Chapter 17.4 Harnessing the Free Energy of Redox Reactions - Voltaic Cells
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
The number of electrons that flow through the system per second (Unit: Ampere)
Electrode surface area determines the number of electrons that can flow
electric current
How are redox reactions related to electric current?
Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons, which has the potential to generate an electric current
What is the first step to utilizing an electric current (i.e. creating a battery)?
To create a battery, the half-reactions (oxidation/reduction) must be separated. Example: constructing a half-cell that corresponds to a half-reactions → voltaic cell
An electrochemical cell that uses redox reactions to produce electricity
voltaic cell
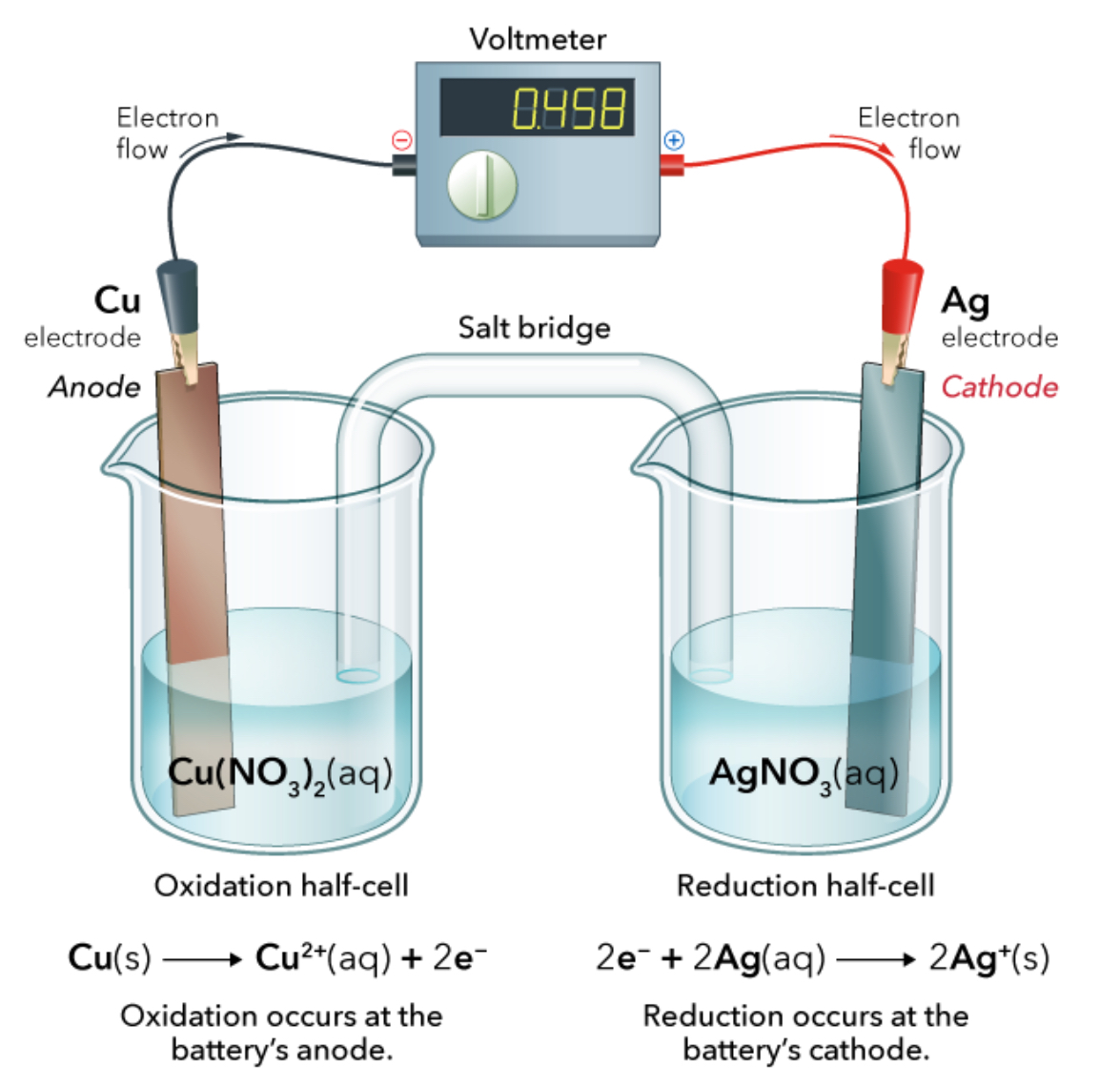
The electrode at which oxidation occurs; anions migrate toward it; has a negative sign
anode
The electrode at which reduction occurs; cations migrate toward it; has a positive sign
cathode
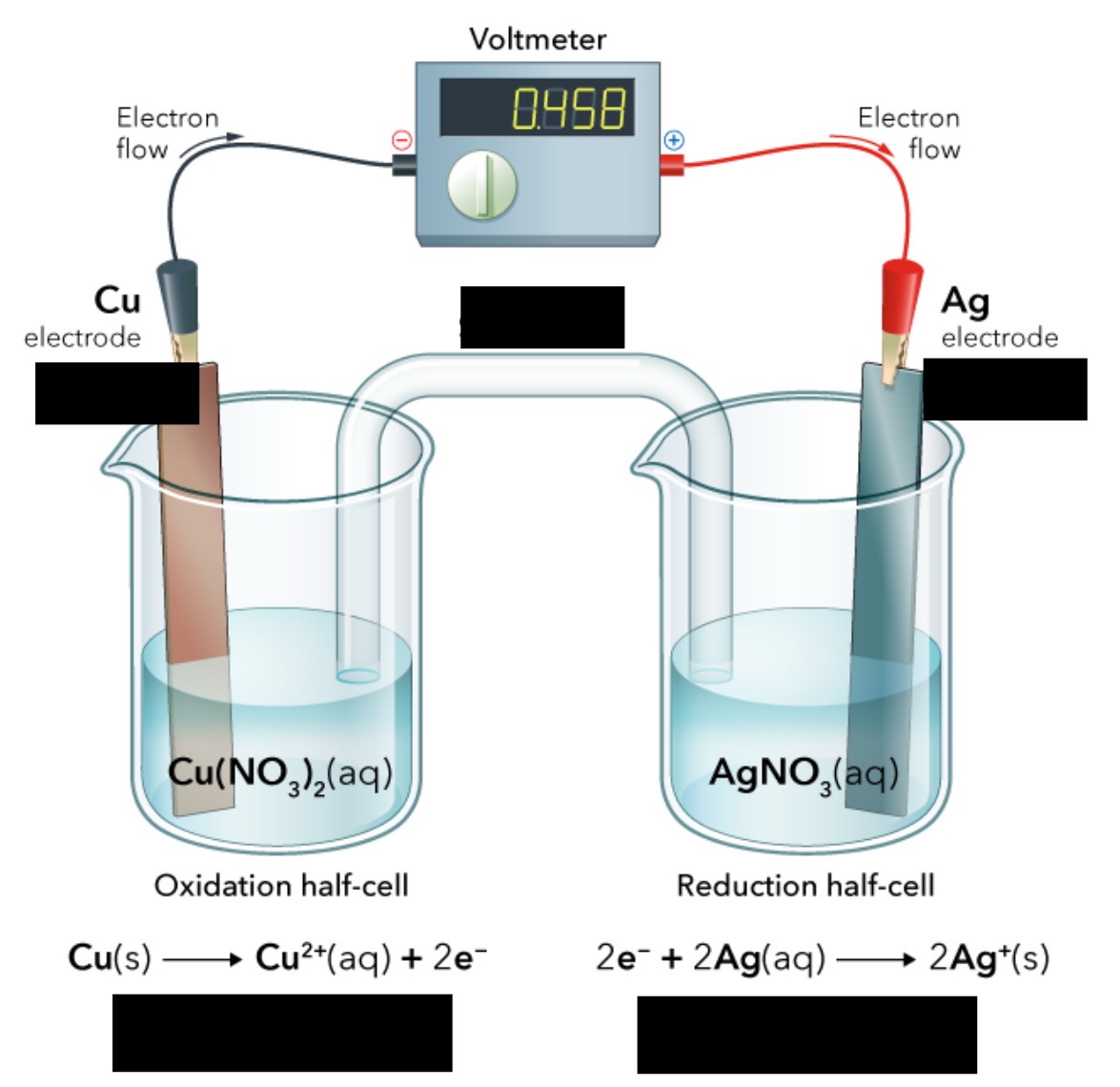
The difference in PE between the anode and the cathode in a voltaic cell (Unit: Volt)
Dependent upon the relative ease with which the oxidizing agent is reduced at the cathode and the reducing agent is oxidized at the anode
cell potential (ε)
The amount of force pushing the electrons through the wire
electromotive force (emf)
The cell potential under standard conditions (25ºC, 1 atm for gases, 1 M concentration of solution); sum of the cell potentials for the half-reactions
standard emf (Eºcell)
What equation relates cell potentials to Gibbs free energy?
∆G = -RTln(K) = -nFε
n = number of moles of electrons in the balanced redox reaction
