Diagnostic Imaging Final
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
164 Terms
True or False:
Degenerative joint disease and osteoarthritis are interchangable.
True
Who and where do we often see DJD?
Medium/large breed dogs
hip, shoulder and stifle
______________ occurs when abnormal biomechanical stresses applied to a joint. Primarily aging change. Can be acquired secondary to developmental disease/trauma.
DJD/ osteoarthritis

Label the image
intra-capsular soft tissue swelling
osteophytes
enthesophytes
subchondral erosions
intra-articular calcified bodies
subchondral sclerosis
subchondral cysts
joint space narrowing
__________________
increased soft tissue opacity within the joint space. A result of joint effusion or soft tissue proliferation.
Intra-capsular swelling
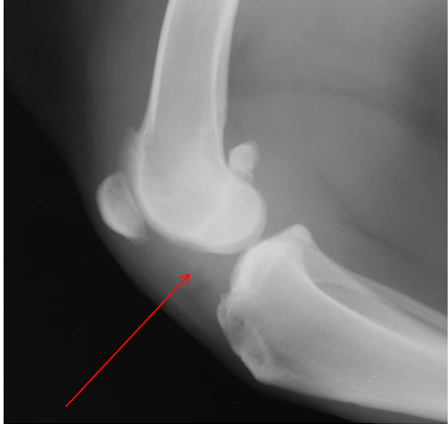
What is the arrow pointing to?
intra-capsular swelling
________________
peri/intra articular new bone formation in areas of non-weight bearing in order to try and stabilize the joint,
Osteophytes
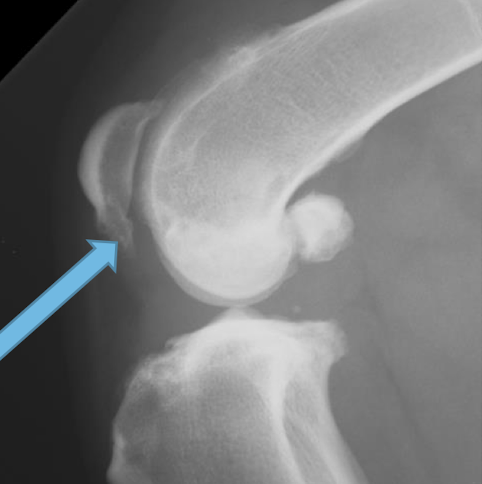
What is the image pointing to?
osteophytes
_____________
periosteal response at the site of attachment of soft tissue to bone (tendon, ligament, muscle).
Enthesophyte
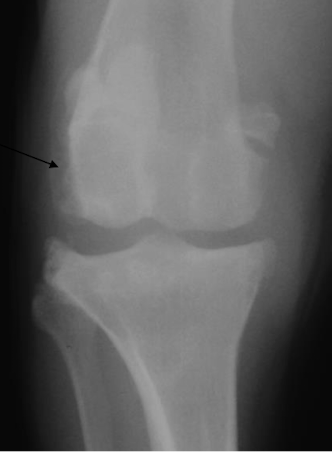
What is the arrow pointing to?
Enthesophyte
__________________
pieces of articular cartilage or peri-articular bone that have become detached.
Intra-articular calcified bodies
aka joint mice
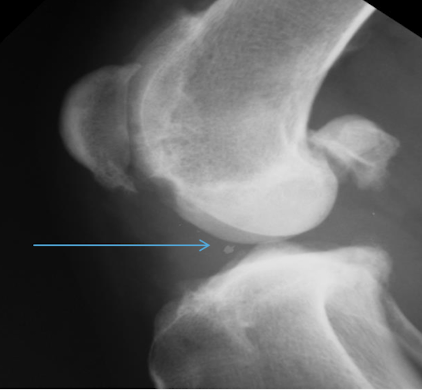
What is the arrow pointing to?
Intra-articular calcified bodies aka joint mouse
_________________
subchondral bone becomes more opaque. Secondary to increased biomechanical forces/stress remodelling
Subchondral sclerosis
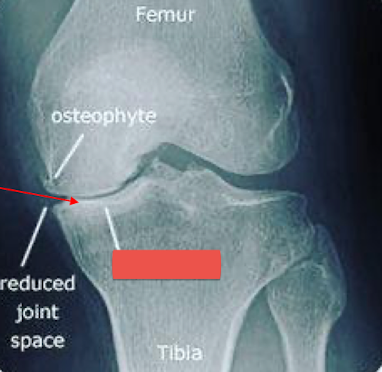
What is the arrow pointing to?
subchondral sclerosis
__________________
decreased size of joint due to destruction of articular cartilage. Rarely diagnosed radiographically because the patient is usually non-weight bearing.
Joint space alteration.
Four common locations for DJD/OA
shoulders
hips
stifle
elbow
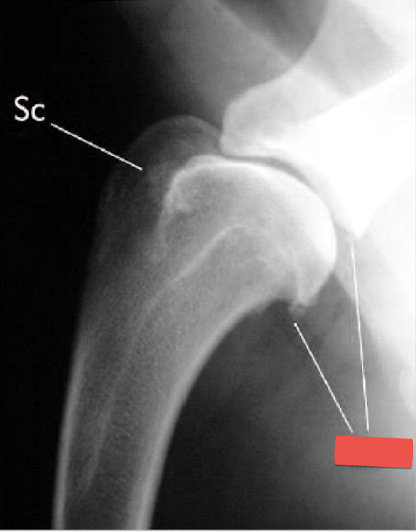
Wha condition is this image depicting? What is the red label showing?
Shoulder DJD
Osteophytes present on the caudal glenoid cavity and caudal humeral head

What is the general condition depicted?
What are the numbers labelling?
Hip DJD
acetabular rim osteophytes
femoral head osteophytes
morgan line (poor example)
subchondral sclerosis of acetabular rim
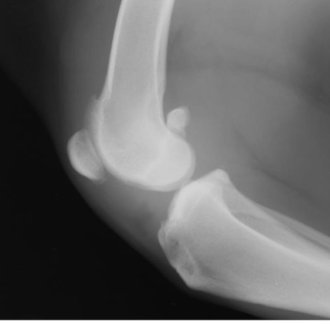
What condition? What main feature does the image show?
Stifle DJD (likely from a cruciate ligament rupture)
intracapsular swelling (cranial displacement of infra patellar fat pad and caudal displacement of fascial stripe)
What are 4 common osteophyte locations for stifle DJD?
apex of the patella
trochlear groove
medial and lateral aspects of the distal femur and proximal tibia
fabellae
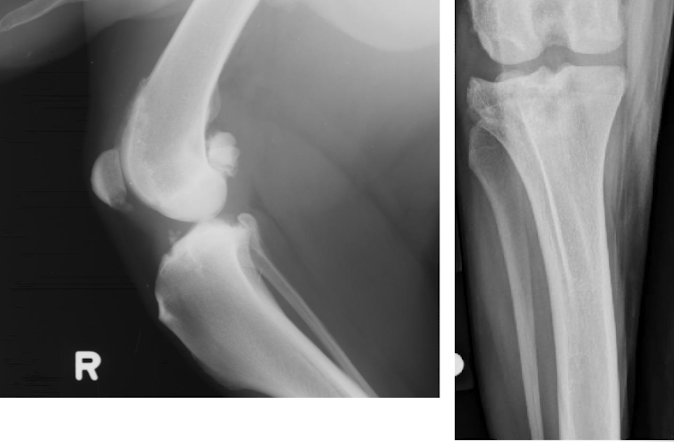
Condition?
