Physics paper 1 questions
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Explain, with reference to the processes within an atom, the difference between an emission spectrum and an absorption spectrum. (3)
Photon is an energy carrier
In absorption, atom becomes excited
In emission, atom de-excites
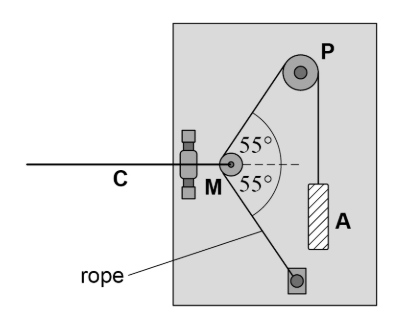
Pulley M is pulled to the left as the gate is opened.
Explain why this increases the tension in the horizontal cable C. (2)
Angle to horizontal decreases
So horizontal components increase
Explain what happens to the brightness of a lamp as resistance in a variable resistor connected in series increases. (2)
Resistance of resistor increases
Reducing current throughout the circuit and dimming the lamp
Explain what happens to the brightness of a lamp as resistance in a variable resistor connected in parallel increases. (2)
Resistance throughout circuit increases
Reduces current in circuit
Meaning less volts are lost in the battery so lamp gets brighter
The potassium isotope can also decay by a second decay process to form a calcium-40 nuclide.
Suggest how the emissions form a nucleus of decaying potassium can be used to confirm which decay process is occurring. (3)
Beta emission
Electron released
Electrons detected via cloud chamber or absorption
Antineutrino released
No photon released
Explain how the actual frequencies produced in an experiment investigating vibrations in stretched nylon string of fixed length would be different to those that a student can predict. (2)
Diameter will decrease as string is stretched
Causing a lower mass per unit length so the frequency increases
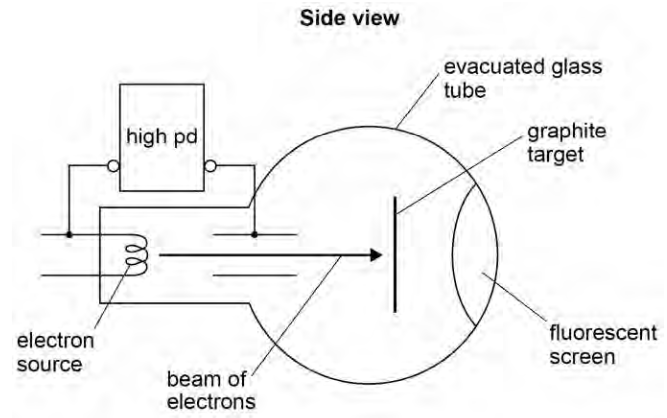
Explain how the pattern produced on the screen supports the idea that the electron beam is behaving as a wave rather than as a stream of particles. (3)
