4.7-4.8 Sustainable development & Measuring development
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Economic growth
Increase in real GDP or GNI per capita over time
Focuses on quantity of output, not distribution or quality of life
Economic development
Multidimensional process improving living standards, education, health, equity
Includes access to merit goods, employment, gender equality, and reduced poverty
Sources of growth in ELDCs
Physical capital, human capital, technology, institutions
Raise productivity and support development
Curse of natural resources
Heavy reliance on commodities may hinder growth
Leads to volatility, debt, poor diversification
Growth may not lead to development if
Income is unevenly distributed or limited investment in human capital
Neglect of informal sector, rural areas, and vulnerable groups
Country classification by income
Low, lower-middle, upper-middle, high-income
Used by World Bank based on GNI per capita
Limit of income-based classification
Income alone does not reflect development
HDI gives better insights into human wellbeing
Common characteristics of ELDCs
Low GDP/GNI
High poverty
High unemployment
High inequality
Weak institutions
Low education
Poor health
Low physical capital
Low productivity
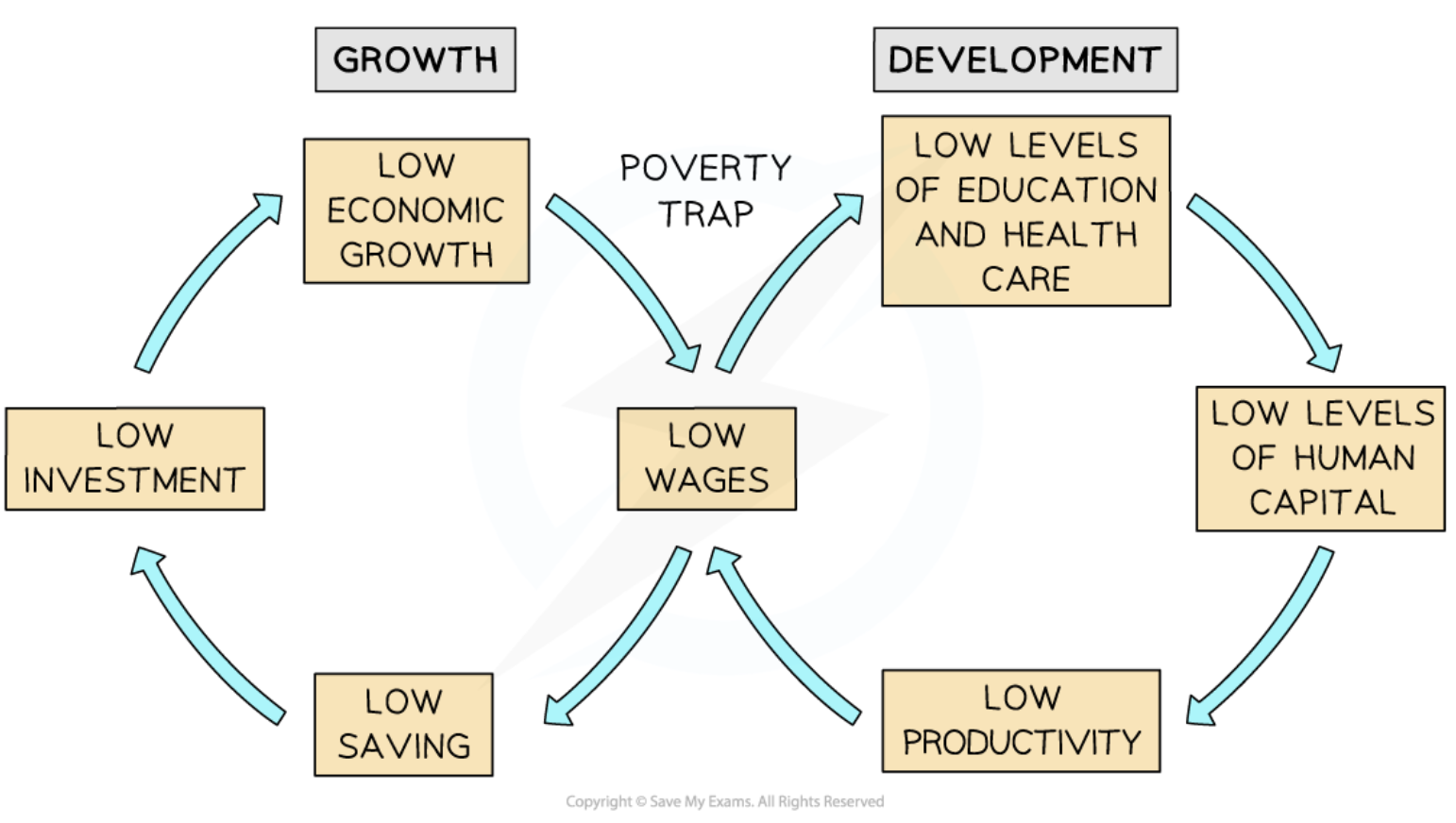
Poverty trap/cycle
Low income leads to low savings and low investment
Reinforces cycle of poverty, low productivity, and low growth
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
17 global goals for ending poverty, improving health, education, and sustainability by 2030
Difficulties measuring development
No single indicator reflects all aspects of development Indicators vary across countries and have limitations
GDP per capita
Measures average output produced per person
Good for comparing productivity
GNI per capita
Measures average income received per person
Better for comparing living standards
Purchasing power parities (PPPs)
Exchange rates adjusting for cost-of-living differences
Makes cross-country income comparisons more valid
Health indicators
Life expectancy, infant mortality, maternal mortality
Reflect population wellbeing and healthcare access
Education indicators
Adult literacy, primary and secondary enrolment, mean years of schooling
Show access and attainment of education
Composite indicators
Combine multiple measures into one index
More accurate for assessing development than single indicators
Human Development Index (HDI)
Measures education, health, and GNI per capita
Ranks countries by human development achievements
HDI vs GNI per capita
HDI includes education and health dimensions
Better reflects human development than income alone
Inequality-adjusted HDI
Adjusts HDI for income, education, and health inequality
Larger inequality lowers HDI score
Gender Inequality Index (GII)
Measures loss due to gender inequality in health, empowerment, and labor
Higher GII = more inequality
Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI)
Measures deprivation in education, health, living standards
Goes beyond income to reflect poverty realities