Biology 20 AP: Unit D - Circulatory System
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
What are the 3 main functions of the circulatory system?
Transportation of gases, nutrients, and wastes
Regulation of internal temp. and transports hormones
Protection against bacteria/viruses, toxins, and blood loss from injury
What are the 3 major components of the circ. system?
Heart: muscular organ that pumps blood through body to generate blood flow
Blood vessels: veins, arteries, capillaries that act as a “roadway” for blood
Blood: carries nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water, and other material throughout the body
Arteries
carry oxygen-rich blood AWAY from heart to the rest of the body
exception: pulmonary arteries
contain thick-layered, elastic walls, and smooth muscle
helps keep the blood under pressure so that it can reach the furthest body parts
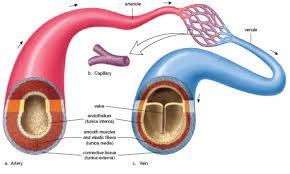
Veins
carry oxygen-poor blood TO the heart from the body
exception: pulmonary veins
smaller veins: venules
thin-layered walls with some smooth muscle and elastic tissue
distinguishing feature: valves (ensures one way flow of blood)
large circumference and less elasticity than arteries
muscle contractions from skeletal muscles keep blood flowing to the heart
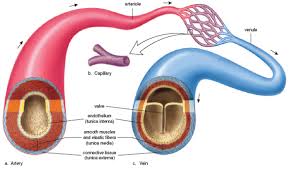
Capillaries
very tiny vessels that join arteries to veins
location of gas, waste, hormone, and nutrient exchange
smallest blood vessels
one-cell thick
diameter that enables only one RBC to travel through at a time