Stifle DJD
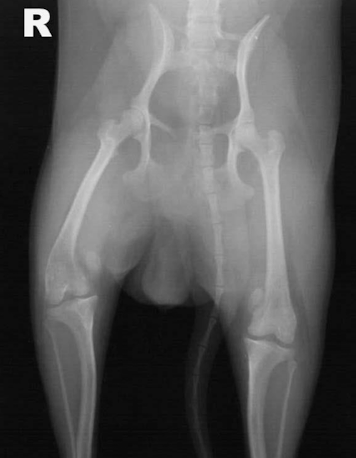
What is this image showing?
patellar luxation
What animals are patellar luxations most common in (breed/age)? Medial or lateral luxation more common?
young toy breeds
medial (but lateral can be seen in large dogs)
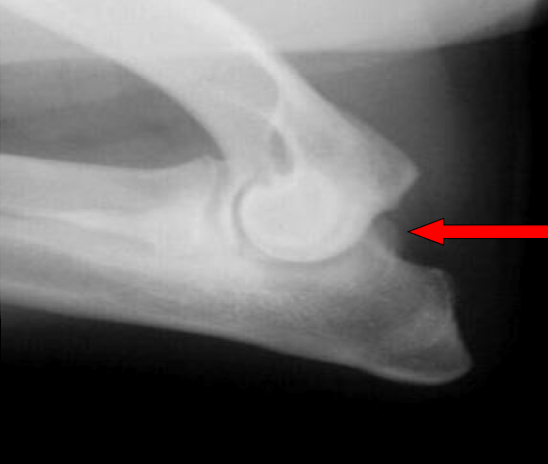
What is the arrow pointing to?
large osteophyte on the anconeal process (earliest change seen in DJD)
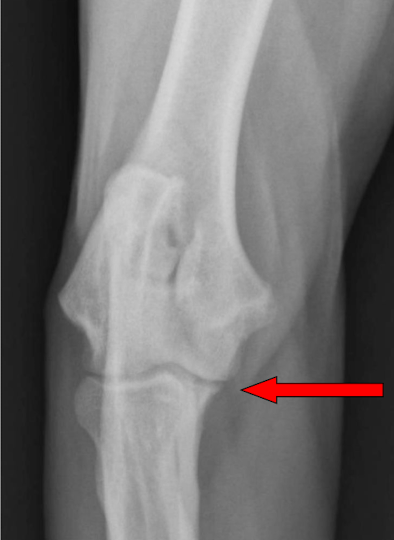
What is the arrow pointing to?
osteophyte on the medial coronoid process in elbow DJD

list the lobes of the lungs
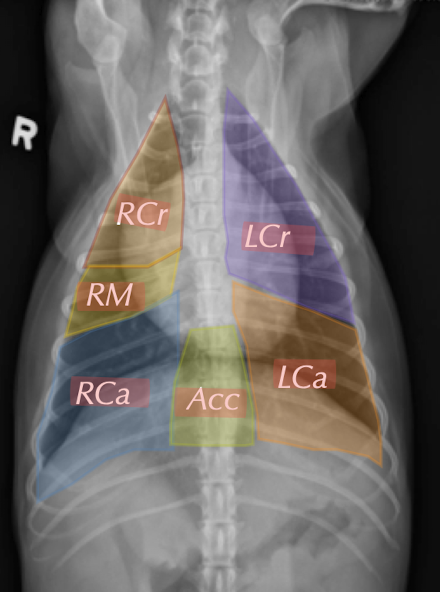
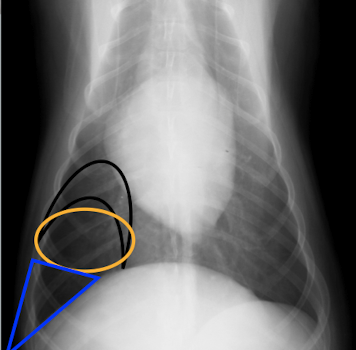
What regions of the lung lobes are the colours representing?
Black: perihilar
orange: midzone
blue: periphery
When trying to see the thoracic inlet to diaphragm, what is one thing you can do to better visualize it?
pull forelimbs forward
When doing thoracic rads, when should you always take the image?
Peak inspiration to maximize lung contrast
_______________ view of thorax:
elongated cardiac silhouette, convex right and left crura, arotic and great vessel changes more noticeable.
ventrodorsal
______________ view of thorax:
round/oval cardiac silhouette, domed diaphragmatic cupula, caudal pulmonary vessels better visualized.
Dorsoventral
What rib generally shows the tip of the lung field?
T12
How do you tell what side the lateral is taken on when viewing the thorax?
What ever side is layed down on comes more cranial and the caudal vena cava enters through the right crura.
Why should you always take 3 views of the thorax when looking for pulmonary lesions?
Only the non-dependent (up) lung can be evaluated. The down lung will not be fully aerated (atelectic) which increases in soft tissue opacity.
What are the 4 pulmonary patterns?
bronchial
interstitial
alveolar
mixed
___________ lung pattern:
increased visualization of the bronchial wall from bronchial wall thickening/mineralization. Lumen remains normal diameter. Will see peri-bronchial cells/fluid.
Bronchial
What are the two main radiographic findings in the bronchial lung pattern?
rings (doughnuts) which are end on bronchi
lines (tram tracks) which are longitudinal bronchi
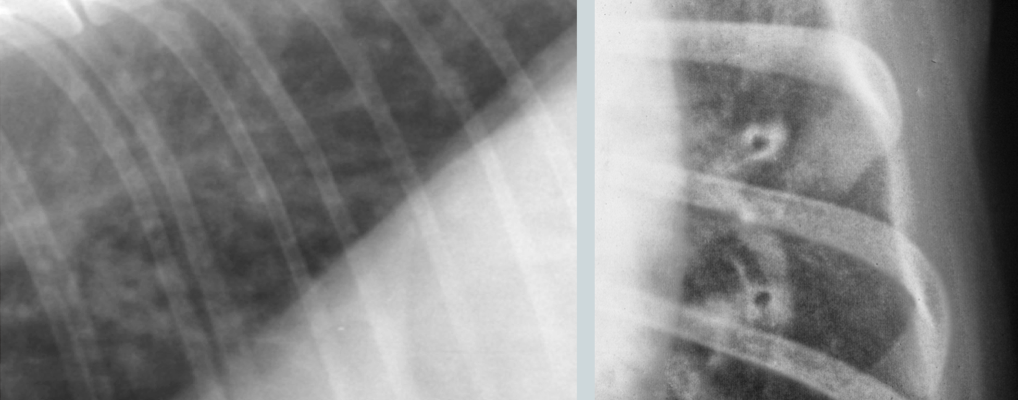
What lung pattern?
Bronchial pattern (see doughnuts)
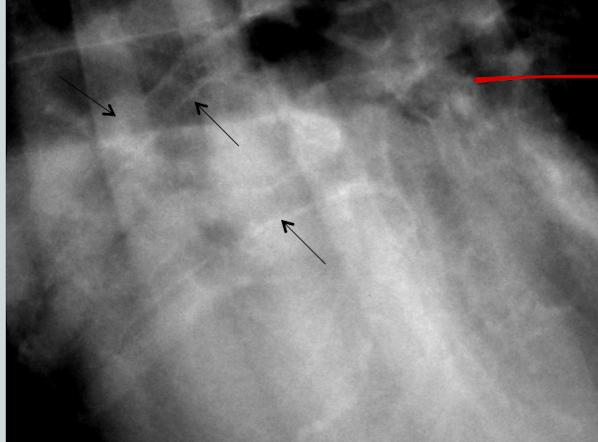
What lung pattern? What are the arrows pointing to?
Bronchial pattern
tram tracks
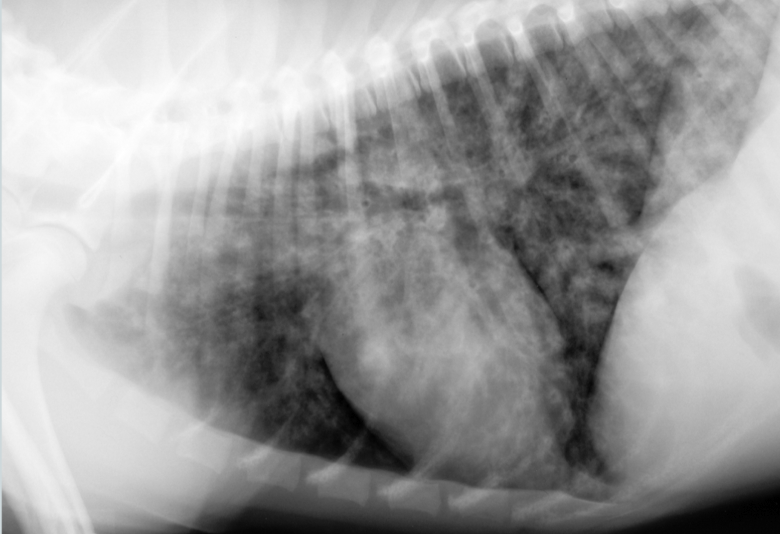
Lung pattern?
diffuse severe bronchial pattern
What are a few ddx for bronchial lung patterns?
Allergic: canine bronchitis, feline asthma
mineralization: age related (dogs)
infectious: parasitic (lungworm), fundal, bacterial (bordetella)

Cat. Likely condition? How do you know?
Feline asthma
flat diaphragm, donuts (bronchial pattern), huge lungs
_____________:
permanent widening of bronchial lumen. Differs from straight forward bronchial pattern because lumen is affected. Will see very large donuts. Can be acquired or congenital.
