Anti-depressants
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:44 PM on 12/23/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
1
New cards
What the monoamine theory of depression?
The pathophysiological basis of depression is **depletion** in the levels of **serotonin**, **noradrenaline**, and/or **dopamine** in the central nervous system.
2
New cards
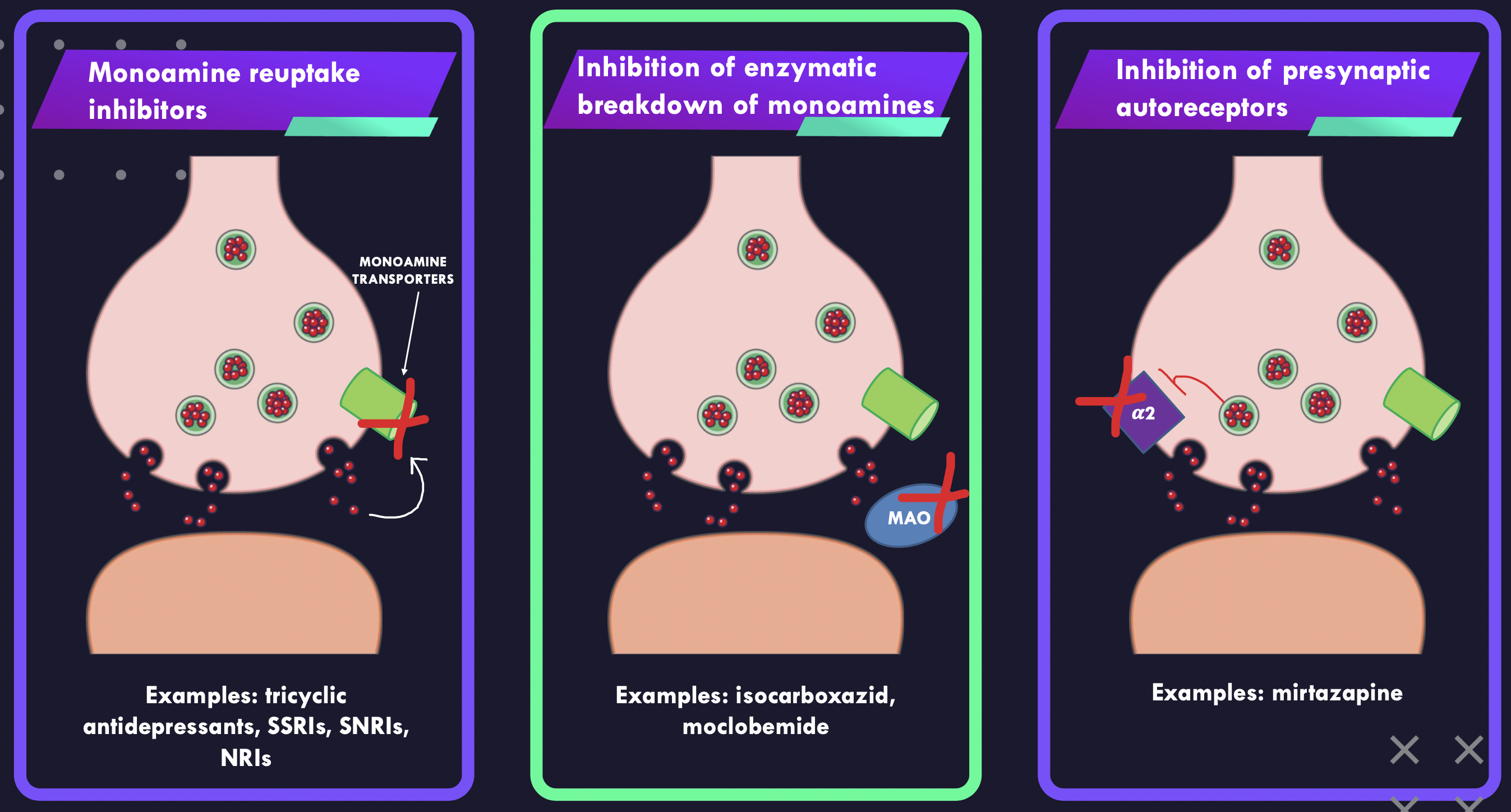
What are the 3 modes of treatment of depression?