Particle behaviour would only produce a patch of light
Wave property shown by diffraction
Graphite causes the electrons to spread out
Bright rings are formed due to constructive interference
For a diffraction grating maxima when sin =n/d
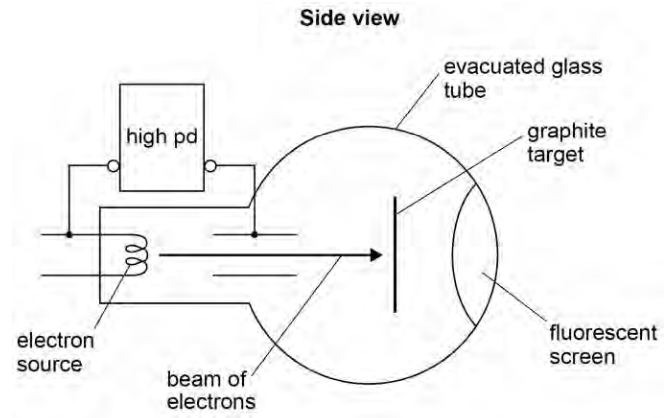
Explain how the emission of light from the fluorescent screen shows that the electrons incident on it are behaving as particles. (3)
Electrons transfer energy in one-to-one collisions
Idea of light emission due to exitation and de-excitation of electrons
Idea of collisions by incident electrons moving electrons in atoms between energy levels
Light emitted when atoms de-excite
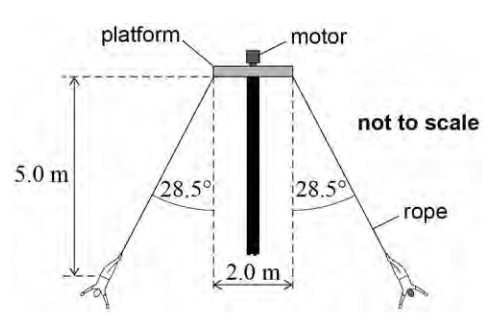
Discuss the consequences for the forces acting on the pole when one acrobat has a much greater mass than the other. (3)
Vertical force on the pole increases
Increase in mass increases weight and so tension in the rope increases
Centripetal force on the acrobats will be different
Unbalanced forces
causing pole to sway towards the more massive acrobat
Explain why virtual photons cannot be detected in a laboratory but are nonetheless required by particle physics. (3)
In order to detect it, it must be measured
This would block the exchange of the force so the interaction will not be able to take place
They must still exist as forces do not act instantaneously so they must still be exchanged
The weak force acts over a much shorter distance than the strong force.
Explain 2 differences between the relevant exchange particles that account for this. (3)
Exchange particle for weak force is W boson, for strong force it is the gluon
The gluon is lighter than the W boson
Therefore it has a larger range
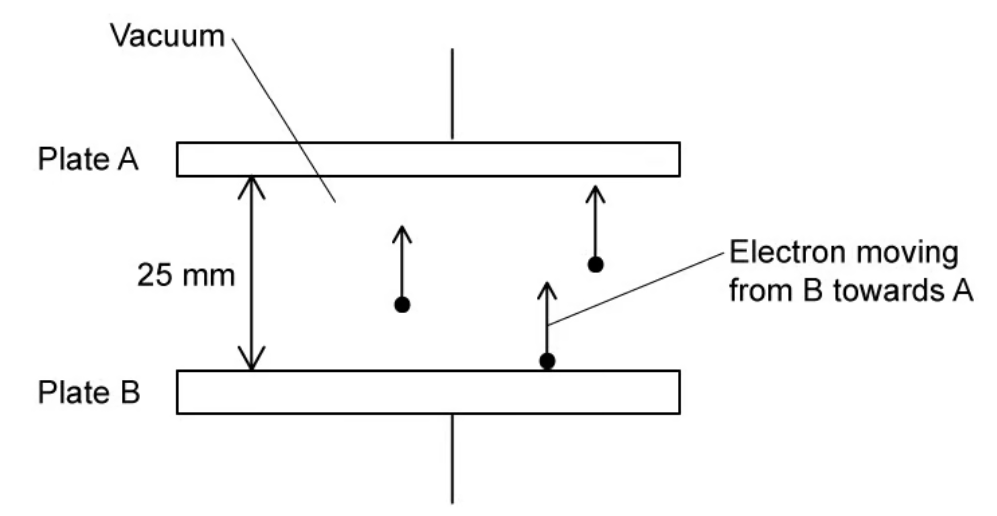
The electric field is going from A to B.
