Biology topic 8 Genetic mutations
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What is a gene mutation?
Change in the DNA sequence or structure of a gene that may alter the protine produced
What is a gene deletion ?
A mutation where a section of DNA is removed from a gene, producing a shorter gene that may be non - functional
What is a gene insertion?
A mutation where extra DNA added into a gene, which can change th reading frmae or alter the protine produced
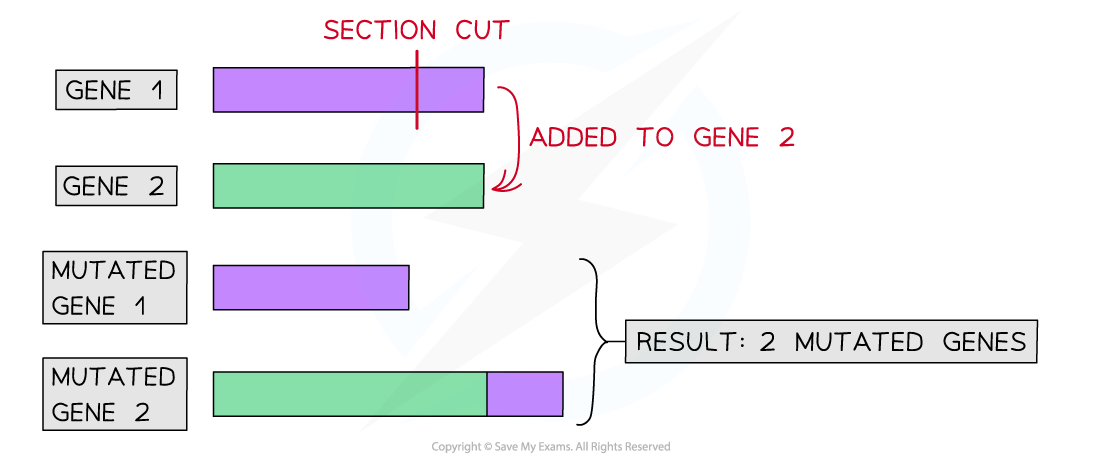
What happens to Gene 1 after deletion?
Gene 1 becomes shorter becomes a DNA section is removed, likely affecting its normal function
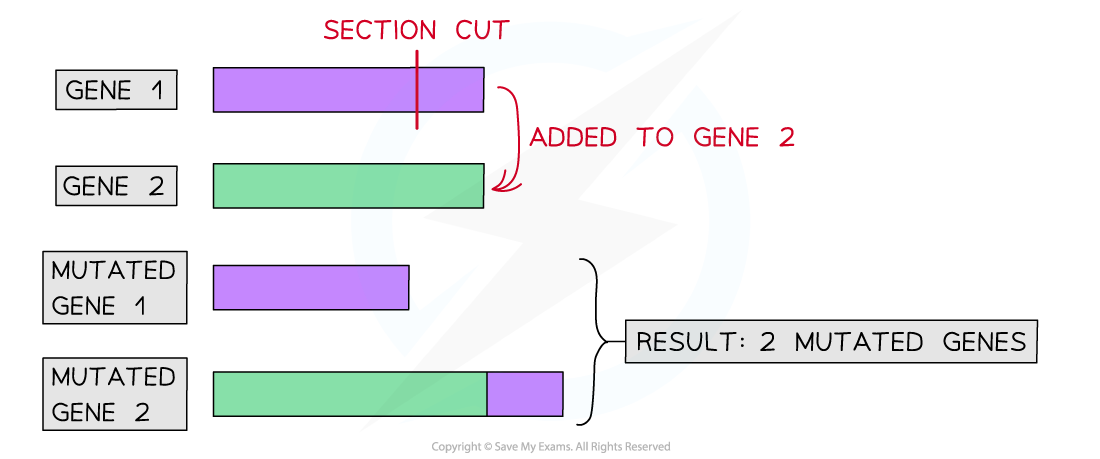
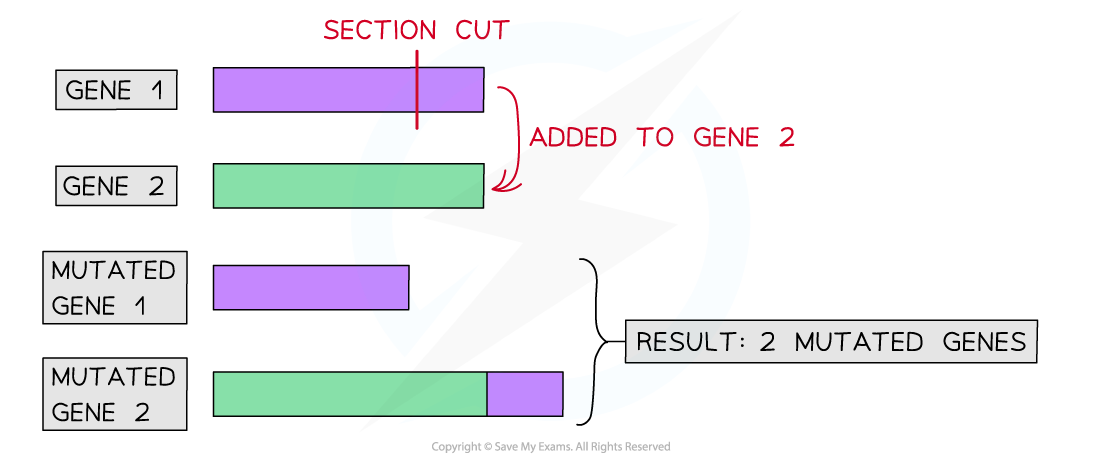
What happens to gene 2 after the insertion ?
Gene 2 becomes longer becouse it recives an extra DNA section, which may change the protine it codes for
What happens to a gene when an extra DNA section is inserted into it ?
The gene becomes longer and may produce a protine with an altered amino acid sequence
What is the outcome when one gene loses DNA and another gains that DNA?
Two mutated genes form from one shortened by deletion and one lengthened by insertion, both likely to affect protine function
Weh do gen mutations occure?
Mutations occur randomly during DNA replication
How can a gene mutation affect a protine?
Mutation may change the DNA base sequence altering the amino acid sequence protine produced
Why do most mutation not change the polypeptide?
The genetic code is degnerate so some base changes still code for the same amino acids
Why do substitution mutations often have small effect?
They usually change only one base and may not alter the amino acid sequence due to degeneracy