Bronchiectasis
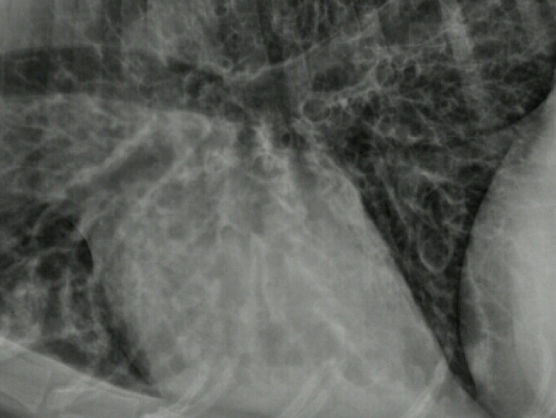
Condition?
bronchiectasis
What are the three main radiographical findings in the alveolar lung pattern?
border effacement of other soft tissue structures
air bronchograms
lobar sign (normal lung abutting consolidated/atelectic lung)
Compare and contrast consolidation vs atelectasis when referring to alveolar pattern?
Consolidation: filling of alveoli with higher density substance, lungs retain shape and size, no mediastinal shoft
Atelectasis: air loss from lung lobe/alveoli, lungs retracted from body wall, mediastinal shift to side with more room.
_____________: replacing air of alveoli with higher density substance. Commonly caused by inflammation, hemmorhage, edema.
Consolidation
____________: reduced aeration of a lung lobe with collapse of alveoli. Commonly caused by prolonged recumbancy, pleural effusions, pneumothorax, etc
Atelectasis
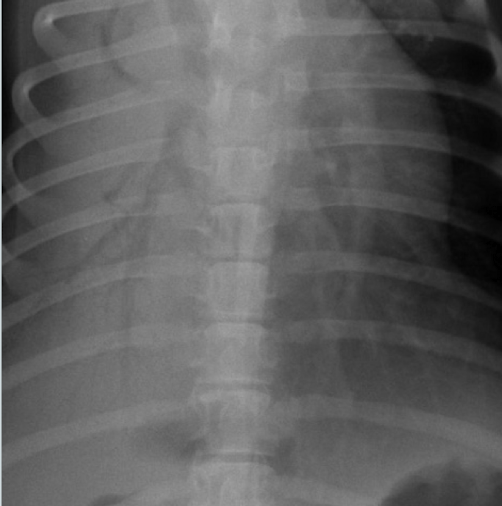
What lung pattern? How do you know?
alveolar pattern
border effacement/silhouetting
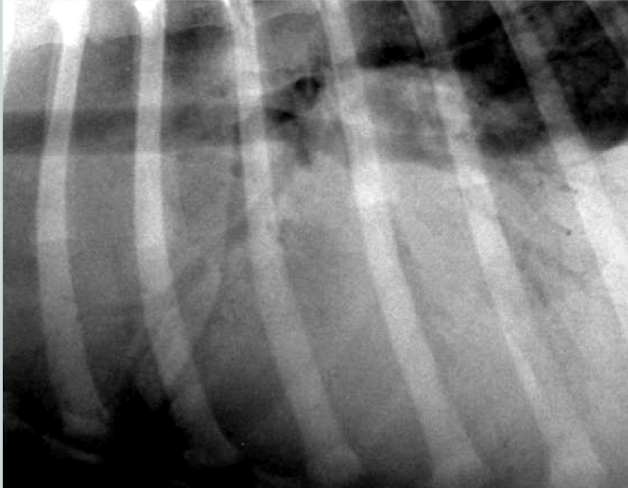
What alveolar pattern? How do you know?
Alveolar pattern
air bronchograms where the bronchi are the only remaining air-filled structure
___________: contrast between lung lobes. Soft tissue opacity of lung lobe (consolidated/atelectic) abuts a normal air filled lung lobe.
Lobar sign
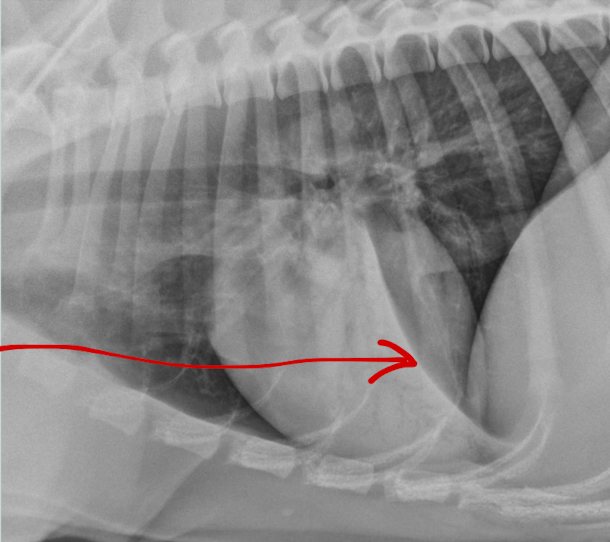
What lung pattern? What is the arrow pointing to?
Alveolar pattern
lobar sign
If the alveolar pattern is in the right middle lobe, what is your main differential? Cranioventral? Perihilar?
RM: aspiration pneumonia
CV: pneumonia, hemorrhage
cardiogenic edema
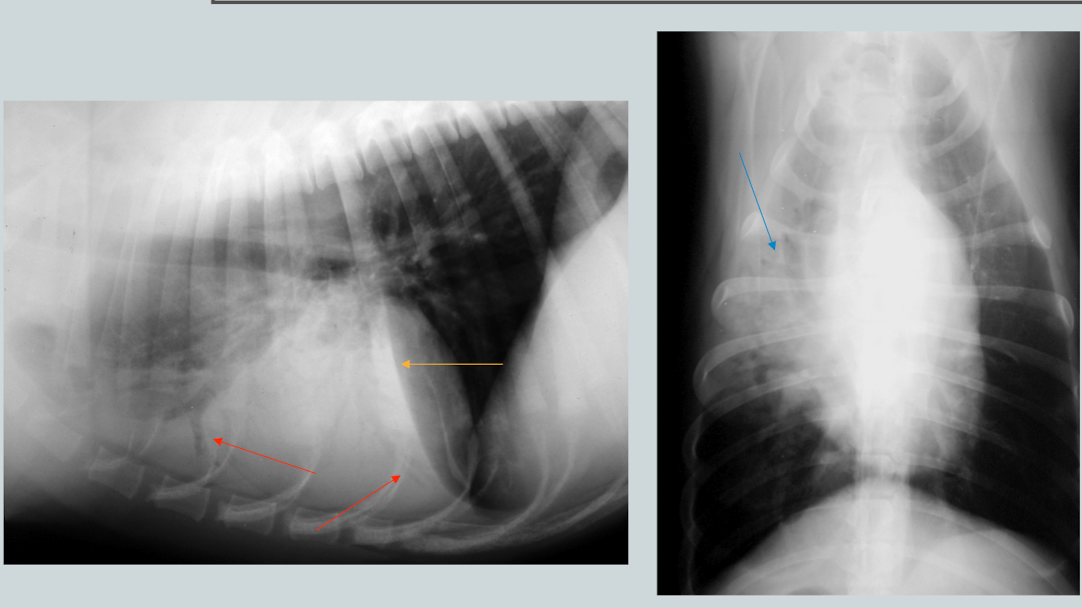
What is the likely condition? What are the arrows pointing to?
Aspiration pneumonia (bc right middle)
red: air bronchogram
blue: border effacement
yellow: lobar sign
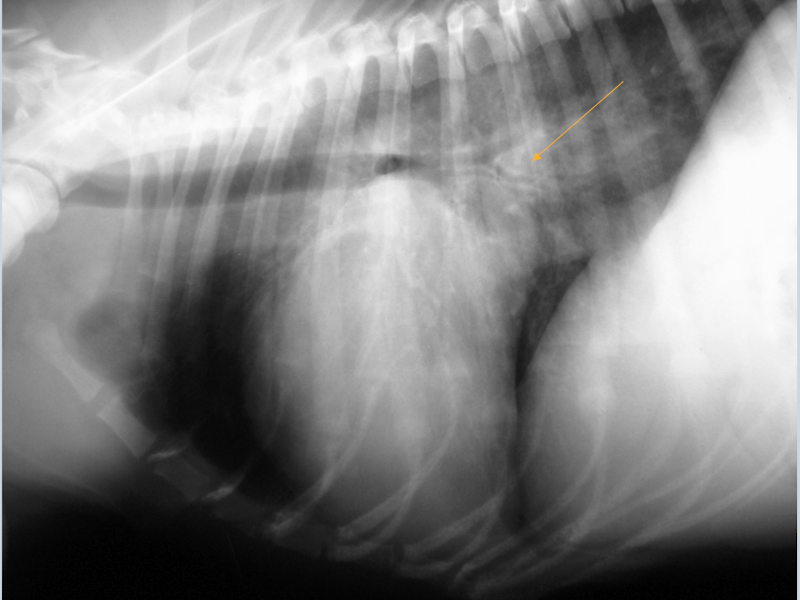
What condition is this showing in a dog? How would it differ in a cat?