Enhance monoaminergic activity in central synapses:
1\.Inhibit monoamine reuptake
2\.Inhibit enzymatic degradation
3\.Block presynaptic autoreceptors
1\.Inhibit monoamine reuptake
2\.Inhibit enzymatic degradation
3\.Block presynaptic autoreceptors
3
New cards
Types of antidepressants available?
TCAs - Tricyclic antidepressants
SNRIs- **S**erotonin and **N**oradrenaline **R**euptake **I**nhibition
SSRIs- selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
MAOI- monoamine oxidase inhibitors
Benzodiazepines
NaSSA/ alpha 2 antagonist
SNRIs- **S**erotonin and **N**oradrenaline **R**euptake **I**nhibition
SSRIs- selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
MAOI- monoamine oxidase inhibitors
Benzodiazepines
NaSSA/ alpha 2 antagonist
4
New cards
Example of a TCA?
==Clomipramine==
Amitriptyline
Amitriptyline
5
New cards
What are TCAs given for?
* Depressive disorder
* Phobic or obsessional states
* Phobic or obsessional states
6
New cards
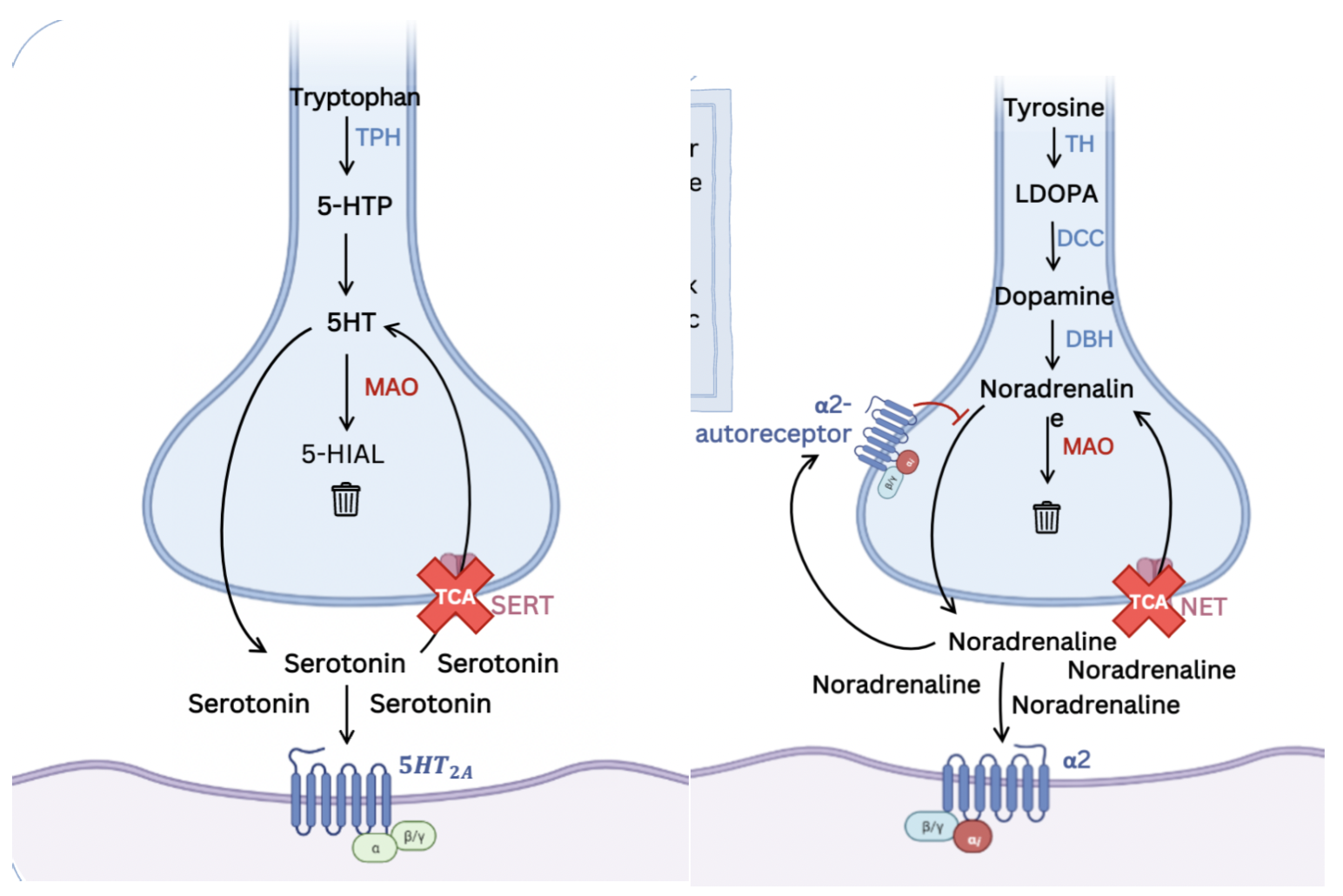
What is the MOA of TCAs?