Suggest and explain an experimental change to the setup as shown that would reduce the photocurrent measured (3)
Reverse terminals of power supply
So photoelectrons would have to do work against the electric field
This reduces photocurrent as only photoelectrons with sufficient energy can reach plate A
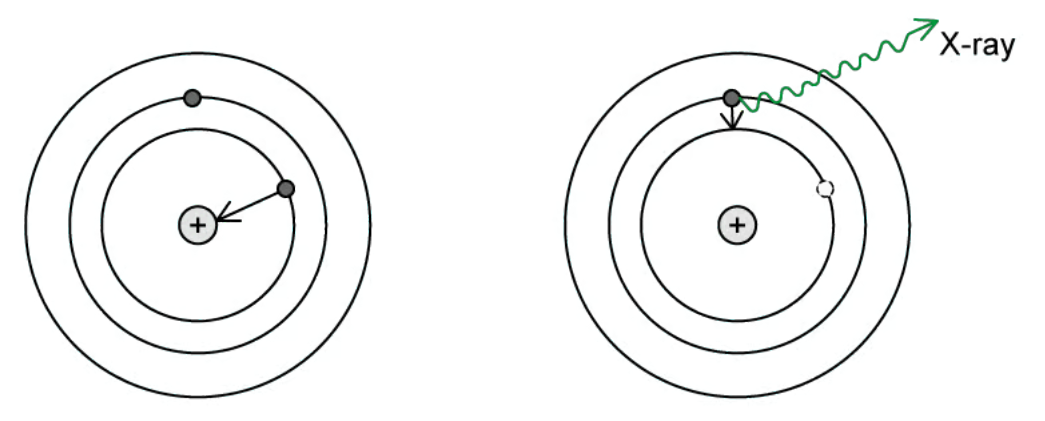
During electron capture, the nucleus ‘captures’ an orbiting inner-shell electron. The resulting nucleus has one less proton and one more neutron. Sometimes this process is accompanied by the emission of a characteristic X-ray photon.
Explain why an X-ray photon is produced in this process and suggest why it is called characteristic (3)
An outer electron replaces the missing electron
Transition to a lower energy state releases an X-ray photon
Characteristic because energy = difference in energy levels
Explain the significance of an electron at an energy level of 0eV (3)
The atom has become ionised
Enough energy has been transferred to the electron so that it can escape
It is no longer bounded by the nucleus
In a fluorescent tube, mercury atoms are excited, leading to a series of events which result in the emission of photons in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Describe the series of events, following excitation of mercury atoms, which results in the emission of visible photons (6)
Electrons de-excite and relax back to original energy levels
They emit photons of energy equal to the energy difference between levels
These are photons of UV light
These photons then get absorbed by the fluorescent coating, exciting the atoms
These atoms then de-excite indirectly
The energy difference in these smaller levels is equal to energy of visible light so visible light is emitted
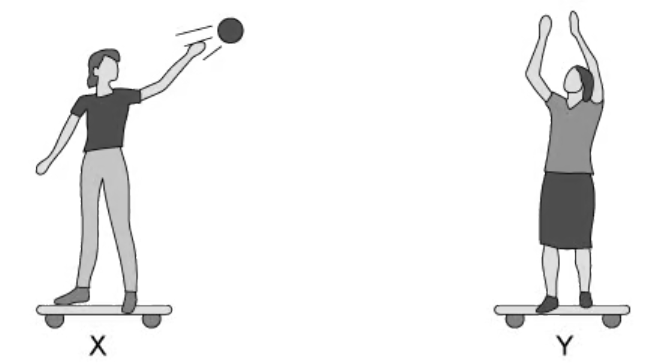
When X holds the ball, they remain still. When X throws a ball to Y, they move to the left. When Y catches the ball, they move to the right and then eventually come to rest.
Explain, using Newton’s 3 laws, the motion of both skateboarders.
Ignore all effects of air resistance and friction. (6)
When X holds ball, both are stationary as there is no resultant force
When X throws ball, he exerts force on ball to the right. Ball exherts an equal and opposite force on him to the left
This is a resultant force so he accelerates to the left
When Y catches ball, ball exherts force on him pushing right. He exherts force back on ball pushing left
Resultant force to right so he accelerates right
Ball also produces resultant force to left so Y decelerates till he stops moving
Weightlessness is a term used to describe the experience of astronauts in orbit. It is an effect of the astronauts being in a state of constant free fall.
