APHUG Unit 2 (Population Only)
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Agricultural Density
The ratio of the number of farmers to the total amount of land suitable for agriculture.
Arithmetic Density
The total number of people divided by the total land area.
Demographic Transition
The process of change in a society's population from a condition of high crude birth and death rates and low rate of natural increase to a condition of low crude birth and death rates, low rate of natural increase, and a higher total population.
Demography
The scientific study of population characteristics.
Dependency Ratio
The number of people under the age of 15 and over the age of 64 compared to the number of people active in the labor force.
Doubling Time
Time number of years needed to double a population, assuming a constant rate of natural increase.
Ecumene
The portion of Earth's surface occupied by permanent human settlement.
Epidemiologic Transition
The Epidemiological Transition Model describes the distinct causes of death in each stage of the Demographic Transition Model. It highlights how disease patterns and causes of death evolve as a country develops.
Epidemology
Branch of medical science concerned with the incidence, distribution, and control of diseases that are prevalent among a population at a special time and are produced by some special causes not generally present in the affected locality.
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)
The total number of deaths in a year among infants under 1 year old for every 1,000 live births in a society.
Life Expectancy
The average number of years an individual can be expected to live, given current social, economic, and medical conditions. Life expectancy at birth is the average number of years a newborn infant can expect to live.
Natural Increase Rate (NIR)
The percentage of growth of a population in a year, computed as the crude birth rate minus the crude death rate.
Pandemic
Disease that occurs over a wide geographic area and affects a very high proportion of the population.
Physiological Density
The number of people per unit of area of arable land, which is land suitable for agriculture.
Population Pyramid
A bar graph resenting the distribution of population by age and sex.
Sex Ratio
The number of males per 100 females in the population.
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
The average number of children a woman will have throughout her childbearing years.
Zero Population Growth (ZPG)
A decline of the total fertility fate to the point where the natural increase rate equals zero.
Pro-natal policies
Also know as expansionist population policies. These are intended to encourage births, and might include economic incentives like subsidies or tax breaks.
Anti-natal policies
Also know as restrictive population policies, these are meant to slow down population growth. Restricting the number of children as China did or making contraception affordable or available are examples of policies.
Demographic momentum
The tendency for a population continue to grow after a fertility decline due to its young population.
Malthusian Theory
Theory proposed by Thomas Malthus in the 18th century that said population growth was outpacing the growth of food supplies.
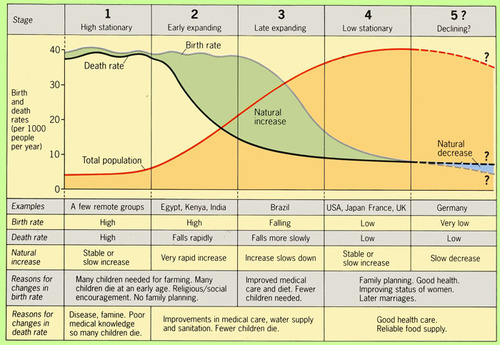
Stage 1 -DTM
High birth and death rates, low population growth
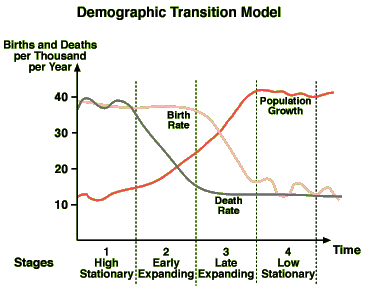
Stage 2-DTM
High birth rates, falling death rates due to improved water, food, and medicine, and rapidly increasing population growth
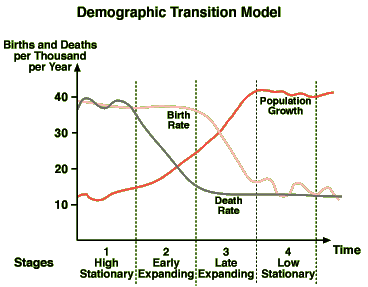
Stage 3-DTM
Death rates and birth rates both begin to fall due to improved conditions, better access to contraception, rising status of women, and urbanization; population growth slows
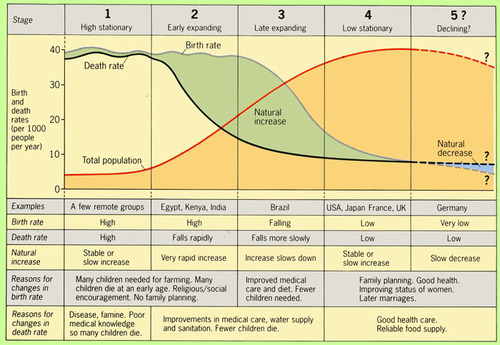
Stage 4-DTM
Low birth and death rates; continued increase in status of women, delayed marriage, improved medicine, reliable food supply; stable or slow population growth
One Child Policy
A program established by the Chinese government in 1979 to slow population growth in China. It was modified in 2015 to allow for 2 children.
Crude birth rate
The total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society.
Crude death rate
The total number of deaths in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society.
population distribution
the pattern in which humans are spread out on Earth's surface
metacity
a city with more than 20 million residents
megacity
a city with more than 10 million residents
population clusters
heavily populated areas that illustrate the unevenness in global population distribution; 4 include South Asia, East Asia, Southeast Asia, and Europe
replacement level fertility
the average number of children needed to replace both parents and stabilize population over time (2.1)
carrying capacity
the maximum population size that a given environment can support; likely varies from place to place and over time