serotonin and/or noradrenaline reuptake inhibition
7
New cards
What are the ADR of TCAs?
* overdose → block Na+ channels → cardiac arrest
* ==**Weight gain**==
* ==**Sexual dysfunction**==
* ==**Depersonalisation**==
* ==**Weight gain**==
* ==**Sexual dysfunction**==
* ==**Depersonalisation**==
8
New cards
Example of a SSRI?
Citalopram
9
New cards
What are SSRIs given for?
* Depressive disorder
* Panic + anxiety
* Panic + anxiety
10
New cards
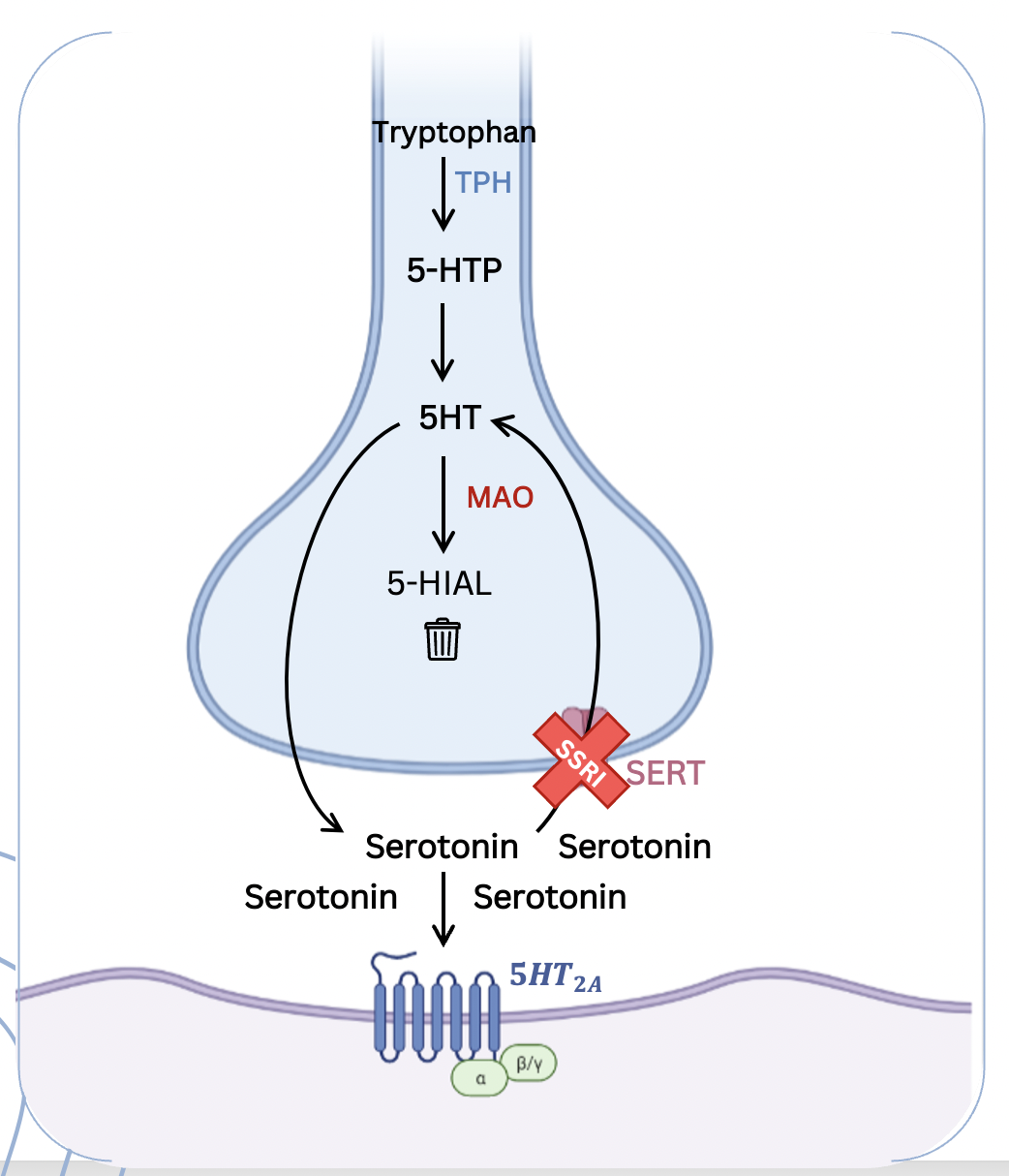
What is the MOA of SSRIs?
Blocks SERT (serotonin re-uptake tranposters)
Serotonin will remain in the synaptic cleft for longer
