anatomy of flowering plants
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
tissue’s structure and function would also be dependent on
location
Elongated, compactly arranged cells, which form a continuous layer
epidermis
parenchymatous with a small amount of cytoplasm lining the cell wall and a large vacuole
epidermal cell
bean shaped stomata seen in
dicots
dumbell shaped stomata seen in
monocots
thin wall of stomata
outer wall
a few epidermal cells, in the vicinity of the guard cells become specialised in their shape and size and are known as
subsidary cellls
thick wall of stomata
inner wall
unicellular hairs
root hairs
multicellular hair
trichomes
which type of cell elongation may be branched or unbranched and soft or stiff, they may even be secretory
trichomes
which type of cell is usually present in cortex
parenchyma
which type of cell is usually present in pericycle
parenchyma cells
which type of cell is usually present in pith
parenchyma
which type of cell is usually present in medullary rays
parenchyma
In leaves, the ground tissue consists of thin-walled chloroplast containing
cells and is called
mesophyll
which type of plants has cambium is present between phloem and xylem
dicots
vascular bundle having cambium b/w phloem and xylem, this type of vascular bundle is called
open vascular bundle
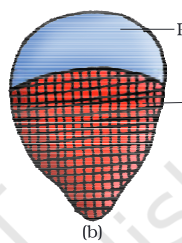
type of vascular bundle
conjoint closed
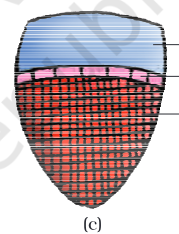
type of vascular bundle
conjoint open
When xylem and phloem within a vascular bundle are arranged in an alternate
manner along the different radii, the arrangement is called
radial
the xylem and phloem are jointly situated along the same radius of vascular bundles
conjoint
radial vascular bundle is seen in
roots
conjoint vascular bundle is seen in
stems and leaves
The cortex of dicot roots consists several layers of thin-walled_____
parenchyma
The innermost layer of the cortex of dicot root is called
endodermis
The tangential as well as radial walls of the endodermal cells of the dicot root have a deposition of water-impermeable, waxy material suberin in the form of
casparian strip
thick-walled parenchymatous cells of dicot root referred to as
pericycle
Initiation of lateral roots and vascular cambium during the secondary growth takes place in which layer of dicot root
pericyle
The parenchymatous cells which lie between the xylem and the phloem of dicot root are called
conjuctive tissue
presence of two to four xylem and phloem patches is seen in
dicot root
All tissues on the innerside of the endodermis such as pericycle, vascular bundles and pith of dicot root constitute the
stele
Presence of polyarch xylem bundles is the characteristic of
monocot root
Pith is large and well developed in
monocot root
pith is inconspicuous in
dicot root
The outer hypodermis of dicot stem, consists of a few layers of
collenchyma cells
cortical cells of dicot stem consists of
