First practice test - wrong in chem section
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
A peptide bond ALWAYS forms between: a
amine (–NH₂), and a carboxyl group (–COOH)
If something has a lone pair then it is a
lewis base
what is the acid and base in this equation
HCl+H2O→Cl−+H3O+
HCl is the acid (H is taken away)
H20 is the base (it added a Hydrogen)
Shorter wavelength =
higher energy
Longer wavelength =
lower energy
what is the energy equation
E = hc/λ
h = 6.62 × 10⁻³⁴ J·c
c = 3.0 × 10⁸ m/s
λ = wavelength in meters
absorbs high-energy photon =
excitation
releases lower-energy photon =
emission
ΔE =
Eexcitation - Eemission
After you move decimals to divide what do you do -
make sure to move decimals back
1 µM =_____ nM
1000
Every carbon in a benzene ring is sp². - so
3 in each ring
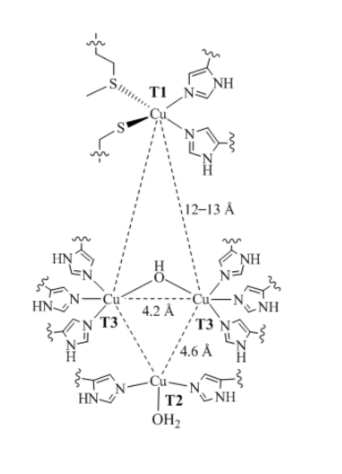
In laccases, the sulfur ligand is
cysteine
What is the Kcat equation:
Kcat = vmax/E
vmax = rate of product formation
E = enzyme concentration
Least to most polar
(alkane/alkene/alkyne, -> ether/ester/aldehye/ketone -> alcohol -> amide/amine -> carboxylic acid)
The half-life of a radioactive material is:
A. half the time it takes for all of the radioactive nuclei to decay into radioactive nuclei.
B. half the time it takes for all of the radioactive nuclei to decay into their daughter nuclei.
C. the time it takes for half of all the radioactive nuclei to decay into radioactive nuclei.
D. the time it takes for half of all the radioactive nuclei to decay into their daughter nuclei.
D. the time it takes for half of all the radioactive nuclei to decay into their daughter nuclei
Energy questions ALWAYS deal with
height
Choose _____ when the question describes:
Standing, Balancing, Not falling over, Shifting weight, Moving center of mass✔ Rotation around a pivot (torque), Preventing tipping, getting up from chair
equilibrium answers
You pick a______n when the question involves:
Lifting something heavy
Applying force at a distance (levers)
Changing the angle of a muscle to increase the mechanical advantage
Using ramps, pulleys, longer arms/levers
force answer
fully folded protein -
tertiary protein
Aromatic amino acids:
trp, phe, tyr
Energy equation:
E = hc/wavelength
an electronic excited state that is closer in energy to the ground state? - will have
the lowest energy (highest wavelength)
Phosphorylating something →
γ-phosphate
β + γ leave as pyrophosphate (PPᵢ) →
Making DNA/RNA
Which phosphate stays in nucleotides →
α-phosphate
When a nucleotide is added during DNA replication, which phosphate(s) are released?
A. α
B. β
C. γ
D. β and γ together
E. all three
D. β and γ together
T =
theronine
Y =
tyrosine
W -
tryptophan
D -
aspartic acid
E -
glutamic acid
Q -
glutamine
the process of a kinase adding a phosphate group to a molecule to regulate its activity or signaling.
phosphorylation
Amine (–NH₂) is _____
Carboxyl (–COOH) is _____
Hydroxyl (–OH) is also _____
polar and basic., polar and acidic, polar
phophorylation happens on the
side chain of the OH group (serine, tyrosine, theronine)
Hydroxyl-containing amino acids (–OH group)
These are the ones that can be phosphorylated by kinases.
