Evolution of Atomic Theory [Part I]
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Plum pudding
And English dessert consisting of moist cake with embedded raisins
Plum-pudding model
The model that suggested that atoms resembled the plum pudding.
Its positively charged matter was the moist cake and the negatively charged matter was raisins.
Sir Joseph John Thompson
An English physicist who suggested the Plum-pudding model.
Cathode Ray Tube
A sealed glass tube that was used by J. J. Thomson to suggest the Plum-pudding model
Hermetically
(Adverb) in a way that is completely airtight
Sealed glass tube
A container that has been hermetically sealed to create an airtight seal
air
Cathode Ray Tube had almost no ___ in it
Two metal electrodes
Very vital components of the Cathode Ray Tube used by J. J. Thomson
Cathode ray
The visible beam that appeared between the two electrodes;
when a high voltage was applied across the electrodes within the Cathode Ray Tube
positive, negative
Cathode Ray was deflected toward the ________ charge and away from the ________ charge
applied magnetic field
In J. J. Thompson’s similar experiment rays were deflected by an ______________________
Measurements of the extent of deflection and the magnetic field strength
Two things that allowed Thomson to calculate the charge to mass ratio of the cathode ray particles.
1897
Year when Cathode Ray Tube was invented
Karl Ferdinand Braun
Inventor of the Cathode Ray Tube
High voltage
(1)
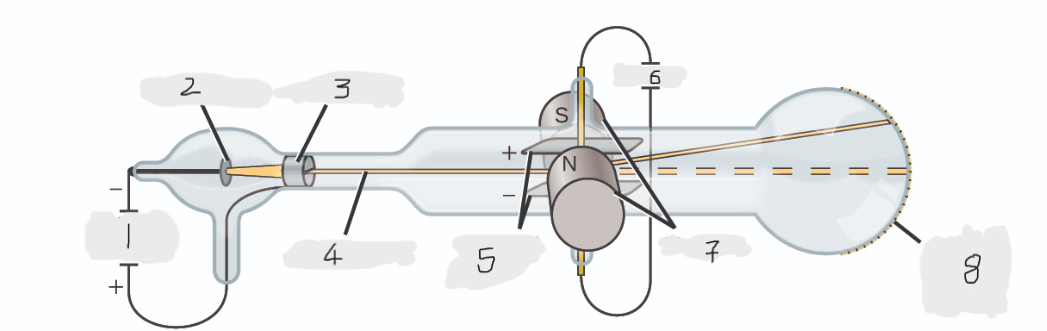
Cathode(-)
(2)
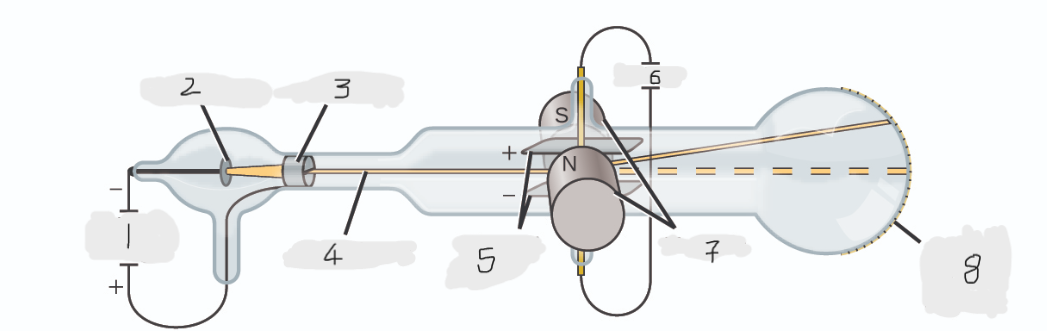
Anode(+)
(3)
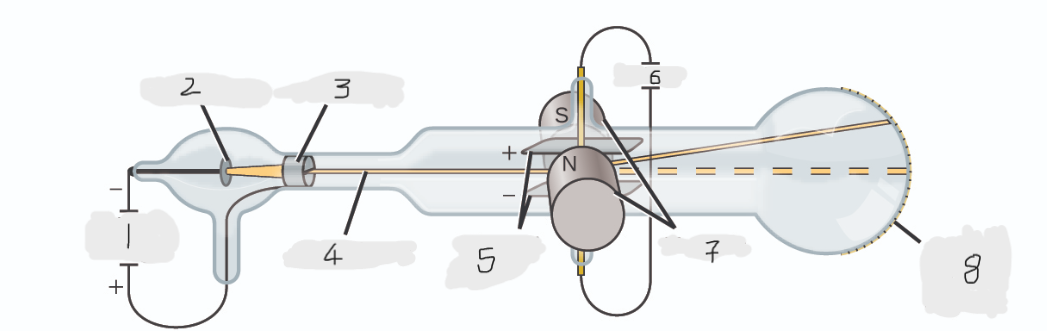
Cathode ray
(4)