Leads to repeated activation of 5-HT receptors (post)
Serotonin will remain in the synaptic cleft for longer
Leads to repeated activation of 5-HT receptors (post)
11
New cards
What are the ADR of SSRIs?
==QT interval prolongation==
GI disturbances
==sexual dysfunction==
==sleep disorders==
GI disturbances
==sexual dysfunction==
==sleep disorders==
12
New cards
What are the contraindications of SSRIs?
If poorly controlled epileptic or pre-existing long QT interval, or manic
13
New cards
Example of a SNRIs?
Reboxetine
14
New cards
What are SNRIs given for?
major depression
15
New cards
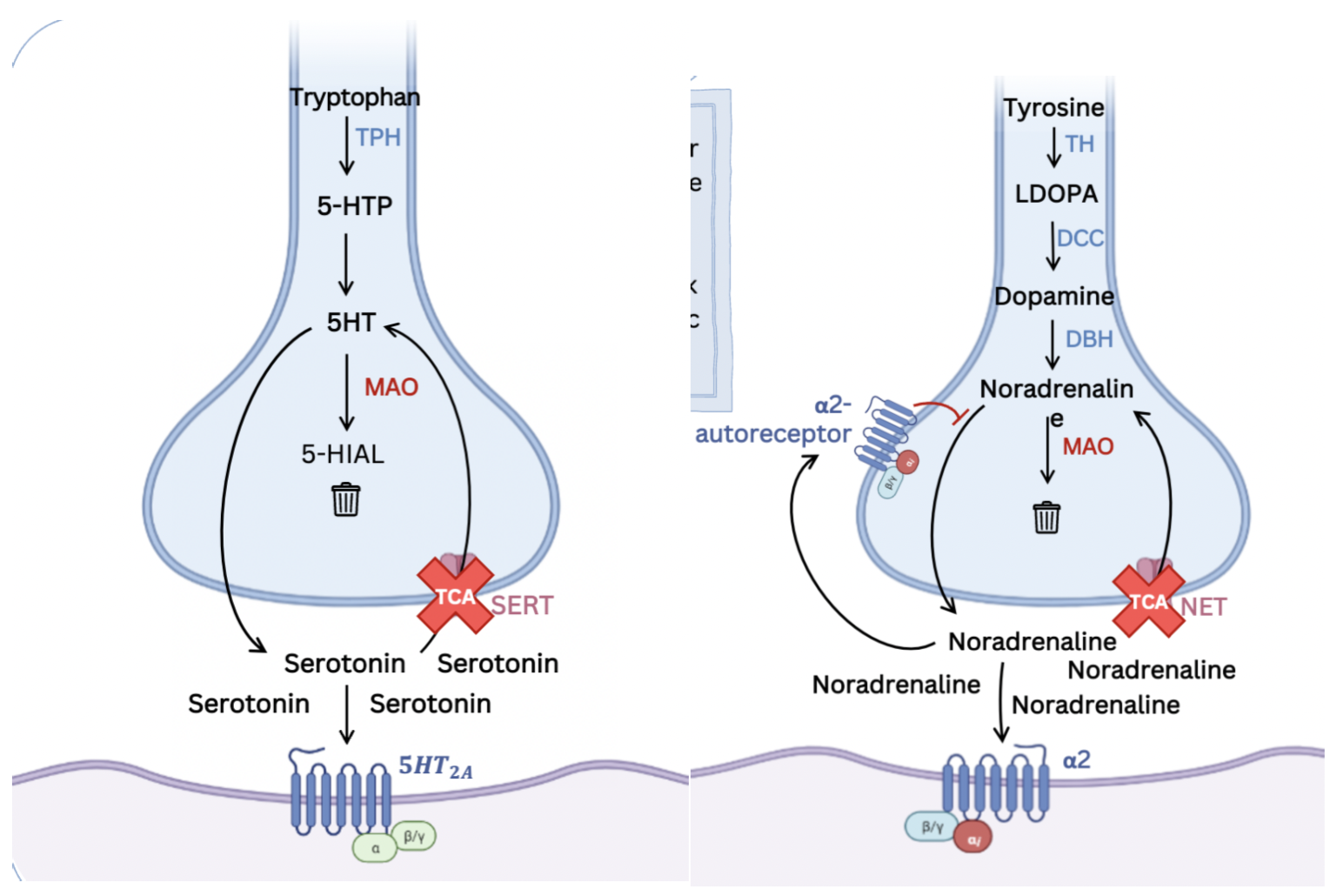
