Chapter 14 Thermal physics
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
what does thermal equilibrium mean
there is no net flow of energy between 2 objects in contact - they are the same temperature
what is the internal energy of a substance
sum of the random distribution of kinetic and potential energies associated with the molecules of a system
why can internal energy never be 0
at the lowest temperatures kinetic energy of the molecules will be 0
but potential energy cannot be 0
why is absolute 0 the lowest limit for temperature
the internal energy of a substance is the lowest possible at absolute 0
due to potential energy of the molecules only
what happens at the triple point of a substance
the three phases of matter of that substance exist in thermal equilibrium
why is the celcius scale not accurate
the boiling point of water varies with temperature
what are 2 conlcusions that can be made from the brownian motion experiment using smoke
the air molecules move with random linear motion
the air molecules are much smaller than the smoke molecules
what is brownian motion
the random motion of particles suspended in a fluid due to their collision with randomly moving fluid molecules
how can brownian motion be demonstrated
using a lamp and a convex lens, shine a light through a smoke cell
use a microscope to observe the smoke
should see the smoke molecules moving linearly in random directions
why does volume of water increase as temperature increases
the molecules gain kinetic energy
their average speed increases
higher frequency of collisions
what happens to the internal energy of a substance as its temperature increases
internal energy increases because the average kinetic energy of the molecules increases
why does temperature not change when a substance is changing phase
the energy transferred to the substance does not increase the average kinetic energy of the molecules
it only increases the potential forces between the molecules
what is the order of potential energies in solids liquids and gases
most negative in solids
less negative in liquids
0J in gases (highest)
define specific heat capacity
the energy required to increase the temperature of 1kg of substance by 1 kelvin
what is the equation for specific heat capacity
E = mcΔtΘ
where E is the energy supplied to the substance
m is the mass of the substance
c is the SHC
ΔΘ is the change in temperature
kinetic model of solids
particles vibrate in a fixed ordered lattice
very little spacing between the molecules
kinetic model of liquids
particles flow past eachother
vibrating but not in fixed positions
larger spacing than in solids
kinetic model of gases
particles far apart