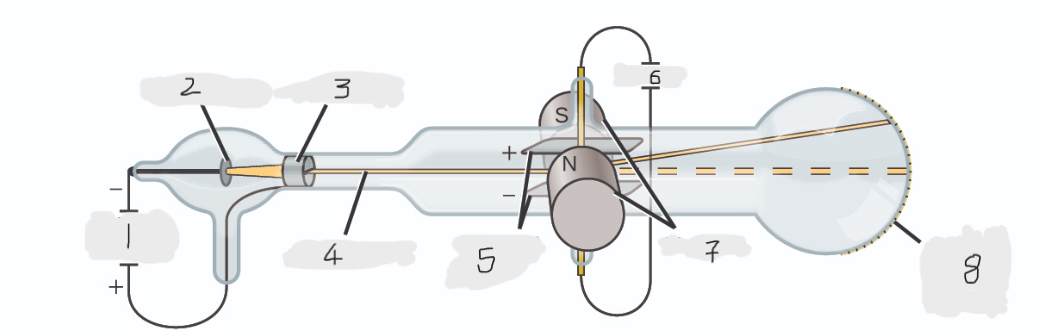
Charged plates
(5)
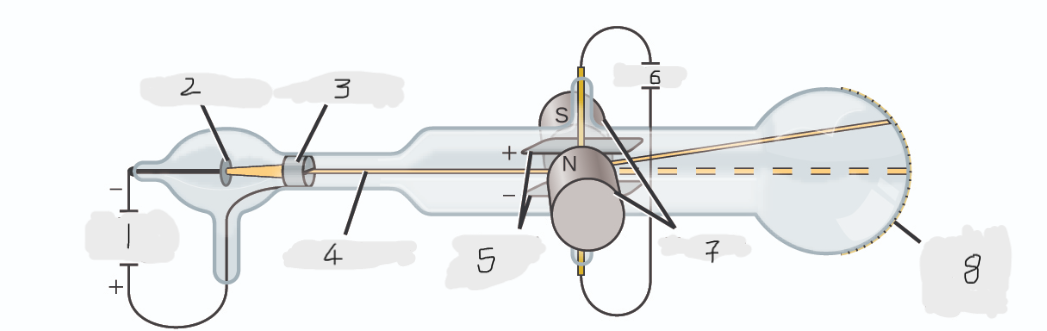
Battery
(6)
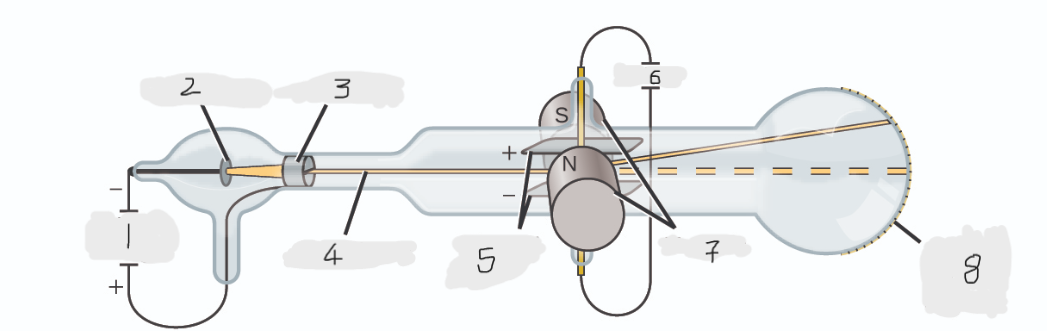
Magnets
(7)
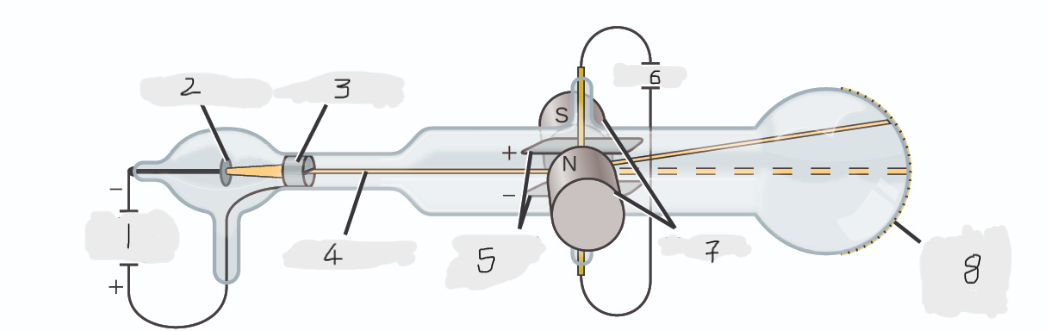
Scale on outside of glass
(8)
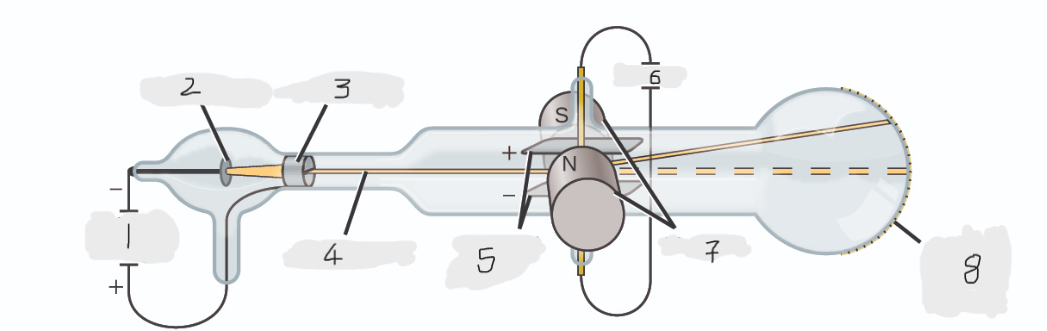
cathode
Cathode ray beam comes from the _______
anode
Cathode beam gets accelerated the _____
Fluorescent scale
A type of scale that glows brightly when light shines on it (especially the UV light)
electron
Cathode ray particle is what we now call an ________
one thousand-times
Electron’s mass is more than __________________ less than that of an atom
1891
Year when the term “electron” was coined
George Stoney
The Irish physicist who coined the term “electron”
Robert Andrew Millikan
American physicist who accurately measured the charge of a single electron