Which mutations cause a frame shift?
Insertion and deletion mutations shif the reading frame , altering all downstream triplets
What is the effect of frame shif mutation?
IT changes all amino acids after the mutation, usually producing a non - functional polypeptide
Why do most mutations not affect protine function?
They may not change th eamino acid sequence or only alter it slightly so structure and function remain unchanged
How can a mutation alter protein function?
A major change in amino acid sequence can change the protines shape, preventing it from working properly
How can a mutation affect a structrual protine?
Change in shape may reduce its strength ot stability
How can gene mutations affect phenotype?
Altered polypeptides can disrupt cellular processes , leading to changes in observable characteristics
How does a mutation in the in the TYR gene affect phenotype?
IT alters an enzyme needed for melanin production cauaisng albinism due to lack of pigment
What are the characteristics of albinism ?
Very pale skin and often white hair due to lack of melanin
What is the natrual mutation rate in humans?
around one mutation per 100,000 genes per generation
What are mutagenic agents?
Factors that increase the frequency of mutations in DNA
What are physical mutagens?
Radiation such as X rays and gamma rays that physically damage DNA
What are chemical mutagens?
Chemicals that interfere with DNA structure or replication
What are biological mutagens?
Viruses or biological molecules that interfere with DNA e.g HPV
(damages DNA or disrupts DNA replication, increasing the chance of a mutation forming.)
How does exposure to mutagenic agents affect mutation rate?
IT increases the frequency of mutation in DNA