allows for maximum gas exchange between blood and body cells

Vasoconstriction
narrowing of blood vessels as a result of contraction of the smooth muscle
will decrease blood flow throughout the vessel
keeps heat in
e.g. cold fingers

Vasodilation
widening of blood vessels as a result of relaxation of the smooth muscle
will increase blood flow through the vessel
releases heat
e.g. red face when running
Pulmonary circulatory system
system of blood vessels that carries DEOXYGENATED blood to the LUNGS (pulmonary) and OXYGENATED blood back to heart
function: to oxygenate blood

Systemic circulatory system
involves various arteries and veins in the BODY
the VEINS carry DEOXYGENATED blood from body tissues back to the heart
the ARTERIES carry OXYGENATED blood away from heart to body tissues
tissue capillaries: where blood becomes DEOXYGENATED and where wastes from tissues enter blood

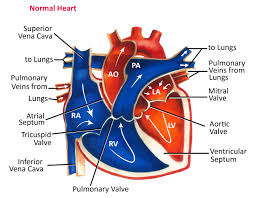
Right and left atria (singular: atrium)
two upper heart chambers fill w/ blood returning from either body (right) or lungs (left)
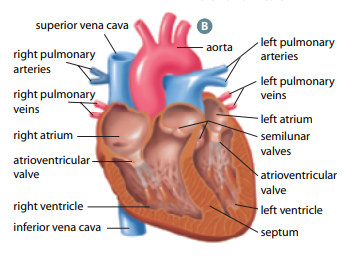
Right and left ventricles
two bottom heart chambers that pump blood either to lung (right) or body (left)
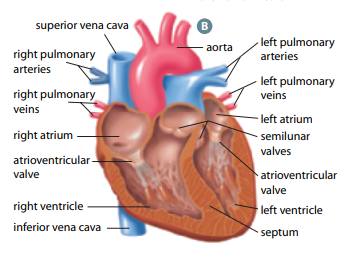
Septum
thick muscular wall that separates left and right chambers of the heart
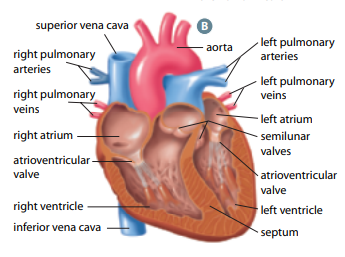
Superior vena cava
large vessel that opens into right atrium that carry oxygen-poor blood from UPPER body
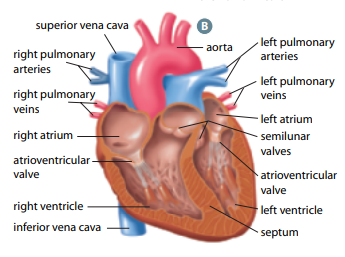
Inferior vena cava