Cardiogenic edema (perihilar distribution)
Cat: would look patchy and mulitfocal anywhere (see image)
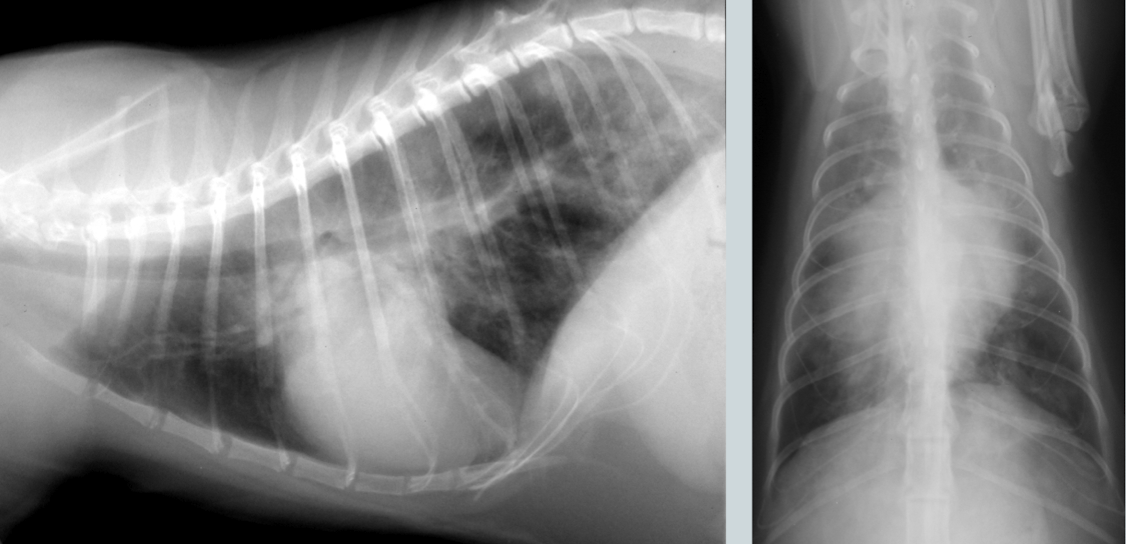
General condition?
Atelectasis
note the mediastinal/cardiac shift to the right and the soft tissue opacity of right middle lung lobe
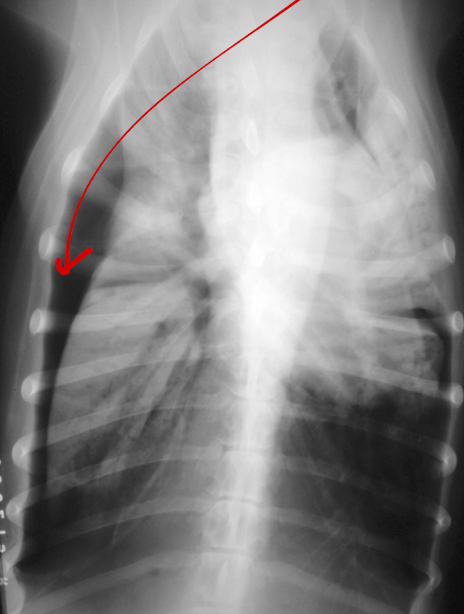
What condition?
Atelectasis secondary to pneumothorax
note: retraction of lung lobes from thoracic wall and soft tissue opacity of left and right middle lung lobe
Radiographic findings of __________ pattern:
increase in pulmonary opacity
loss of contrast between vessels and pulmonary parenchyma
can have hazy or busy appearance
does NOT border efface soft tissue structures in thorax
Unstructured interstitial pattern
What is the most commonly misdiagnosed pulmonary pattern?
unstructured interstitial pattern
bc external factors can cause the pulmonary parenchyma to appear falsely opaque/hazy (like obese patients, technique, etc)
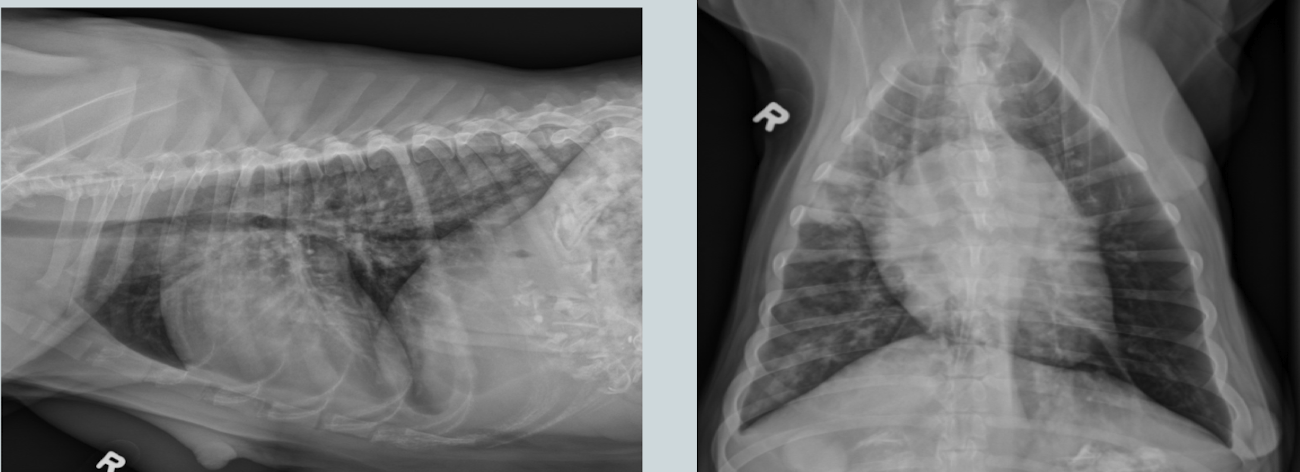
What lung pattern?
interstitial
____________________ pattern:
aggregates of cells within the interstitium including nodules and masses >5mm. Used to see neoplasia, granulomas, cysts, abscesses and bullae
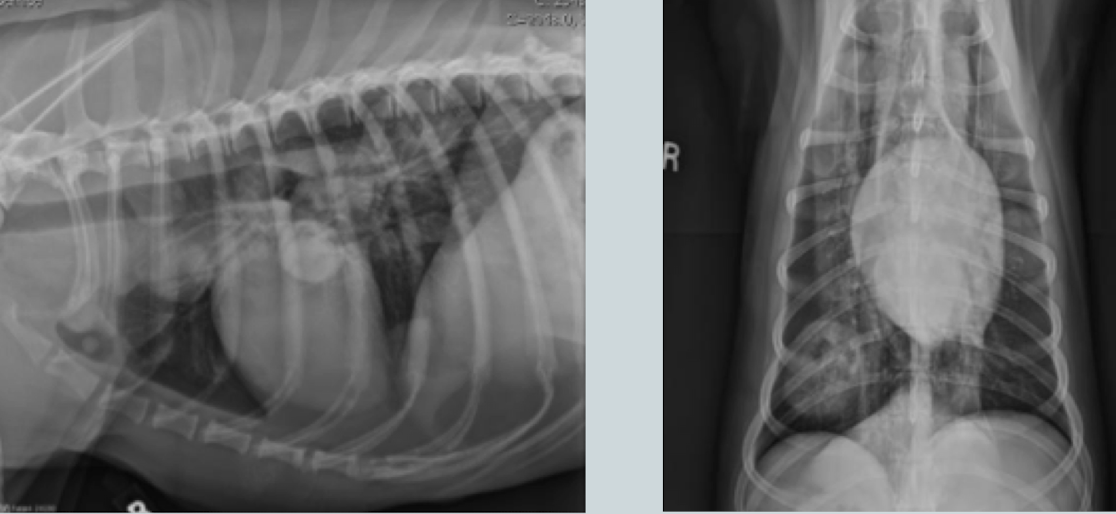
Lung pattern?