F = Faraday’s constant (96,485 coulombs / mol of electrons)
ε = cell potential
A reference electrode used to measure cell potentials of other electrodes, with a defined value of 0 V
standard hydrogen electrode (SHE)
When two half-cells are connected, the electrons will flow so that _______.
the half-reaction with the stronger tendency will occur
The electrode cell potential of a half-reaction relative to the SHE and a quantitative measure of the tendency of a chemical species to be reduced
standard reduction potential
Can we measure the absolute tendency of a half-reaction?
No, we can only measure it relative to another half-reaction.
What is the significance of having a more positive standard reduction potential?
The substance is more easily reduced (i.e. the oxidized species in a volatic cell has smaller reduction potential).
What is the equation(s) for calculating standard cell potential?
εºcell = εºred,cathode + εºox,anode
εºcell = εºred,cathode - εºred,anode
Note: do not switch the sign of εanode and use the second equation
How can we obtain the oxidation reaction from the reduction reaction in the standard reduction potential table?
Reverse the reduction reaction
Because voltaic cells are spontaneous reactions, they must have ________ ∆G values and ________ εº values.
negative , positive
The standard cell potential is always the ___________ resulting from the addition or subtraction of the two half-cell reduction potentials.
largest positive value
EMFs ________ dependent on coefficients: they _______ change with the amount of material involved. When adding half-cell εº values, even if you need to multiply the half-reactions to balance the equation, DO NOT multiply the half-cell εª values.
are not , do not