only exert forces on eachother during collisions
particles move in random linear motion
what happens to the vibrations of particles as temperature is increased
amplitude of vibrations increases
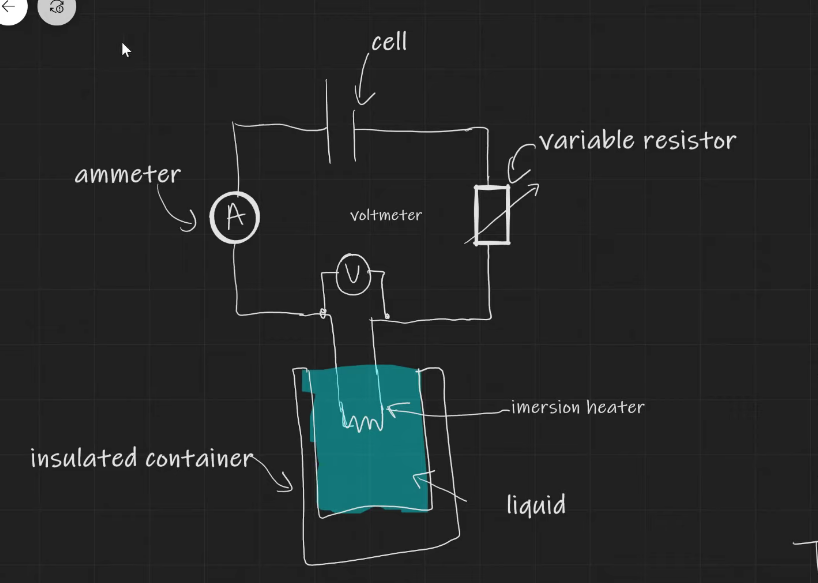
practical to work out specific heat capacity
Set up circuit as shown in diagram
Measure mass of substance using top pan balance
Measure V, I, and temperature at regular time intervals
Plot a graph of temperature on y axis and time on x axis
VI = mc Θ/t
Θ/t is the gradient so VI = mc x gradient
c = VI/m x gradient
To improve accuracy make sure heater is fully submerged
Make sure everything is insulated to minimise transfer of energy to surroundings
define specific latent heat
the energy required to change the phase of 1kg of substance without changing its temperature
define specific latent heat of fusion
energy required to melt 1 kg of substance at a constant temperature
define specific latent heat of vapourisation
energy required to vapourise 1 kg of substance at a constant temperature
equation for specific latent heat
E = mL
where E is the energy supplied to the substance
m is the mass of the substance
L is the SLH
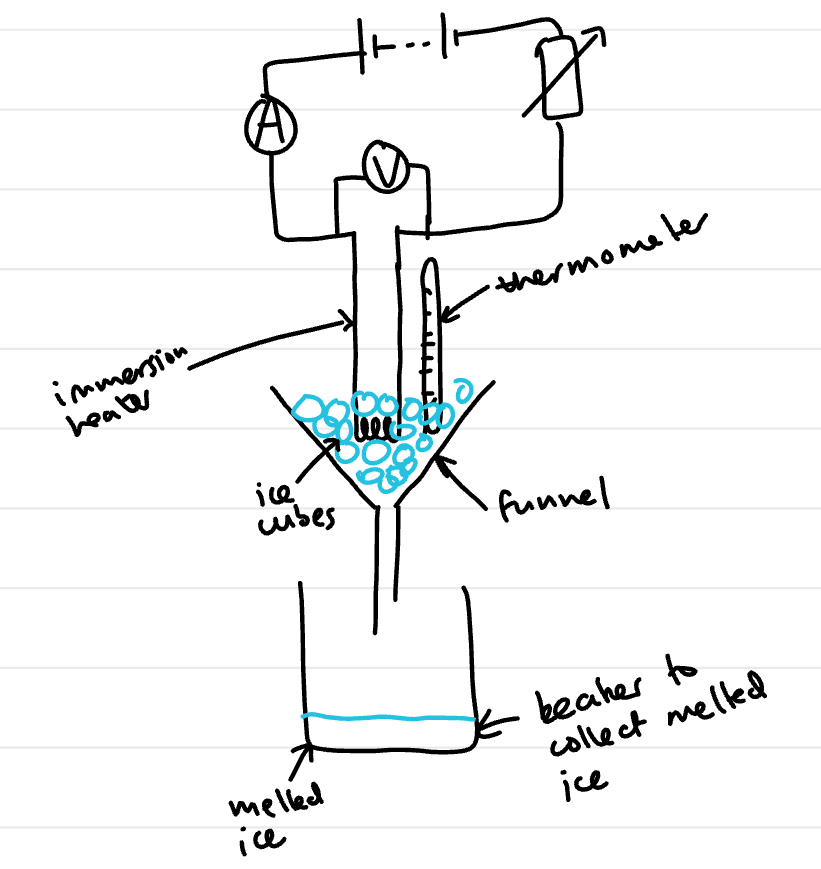
practical to work out specific latent heat of fusion
Set up apparatus as shown in diagram
Use thermometer to make sure the ice is just at its melting point and not a lower temperature
use a stop watch to measure how long the heater is used
Calculate energy transferred to the ice using E = VIt
Measure the mass of the ice melted in the beaker using a top pan balance
To get an accurate value for the mass melted due to the heater set a control beaker with ice in a funnel and measure the mass of ice melted just due to room temperature. Subtract this mass from the mass in the beaker with the heater.
E = mL so L = E/m so L = VIt/m
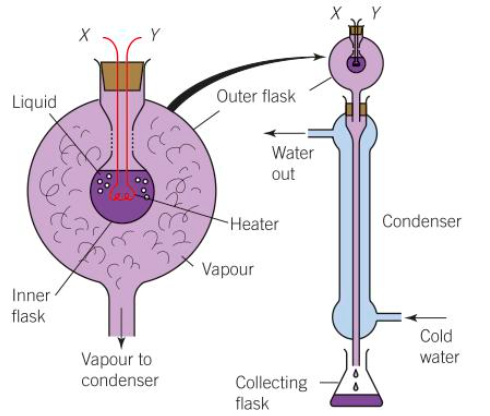
practical to work out specific latent heat of vapourisation
Measure the mass of water in the collecting flask using a top pan balance
Use a thermometer to bring the heater to 100 degrees and ensure it stays at that temperature
Record V and I when the heater is at 100 degrees
Use a stop watch to measure how long it takes for all the water to evapourate
E = VIt
L= E/m so L = VIt/m
what are 3 key assumptions in the kinetic theory of gases
forces between particles are negligible except during collisions
collisions are perfectly elastic
large number of molecules are in random linear motion
explain the changes to the internal energy of molecules of a substance as it melts
no change in kinetic energy
as temperature is constant
the potential energy of the molecules increases
so the internal energy increases