Structured interstitial pattern (metastatic disease)
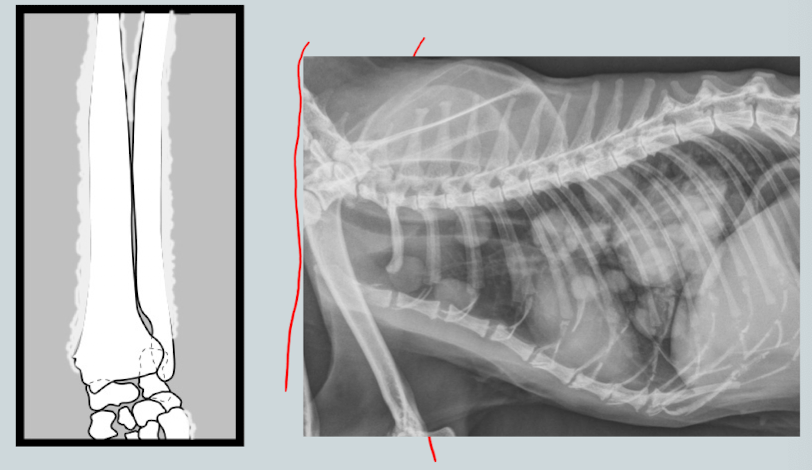
________________: neoplastic sydrome of unknown etiology affecting middle-older dogs. Will see periosteal reaction of digits/long bones associated with neoplastic or infectious lung disease. Distal limbs.
Hypertrophic osteopathy (Maries disease)
What are the arrows pointing to?
end on vessels which attenuate more of the X ray beam than a small nodule so they appear more opaque. Look for rail to connect to vessel to help differentiate.
Lesion? Who is predisposed?
Pulmonary osteomas (small mineralized nodules <3mm).
More irregularly shaped, mineral opacity, too small to be seen if soft tissue, no tail.
Collies and older large breed dogs
What are two common mixed lung patterns?
broncho-interstitial
interstitial coalescing to alveolar
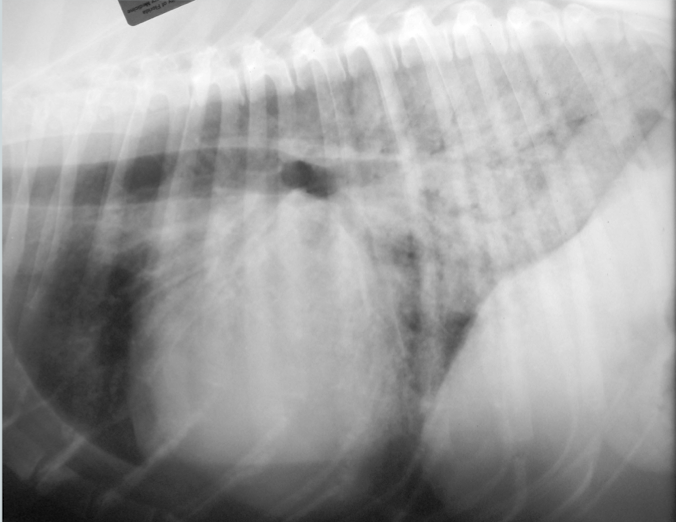
Pattern?
mixed interstitial to alveolar pattern
______________ pattern
increased or decreased visualization of pulmonary vessels. Altered course of vessels.
Vascular
What lung pattern?
vascular
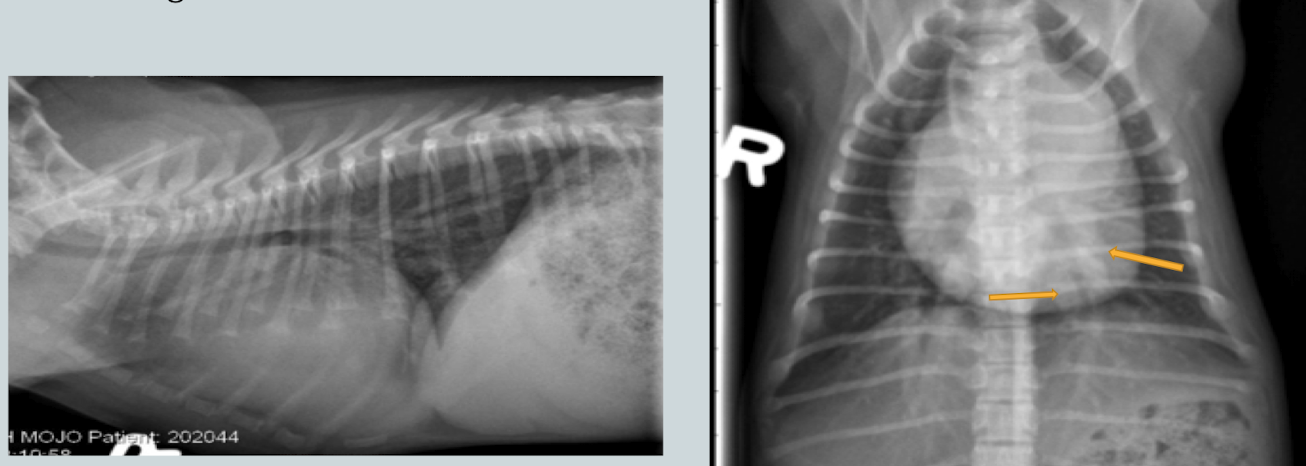
What lung pattern?
Vascular pattern
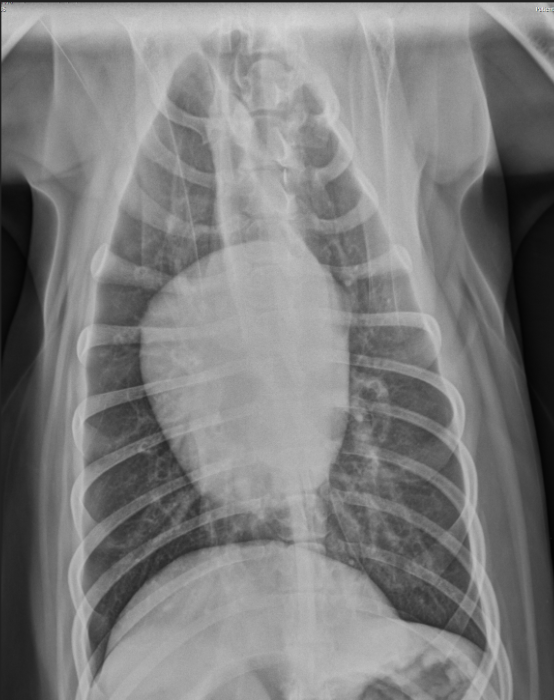
Is this a VD or DV projection based on the appearance of the diaphragm?
VD
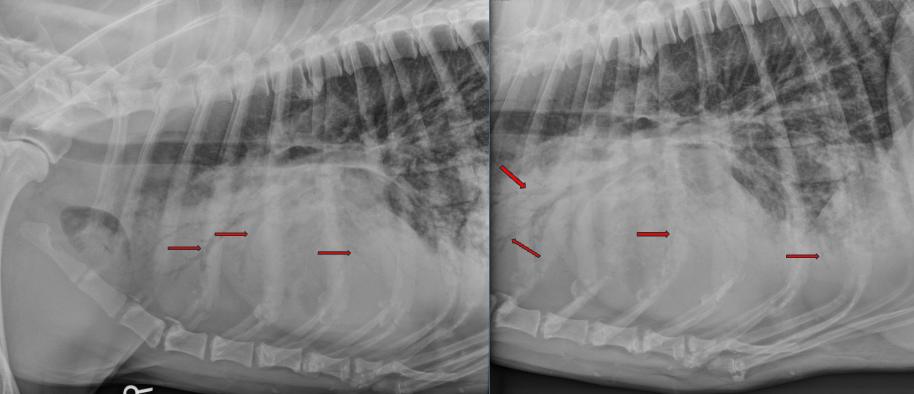
Harry is a 7yo Boxer who underwent surgery for a gastric foreign body. He had a difficult anesthetic recovery and his ET tube contained fluid when he was extubated. The following day he he is febrile, depressed, tachypnea and dyspnea.
What lung pattern?
ddx?
Alveolar Pattern (note air bronchograms and border effacement of the silhouette)
ddx: bronchopneumonia secondary to aspiration post surgically
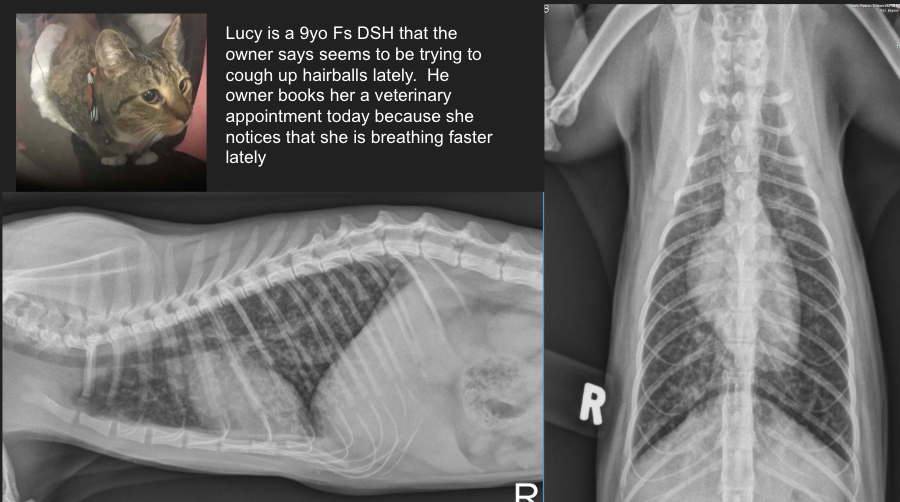
Lucy is a 9yo Fs DSH that the owner says seems to be trying to cough up hairballs lately. He owner books her a veterinary appointment today because she notices that she is breathing faster lately.