What is the MOA of SNRIs?
Mostly blocks noradrenaline but also some blocking of serotonin
16
New cards
What are the ADR of SNRIs?
==Palpitations==
==Sexual dysfunction==
==Decreased appetite==
Nausea
dry mouth
dizziness
excessive sweating
==Sexual dysfunction==
==Decreased appetite==
Nausea
dry mouth
dizziness
excessive sweating
17
New cards
Example of a MOAs?
Moclobemide
18
New cards
What are MOAs given for?
Depressive disorder
Social anxiety
Social anxiety
19
New cards
What is an example of MAO-A I?
Moclobemide
20
New cards
What is the MOA of MAO-A I?
Inhibit **monoamine oxidase A**, preventing breakdown of **5HT** and **NA**
A **selective** (reversible) **monoamine oxidase inhibitor** which can p**revent MAO-mediated clearance of serotonin, noradrenaline and dopamine** from synaptic clefts
A **selective** (reversible) **monoamine oxidase inhibitor** which can p**revent MAO-mediated clearance of serotonin, noradrenaline and dopamine** from synaptic clefts
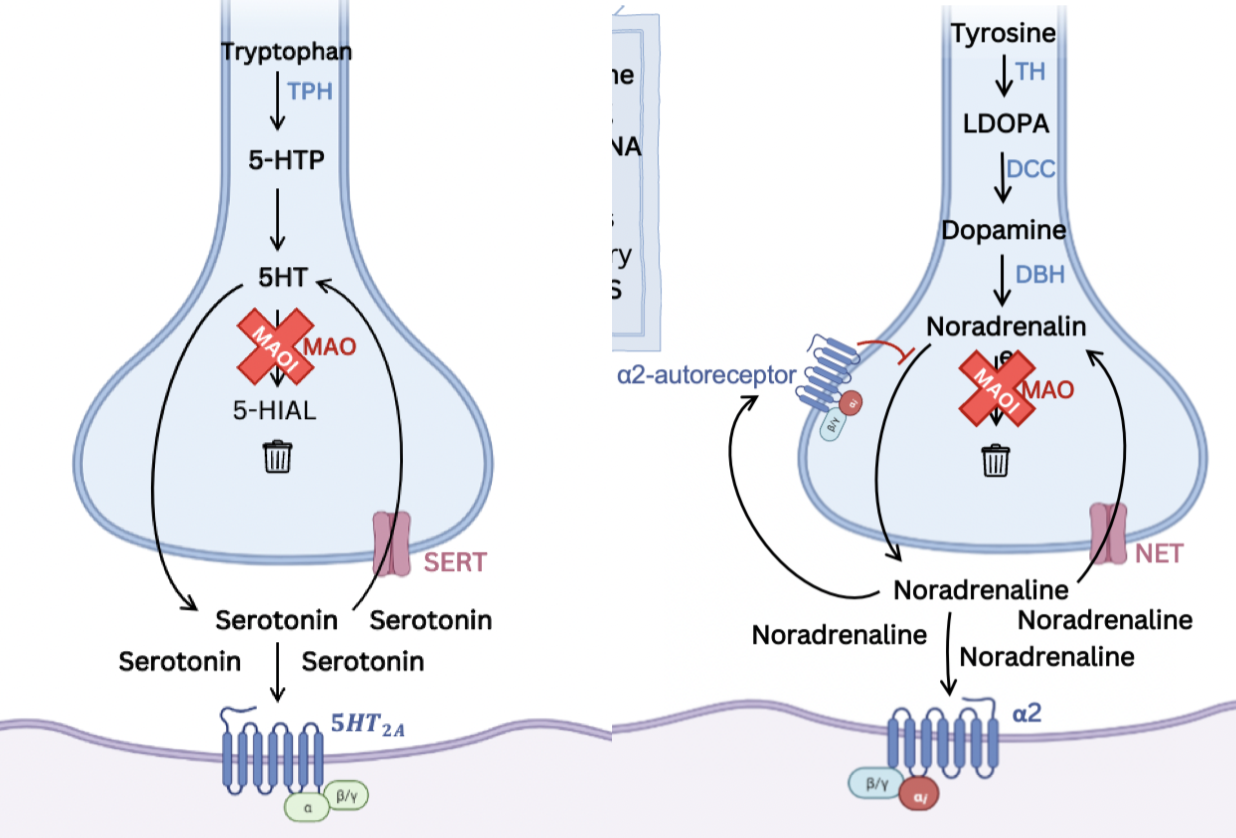
21
New cards
What are the ADR of MAO-A I?
Confused states (agitation), dizziness, dry mouth, **CHEESE CRISIS**
22
New cards
What is the hypertensive cheese crisis?
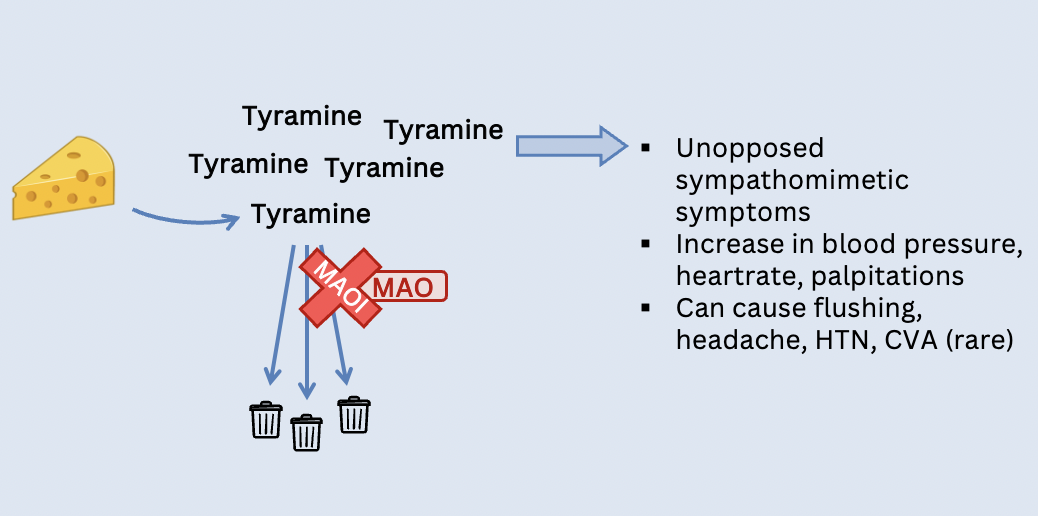
23
New cards
What is a contraindication of MAO-A I?
