Biology Protein Synthesis
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
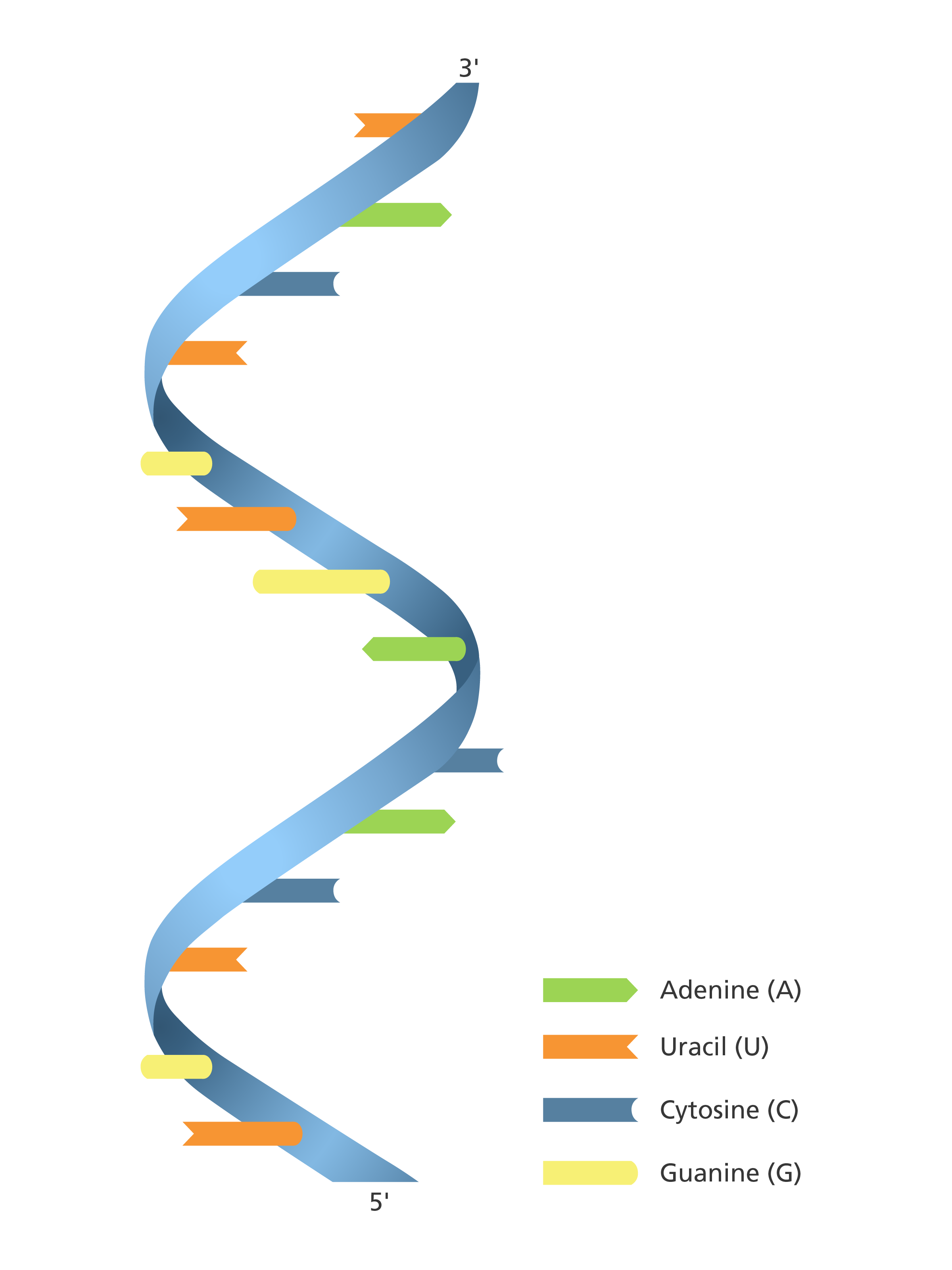
RNA
Macromolecule - made of nucleotides; sends genetic information
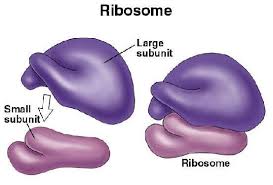
Ribosome
A cell structure that is the site of protein synthesis
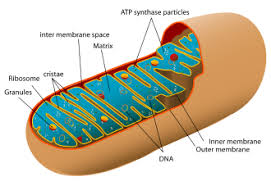
Mitochondria
A cell structure that is the site of ATP (energy) production
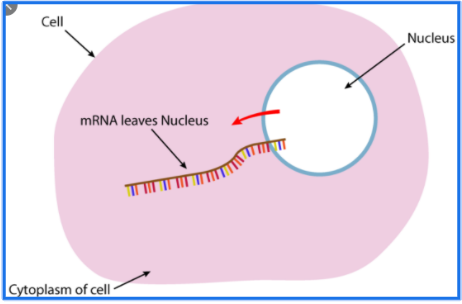
mRNA
Messenger RNA - brings genetic information to ribosome
rRNA
Ribosomal RNA - Makes up ribosome
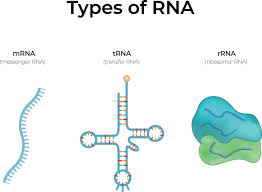
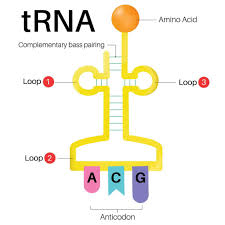
tRNA
Transfer RNA - Brings amino acids to the ribosome
Decodes the mRNA strand into a sequence of amino acids to make a functional protein.
