Pedigree, Cancer Genetics & Karyotyping
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Pedigree
a diagram that depicts the biological relationships between an organism and its ancestors
Commonly used symbols
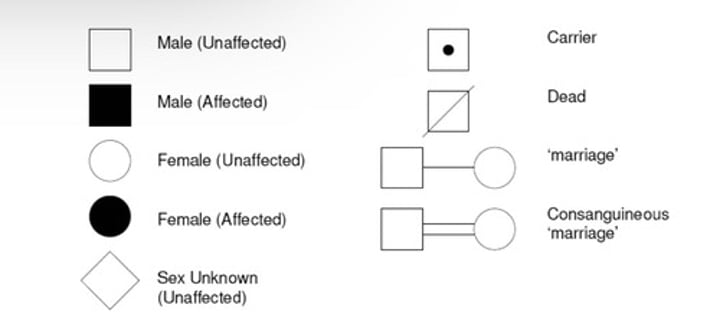
If all affected individuals have affected parents, then the pedigree is most likely...
dominant
If the pedigree skipped a generation, then the pedigree is most likely...
recessive
Autosomal dominant
father to son is present
X-linked dominant
- no father to son
- all affected males have affected mother
- when father is affected, only daughters are affected
X-linked recessive
mostly affects males
Characteristics of autosomal dominant disease
- affected person usually has at least one affected parent
- affects either sex
- transmitted by either sex
- child of an unaffected x affected mating has 50% chance of disease (assuming affected parents are heterozygous)
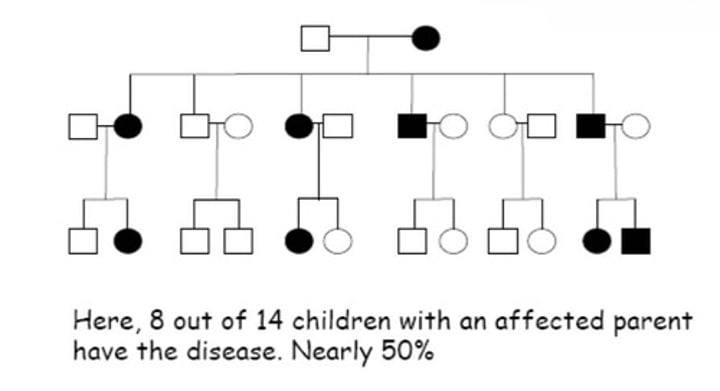
Characteristics of autosomal recessive disorder
- affecteds usually have unaffected parents
- parents are usually carriers
- affects either sex
- increased incidence of inbreeding
- carriers and non-carriers are indistinguishable
- if two carriers mate their offspring have a 1 in 4 chance of being affected and 1 in 2 chance of being a carrier
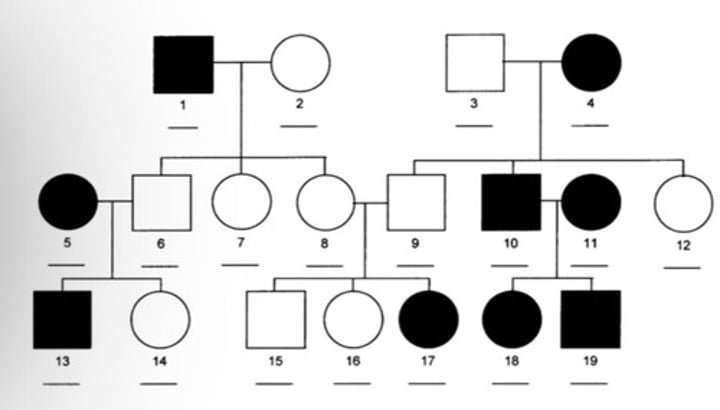
Examples of autosomal recessive disorders
- albinism
- sickle cell anemia
- cystic fibrosis
- attached ear lobes
Characteristics of X-linked dominant
- trait is common in pedigree
- affected fathers pass to ALL of their daughters
- males and females are equally likely to be affected
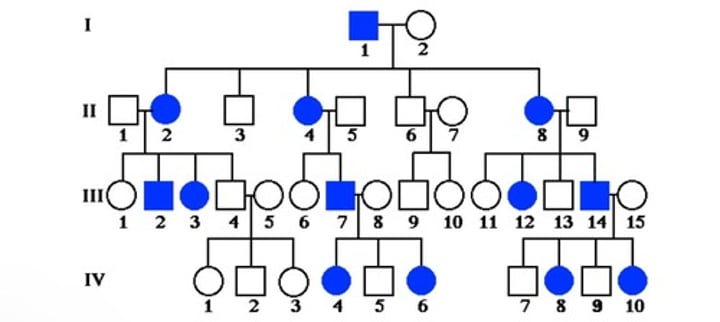
Characteristics of X-linked recessive inheritance
- trait is much more common in males than females
- male-to-male transmission never occurs
- trait is rare
- trait skips generations
- males are more often affected than females
- an affected man passes the gene to all of his daughters
Examples of X-linked recessive disorders
- Duchenne Muscular dystrophy
- Red-green color blindness
- Hemophilia
Characteristics of Y-linkage
- affects only males
- all sons of an affected man are affected
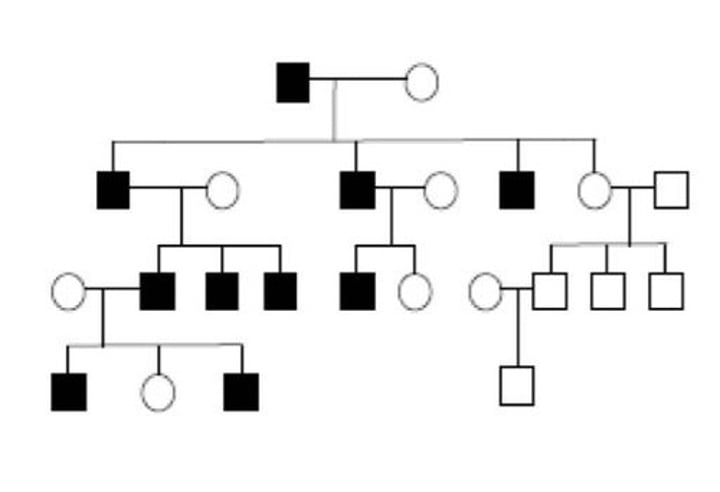
Examples of Y-linkage
- maleness
- hairy ear rims