By referring to Newton’s laws of motion, discuss the term ‘weightlessness’ as applied to astronauts in orbit. Include
The misconception of an absence of gravity
What it means to be in a state of constant free fall (4)
Astronauts experience weightlessness but the Earth still exherts a gravitational force on them
This is a resultant force causing them to accelerate towards the Earth
The space station accelerates at the same rate
So there is no floor to stop astronauts which makes it seem like there is 0 gravity
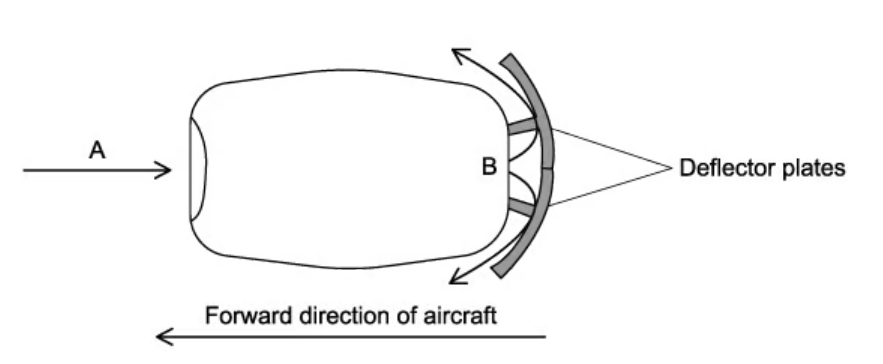
When an aircraft lands, its jet engines exert a decelerating force on the aircraft by making use of deflector plates, cuasing the air leaving the engines to be deflected at an angle.
The speed of the air leaving B is the same as the speed of the deflected air.
Explain why momentum of air changes and suggest why in practice the decelerating force provided by the deflector plates may not remain constant. (4)
Momentum is vector
Air changes direction
Rate of intake of air decreases
Due to a smaller rate of change of momentum
Explain, with reference to the conservation of momentum, the effect that the motion of a tennis ball released from a height and bouncing on a hard plate has on the mostion of the Eart from the instant it is released until it bounces at the plate. (3)
Total momentum before an event = total momentum after provided no external force acts
Momentum of ball towards Earth = momentum of Earth to ball
On impact, the momentum of both is 0
Momentum of ball away from Earth = momentum of Earth in opposite direction
Collisions can occur between neutrons and stationary uranium nuclei, for example, during nuclear fission. Discuss how this collision would be if this was inelastic compared with elastic. (4)
Neutrons would be absorbed
Both will now continue to travel in the same direction as the initial neutron
Kinetic energy lost
Neutron will rebound with velocity
The momentum transferred to the uranium nucleus will be greater
No kinetic energy lost
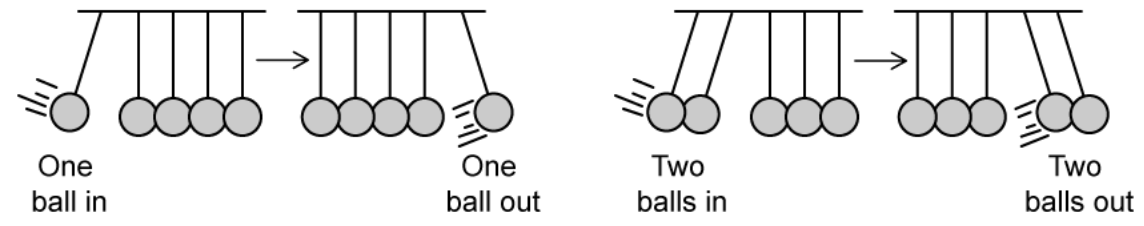
Explain, with energy and momentum considerations, why swinging one ball from the left will not release 2 balls on the right.
