Mangroves
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Main areas in the world mangroves grow
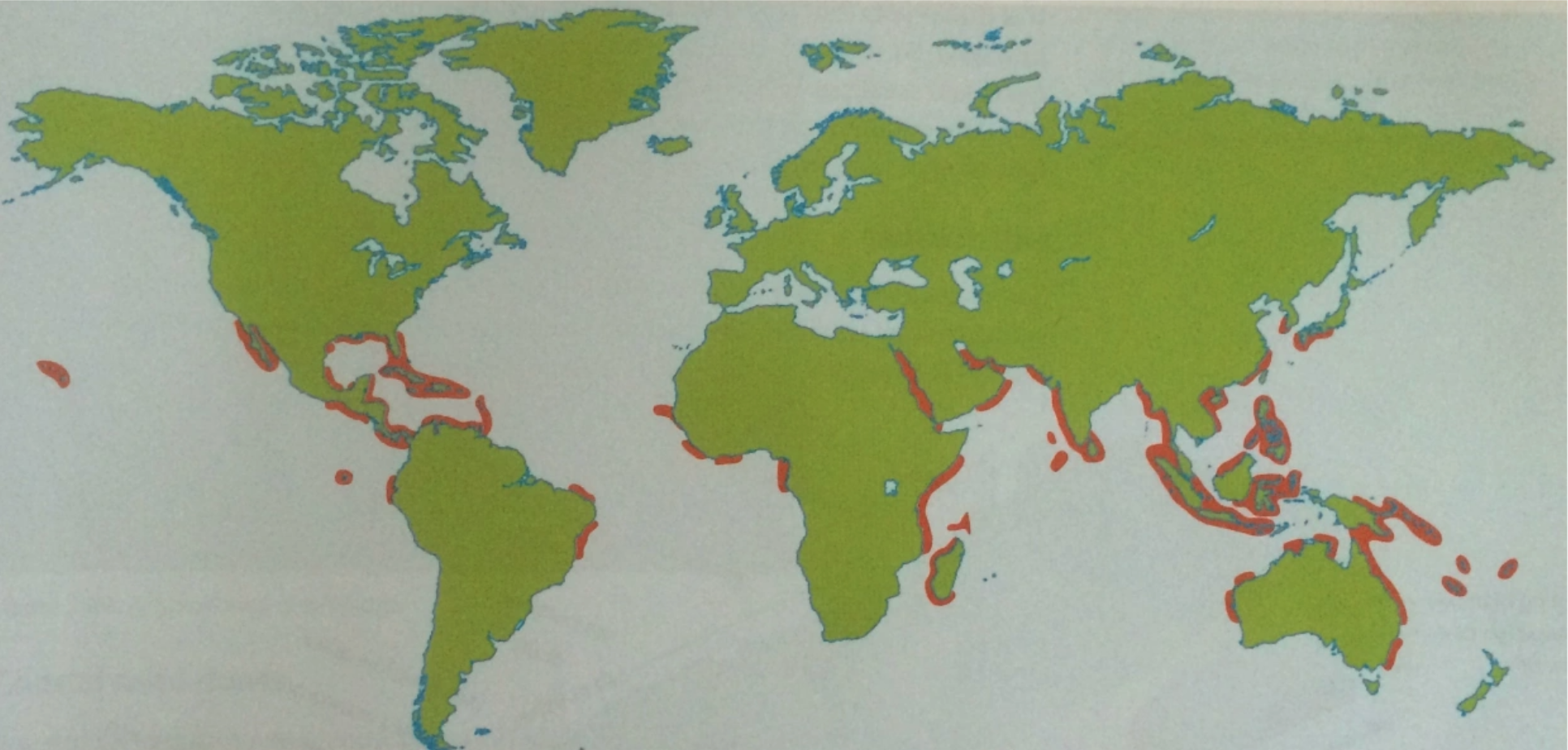
What factors affect where mangroves grow?
Temperatures
Salinity
Exposer to Air
Temperature
Most mangroves grow only 30 degrees latitude of the equator
Salinity
The water around mangroves has to be of a certain salt content if not the mangrove will suffer, so if fresh water is added to salty water this would be harmful.
Exposure to air
Air is too rich in oxygen will harm to mangrove if the mangrove is exposed for too long.
Why are mangroves valuble?
Contain Natural Resources
Foraging and Living Place for Wildlife
Reducing Water Pollution
Protecting the Coastline
Flood Prevention
Ornamental Value
Contain natural resources
Charcoal, firewood, fish, medicines and other substances can be extracted form mangroves.
Foraging and Living Place for Wildlife
Without mangroves there would be no habitat for animals so there would be no animals.
Reducing Water Pollution
The root systems of mangrove species absorb inorganic substances and reduce water pollution.
Protecting the Coastline
Protecting the Coastline - Because the roots of a mangroves act can stabilise the coastlines of the river shores and river mouths. They also protect the coastline from wave erosion.
Flood Prevention
Mangroves can stabilise water capacity of the substratum and on the soil surface, hence steady and retain water to prevent flooding.
Ornamental Value
A mangrove forest is a beautiful environment with a diversity of life that in some peoples eyes is with saving.
Threats to mangroves
Clearing
Overharvesting
River Changes
Overfishing
Destruction of Coral Reefs
Pollution - Fertilizers, pesticides, and other toxic man-made chemicals carried by river systems from sources upstream can kill animals living in mangrove forests.
Climate Change - Mangrove forests require stable sea levels for long-term survival.
Clearing
Mangrove forests have often been seen as unproductive and smelly, and so cleared to make room for agricultural land, human settlements and infrastructure, and industrial areas.
Overharvesting
While harvesting has taken place for centuries, harvesting of mangroves become unsustainable and threaten their future.
River Changes
Dams and irrigation reduce the amount of water reaching mangrove forests, changing the salinity of water in the forest.
Overfishing
The global overfishing crisis facing the world's oceans has effects far beyond the directly overfished population. The ecological balance of food chains and mangrove fish communities can also be affected.
Destruction of Coral Reefs
Coral reefs provide the first barrier against currents and strong waves. When they are destroyed, the stronger-than-normal waves and currents reaching the coast can undermine the fine sediment in which the mangroves grow. This can prevent seedlings from taking root and wash away nutrients essential.
Pollution
Fertilizers, pesticides, and other toxic man-made chemicals carried by river systems from sources upstream can kill animals living in mangrove forests.
Climate Change
Mangrove forests require stable sea levels for long-term survival.