serine, tyrosine, theronine
aromatic amino acids
phenylanine, tyrosine, tryptophan (absorb light)
→ –CH₂–SH
→ can form disulfide bonds
→ can be deprotonated to S⁻ (nucleophile)
cysteine
→ –S– in the middle (thioether)
→ cannot form disulfides
mehtionine
cyclic, breaks α-helices
proline
smallest
glycine
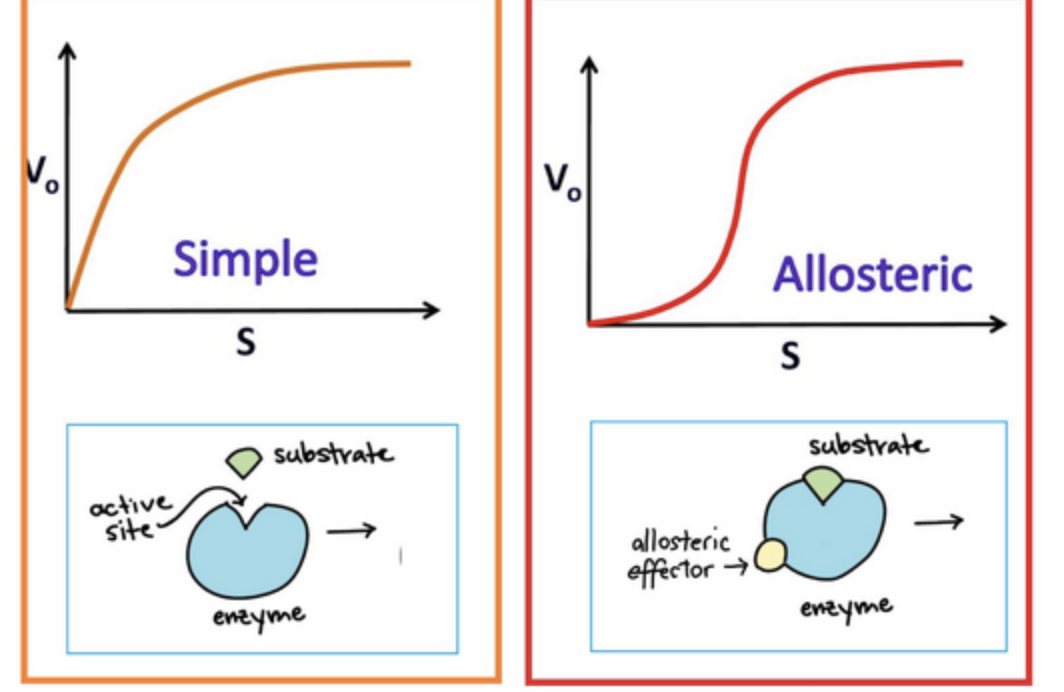
If a curve is sigmoidal → the process is
cooperative
A higher melting temperature is indicative of a
more stable protien
lungs/oxygen-
venturi
____ base pairs create stronger pi-stacking interactions in the duplex than ____
GC, AT
For two liquids with different boiling points, the one with the lower boiling point will have the
higher vapor pressure at the same temperature.
Two fatty acids ester-linked to a single glycerol plus a charged head group
phospholipid
Three fatty acids ester-linked to a single glycerol
storage lipid
Two fatty acids ester-linked to a single sphingosine plus a charged head grouo
sphingomyelin
Three fatty acids ester-linked to a single sphingosine
ceramide
A ___ affects the reaction rate but not the total amount of product produced at equilibrium.
catalyst
[Cu(NH₃)₄]²⁺
[Fe(CN)₆]³⁻
BF₃·NH₃
coordinate covalent bonds
NH3 is a stronger Lewis base than H2O because the
nitrogen atom is less electronegative than the oxygen atom.
the number behind the element K3F5Cl7
coordination number
Ph equation
pH = pka + log (base/acid)
log(1) =
0
log(10) =
1
log(0.1) =
-1
Diastolic -
denominator
single bond -
longest bond length, lowest bond energy, most flexible
triple bond
shortest bond length, highest bond energy
Sugar–phosphate backbone =
outside
Nitrogenous bases =
inside
A glass rod is rubbed with a silk scarf producing a charge of +3.2 × 10–9 C on the rod. (Recall that the magnitude of the proton and electron charges is 1.6 × 10–19 C.) The glass rod has:
A. 5.1 × 1011 protons added to it.
B. 5.1 × 1011 electrons removed from it.
C. 2.0 × 1010 protons added to it.
D. 2.0 × 1010 electrons removed from it.
D. 2.0 × 1010 electrons removed from it
the + means that electrons were removed
At STP, the molar volume of an ideal gas is
22.4
Which single bond present in nitroglycerin is the LEAST polar?
A. C–H
B. C–O
C. C–C
D. O–N
C. C–C
Power =
energy/time or mgh/time
AHED
absorption, higher potential, excited, distance from nucleus