Assume the Newton’s cradle is in a vacuum. (5)
Conservation of momentum states total momentum before = total momentum after
If 1 ball is swung, momentum can be conserved if 2 are released as long as speed is halved
Conservation of energy states total kinetic energy before = total KE after
If 2 balls are released, speed must be 1/2v
This results in 1/2KE
Define the volt (1)
1 joule per coulomb
What is the benefit of using a high value of resistance in potential divider circuits? (1)
Reduced current
What are the advantages of using a potential divider arrangement over a variable resistor? (2)
Provides more sensitive control of current
Variable resistor can provide higher current but cannot get near 0A
Explain, in terms of charge carriers, why the resistance of the thermistor deccreases as the temperature rises. (3)
Extra charge carriers released as temperature increases
Increased thermal agitation of atoms resists flow of charge carriers
1st effect overwhelms 2nd
Explain one advantage and one disadvantage for using a potential divider and using a rheostat. (4)
Better control with potential divider
Potential divider wastes energy - the lower half of the resistor always carriers current
Rheostat is easier to connect
Cannot get values for 0A with rheostat
Define work function (2)
Minimum energy
Needed to release an electron from a metal surface
State and explain one reason why the core of the optical fibre is made as narrow as possible (2)
Reduces multipath dispersion
Which would cause pulse broadening
State one appliaion of optical fibres and explain how this has benefitted society (2)
Endoscope
Improves medical diagnosis
Explain why total internal reflection will not occur when the ray travels from air to glass (1)
Only happens when the ray travels from a higher n to a lower n
Give 2 reasons why optical fibres used for communications have a cladding (2)
To protect the core from scratches
To increase critical angle
To prevent crossover of signals
Increase rate of data transfer
Explain why the pulse coming out from an optical fibre has a lower amplitude and a longer wavelength (2)
Reduced amplitude due to absorption
Pulse broadening due to modal dispersion

Deep space probes often carry modules which may be ejected from them by an explosion.
Discuss how the principles of conservation of momentum and conservation of energy apply in this instance. (6)
Momentum conserved as there are no external forces acting
They are moving in free space so are far from large masses and so gravitational forces are neglible
Equal and opposite forces acting between probe and capsule during explosion
These are internal forces
As momentum has to be conserved and is a vector, the capsule must move along the original line of movement after explosion
Total energy is always conserved in any physical process as energy can neither be created nor destroyed
Energy may be converted from one form to another
Probe is already moving and has kinetic energy
Some chemical energy is converted into kinetic
So the system has more kinetic energy than it began with
A ball of mass is swung round on the end of a string so that the ball moves in a horizontal circle. Discuss the motion of the ball in terms of the forces that act on it.
Explain how Newton’s 3 laws of motion apply to its motion in a circle
Explain why, in practice, the string will not be horizontal (6)
First law - ball does not travel in a straight line so a force acts on it
Constant speed but changing velocity
So it is accelerating
Second law - Force on the ball causes it to accelerate
Acceleration in the same direction as the force
Force is centripetal
Third law - ball must pull on the central point of support with a force that is equal and opposite to the force pulling on the ball from the centre
Force acting on the point of support acts outwards
Support of ball - supported because the rope is not horizontal
Equilibrium in vertical plane
Weight supported by tension
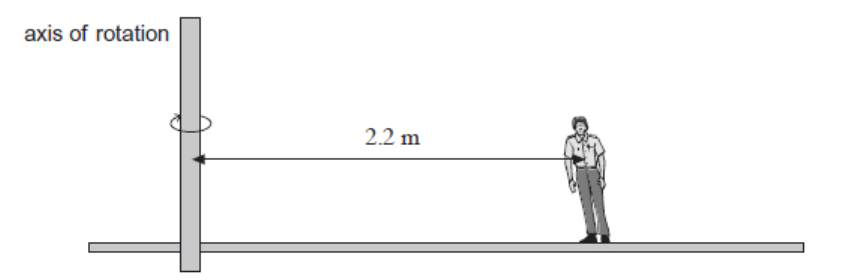
State the origin of this centripetal force and suggest why the operator has to incline his body towards the centre of rotation to avoid falling over (2)
Force produced by friction between feet and roundabout
Centripetal force has to act through the centre of mass of operator
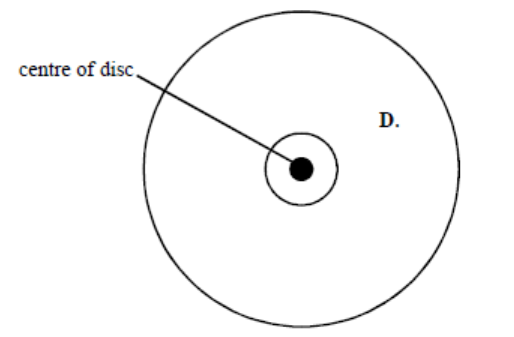
Dust particle D is on a rotating vinyl disc. A combination of electrostatic and frictional forces act on the dust particle to keep it in the same position.