Lung pattern?
ddx?
Diffuse bronchial pulmonary pattern (donuts and tram tracks)
ddx: feline asthma
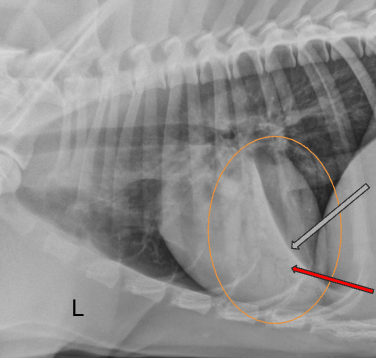
“Ziggy” is a 3 mth old pup that choked on a Greenie earlier in the day. The owner was able to pull it out of his mouth. Now he presents at clinic with dyspnea.
Pattern?
ddx?
Alveolar pulmonary pattern of the right middle lobe
ddx: aspiration pneumonia
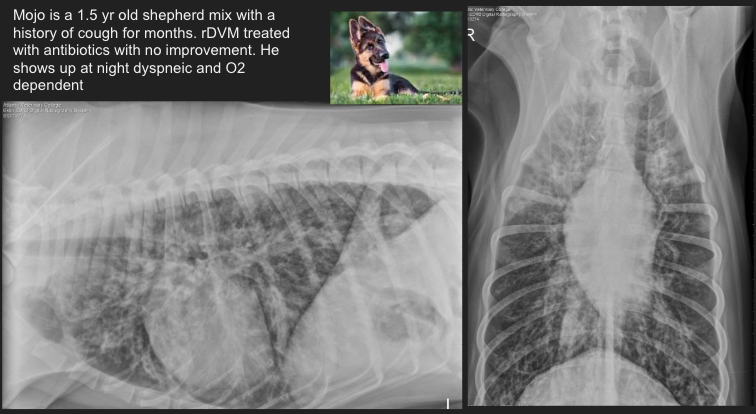
Pattern?
ddx?
severe diffuse bronchial pulmonary pattern
ddx: infectious etiologies like lungworm, Bordetella etc.
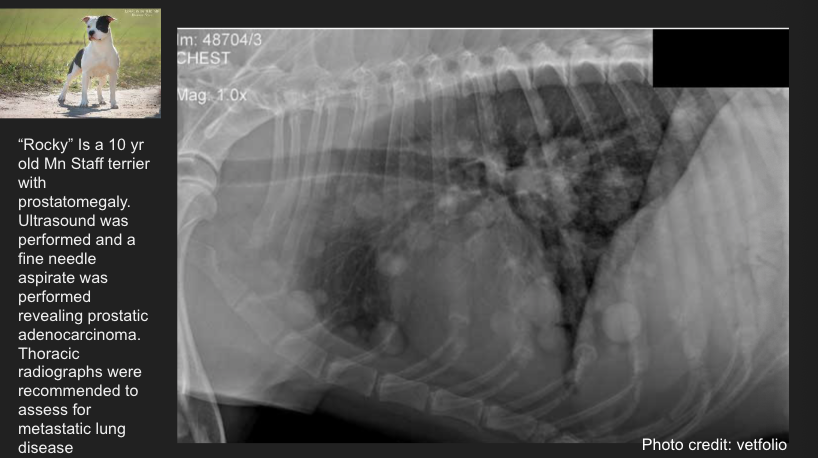
Pattern?
ddx?
diffuse structured interstitial pulmonary pattern
ddx: metastatic neoplasia
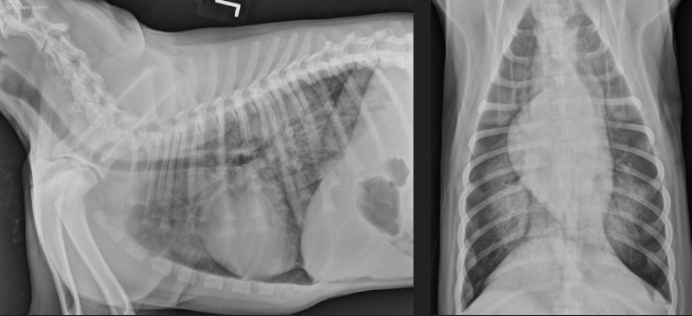
Ted is a 4 mth old Lab Retriever who ran away for 3 hours - he came home panting but not dyspneic. Later in the evening owners notice he is still panting and seems to be struggling for breath
Pattern?
ddx?
Marked interstitial coalescing to alveolar pulmonary pattern of the caudal dorsal lung parenchyma
ddx: non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema, hemorrhage
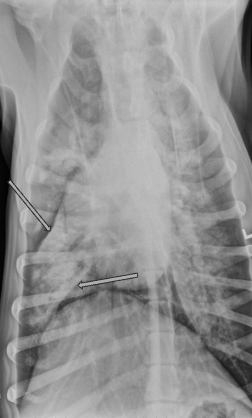
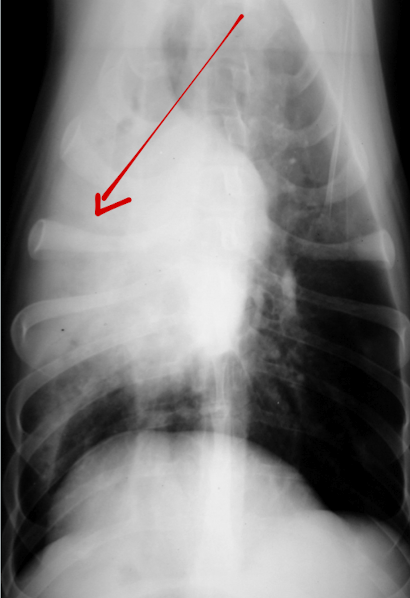
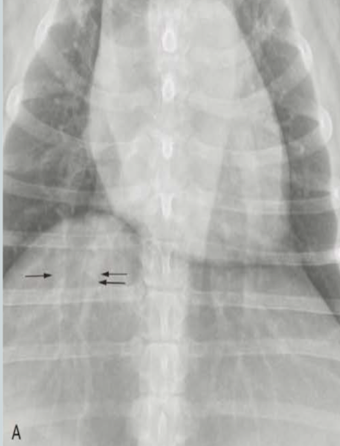
What are the arrows pointing to? Pattern?
Lobar signs
alveolar pattern
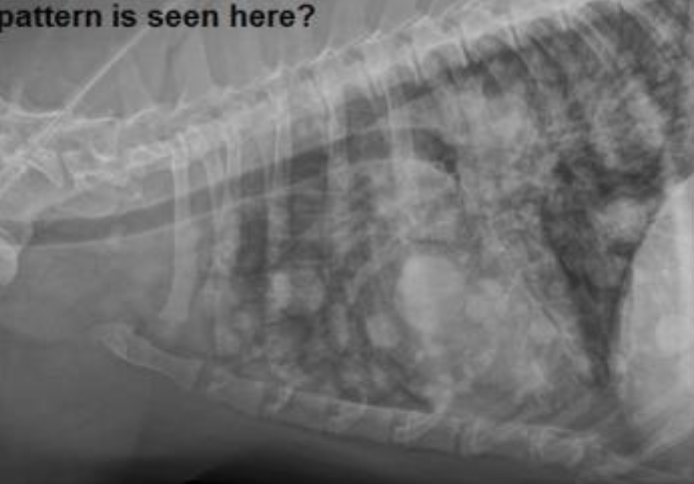
Pattern?
Structured interstitial pattern
Which view shows aortic/great vessel changes more noticeable?
Caudal pulmonary vessels?
VD
DV
How many intercostal spaces should a dogs heart be? A cats?
Dog: 2.5-2.5 ICS
Cats: 2-2.5ICS
When doing a vertebral heart score, both long and short axis lines transposed on the vertebral column begin at ___ vertebrae
cranial T4
What is the average vertebral heart score for cats? Dogs?