large vessel that opens into right atrium that carry oxygen-poor blood from LOWER body
Pulmonary arteries
vessels by which oxygen-poor blood passes from right ventricle to lungs for gas exchange
Pulmonary veins
vessels by which oxygen-rich blood returns from lungs to left atrium
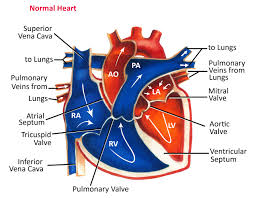
Aorta
largest vessel in the body through which oxygen-rich blood is pumped from left ventricle to body
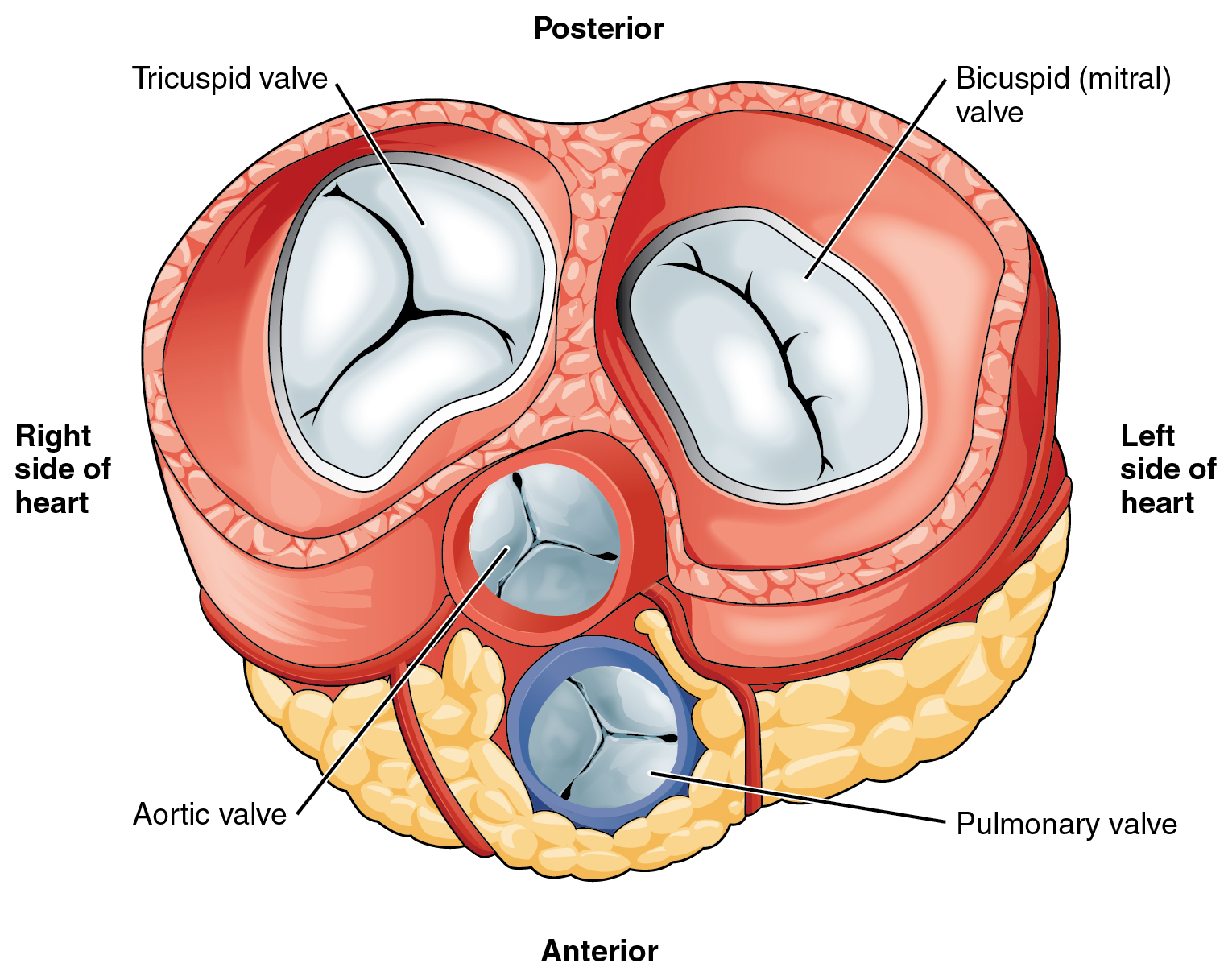
Tricuspid valve
helps blood flow in the correct direction from the right atrium to the right ventricle

Bicuspid valve
allows blood flow b/w the left atrium and the left ventricle
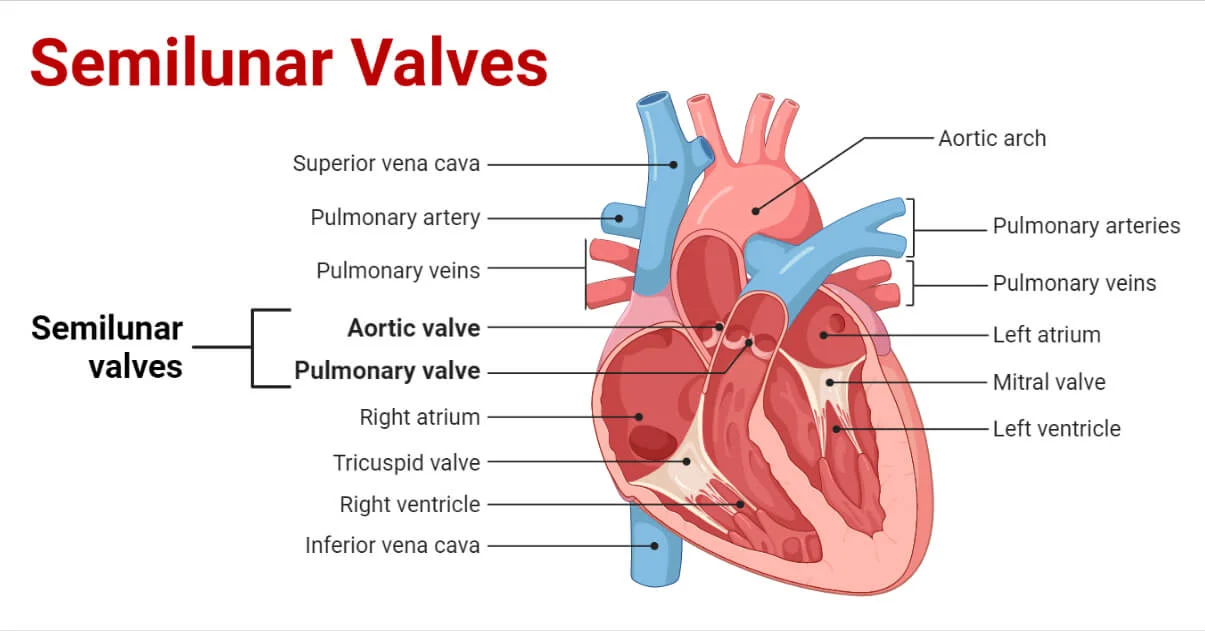
Semilunar valves
permits blood to flow into the arteries from the ventricles
prevents the backward flow of blood from the arteries into the ventricles
Systole
pumping chambers contract to push blood out
Diastole
pumping chambers relax and fill with blood
What sound does the heart make?
lubb-dubb sound
What is the lubb-dubb sound caused by?
opening and closing of the valves within the heart
What is the heartbeat set by?
the sinoatrial node/pacemaker
allow it to contract without external nerve stimulation
own nerve impulse
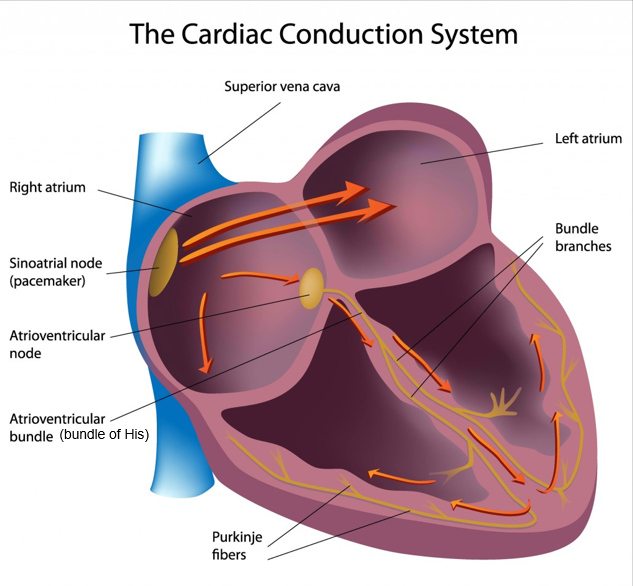
Sinoatrial node/pacemaker
bundle of specialized muscle cells that electrically stimulate the atria to relax and contract
right atrium
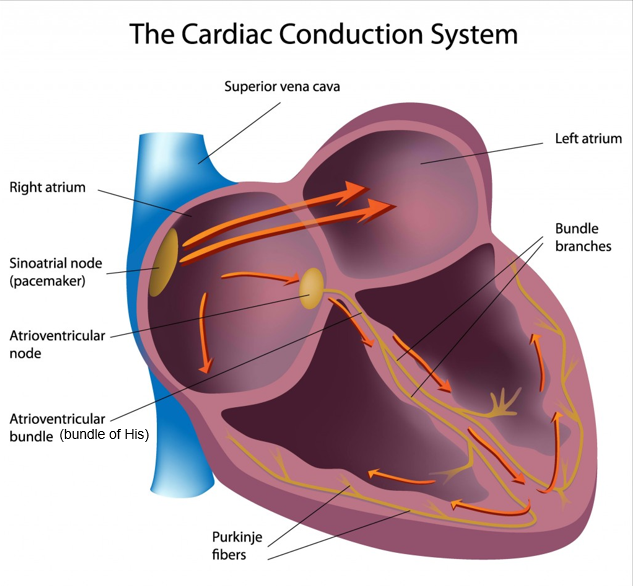
Atrioventricular node
transmits the electrical signal through specialized fibers (bundle of His & Purkinje fibers that cause contraction)