There is more dust concentrated on the inner part of the disc than the outer part. Suggest why. (3)
Closer to the centre, particles need a smaller centripetal force
v is proportional to r
Friction is sufficient to meet requirements of particles close to the centre but not further away
What is simple harmonic motion? (2)
Acceleration is proportional to displacement
Acceleration is in the opposite direction to displacement
What are forced vibrations? (2)
Repeated upwards and downwards movement
Vibrations are at the frequency of the support rod
The amplitude is smaller for a larger frequency
When the frequency of the driver is out of phase by 180
What is resonance? (2)
When the forced vibrations oscillate with the same frequency as the natural vibrations
Oscillate with a large amplitude
Max energy transfer
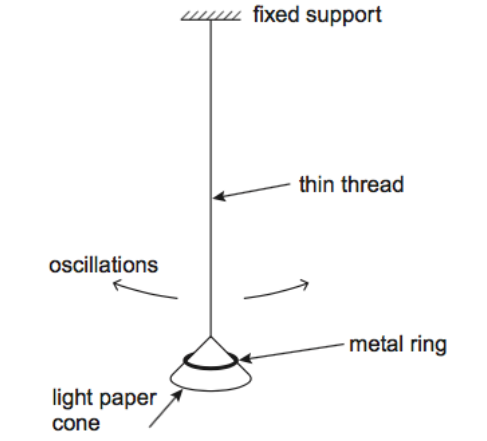
Are the oscillations of the pendulum more heavily damped when the cone oscillates with the metal ring on it or without? Explain. (4)
More heavily damped when the cone oscillates without the ring