Cats: 7.5 ±0.3
dogs: 9.7± 0.5
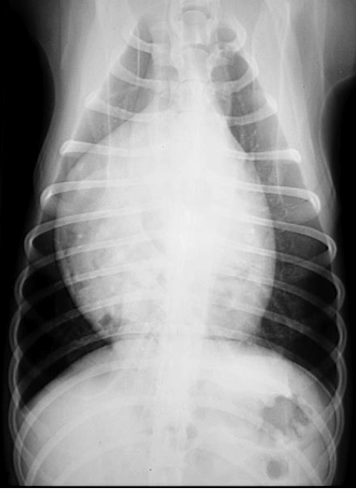
What heart condition?
4 ddx?
globoid cardiomegaly
pericardial effusion
dilated cardiomyopathy
peritoneal pericardial diaphragmatic hernia
severe tricuspid valve disease
What are two ddx for microcardia?
hypovolemia
artifact (deep chested dogs, pulmonary overinflation, etc)
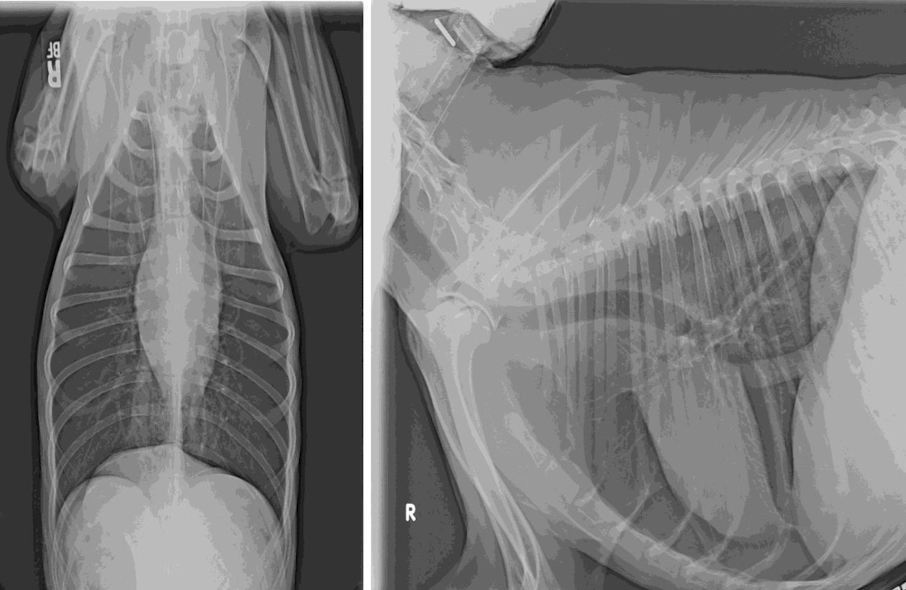
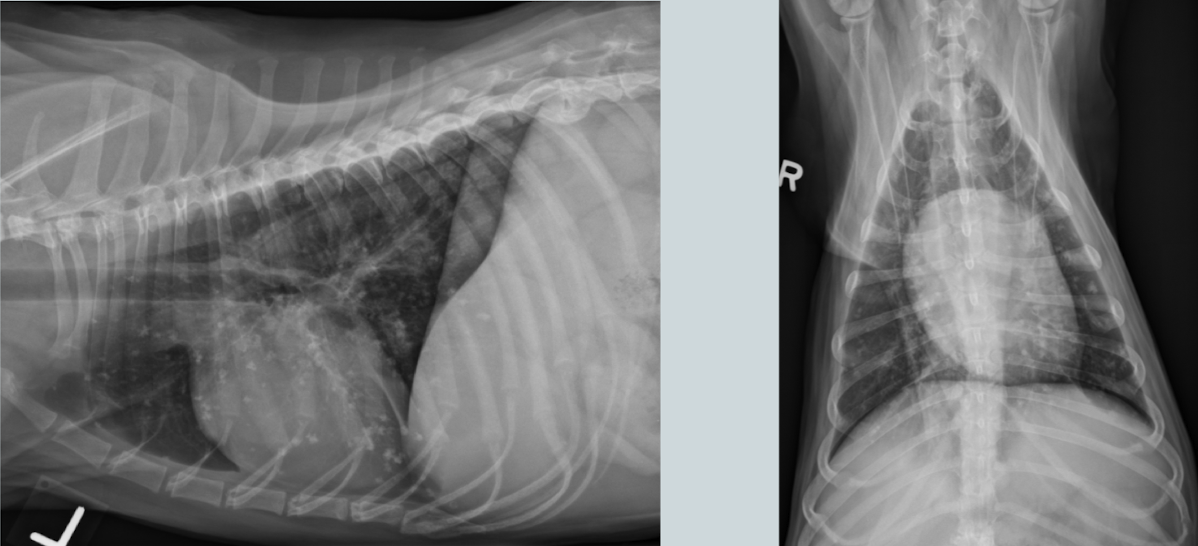
Condition?
Microcardia
aka small cardiac silhouette
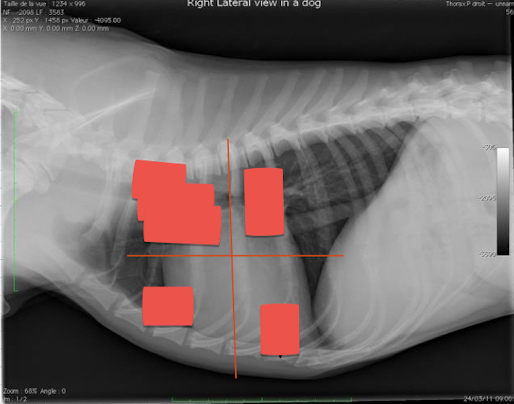
What are seen in each quadrant?
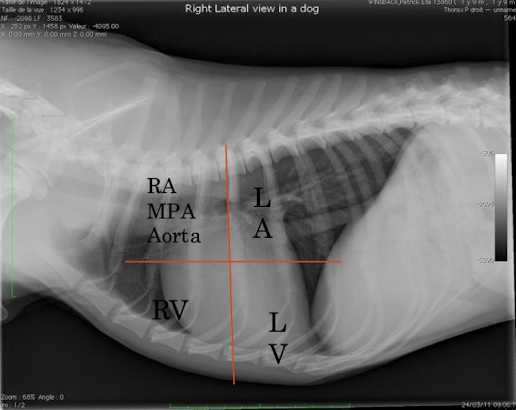

Label
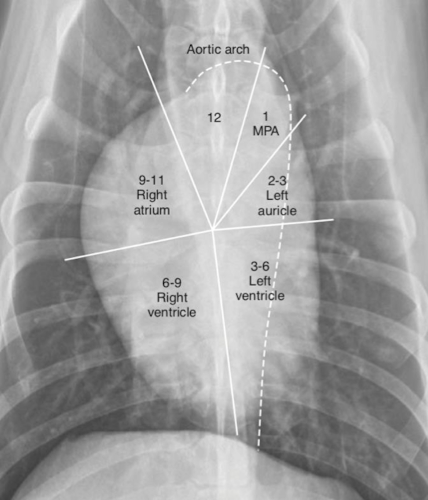
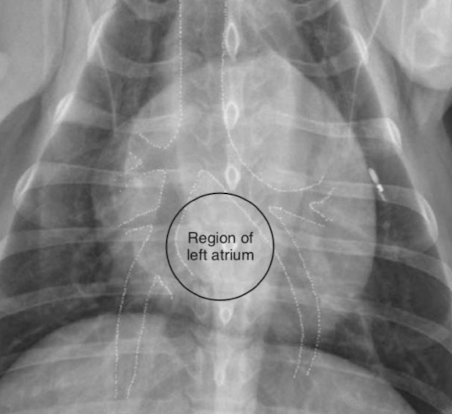
Where is the left atrium seen on vd?
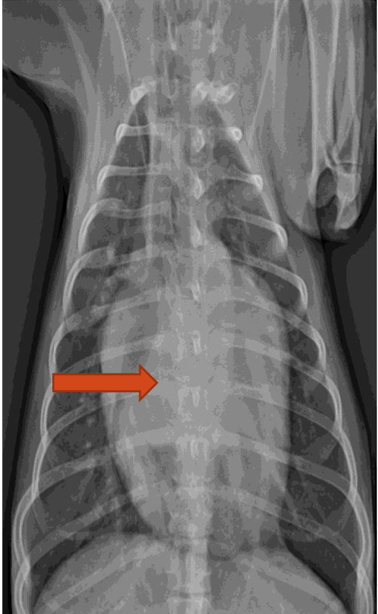
What is the arrow pointing to?