delays then relays the signal to both ventricles
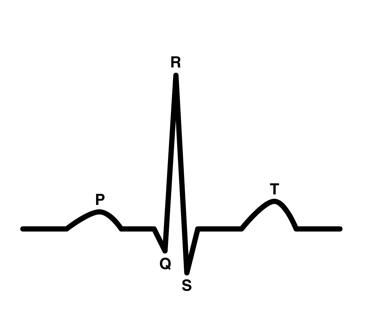
ECG
monitors electrical signals through heart
P wave
electricity of contraction of atria (ventricles fill with blood)
AV valves open
semilunar valves close
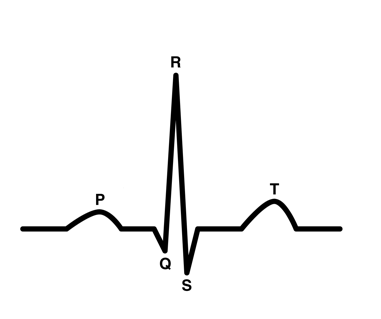
QRS wave
contraction of ventricle
AV valves shut (“lubb” sound)
semilunar valves open
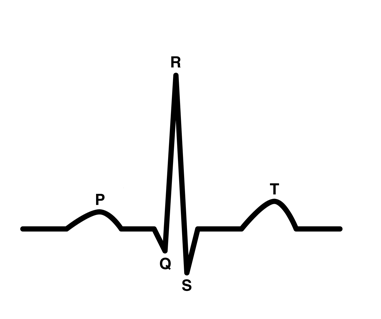
T wave
heart reset period
ventricles relax
AV valves open
atria fill with blood
semilunar valves close (“dubb” sound)
Blood pressure
measured by sphygmomanometer
blood being pumped through vessels cause pressure changes which corresponds with phases of the heart
Systolic pressure
maximum pressure during ventricular contraction
top #
Diastolic pressure
minimum pressure before ventricles contract again
bottom #
What is a normal resting BP?
120(systolic) / 80 (diastolic)
What is the main indicator of a healthy/unhealthy heart?
Heart rate
Cardiac output
indicator of how much oxygen is being delivered to the body
measured in mL/min
heart rate x stroke volume
Heart rate
number of beats per minute (bpm)
Stroke volume
amount (mL) of blood forced out of heart with each beat
Arteriosclerosis
thickening of artery walls causing hardening and loss of elasticity
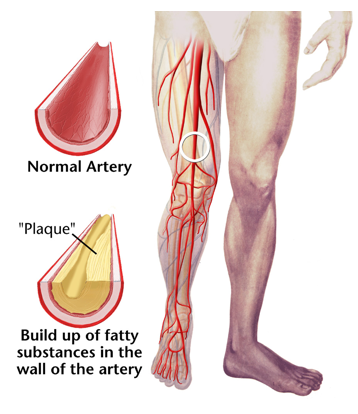
Atherosclerosis
build-up of plaque on interior walls of artery
causes narrowing/blockage
increased BP
decreased blood flow
type of arteriosclerosis
What are the two main components of blood?