**If thyrotoxicosis, if bipolar**
24
New cards
What is an example of f MAO-B I?
Selegiline
A type of Parkinson’s drug
A type of Parkinson’s drug
25
New cards
What is the MOA of MAO-B I?
Inhibit **monoamine oxidase B**, preventing breakdown of **dopamine**
A **selective** (reversible) **monoamine oxidase inhibitor** which can p**revent MAO-mediated clearance of serotonin, noradrenaline and dopamine** from synaptic clefts
A **selective** (reversible) **monoamine oxidase inhibitor** which can p**revent MAO-mediated clearance of serotonin, noradrenaline and dopamine** from synaptic clefts
26
New cards
What are the ADR of MAO-B I?
Confused states (agitation), dizziness, dry mouth
27
New cards
General MAOIs ADRs?
Irritability
Sleep disorder
Nausea + vomiting
Sleep disorder
Nausea + vomiting
28
New cards
Example of a NaSSA/ alpha 2 antagonist?
Mirtazapine
29
New cards
What is the MOA of NaSSAs?
NaSSAs **bind** to and **inhibit both noradrenaline a2-autoreceptors** and **noradrenaline a2-heteroeceptors.**
This action **prevents** the **negative feedback** effect of synaptic noradrenaline on 5-HT and noradrenaline neurotransmission, **sustaining neurotransmission**.
NaSSAs also **block 5-HT2 and 5-HT3** receptors on the post-synaptic membrane, which causes **enhanced 5-HT1 mediated neurotransmission**.
This action **prevents** the **negative feedback** effect of synaptic noradrenaline on 5-HT and noradrenaline neurotransmission, **sustaining neurotransmission**.
NaSSAs also **block 5-HT2 and 5-HT3** receptors on the post-synaptic membrane, which causes **enhanced 5-HT1 mediated neurotransmission**.
