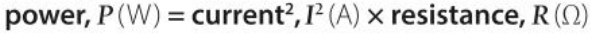
Why does the previous equation work?
Because V = IR and P = IV, this must mean that P = IIR, therefore P = I²R
What is the equation for Charge?

Explain why resistors become hotter when charge flows through them.
Work is done by a battery to make electrons pass through the resistor.
Each electron repeatedly collides with the vibrating metal ions of the resistor, transferring energy to the ions.
The ions of the resistor gain kinetic energy and vibrate more, becoming hotter.
When a charge flows through a resistor...?
Energy is transferred to the resistor, so the resistor becomes hotter.
State the equation including energy, charge, and potential difference.
Energy, E = Charge Flow, Q x potential difference, V
State the equation including energy, power, time, PD, and current.
Energy, E = Power, P x time, t = potential difference, V x current, I x time, t
What is the equation for energy transferred from the mains?
Energy transferred from the mains, E = Power, P x Time, t
State the equation involving power, current, and PD.
Power, P = Current, I x Potential Difference, V
What's the equation for efficiency?
Efficiency = ( Output Power / Input Power ) x 100
Therefore, what's the equation for output power?
Output Power = Efficiency x Input Power
How do you find the percentage of energy wasted?
Percentage Energy Wasted = 100% - Percentage Efficiency
Why do electrical appliances waste energy?
Because the current in both the wires and the components of the appliance has a heating effect due to the resistance of the wires/components.
Electrical appliances with moving parts also waste energy due to friction, and therefore heating.