Oil drop experiment
The experiment that was used to measure the elementary charge of an electron
X-rays
The type of light rays that Millikan utilized to electrically charge the microscopic oil droplets.
Friction
________ by the rays made the microscopic oil droplets electrically charged
X-rays to electrically charge the microscopic droplets
(i)
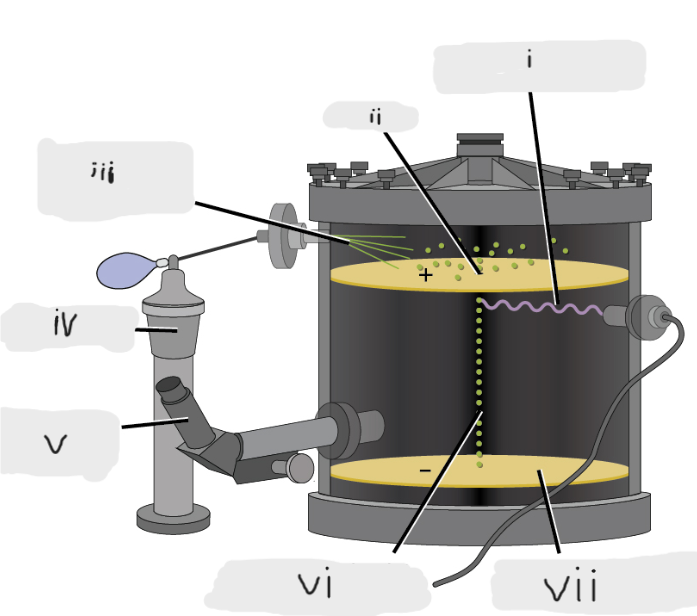
Pinhole
(ii)
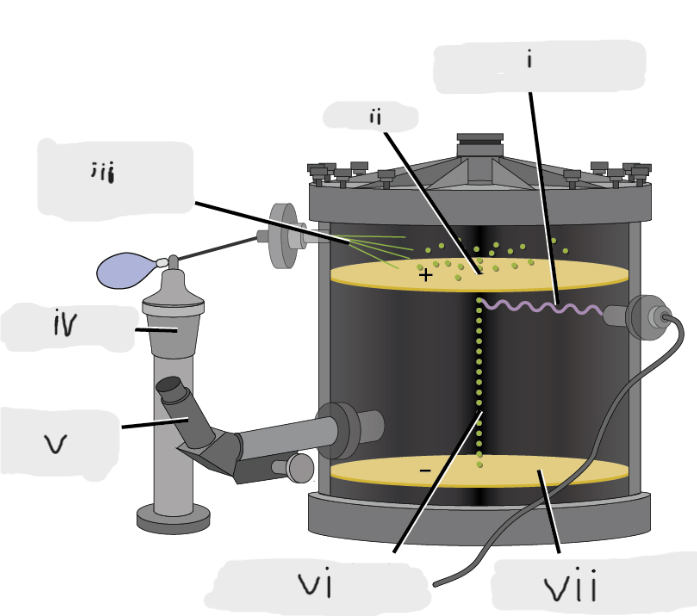
Oil sprayed in fine droplets
(iii)
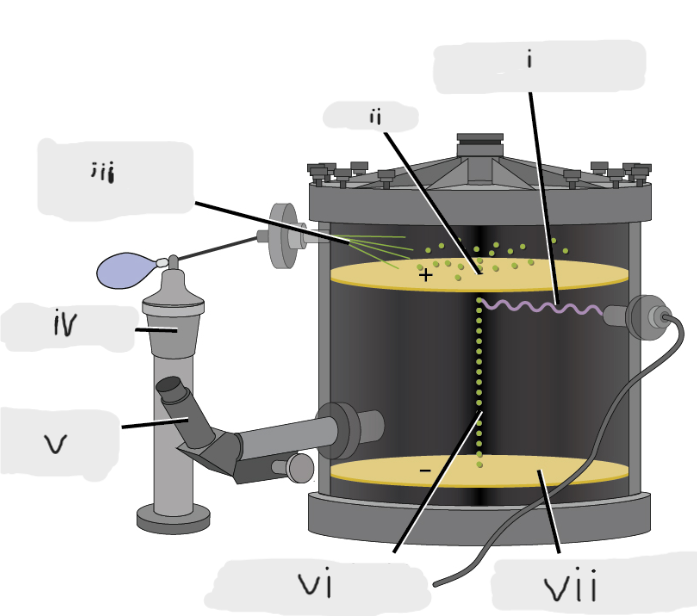
Oil atomizer
(iv)
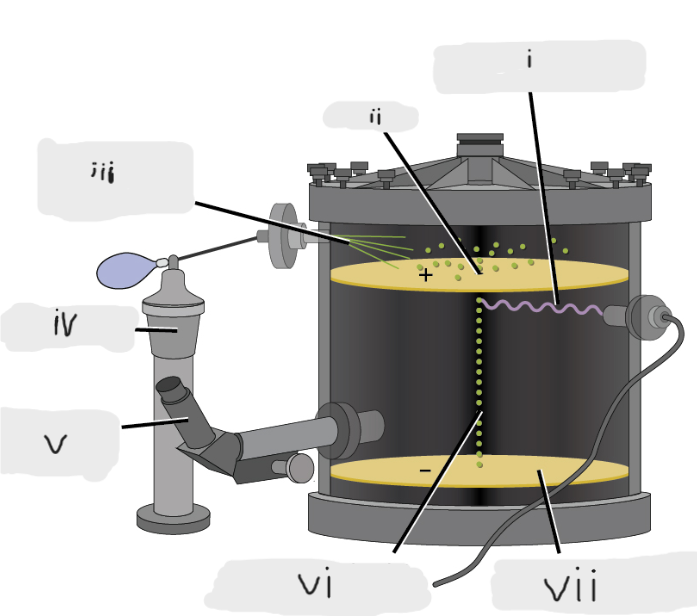
Telescopic eyepiece
(v)
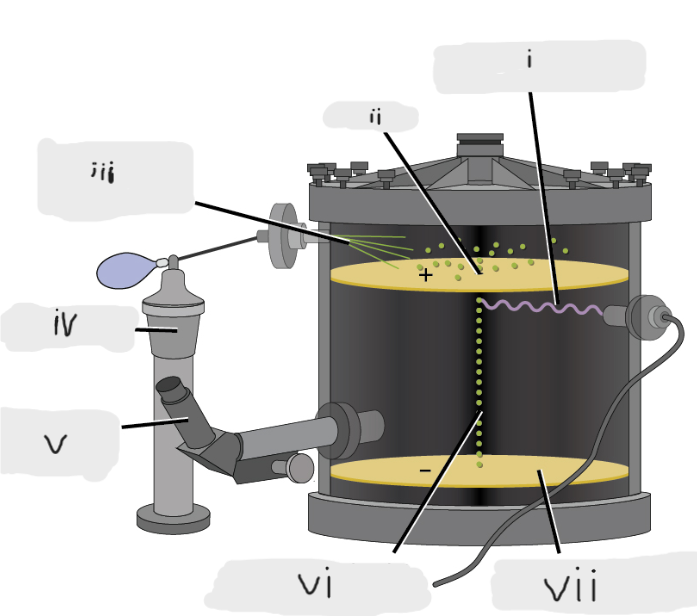
Charged oil droplet under observation
(vi)
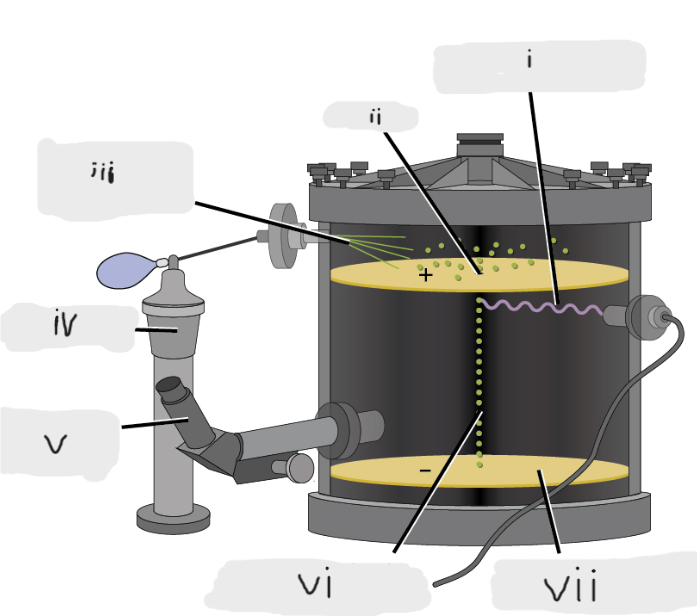
Electrically charged brass plate
(vii)
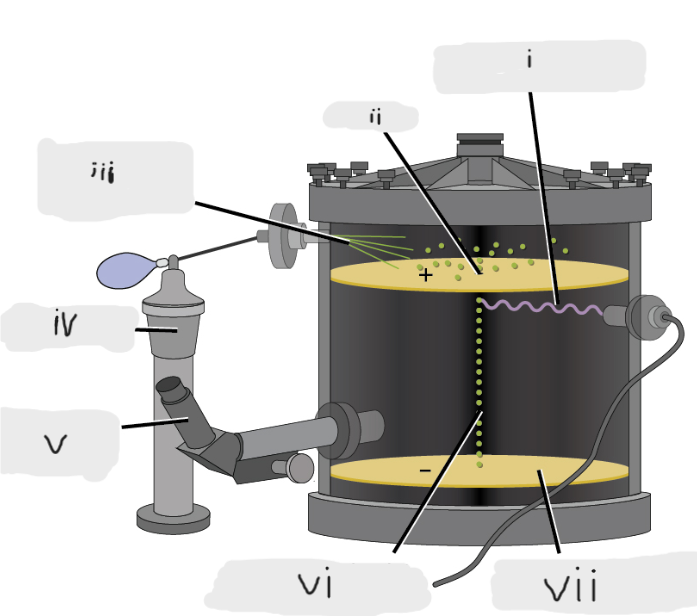
gravity, slowed, reversed, electric field
Microscopic oil droplets initially fell due to _______, but their downward progress could be ______ or even ________ by an ______________ lower in the apparatus.
1.602×10^-19 C
Charge of a single electron
1kg/1.759×10^11 C
Charge to mass ratio of electrons calculated by J. J. Thomson
(Electron’s elementary charge)*(charge to mass ratio of electrons)
Equation for the mass of electron
9.109×10^-31 kg
Mass of a single electron
1903
Year when the Saturn-like atom model was postulated
Hantaro Nagaoka
The Japanese physicist who postulated the Saturn-like atom model
Ernest Rutherford
A Kiwi physicist who performed a series of experiments using a beam of high speed positively charged alpha particles.
The radioactive decay of radium
Produced the α particles
2
No. of protons in the α particle