parenchyma cells
which layer of dicot stem is rich in starch grains
endodermis
present on the inner side of the endodermis of dicot stem and above the phloem in the form of semi-lunar patches
pericycle
pericycle is formed of
sclerenchyma
In between the vascular bundles of dicot stem there are a few layers of radially placed parenchymatous cells, which constitute
medullary rays
the cross section of ____ shows the ring arrangement of vascular bundles
dicot stem
dicot stem has
endarch protoxylem
dicot root has
exarch protoxylem
A large number of rounded, parenchymatous cells with large intercellular
spaces which occupy the central portion of the dicot stem constitute the
pith
hypodermis of monocot stem has
sclerenchyma
Palisade parenchyma is present on
adaxial surface
Peripheral vascular bundles are generally smaller than the centrally located ones seen in
monocot stem
Spongy parenchyma is present
abaxial surface
The vascular bundles of dicot leaf are surrounded by a layer of thick walled
bundle sheath cells
certain adaxial epidermal cells along the veins modify themselves into large, empty, colourless cells
bulliform cells
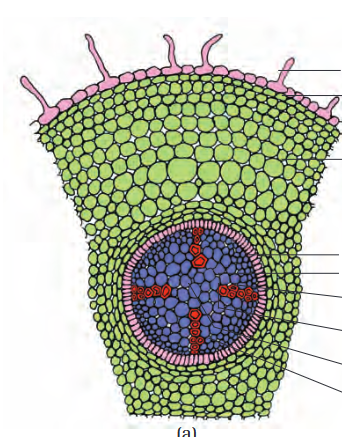
dicot root
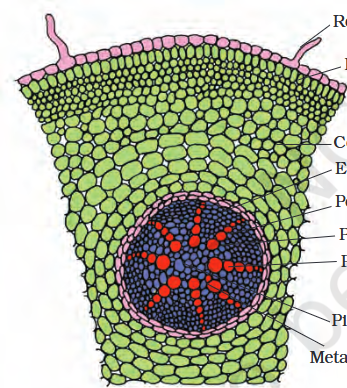
monocot root
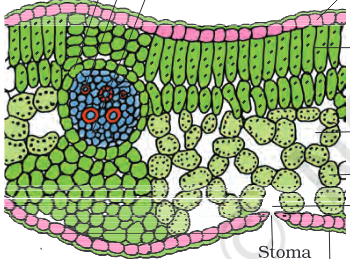
dicot leaf
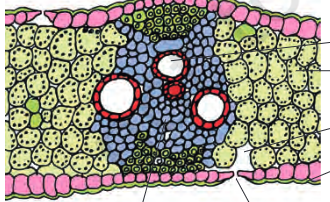
monocot leaf
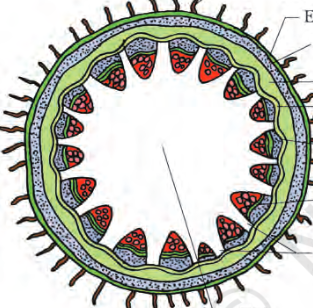
dicot stem
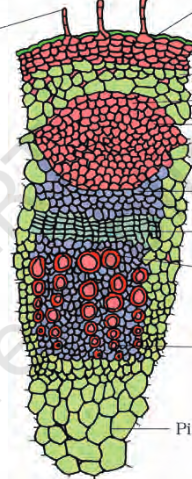
dicot stem
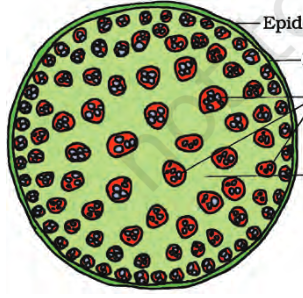
monocot stem
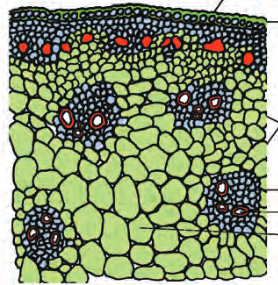
monocot stem
identify the plant part based on the anatomical features
no differentiation of mesophyll
equal no of stomata present on both surfaces
presence of bulliform cells
absence of reticulate venation
monocot leaf
Identify the plant part based on the anatomical features
differentiation of mesophyll cells
unequal distribution of stomata
presence of air spaces between spongy cells
size of vascular bundle depends on size of veins
absence of parallel venation
dicot leaf
Identify the plant part based on the anatomical features
sclerenchymatous hypodermis
sclerenchymatous bundle sheath
peripheral vascular bundle are smaller
presence of water containing cavities
monocot stem
Identify the plant part based on the anatomical features
cells arranged in multiple layers between epidermis and pericycle constituting the cortex
presence of starch sheath
presence of semilunar patch of sclerenchymatous cell
presence of pith at the centre
dicot stem
Identify the plant part based on the anatomical features
polyarch condition
well developed and large pith
lack of secondary growth
presence of casparian strip
presence of conjuctive tissue
monocot root
Identify the plant part based on the anatomical features
presence of casparian strip
presence of conjuctive tissue
development of cambium ring between xylem and phloem
presence of inconspicuous pith
dicot root