Transcription
Production of RNA (made from DNA molecule)
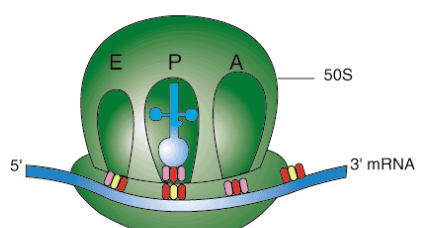
Translation
mRNA exits nucleus and travels to ribosome.
Connects to mRNA binding site next to A site on ribosome
Protein
Macromolecule made of amino acids; speeds up chemical reactions and communicates between cells
Central Dogma
DNA - mRNA (Transcription) mRNA - Protein (Translation)
Ribosomes
Organelle responsible for making proteins
Where does transcription occur?
Inside the nucleus
Where does translation occur?
Cytoplasm and ribosomes
What does DNA contain that is the recipe for proteins?
Genes
How does mRNA know where to start transcribing?
DNA strands contain sections of DNA known as promoter regions at the beginning of their gene sequences — The promoter regions (TATA box) job is to get the attention of RNA polymerase, the enzyme whose job it is to transcribe DNA into mRNA
Methyl Groups
Promoter regions can be silenced by methyl groups, preventing them from being transcribed.
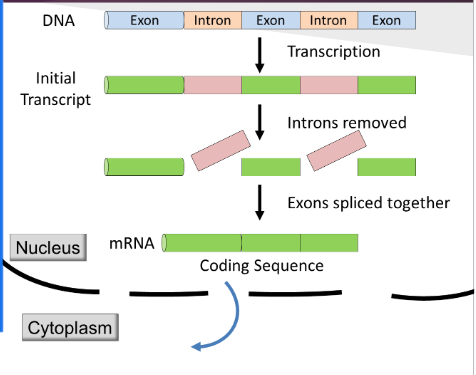
Introns
A type of DNA that stays in the nucleus because it doesn’t code for proteins
Exons
Type of DNA that exits the nucleus because they have the code needed to make a protein
RNA Splicing
Enzymes will cut out introns, so only exons are transcribed into mRNA and carried out of the cell.
Location of ribosomes
Cytoplasm (all cells)
Rough ER (Eukaryotes only)
Codon
The mRNA sequence is translated 3 nucleotides at a time. Each section is a …
Anticodon
The complementary tRNA 3 nucleotide sequence
When do mutations occur?
During S-phase
Mutation
Any change in A, T, G, or C when the DNA is copying itself
Some beneficial mutations are
Sickle Cell Anemia (ONLY BENEFICIAL IN PLACES WITH MALARIA)
Antibiotic Resistance
Murray Gray Cows
HIV Immunity in Humans
- CCR5-delta32 (deletion of 32 base pairs which blocks HIV from entering!)
Harmful Mutations
Cystic fibrosis: Causes thick mucus to clog lungs and block ducts in digestive organs
Canavan disease: Brain degenerates
Turner Syndrome: Females born with only one X chromosome
Tay-Sachs Disease: Destroys nerve cells in brain and spinal cord
Point Mutation
Substitution
Frameshift Mutation
Insertion or Deletion