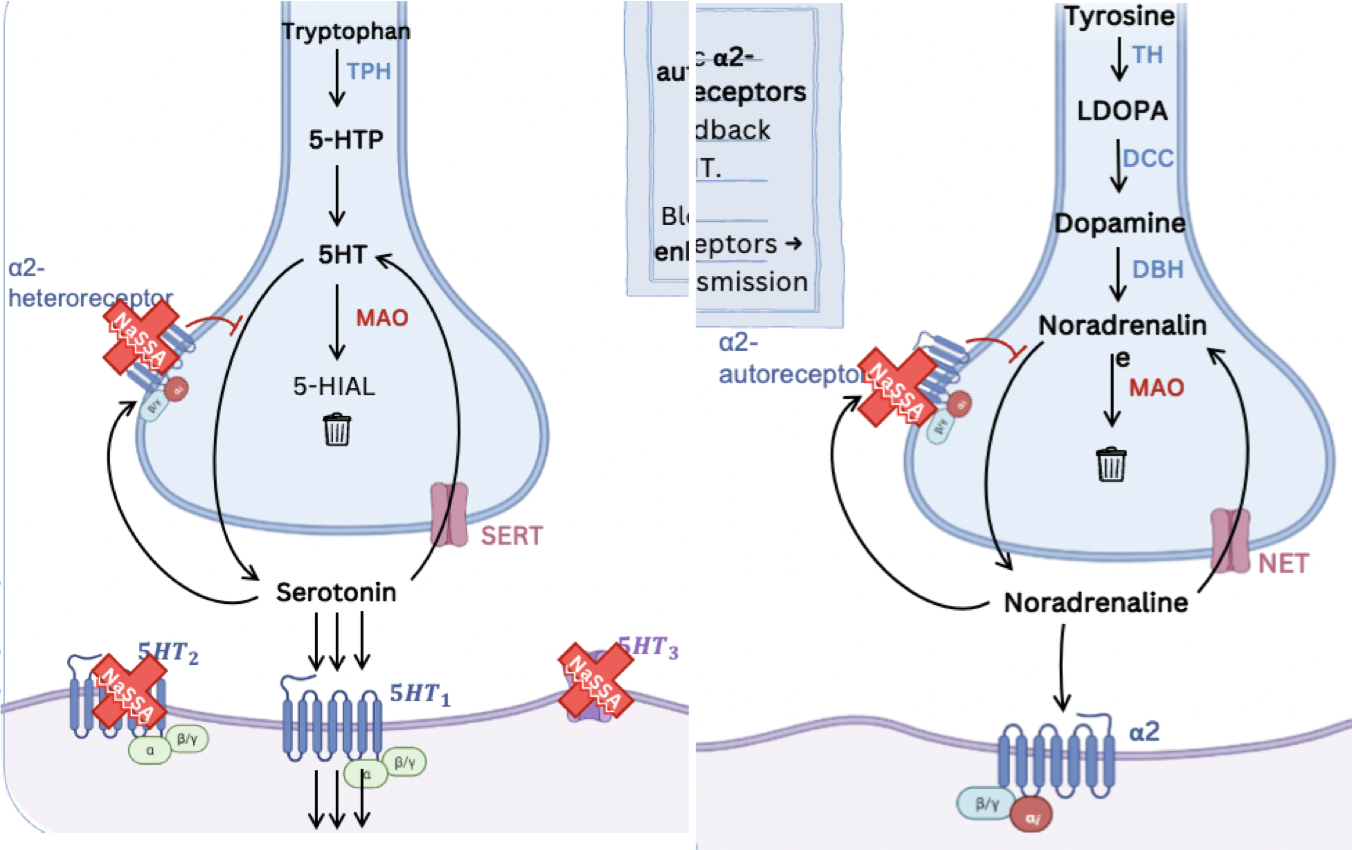
30
New cards
What are the ADR of NaSSA?
**5HT3 antagonist:** increased **appetite**
**H1** (histamine) **antagonist**: **drowsiness**, ***weight*** gain
**H1** (histamine) **antagonist**: **drowsiness**, ***weight*** gain
31
New cards
What are the serotonin receptors?
5-HT1: Gi/Go-protein coupled
5-HT3: Ligand-gated Na+ and K+ channels
5-HT2: Gq/G11-protein coupled
5-HT4: Gs-protein coupled
5-HT3: Ligand-gated Na+ and K+ channels
5-HT2: Gq/G11-protein coupled
5-HT4: Gs-protein coupled
32
New cards
What is serotonin syndrome?
Increased 5HT activity in the CNS
Caused by drug overdose or **interaction between two 5HT-enhancing drugs** (more common)
Caused by drug overdose or **interaction between two 5HT-enhancing drugs** (more common)
33
New cards
What can cause serotonin syndrome?
It's usually triggered when you take an SSRI or SNRI in combination with another medicine (or substance) that also raises serotonin levels, such as another antidepressant or St John's wort.
\
Avoid sympathomimetic and dopaminergic drugs (monoamine overload)
\
Avoid sympathomimetic and dopaminergic drugs (monoamine overload)
34
New cards
Symptoms of serotonin syndrome?
* **Mental state**: anxiety, agitation, disorientation
* **Autonomic (SNS) symptoms**: diaphoresis, raised HR/RR/BP/temp, vomiting/ diarrhoea/ increased bowel sounds; dilated pupils
* **Neuromuscular**: tremor, rigidity, hyperreflexia, bilateral Babinksi
* **Autonomic (SNS) symptoms**: diaphoresis, raised HR/RR/BP/temp, vomiting/ diarrhoea/ increased bowel sounds; dilated pupils
* **Neuromuscular**: tremor, rigidity, hyperreflexia, bilateral Babinksi