Left atrial enlargement (increase opacity)

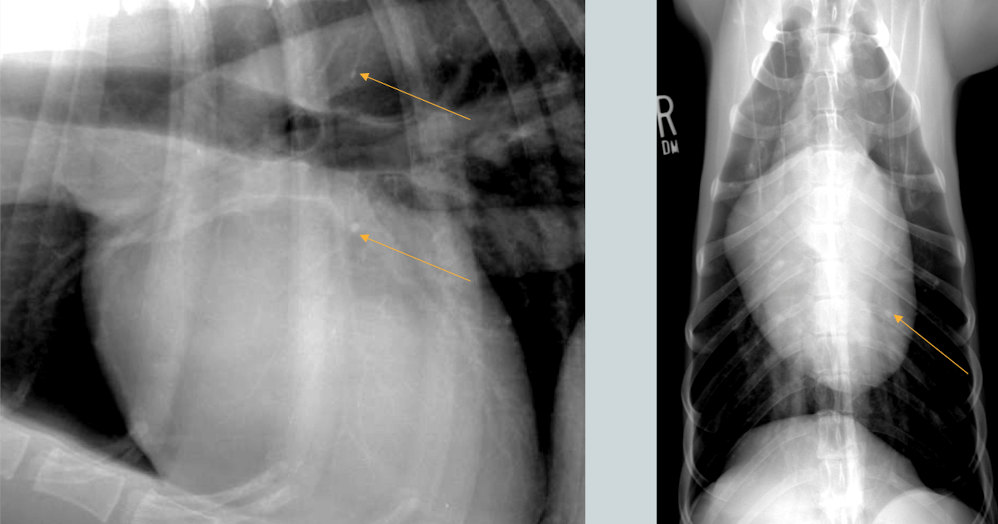
What is this image showing?
Left atrial enlargement
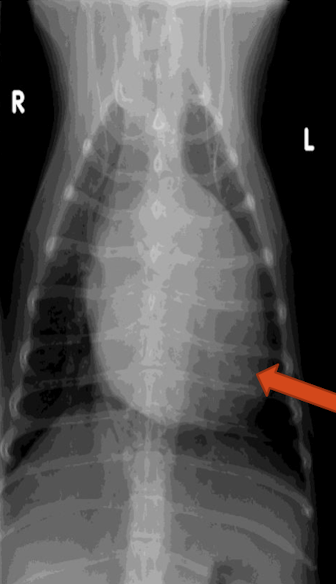
What is the arrow pointing to?
left ventricular enlargement
on a lateral view, how tall should the heart be? What do you expect if it is taller?
2/3 of thoracic height
LV enlargement
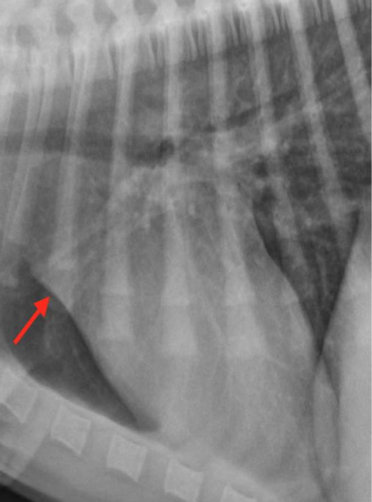
What is the arrow pointing to?
Right atrial enlargement
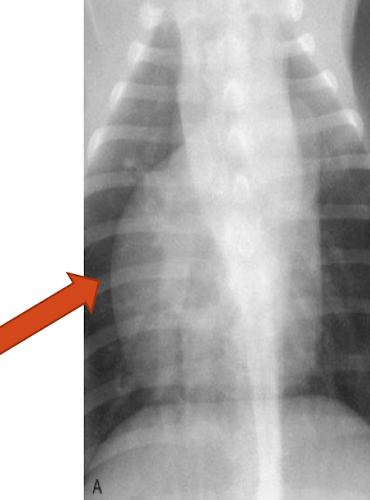
What is the arrowing pointing to?
Right ventricular enlargement
note the reverse “D” shape
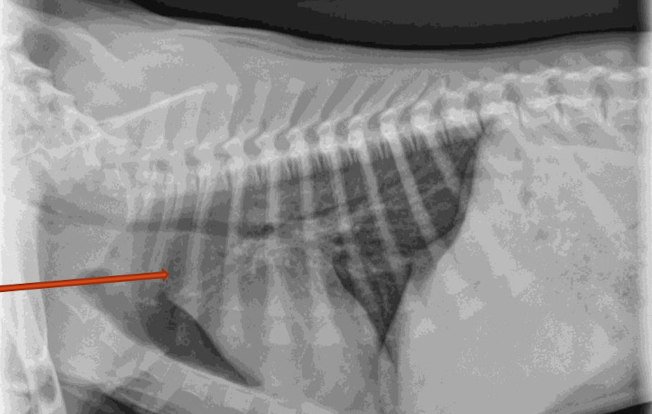
What is the arrow pointing to?
aortic enlargement
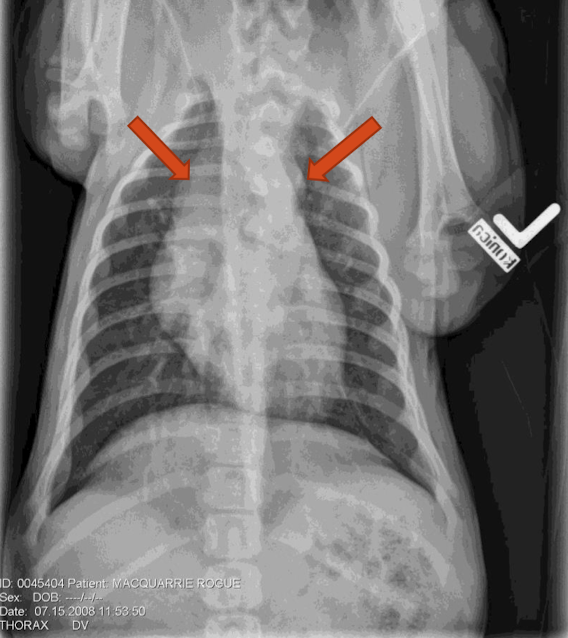
What are the arrows pointing to?
Aortic enlargement
Note: hat on top of the heart
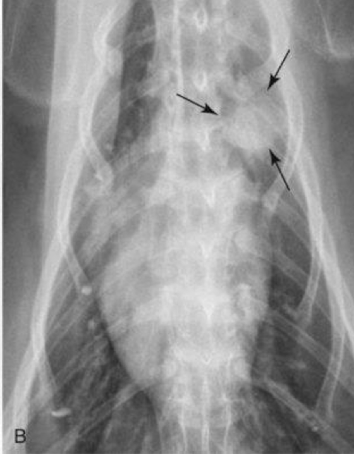
What is the anomaly and who is it seen in?
Tortuous aorta
brachycephalics, older cats
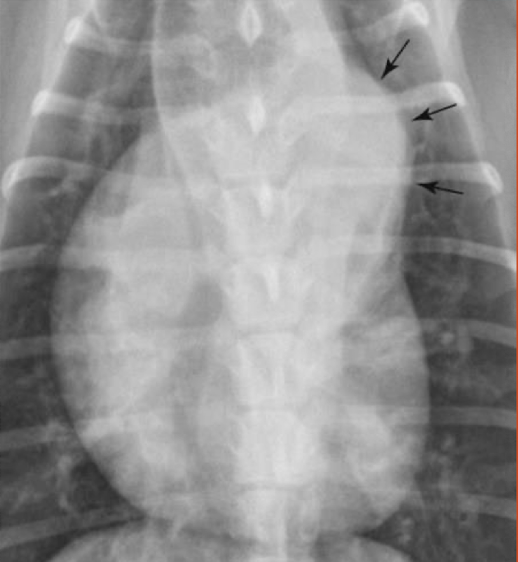
What is the arrow pointing to?
Pulmonary trunk enlargement
note: knuckle pointing to animals armpit
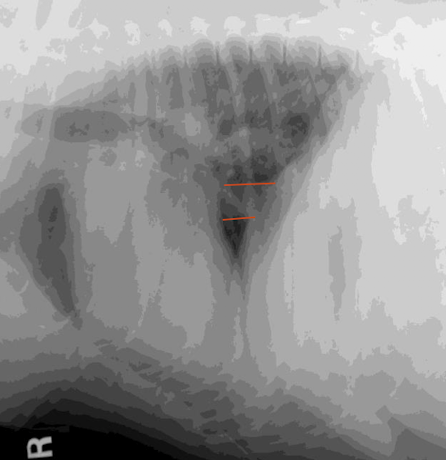
2 ddx for caudal vena cava enlargement?
right heart failure
heartworm disease