plasma
formed portion
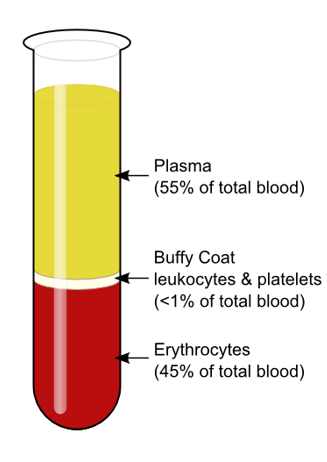
Plasma
fluid consisting of water, dissolved gases, proteins, vitamins, minerals, hormones, and wastes
Formed portion
red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets
Red blood cells (RBCS) / Erythrocytes
NO NUCLEUS
oxygen carrying-capacity depends on a number of RBC present and amount of hemoglobin
transport oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues and carry carbon dioxide waste back to the lungs for exhalation
Hemoglobin
iron-containing pigment/protein found inside erythrocyte
allows large amounts of oxygen to bind and some carbon dioxide
Anemia
condition where a person has too few RBCS or hemoglobin
causes fatigue
causes: acute bleeding, lack of iron in diet, bone marrow damage, or chronic disease
White blood cells (WBCs) / Leukocytes
have a nucleus
3 types
What are the 3 types of WBCs and their functions?
granulocytes: neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils; stay in blood stream
monocytes: can exit blood stream and become specialized macrophages
lymphocytes: produce antibodies that tag and incapacitate pathogens
the first two engulf & destroy bacteria and foreign bodies
Platelets
cell fragments that form when cells and bone marrow break apart
key role in blood clotting
enzyme: thromboplastin

What does plasma consist of?
water: ~92%
blood proteins (fibrinogen, serum albumin): ~7%
organic substances (urea, organic nutrients): ~0.1%
inorganic ions: ~0.9%
Leukemia
cancer of WBCs
two main types: myeloid and lymphoid
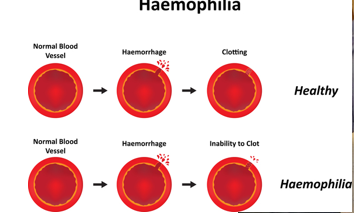
Hemophilia
inherited, life-threatening disorder
causes: insufficient blood clotting proteins
treated with coagulation protein injectioins
Why do athletes train at high altitudes?
thinner air
lower oxygen pressure
lead to higher RBC count = more hemoglobin for oxygen saturation
What other body systems is blood transport connected to and how?
Digestion: capillaries in small intestinal wall absorb nutrients
Respiration: capillary beds in lungs allow for gas (and other chemical) exchange
Urinary: metabolic wastes, mineral ions, and other waste products are carried by blood to kidney for excretion
Homeostatic Regulation
blood coming to skin from interior is usually warmer than skin therefore difference in temp. creates a heat gradient
vasodilation/constriction
Countercurrent heat exchange
deep arteries and veins are adjacent to each other therefore warmer blood (~37) from core exchanges heat with cooler extremities
Capillary action
walls are single cell think
location of nutrient, waste, and gas exchange via diffusion = slow blood flow
Capillary bed
vast network of capillaries found in most tissues and major organs
will “open” or “close” depending on metabolic activity taking place (e.g. digestion vs. muscles)
Interstitial fluid
any material exchanged between capillaries and cells must pass through
Edema
swelling caused by “leaky” capillaries into interstitial spaces
Blood transfusions
transfer of blood from one person to another
Antigens
specific proteins that are embedded in the membrane of RBC
used for ID
Antibodies
specific proteins found in blood plasma
What are antigens & antibodies part of and how?
natural immune response system
when RBCs with a specific antigen come into contact with plasma that has the matching antibody, it causes agglutination which means they are incompatible and cause major organ damage
Agglutination
clumping of RBCs
Rhesus factor
another group of antigens that can be found in the membranes of RBCs
Rh positive
antigen present
Rh negative
antigen not present
Risk of Rh negative individuals
most Rh negative people will NOT have antibody present UNLESS they have been exposed to the Rh-factor during transfusion or pregnancy
Antigens & antibodies (A, B, O)
A: antigen A & anti-B antibody
B: antigen B & anti-A antibody
AB: both antigen A and B & no antibodies (universal recipient)
O: no antigen & both anti-A and B antibody (universal donor)