Damping is caused by air resistance
Cone has large surface area for small mass
Loaded cone has more kinetic energy
Smaller proportion of kinetic energy removed per oscillation
Intertia of loaded cone is greater
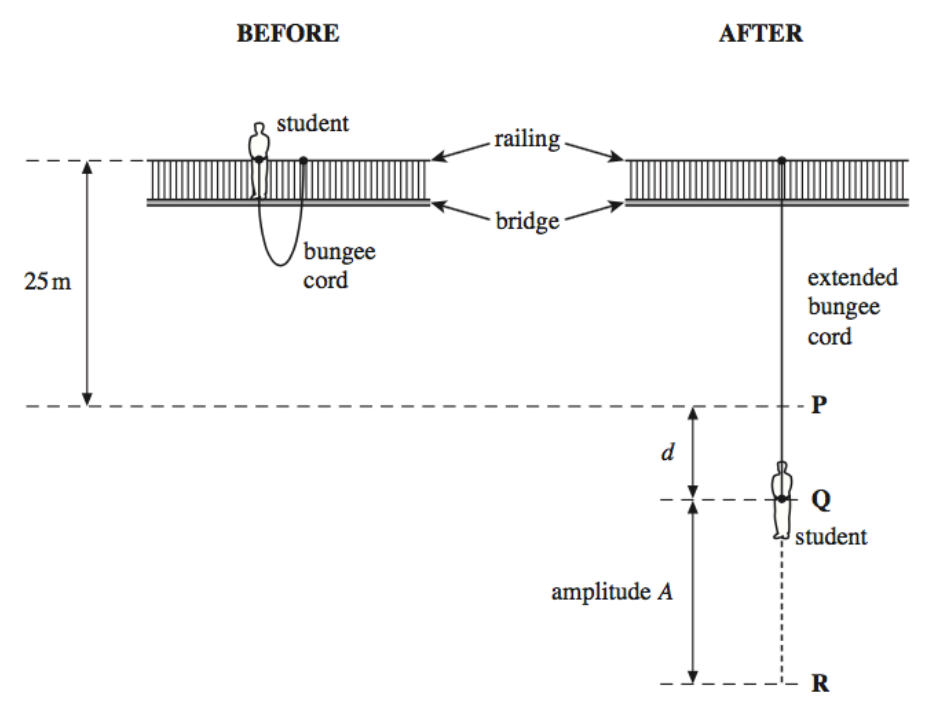
Explain why, when the student rises above P, her motion is no longer simple harmonic. (2)
Bungee cord becomes slack
Student’s motion is under gravity
Constant downwards acceleration
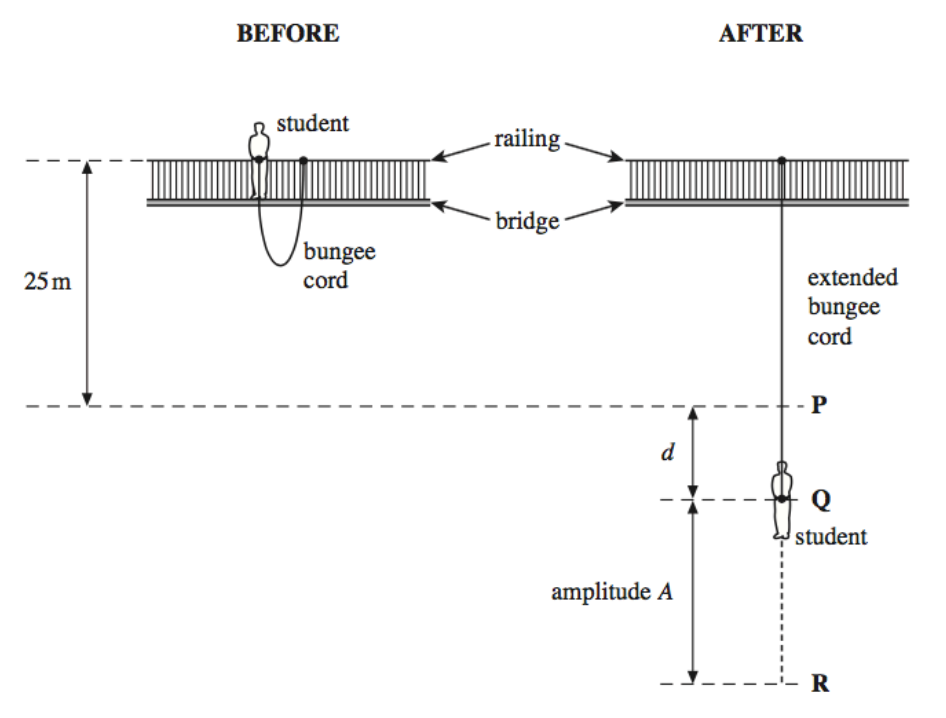
The bungee cord has a significant mass. Where along the bungee cord is the stress a maximum? (2)
Uppermost point
Stress=F/A and force at this point includes the weight of the whole cord
What is sound intensity? (1)
Power per unit area
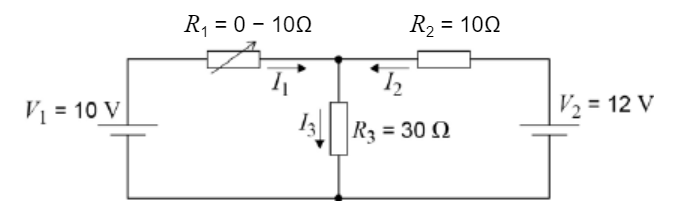
State an explain what happens to pd over R2 as potential difference over R1 is gradually increased
Pd across R2 increases
As R1 increases, pd across R1 increases
Pd across R3 = 10V - pd across R1 so pd across R3 decreases
Pd across R2 = 12 - pd across R3 so pd across R2 increases